A Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, is a financial document that summarizes a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period of time, typically a month or a year. The P&L statement shows the company’s net profit or loss, which is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenues.
The P&L statement is an important tool for businesses, as it provides a snapshot of the company’s financial performance and helps management make informed decisions about the direction of the business. In this article, we will explore the key components of a P&L statement and discuss how to read and analyze this important financial document.
Table of Contents
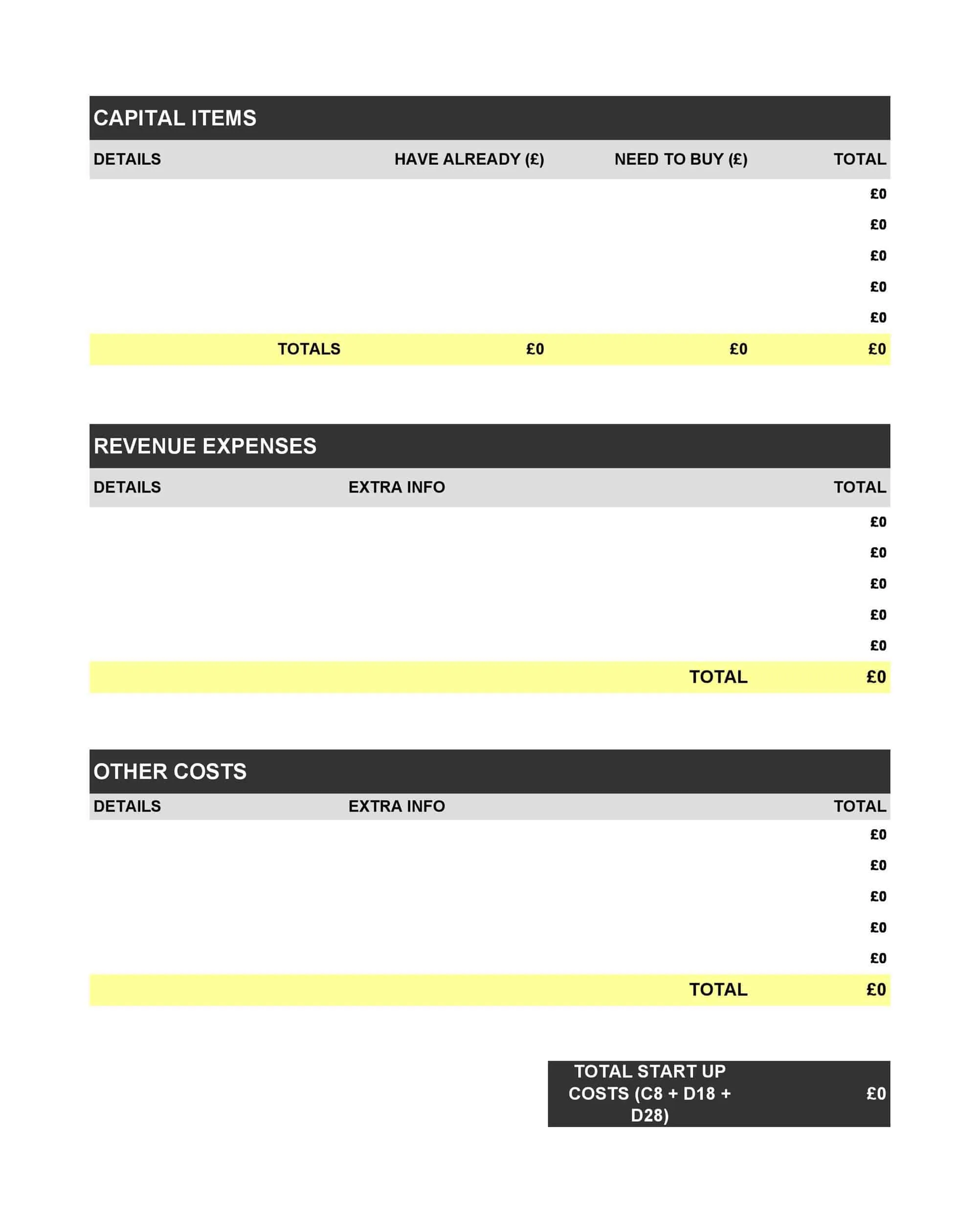
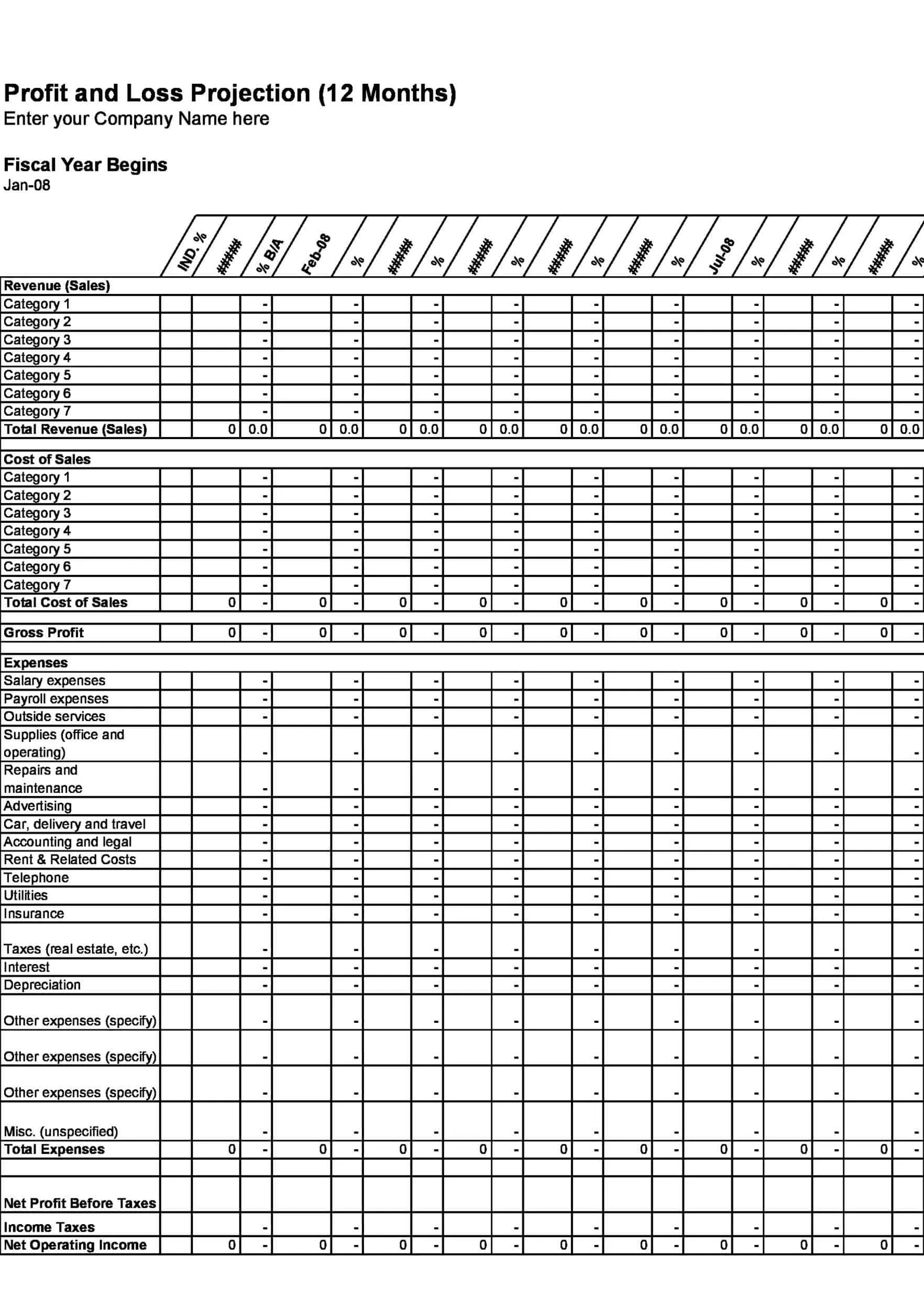
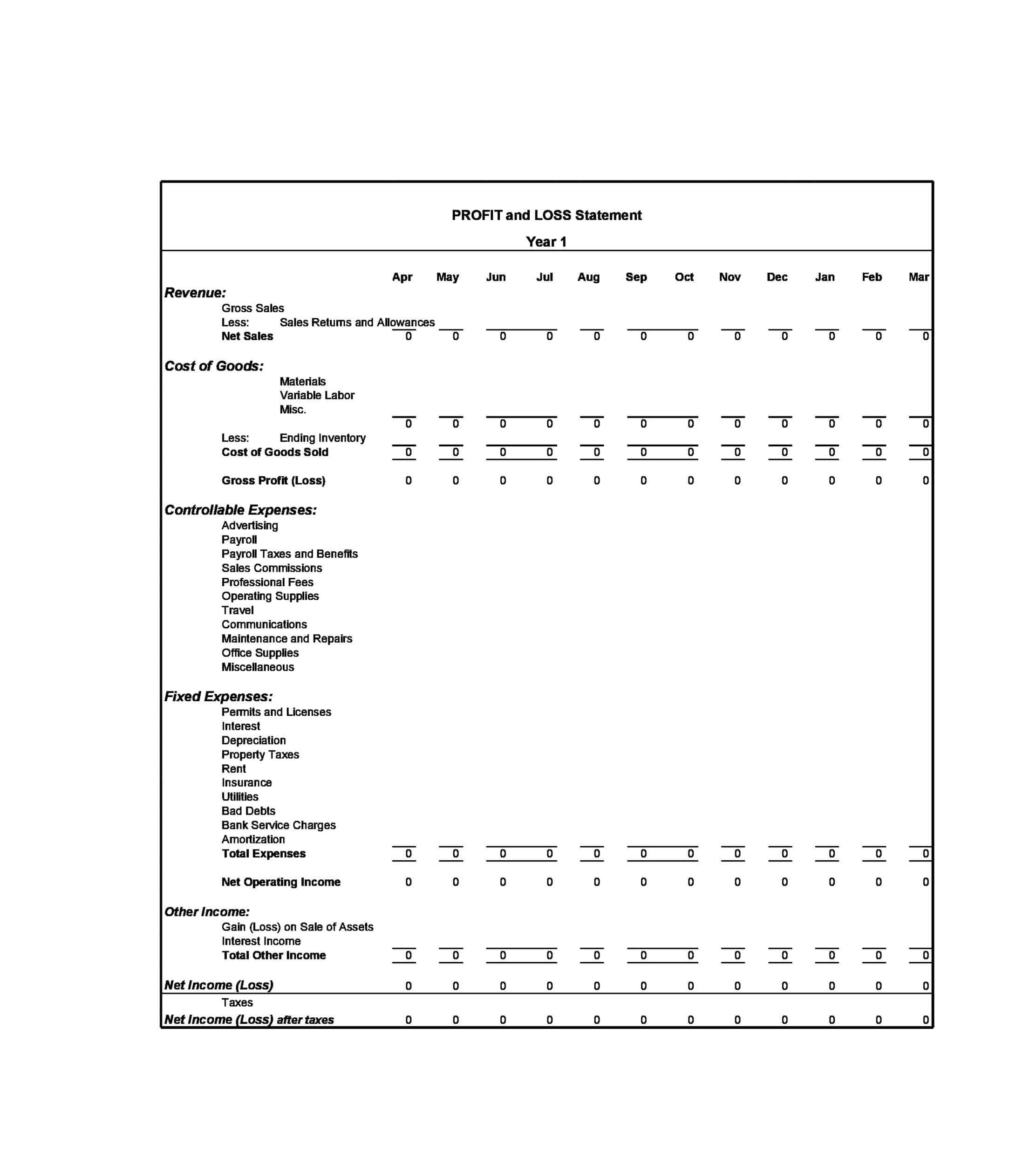
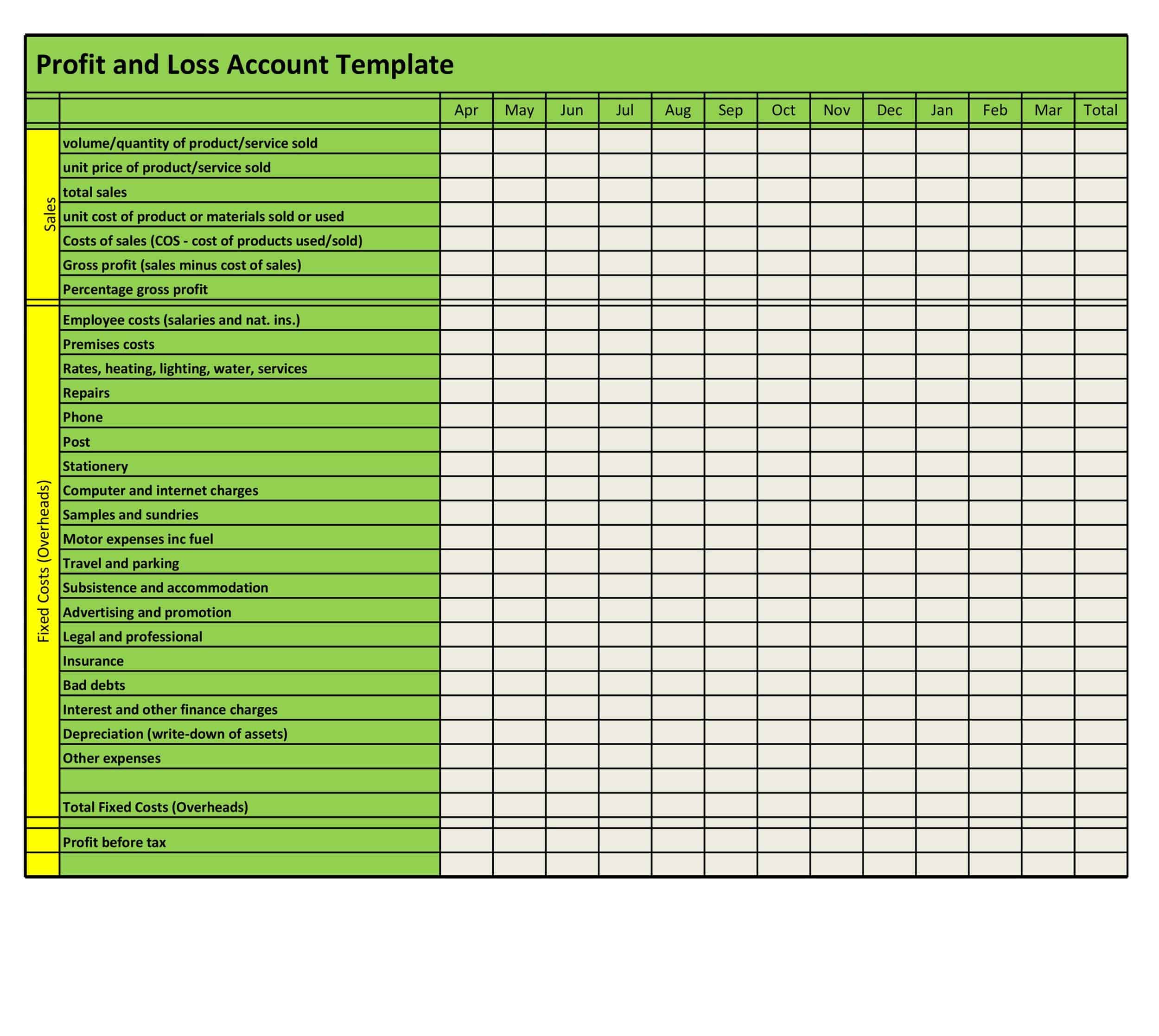
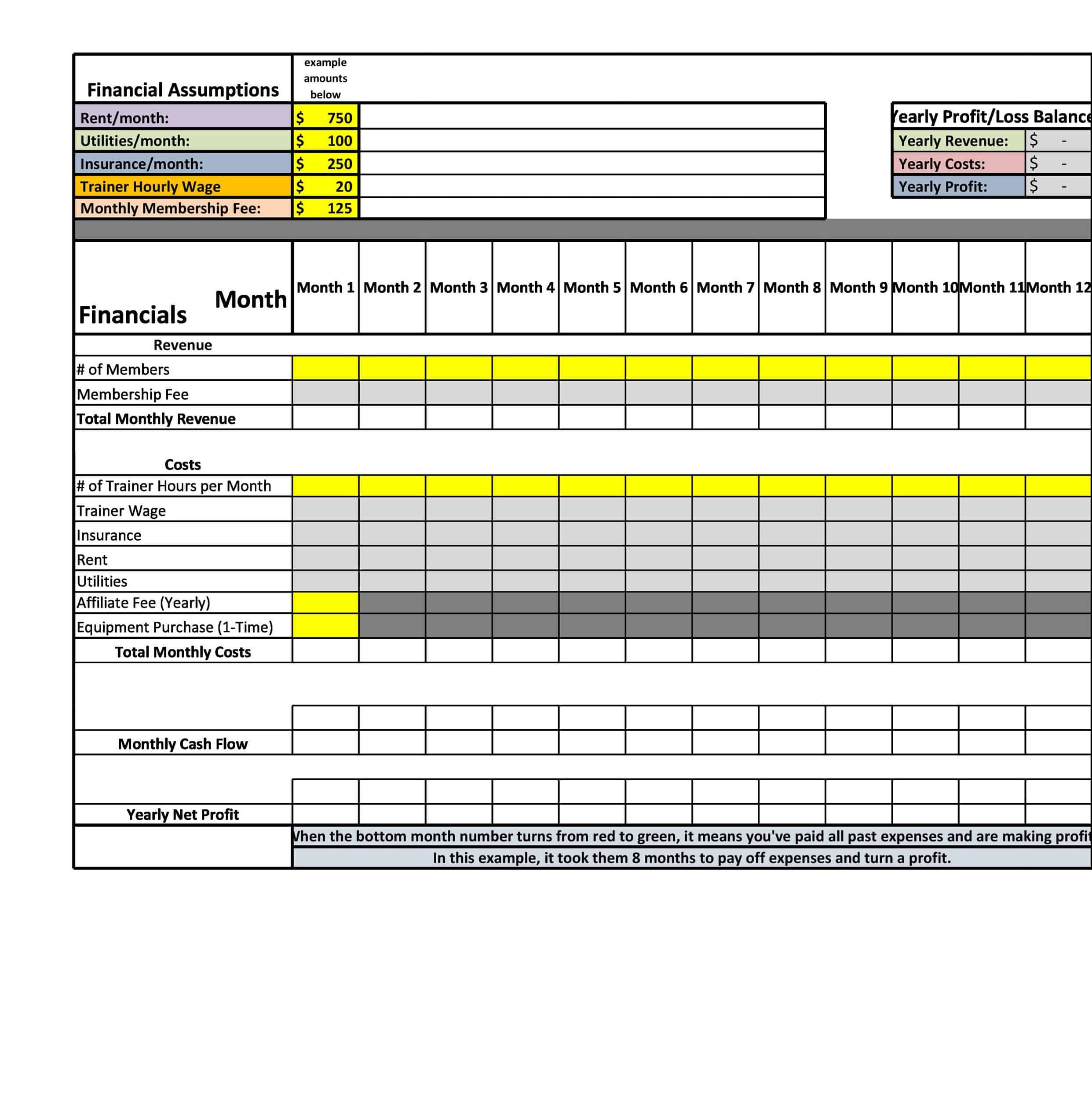
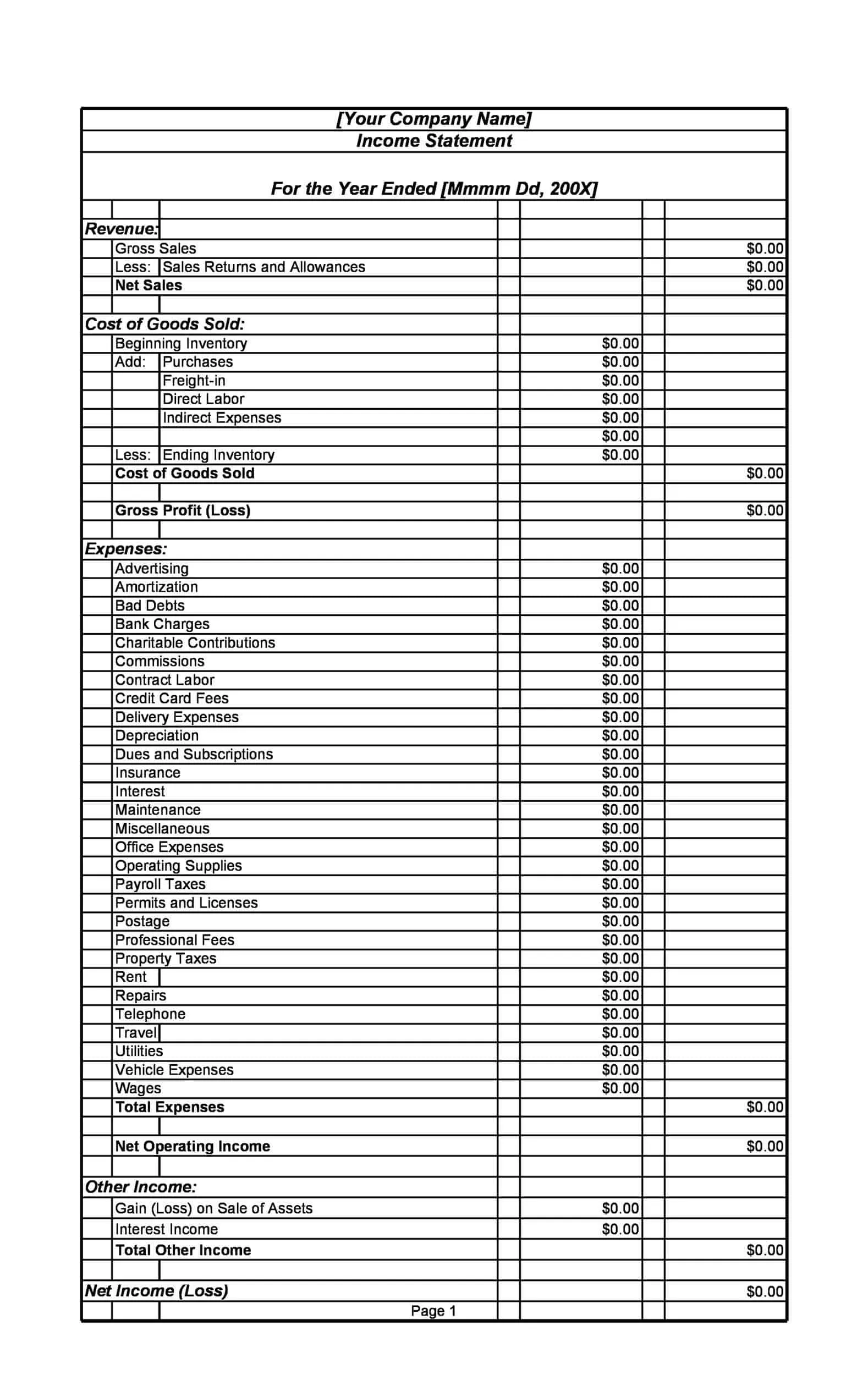
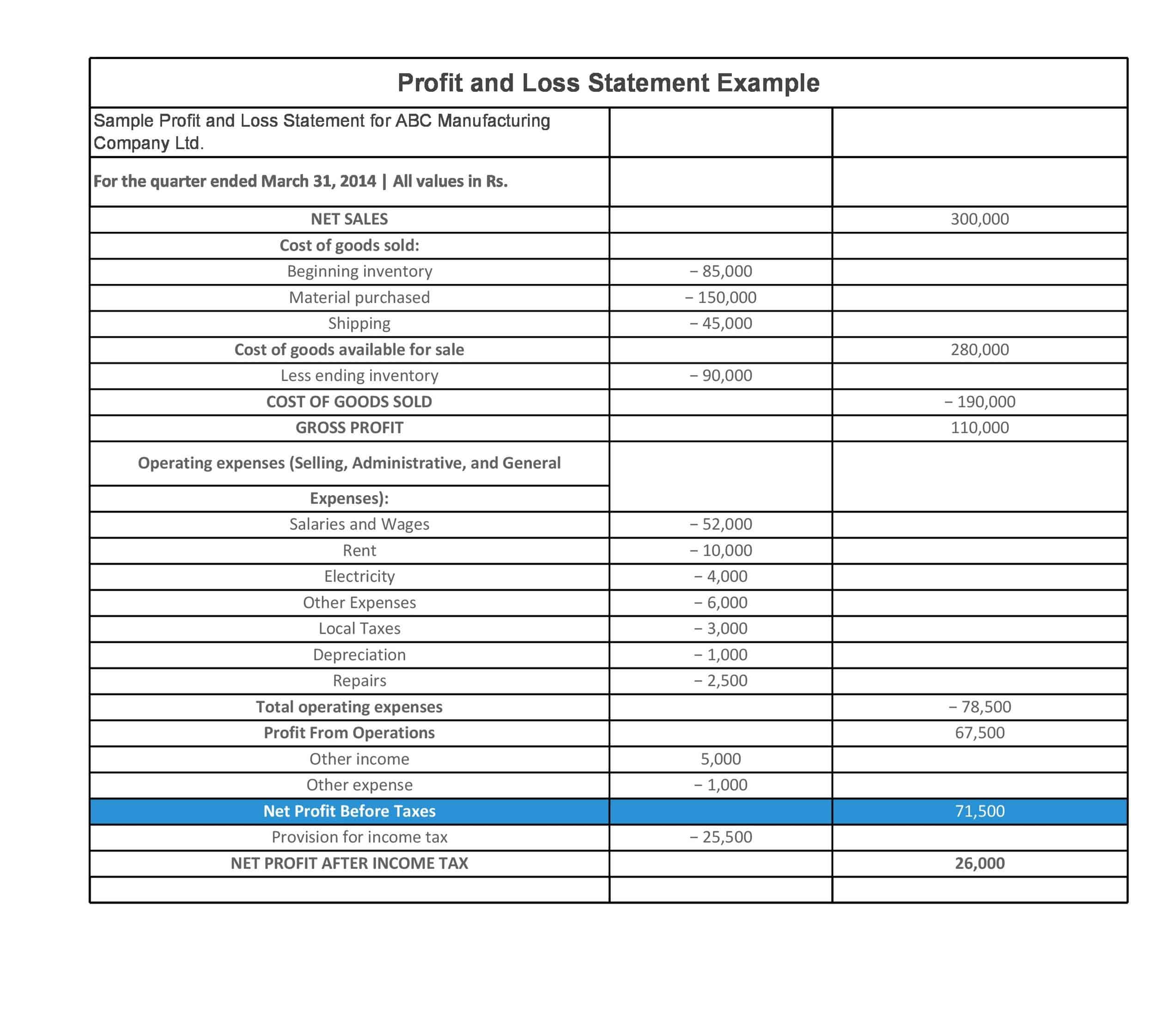
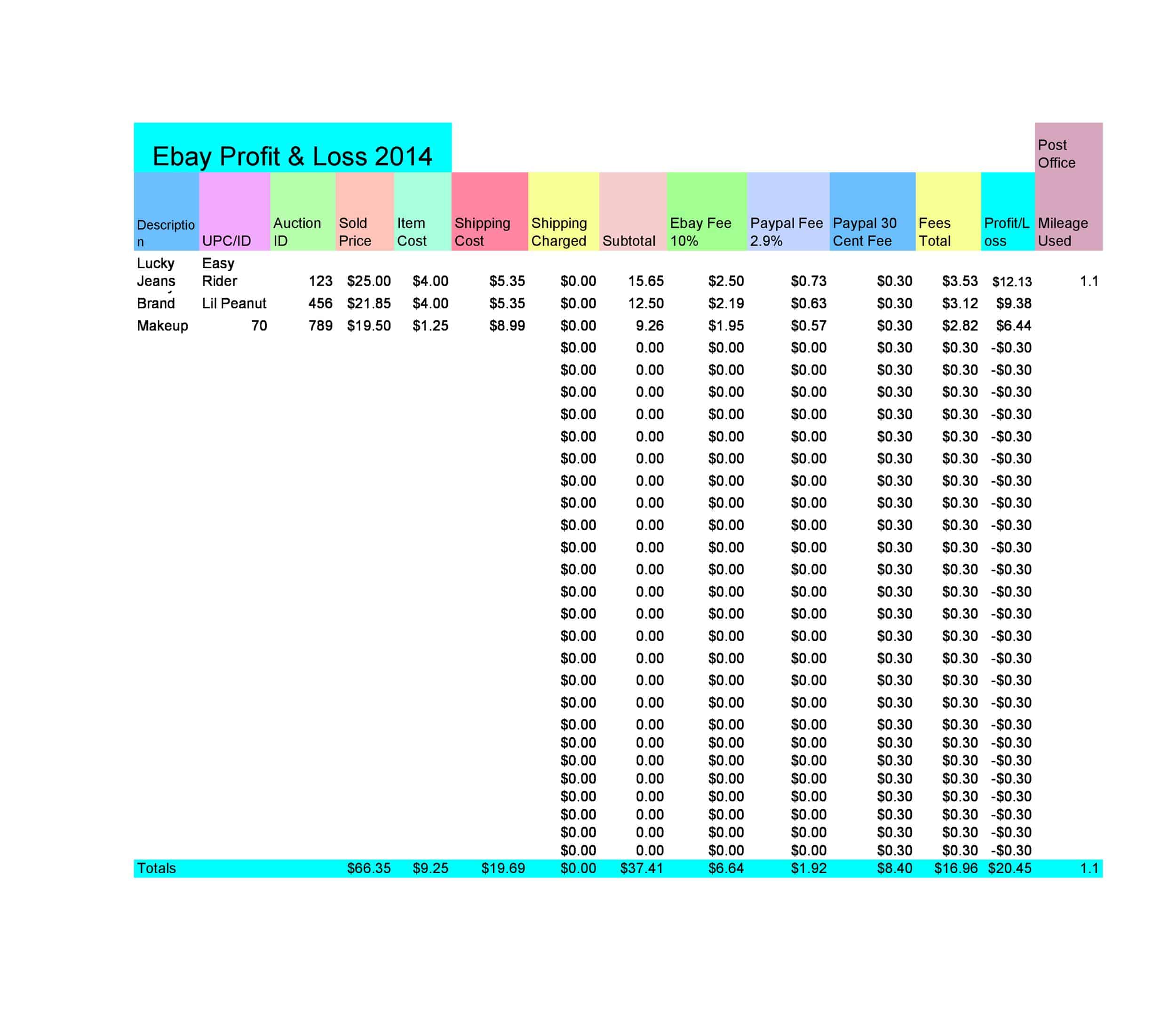
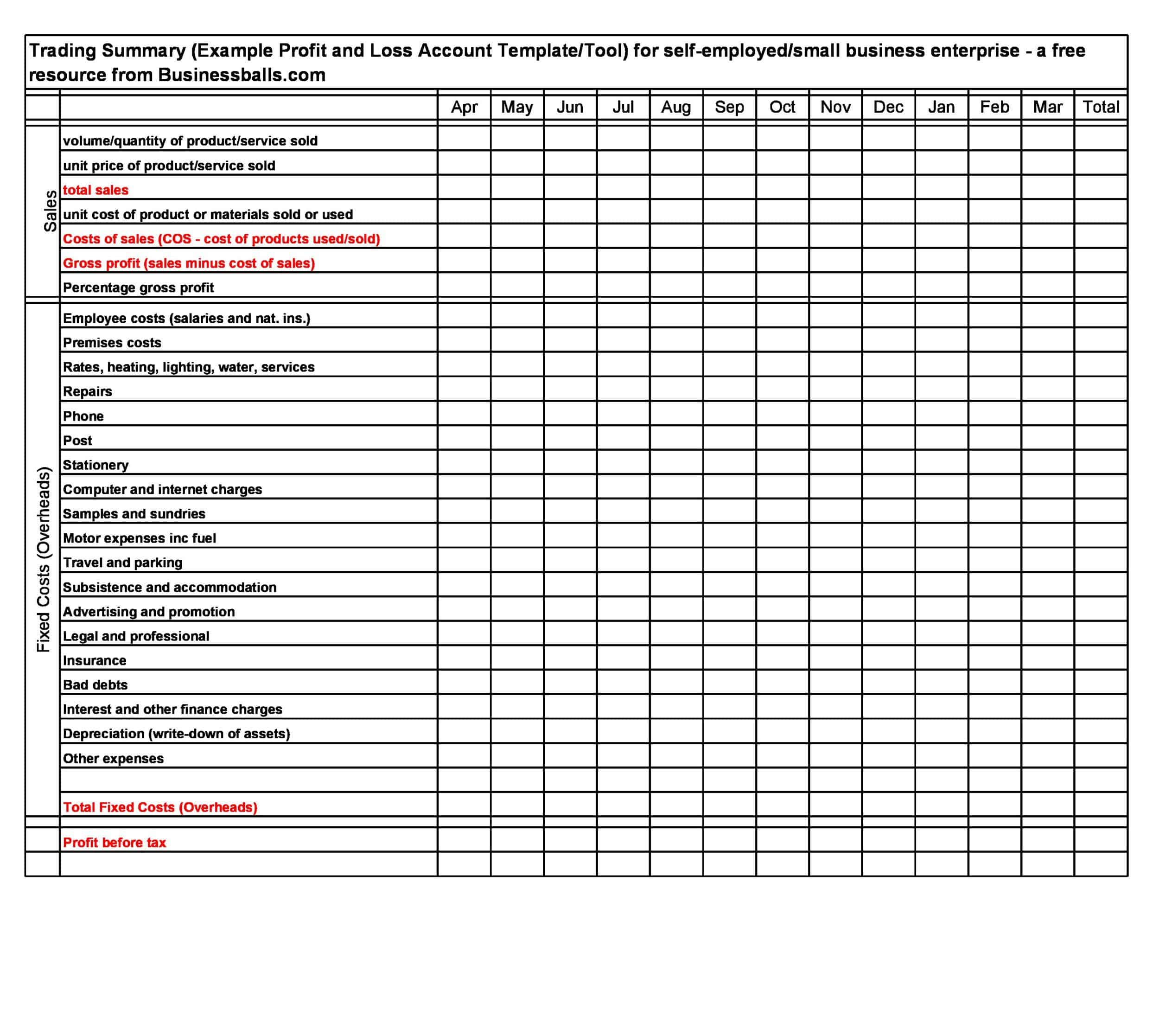
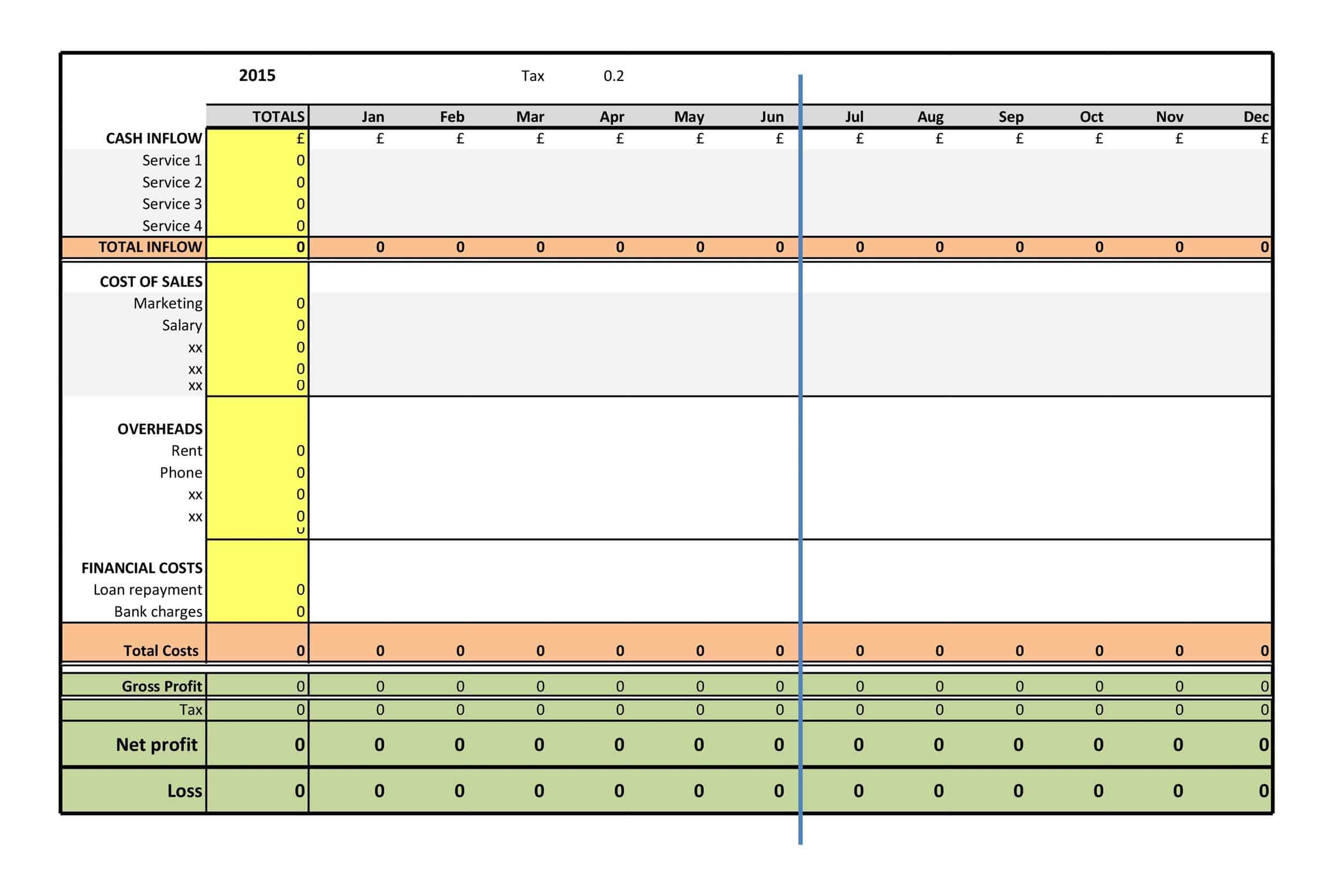
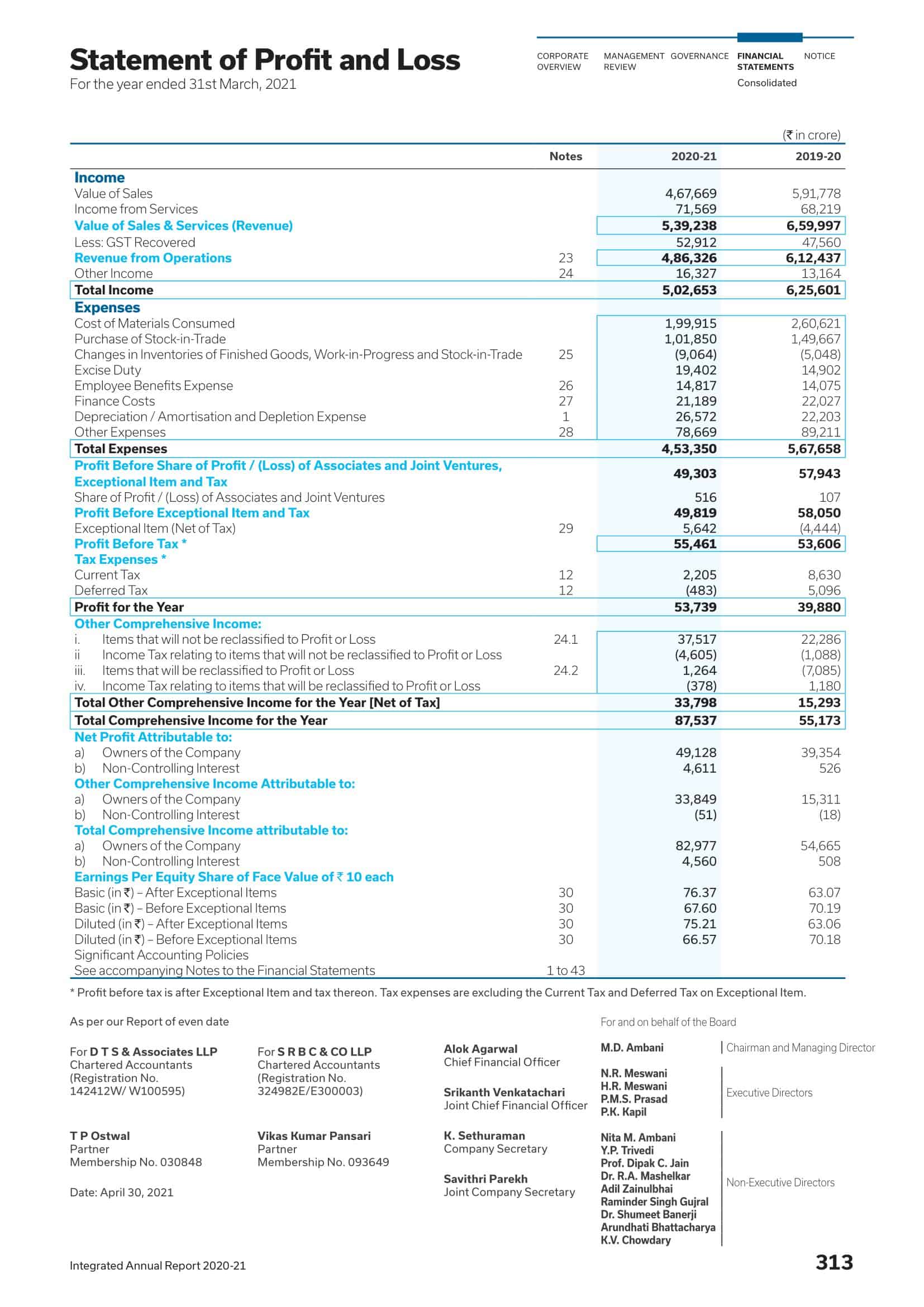
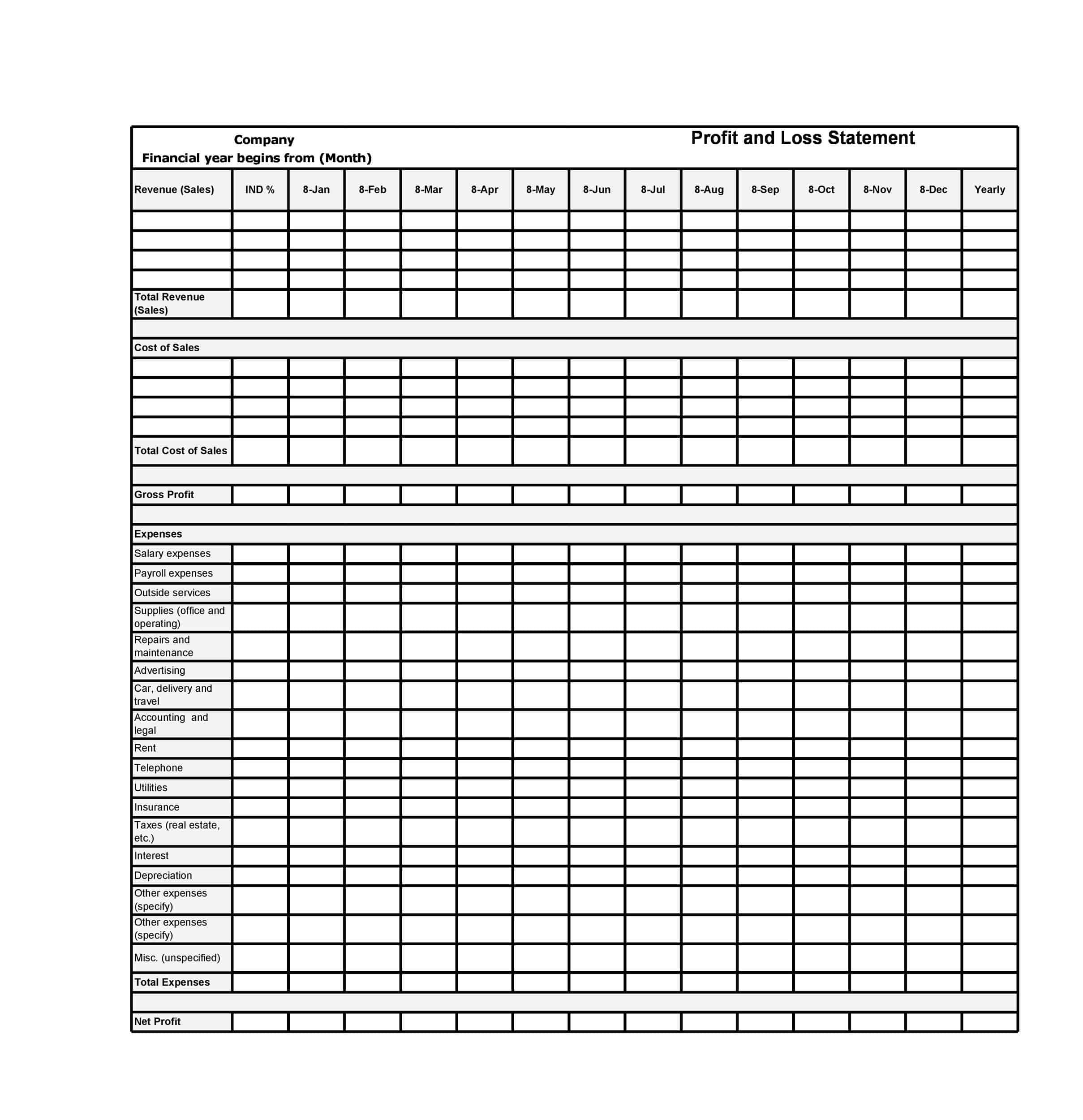
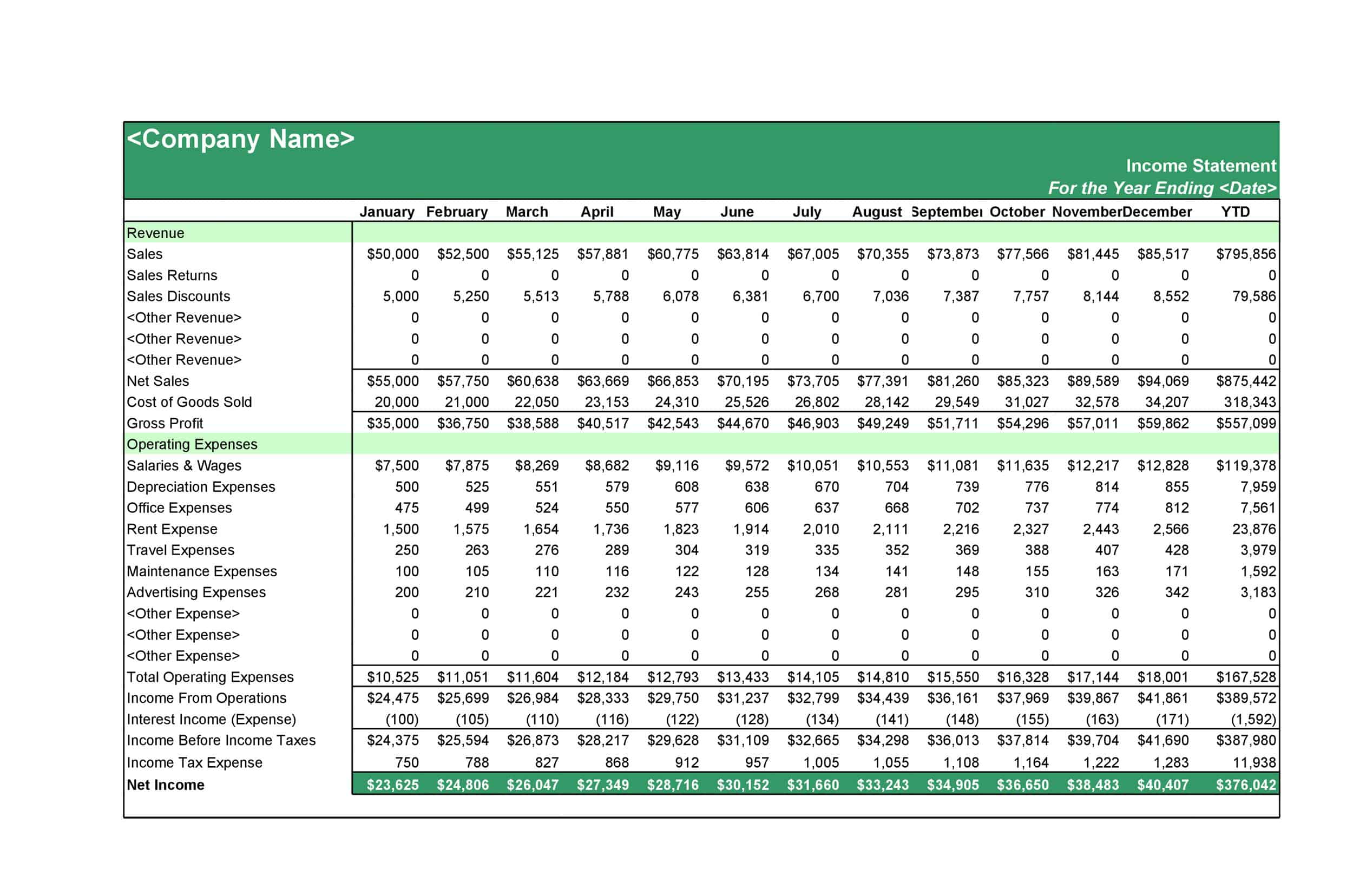
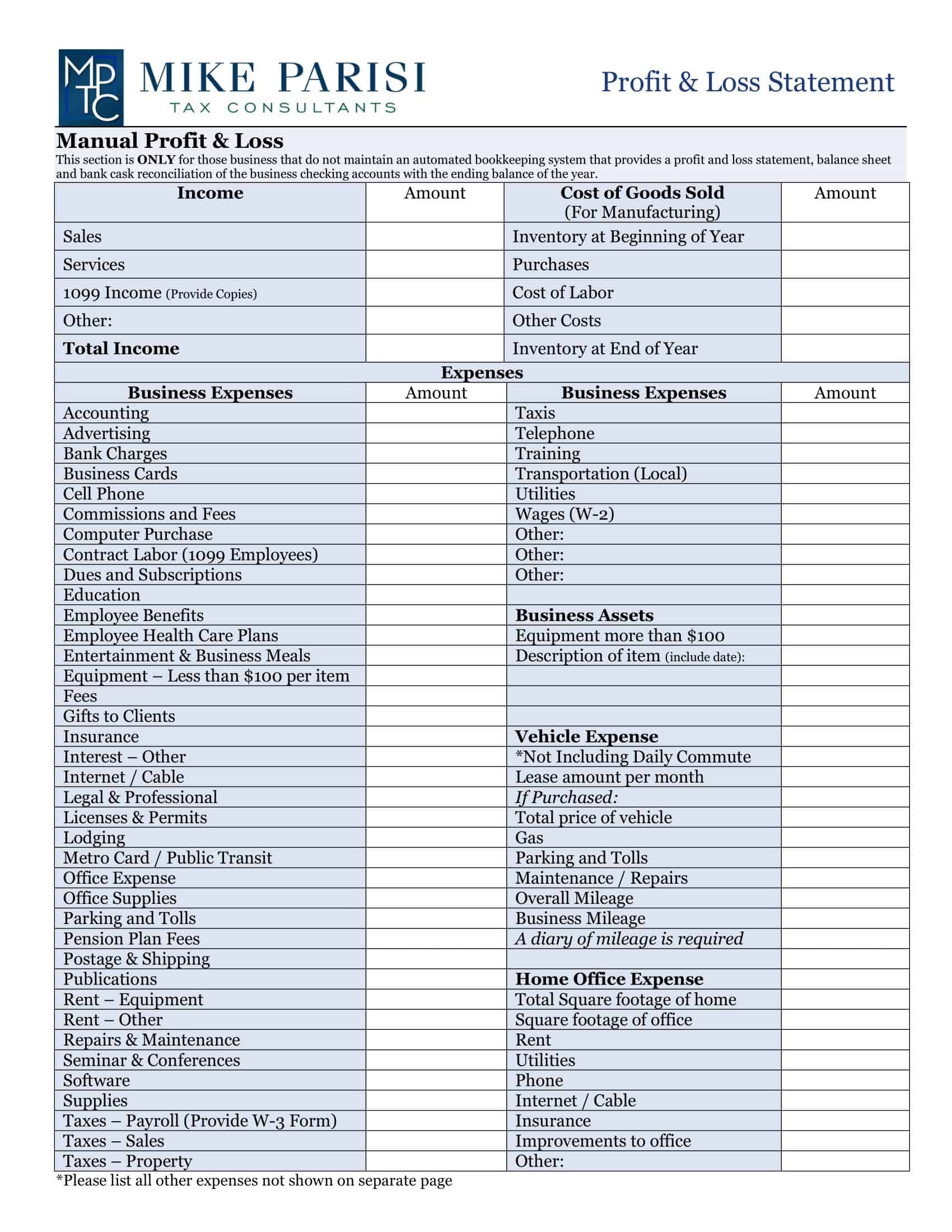
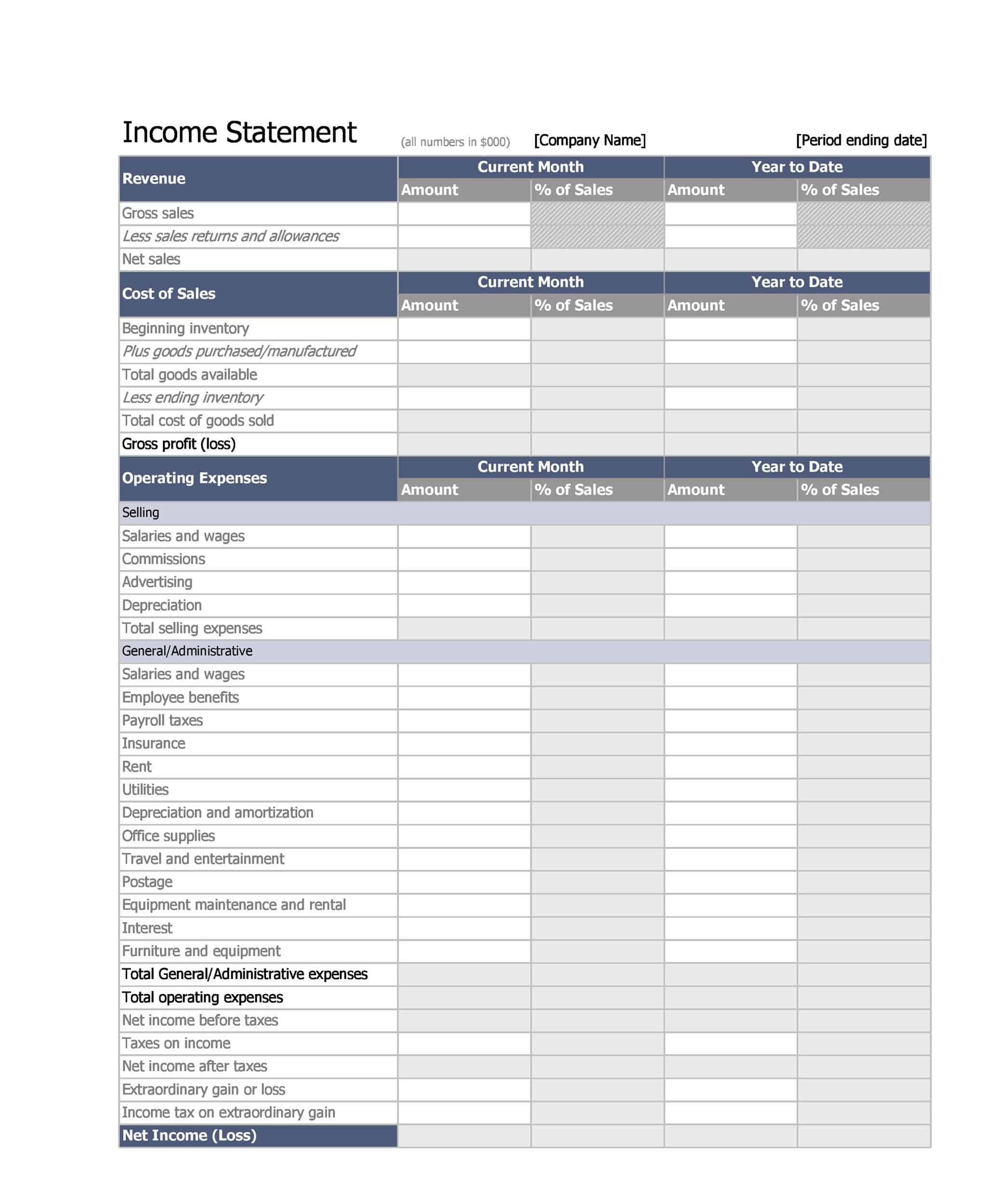
Profit and Loss Statement Templates
Profit and Loss Statement Templates, also known as Income Statement Templates, are essential financial tools used to assess the profitability and financial performance of a business or organization. These templates provide a structured format for presenting the revenues, expenses, and net income or loss generated over a specific period. Profit and Loss Statement Templates help business owners, managers, and stakeholders analyze the financial health of a company and make informed decisions regarding operations, investments, and strategic planning.
Profit and Loss Statement Templates are crucial for evaluating the financial performance of a business and understanding its profitability. By utilizing these templates, business owners and stakeholders can assess revenue trends, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed financial decisions. Profit and loss statements serve as a benchmark for monitoring the financial health of the business over time and comparing performance against industry standards or previous periods. Whether used for internal analysis, investor reporting, or financial planning purposes, Profit and Loss Statement Templates provide a comprehensive and standardized format to assess the financial viability and success of a business.
How Profit and Loss (P&L) Statements Work

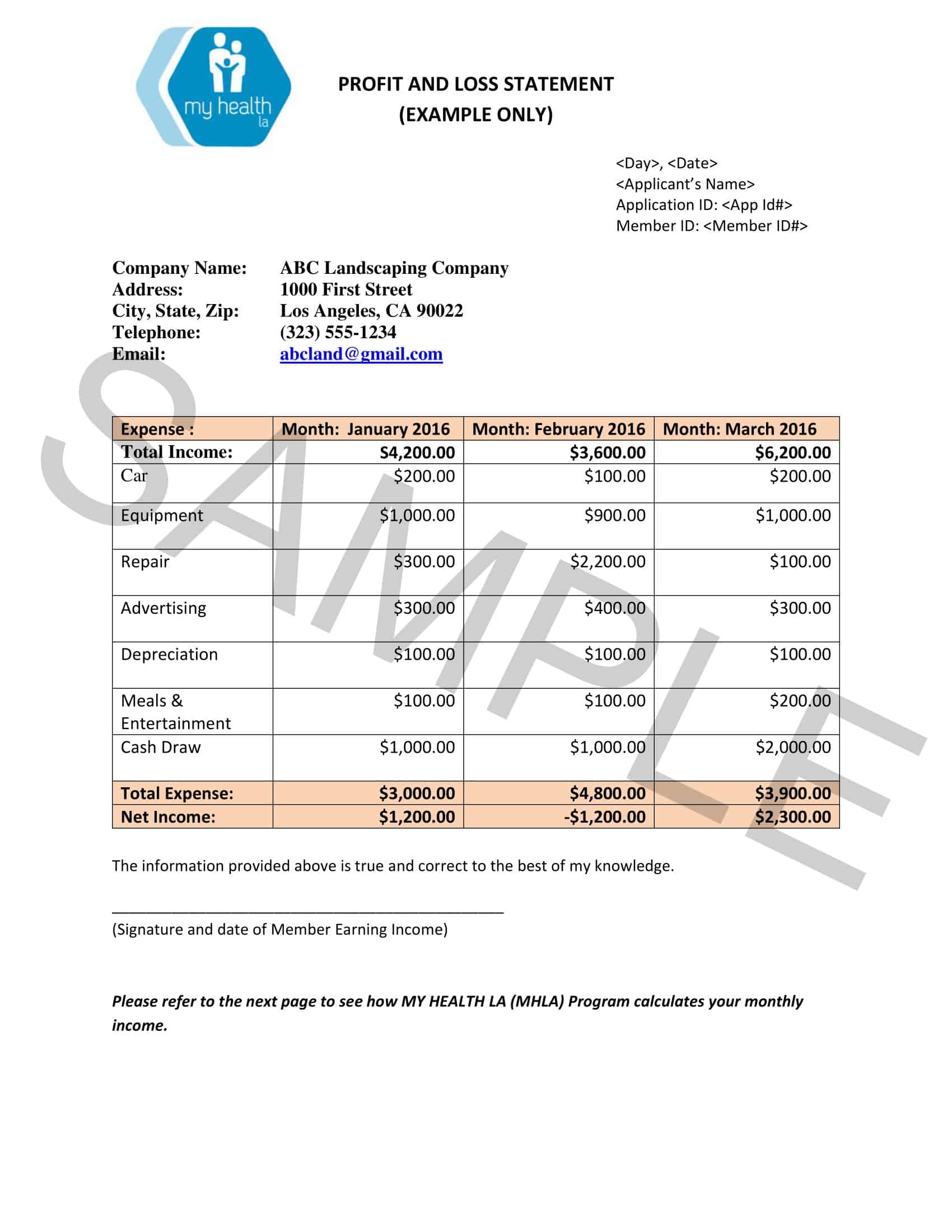
A Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, is a financial document that shows a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period of time, typically a month or a year. The P&L statement is used to calculate the company’s net profit or loss, which is determined by subtracting total expenses from total revenues.
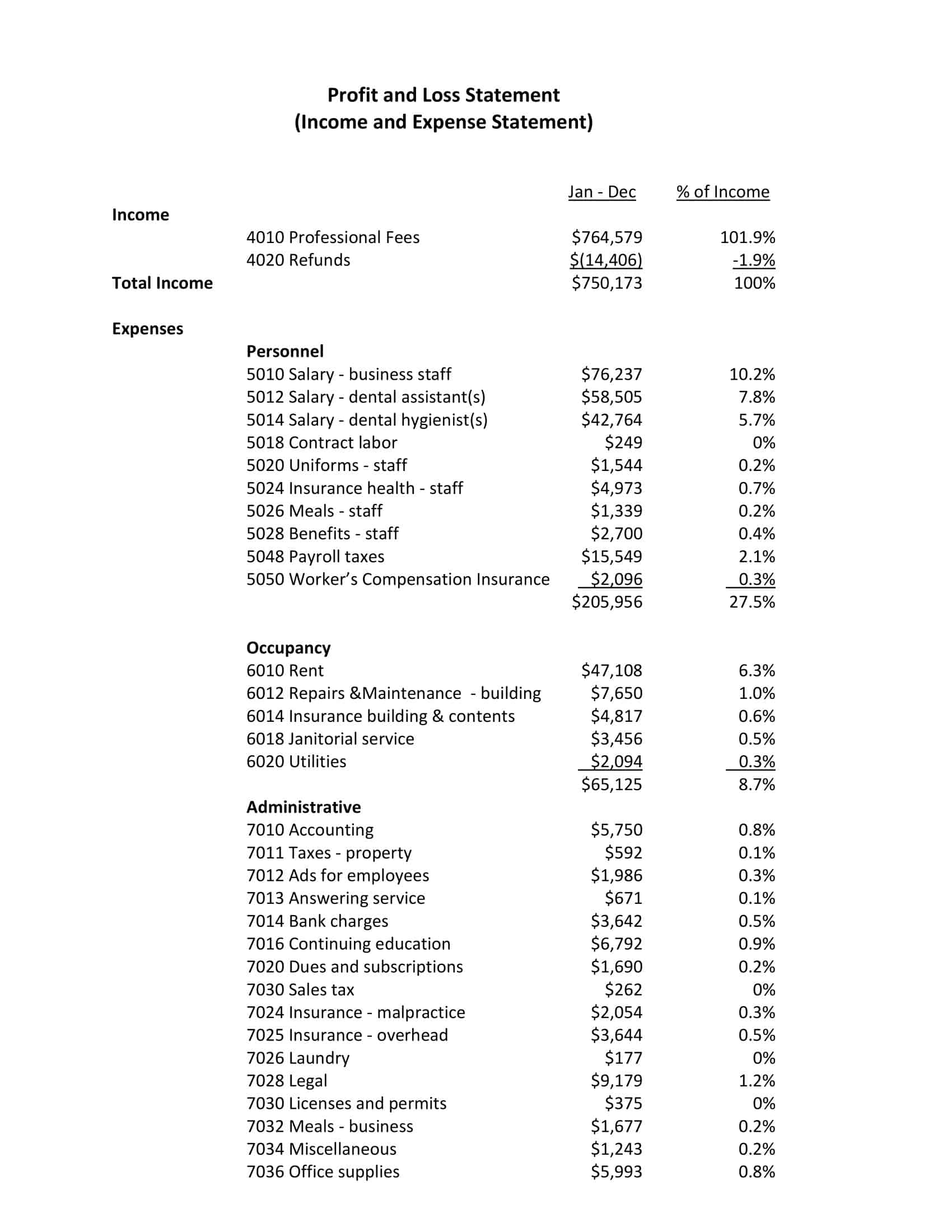
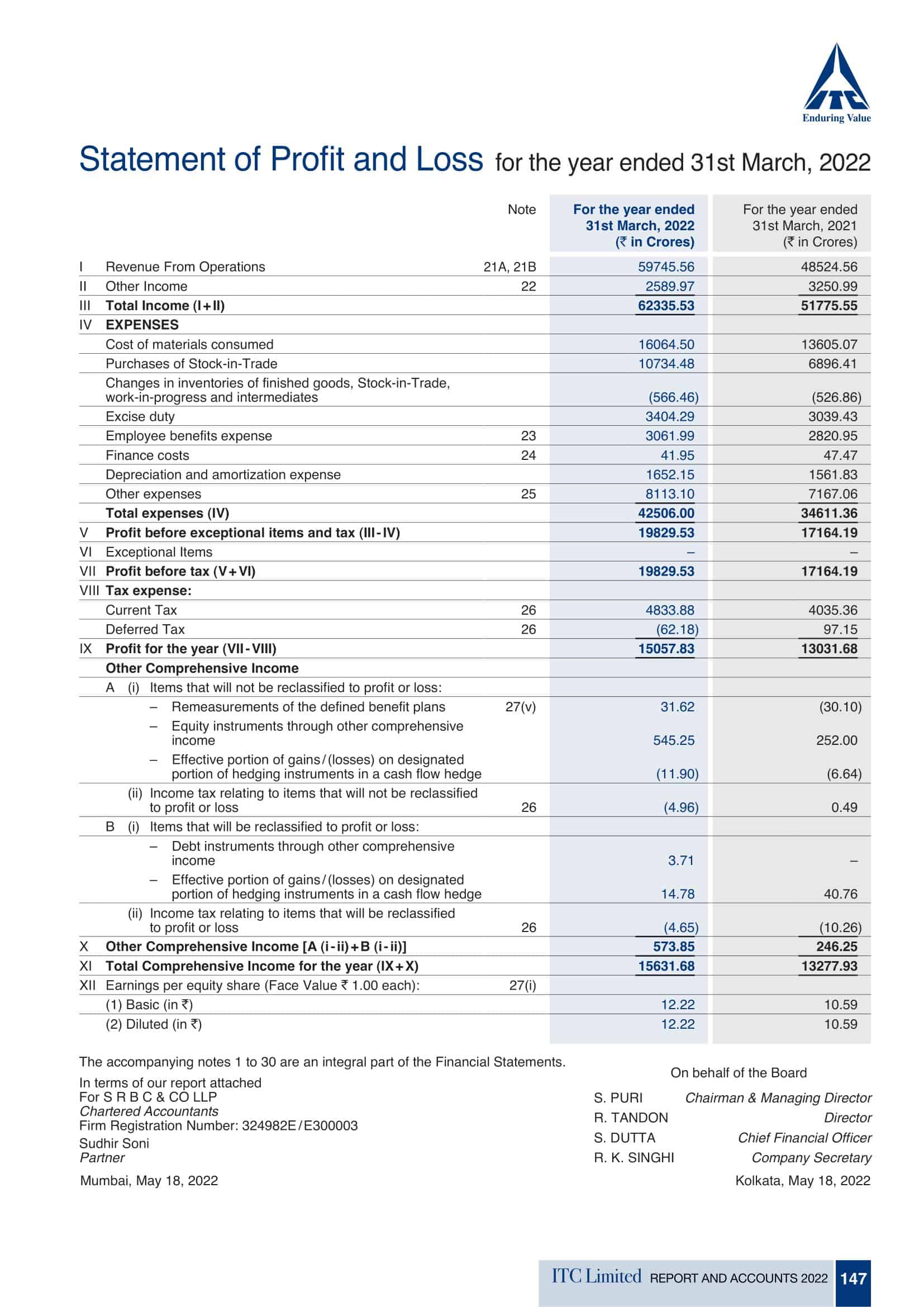
The P&L statement begins with the company’s total revenues, which includes all income generated from the sale of goods or services. This may include sales revenue, rental income, and other sources of income. Next, the P&L statement lists the company’s total expenses, which includes the cost of goods sold (COGS), as well as other operating expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing costs.
To calculate the net profit or loss, the total expenses are subtracted from the total revenues. If the result is positive, the company has made a profit. If the result is negative, the company has incurred a loss. The net profit or loss is often expressed as a percentage of the total revenues, which allows for comparison to prior periods or to industry benchmarks.
The P&L statement is an important tool for businesses, as it provides a snapshot of the company’s financial performance and helps management make informed decisions about the direction of the business. By analyzing the P&L statement, businesses can identify areas where they are generating the most revenue and where they are incurring the most expenses, and make adjustments as needed to improve profitability.
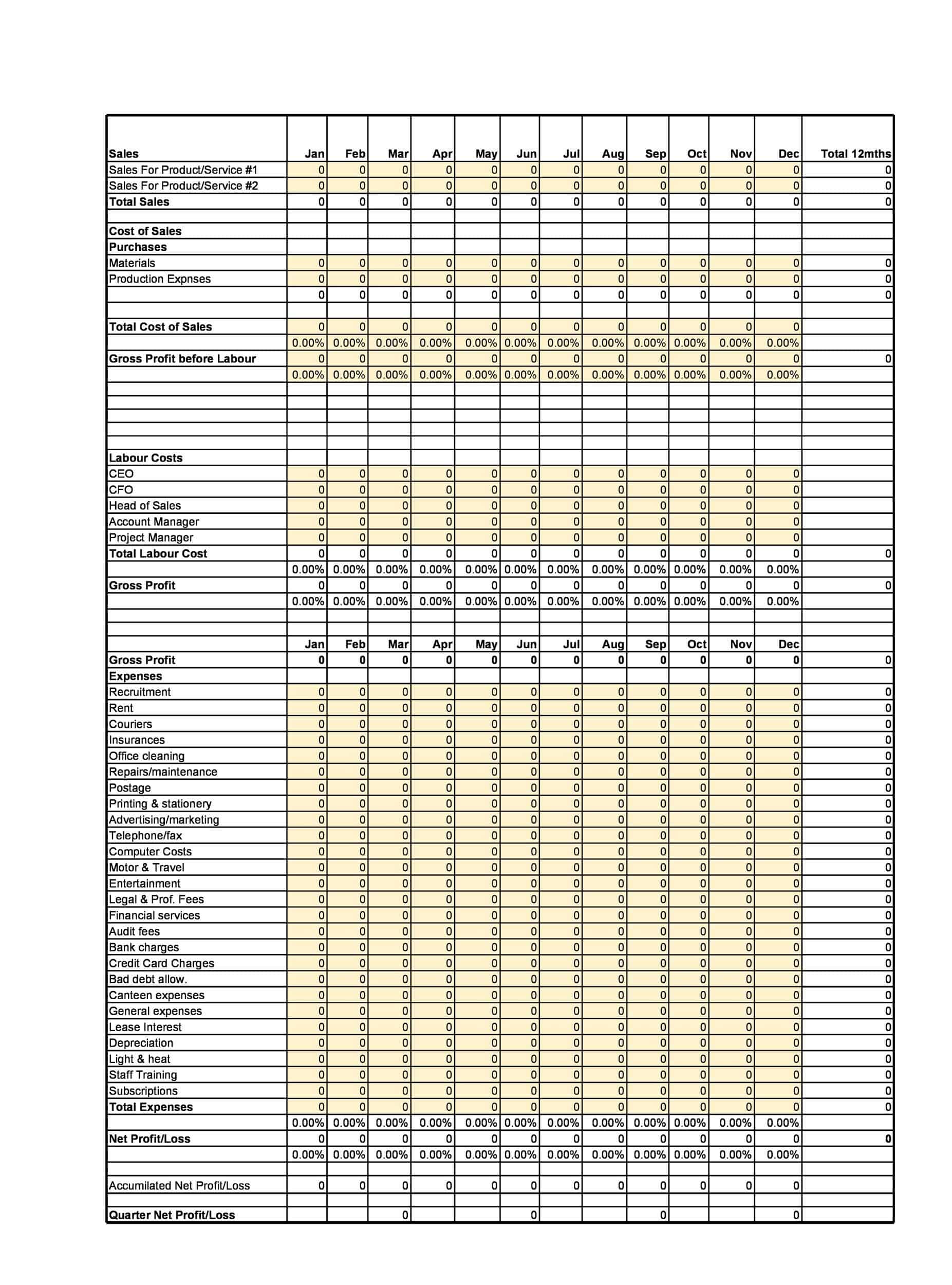
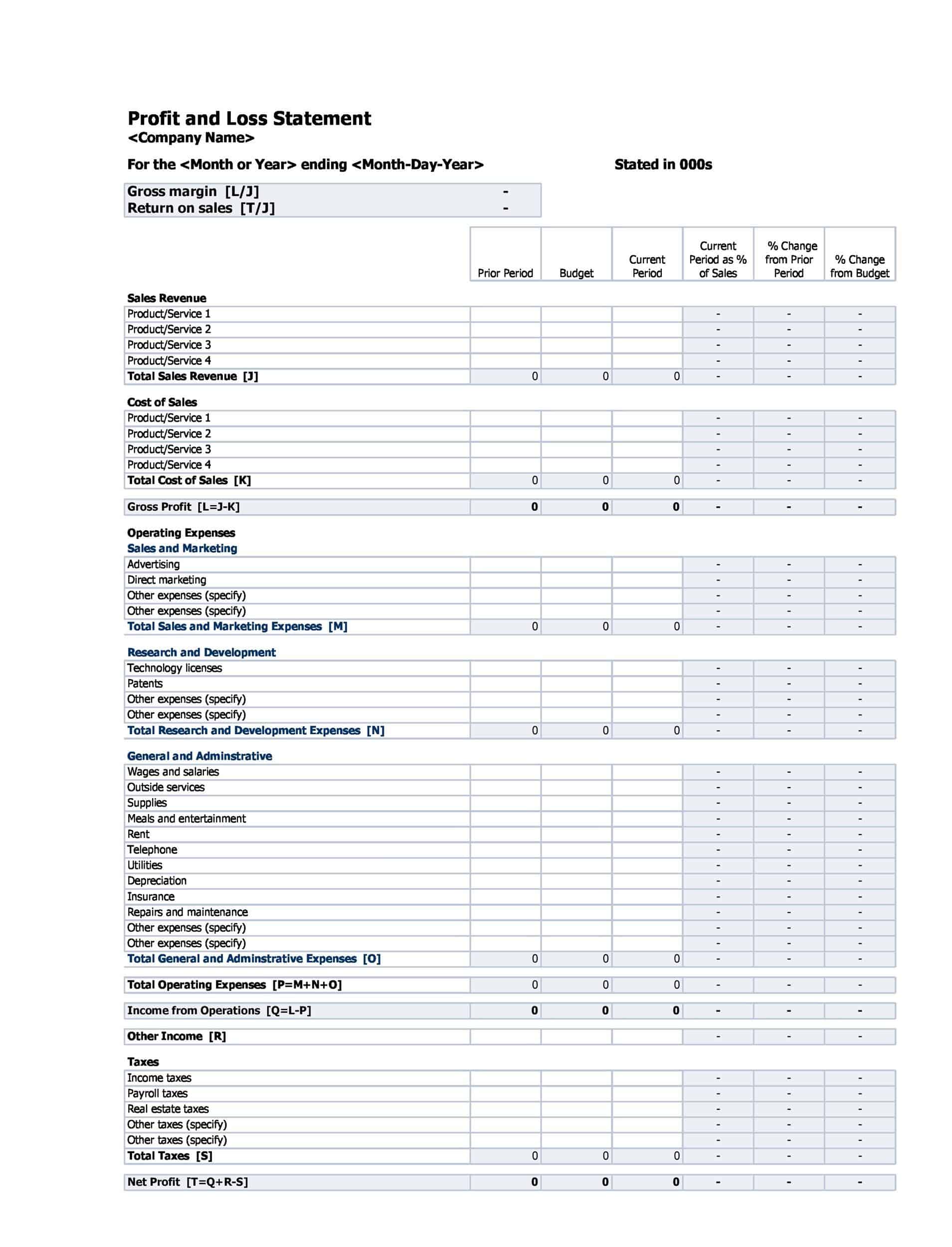
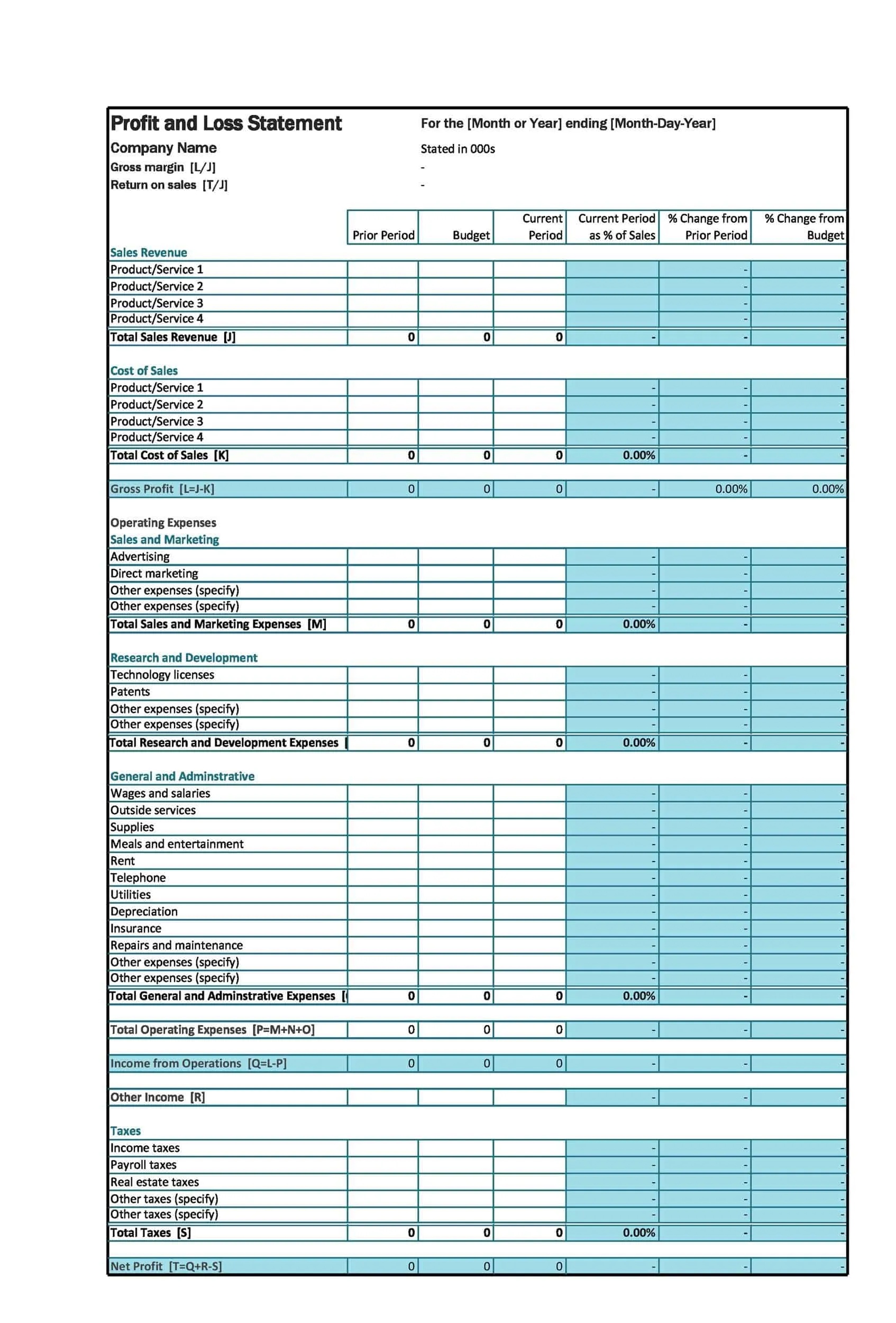
Structure of the Profit and Loss Statement
The structure of a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement varies depending on the type of P&L statement and the specific needs of the company. However, most P&L statements include the following elements:
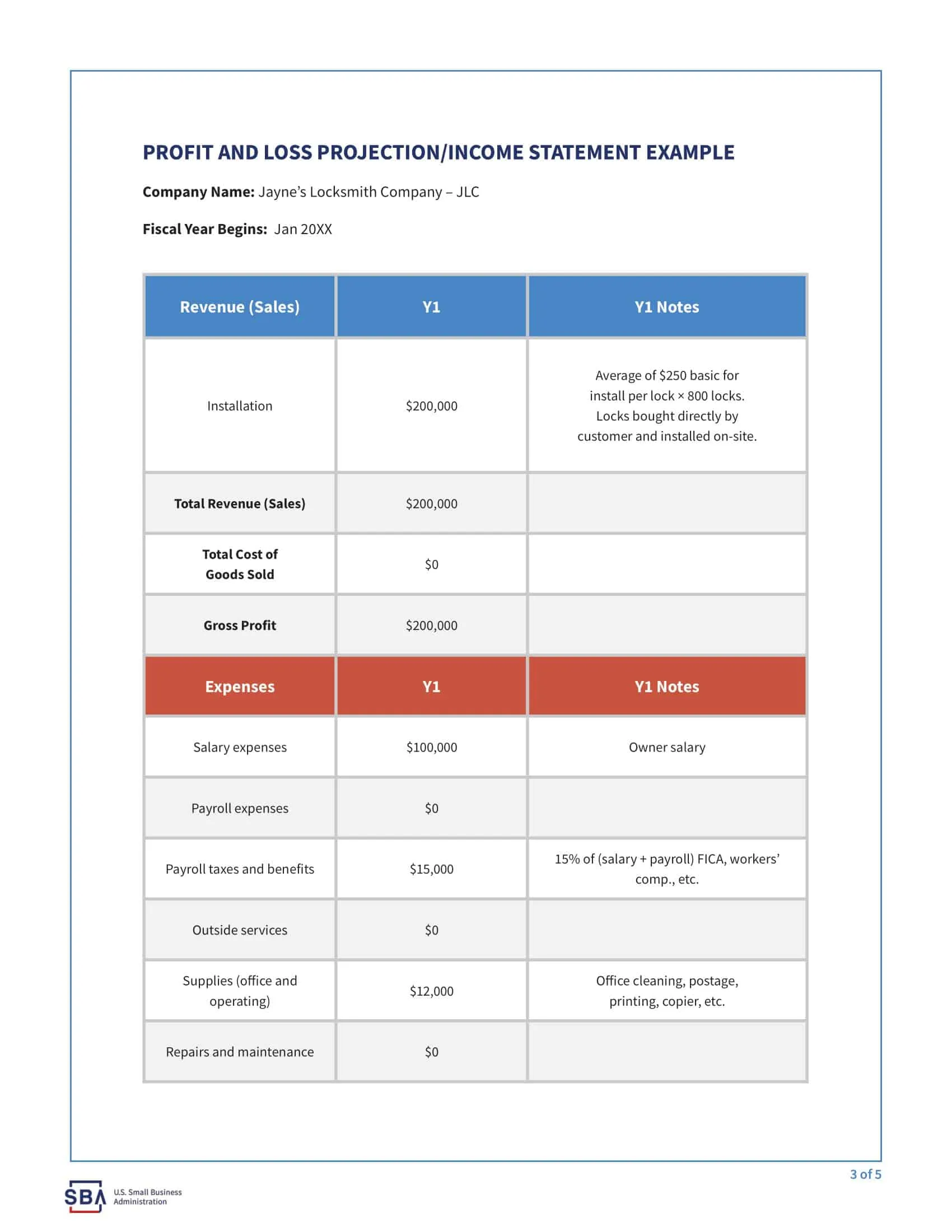
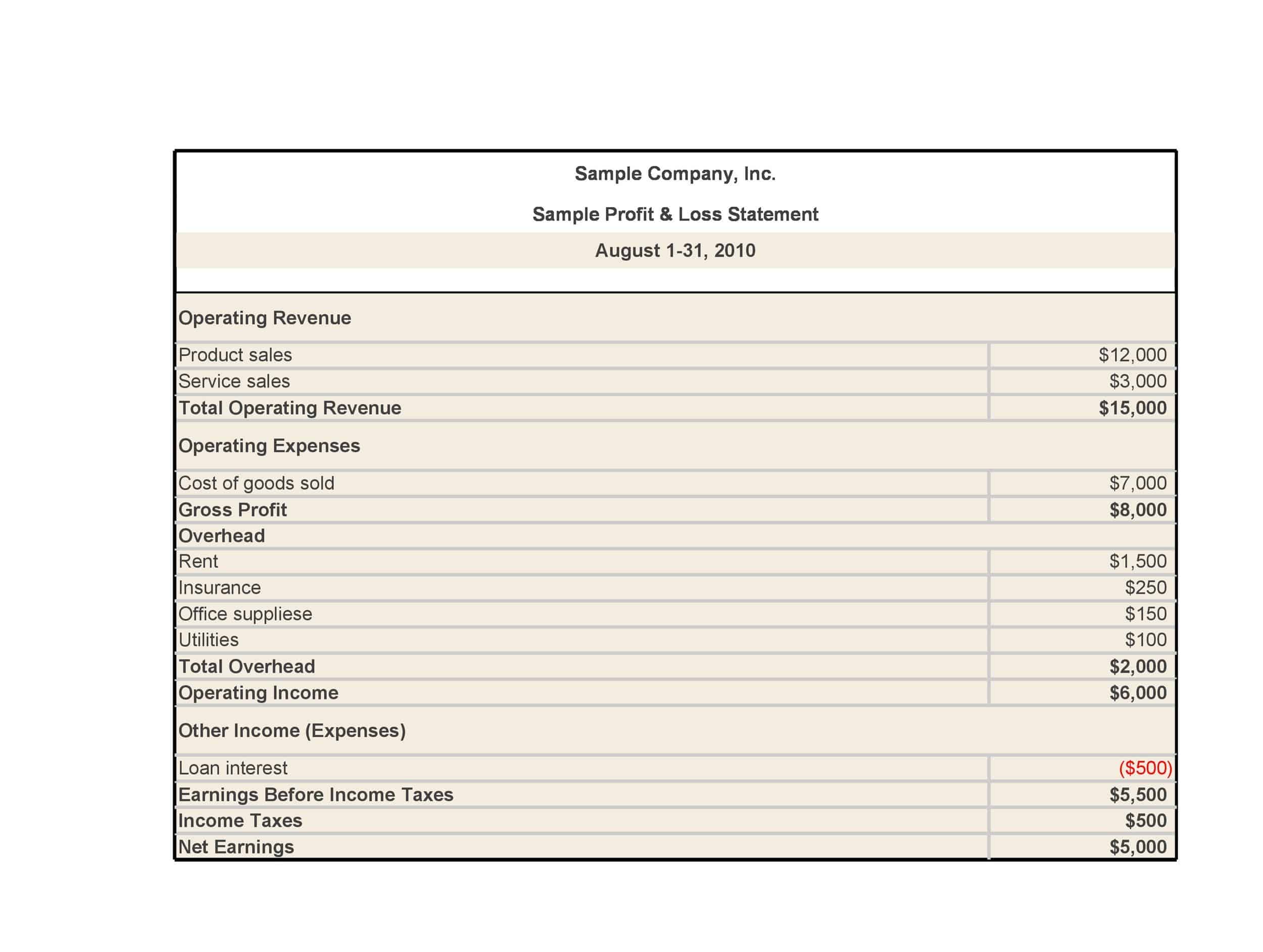
Revenues: The P&L statement begins with the company’s total revenues, which includes all income generated from the sale of goods or services. This may include sales revenue, rental income, and other sources of income.
Cost of goods sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing the goods or services that the company sells. This includes the cost of materials, labor, and other expenses directly related to the production of the goods or services.
Gross profit: The gross profit is calculated by subtracting the COGS from total revenues. This represents the company’s profit before operating expenses are subtracted.
Operating expenses: Operating expenses include the costs of running the business, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing costs.
Operating profit: The operating profit is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from the gross profit. This represents the company’s profit from its core business operations.
Non-operating expenses: Non-operating expenses are expenses that are not directly related to the company’s core business operations. This may include interest expenses, taxes, and other one-time or non-recurring expenses.
Net profit or loss: The net profit or loss is calculated by subtracting non-operating expenses from the operating profit. If the result is positive, the company has made a profit. If the result is negative, the company has incurred a loss. The net profit or loss is often expressed as a percentage of the total revenues, which allows for comparison to prior periods or to industry benchmarks.
Earnings per share (EPS): EPS is a measure of the company’s profitability that is calculated by dividing the net profit by the number of outstanding shares of stock.
Footnotes: P&L statements may include footnotes or other explanatory information to provide more context or detail about the financial information presented in the statement.
Comparative data: Some P&L statements present financial results for multiple periods side-by-side, allowing for easy comparison of the company’s financial performance over time.
Types of Profit and Loss (P&L) Statements
There are several types of Profit and Loss (P&L) statements, including single-step, multi-step, and contribution margin P&L statements.
- Single-step P&L statements present the company’s revenues and expenses in a single calculation to determine the net profit or loss. This type of P&L statement is useful for companies with relatively simple operations, as it provides a straightforward overview of the company’s financial performance.
- Multi-step P&L statements provide a more detailed analysis of the company’s financial performance by presenting revenues and expenses in multiple steps. This type of P&L statement begins with the company’s gross profit, which is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenues. The gross profit is then used to calculate the company’s operating profit, which is determined by subtracting operating expenses (such as salaries and rent) from the gross profit. The operating profit is then used to calculate the company’s net profit or loss, which is determined by subtracting taxes and other non-operating expenses from the operating profit.
- Contribution margin P&L statements focus on the contribution margin, which is the amount of revenue that remains after deducting the COGS. This type of P&L statement is useful for companies that produce a large number of products or services, as it allows management to analyze the profitability of individual products or services.
- Consolidated P&L statements: Consolidated P&L statements present the financial results of multiple companies that are consolidated into a single entity. This type of P&L statement is useful for companies that own multiple subsidiaries or have a complex organizational structure.
- Projected P&L statements: Projected P&L statements are based on a company’s projected or forecasted revenues and expenses, rather than actual results. These types of P&L statements are often used to create budgets or to make business decisions based on anticipated financial performance.
- Comparative P&L statements: Comparative P&L statements present financial results for multiple periods side-by-side, allowing for easy comparison of the company’s financial performance over time. This type of P&L statement is useful for tracking the company’s progress and identifying trends or patterns in its financial performance.
How to Analyze a Profit and Loss Statement (P&L)
Analyzing a P&L statement is an important step in understanding a company’s financial performance and making informed business decisions. By reviewing the net profit or loss, gross profit margin, operating expenses, non-operating expenses, and comparing the P&L statement to prior periods or industry benchmarks, you can get a clear picture of the company’s financial health.
There are several key steps to follow when analyzing a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement:
Review the overall net profit or loss: The net profit or loss is a key indicator of the company’s financial performance. A positive net profit indicates that the company is generating more revenue than expenses, while a negative net profit indicates that the company is incurring more expenses than revenue.
Analyze the gross profit margin: The gross profit margin is calculated by dividing the gross profit by total revenues. This ratio indicates the company’s profitability before operating expenses are subtracted. A higher gross profit margin indicates that the company is generating more profit from its core business operations.
Examine the operating expenses: Operating expenses include the costs of running the business, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing costs. By analyzing the operating expenses, you can identify areas where the company is spending the most money and determine whether those expenses are necessary or can be reduced.
Review the non-operating expenses: Non-operating expenses are expenses that are not directly related to the company’s core business operations. These may include interest expenses, taxes, and other one-time or non-recurring expenses. By analyzing the non-operating expenses, you can get a better understanding of the company’s overall financial performance.
Compare the P&L statement to prior periods or industry benchmarks: By comparing the P&L statement to prior periods or industry benchmarks, you can identify trends or patterns in the company’s financial performance and determine whether the company is improving or declining.
FAQs
Here are some common questions and answers about Profit and Loss (P&L) statements:
What is a P&L statement?
A P&L statement, also known as an income statement, is a financial document that summarizes a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period of time, typically a month or a year. The P&L statement shows the company’s net profit or loss, which is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenues.
Why is a P&L statement important?
A P&L statement is an important tool for businesses, as it provides a snapshot of the company’s financial performance and helps management make informed decisions about the direction of the business. By analyzing the P&L statement, businesses can identify areas where they are generating the most revenue and where they are incurring the most expenses, and make adjustments as needed to improve profitability.
Who uses P&L statements?
P&L statements are used by businesses of all sizes, as well as investors, creditors, and other stakeholders who are interested in understanding the company’s financial performance.
How often are P&L statements prepared?
P&L statements are typically prepared on a monthly or quarterly basis, although some companies may also prepare annual P&L statements. The frequency of P&L statements depends on the specific needs of the company and the information it needs to track and analyze its financial performance.
What are the key components of a P&L statement?
The key components of a P&L statement include total revenues, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, operating profit, non-operating expenses, and net profit or loss.
What is a contribution margin P&L statement?
A contribution margin P&L statement focuses on the contribution margin, which is the amount of revenue that remains after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). This type of P&L statement is useful for companies that produce a large number of products or services, as it allows management to analyze the profitability of individual products or services.
Can a P&L statement be amended or corrected?
In some cases, it may be necessary to amend or correct a P&L statement if there is an error or omission on the document. The process for amending or correcting a P&L statement varies depending on the location, but it typically involves submitting a request and any supporting documentation to the agency that issued the statement.
How do I create a P&L statement for my business?
To create a P&L statement for your business, you will need to gather financial information about your revenues and expenses. This may include sales data, invoices, receipts, and other financial documents. You can then use this information to calculate your net profit or loss by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. There are also many software programs and online tools available that can help you create a P&L statement for your business.





































![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)

This blog’s sample profit and loss statement template is so helpful for small business owners like me. Thanks, author, for sharing this valuable resource. You’ve made financial tracking a breeze!