Once upon a time, the only tool a teacher had to keep track of a student’s progress was a simple notebook filled with columns of numbers and letters. This modest ledger, known as a gradebook, played a crucial role in the journey of education.
Fast forward to today, the gradebook has morphed into a digital titan, providing real-time updates and fostering communication like never before. This article will spin the tale of the gradebook, its transformations, and its indispensable role in modern education.
Table of Contents
What is a Gradebook Template ?

A gradebook template is a pre-designed format or structure for a gradebook, typically available in digital tools such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or various learning management systems. It often consists of rows and columns where teachers can input students’ names and their corresponding grades for various assignments, quizzes, exams, and other assessments. It’s a convenient tool to help educators manage and track students’ academic performance over a term.
Some templates might also include functionality to automatically calculate total scores, averages, percentage grades, or even convert raw scores into letter grades based on predetermined grading scales. In some advanced templates, there can be features for attendance tracking, weighting grades, or visualization of student performance.
A gradebook template provides a streamlined, organized system for recording and managing grades, saving educators time and reducing the potential for errors. It also offers a consistent and transparent way for students and parents to understand grading methods and observe progress throughout the academic year.
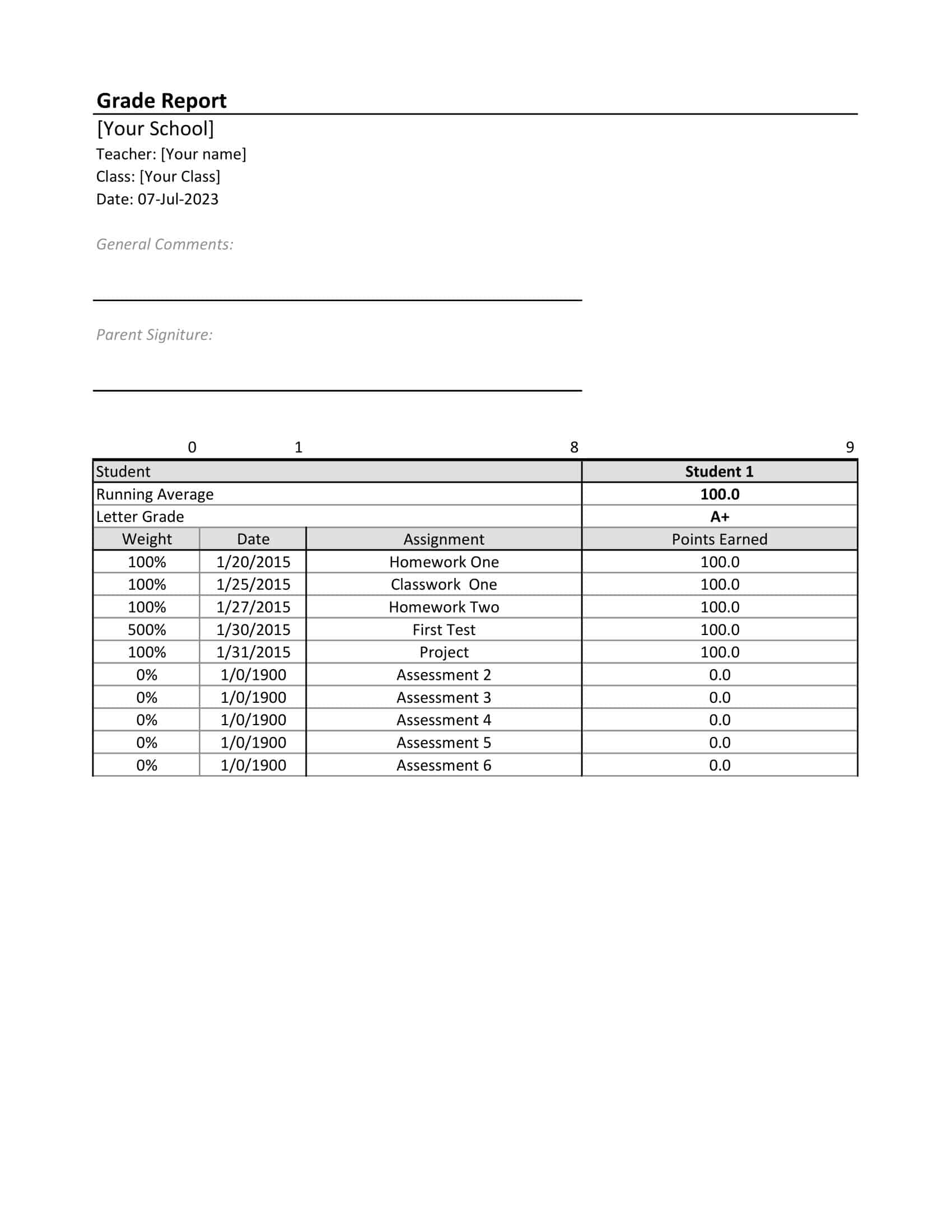
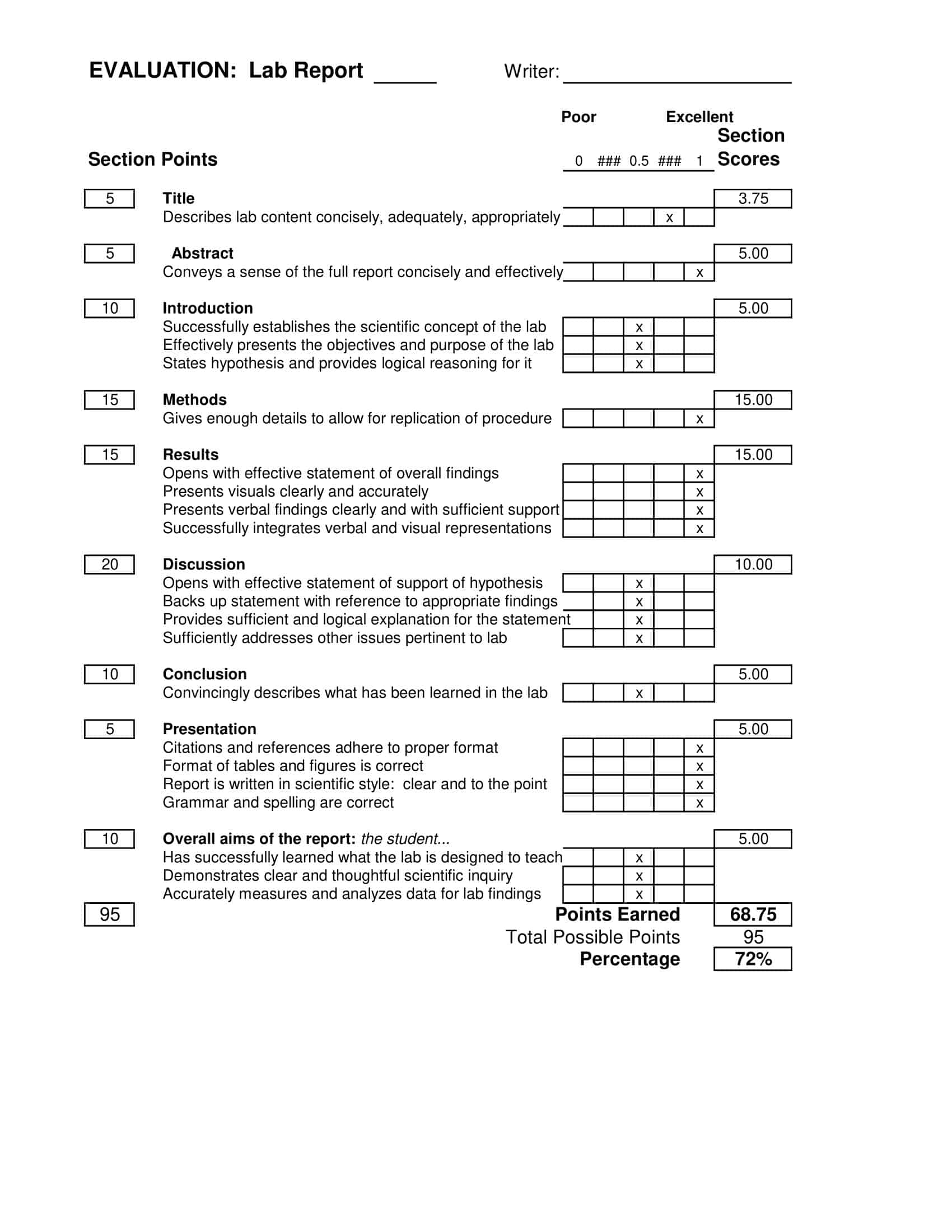
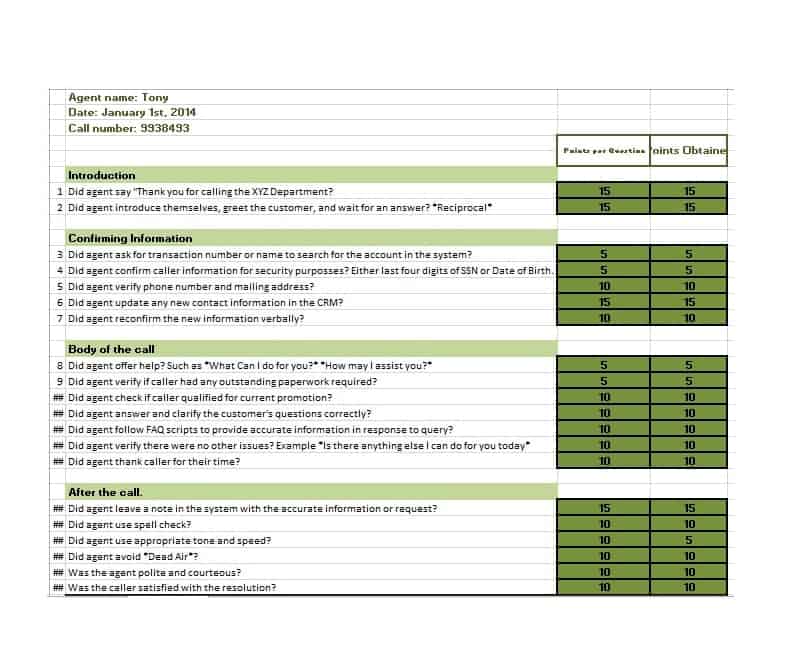
Gradebook Templates
Gradebook Templates are integral instruments for educators, enabling them to track and evaluate the academic progress of their students. Designed to record grades for various assignments, projects, quizzes, and tests, these templates contribute to an efficient grading process.
Typically structured in a table or spreadsheet format, Gradebook Templates feature rows for student names and columns for individual assignments. An additional set of columns is often present to calculate averages or final grades, offering an at-a-glance understanding of student performance.
Customizable to the needs of each class or curriculum, Gradebook Templates can accommodate diverse grading systems. Percentage-based grading, point systems, or even letter grades can be incorporated into these templates, making them adaptable to various academic requirements.
What is the purpose of gradebook?
A gradebook serves as an essential tool for educators to record and track students’ academic performance throughout a course. The primary purpose of a gradebook is to organize and monitor students’ scores on assignments, tests, projects, and other forms of assessment in a systematic way. It enables educators to evaluate individual and overall class performance, identify areas where students may be struggling, and determine final grades at the end of a term.
Additionally, a well-maintained gradebook can provide transparency for students and parents, allowing them to see how each score contributes to the final grade, therefore fostering awareness and encouraging responsibility for learning progress. It can also help teachers make informed decisions about instruction adjustments, reteaching needs, or personalized learning strategies. Overall, the gradebook is integral to facilitating effective teaching, learning, and communication within the educational process.
What are the reasons behind grading students in education?
Grading students in education serves several essential purposes, including:
Assessment of Learning
Grading allows teachers to evaluate a student’s understanding and knowledge in a specific subject area. Through various assessments (like tests, projects, essays, and presentations), teachers can gauge the degree to which students have mastered the content, skills, or competencies associated with a course.
Feedback Mechanism
Grades provide students with feedback on their performance, helping them understand their strengths and areas for improvement. They allow students to gauge their progress and determine what they need to focus on for further learning. Additionally, grades can also provide feedback to teachers, showing them where their instruction might need adjustment.
Motivation
Grading can serve as a motivator for students to engage in and take responsibility for their learning. Grades can incentivize students to study and strive for improvement, especially when they understand the grading system and see a clear link between effort, learning, and grades.
Structuring Expectations
Grades offer a standardized measurement that sets expectations for academic achievement. They provide benchmarks that can guide students’ study habits and effort levels, informing them of the academic standards they need to meet or exceed.
Record of Achievement
Grades serve as a formal record of students’ academic performance, which can be used by educational institutions for promotions, placements, scholarships, or admissions into higher education programs. Grades can demonstrate a student’s ability, commitment, and readiness for more advanced study.
Communication Tool
Grades serve as a universal language that communicates a student’s performance to various stakeholders – parents, teachers, school administrators, and even potential employers or higher education institutions. They allow these groups to understand a student’s academic performance, irrespective of the teaching methods or curriculum used.
However, while grading is a common practice, it’s essential to consider that it should be part of a broader assessment strategy. It’s important to balance grades with other forms of assessment that provide a more holistic view of a student’s abilities, like portfolio work, project-based assessments, peer evaluations, self-assessments, and teacher observations.
What are the different types of gradebook?
Gradebooks come in various forms and styles, each designed to suit different teaching methods and needs. Here are some types of gradebooks:
Paper Gradebooks
These are traditional, physical gradebooks where teachers manually record student grades. They typically contain a grid of rows and columns where the teacher lists student names and the assignments, with each cell corresponding to a specific student’s grade for a particular assignment.
Electronic Spreadsheet Gradebooks
Teachers can use digital spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets to track grades. These electronic gradebooks can automatically calculate total scores, averages, and percentages, and they often have templates that allow for quick setup and easy customization. They also enable easy data manipulation, like sorting students by scores, highlighting students below a certain grade, or creating charts for visual representation.
Learning Management System (LMS) Gradebooks
Many Learning Management Systems (such as Canvas, Blackboard, or Moodle) have built-in digital gradebooks. These LMS gradebooks can automatically update when students complete online assignments or assessments, and can even allow students to see their grades in real-time. They often feature options for weighting grades, dropping lowest scores, providing written feedback, and more.
Online Gradebook Services
These are standalone, often cloud-based, services like PowerSchool or Infinite Campus that teachers can use to track grades. These services usually have robust features, including integration with school databases, real-time parent and student access, attendance tracking, report card generation, and analytics.
Standards-Based Gradebooks
These gradebooks are organized around specific learning standards or competencies rather than around assignments or tests. In these gradebooks, students are graded on their mastery of various skills or concepts. This approach provides a more detailed view of student progress and can help identify gaps in understanding.
Portfolio Gradebooks
In these types of gradebooks, student progress is documented through a collection of their work over time. Portfolio gradebooks can include assignments, projects, self-assessments, teacher observations, and more. This approach provides a more holistic view of student achievement, focusing not only on the final result but also on the learning process.
Narrative Gradebooks
These gradebooks replace traditional grades with detailed written feedback. They provide in-depth commentary on students’ skills, understanding, and progress, which can help students understand their strengths and areas for improvement. Narrative gradebooks can provide a more nuanced view of student performance than a single numerical grade.
Grade Calculations
Calculating grades can be a complex process depending on the grading structure you’re using. Here’s a detailed guide to help you understand various methods, including weighted grades, total points, extra credit, and dropping lowest scores:
- Weighted Grades: This method involves assigning a specific percentage of the overall grade to each assignment type or category. This way, different types of assignments have different impacts on the final grade. Here’s how you calculate it:
- First, decide what percentage of the final grade each category (e.g., quizzes, projects, tests) will make up. Ensure all percentages add up to 100%.
- Next, calculate the average grade for each category. This is typically done by adding up all the grades in a category and dividing by the total number of assignments in that category.
- Then, multiply the average grade for each category by its weight (in decimal form). For instance, if quizzes are 20% of the grade and the average quiz grade is 85%, you would multiply 85 by 0.2.
- Finally, add up all these weighted averages. The result is the final grade.
- Total Points: This system involves assigning points to each assignment, and the final grade is determined by the number of points a student has earned out of the total possible points. Here’s how to calculate it:
- First, determine how many points each assignment will be worth. The more significant an assignment is, the more points it should be worth.
- Add up all the points a student has earned from all assignments. Do the same for the total possible points from all assignments.
- Divide the total points earned by the total possible points, and multiply by 100 to get the percentage grade.
- Extra Credit: Extra credit provides students with opportunities to improve their grades by doing additional work. It can be added in different ways:
- One way is to simply add the extra credit points to the total points a student has earned. However, this method can inflate grades if you’re not careful.
- A more balanced method is to add the extra credit points to both the total points earned and the total possible points. This method provides a boost to the student’s grade, but it doesn’t overly inflate their grade because the total possible points also increases.
- Dropping Lowest Scores: This method involves removing one or more of a student’s lowest scores from the calculation of the final grade. Here’s how to do it:
- First, decide how many low scores you want to drop from each category of assignments.
- Sort the grades in each category from lowest to highest.
- Remove the lowest scores as per your decision.
- Calculate the final grade (whether using weighted grades or total points) based on the remaining scores.
How to Use the Grade Book Template
Using a grade book template can vary depending on the software you’re using, but here’s a general step-by-step guide that should apply to most common tools like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets:
Find and Open the Template: Look for a pre-existing grade book template online or in your chosen software. Microsoft Excel, for example, has a library of templates, and there are many free templates available online for Google Sheets as well. Once you find the template you want, open it up.
Customize the Template: Once opened, customize the template to suit your needs. Most templates will have a place for you to input the names of your students, the assignments, and the corresponding grades. Replace the placeholder text with your own information.
Input Student Names: In the first column, list down all your students’ names. It’s often helpful to list them alphabetically to easily locate individual students.
Input Assignment Details: Across the top row, write down the names of all the assignments, tests, and quizzes. You could also include the total marks or points for each assignment, and the date it was given or due.
Enter Grades: As you mark each assignment, enter the grades in the cell that corresponds to each student and assignment. The template should calculate the total and average scores for you.
Review the Automatic Calculations: Many templates will automatically calculate total points, averages, percentages, or letter grades. Check to make sure these formulas are working correctly and adjust them if needed. For instance, you may want to change the formula if your grading system uses weighting or if you drop the lowest scores.
Update Regularly: As you give out more assignments and tests, update the grade book by adding new columns and entering the grades.
Use Sorting or Filtering Features: You may want to sort or filter students based on their grades, especially if you’re looking to identify students who may need extra help or attention.
Secure the Data: If the grade book is digital, ensure it’s secured and backed up to prevent loss of data. If it’s shared online (like on a cloud service), make sure it’s shared with the right permissions to keep student information private.
How to make the gradebook template more visual
Creating a more visual gradebook template can be achieved by utilizing different formatting options and incorporating visual elements like charts or conditional formatting. Here’s a step-by-step guide for Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel:
- Start with Your Basic Gradebook Template: You should have a template set up with student names, assignments, and grades.
- Color Coding: Use different colors to highlight different categories. For instance, use one color for quizzes, another for tests, and a third for projects. This helps visually distinguish between different types of assignments.
- Conditional Formatting: This feature allows cells to change color based on their content. For example, you could set the gradebook to automatically color-code grades below a certain threshold to quickly identify students who might be struggling.
- In Google Sheets, select the range of cells you want to format, click on “Format” in the menu, and then “Conditional formatting”.
- In Excel, select the cells, then go to “Home”, “Conditional Formatting”, and choose your rules.
- Borders and Gridlines: Make your gradebook easier to read by adding borders around cells or groups of cells. This can help separate different categories of grades.
- Headers and Bold Text: Use bold text for headers such as student names and assignment titles. This will help them stand out from the rest of the information in your gradebook.
- Insert Charts or Graphs: Visual representations can be a powerful tool for understanding data.
- Create a graph that shows the class average on each assignment, or individual student progress over time.
- In Excel, you can do this by selecting your data, going to “Insert” in the menu, and then choosing the chart type that best represents your data.
- In Google Sheets, select your data, click on “Insert” in the menu, then “Chart”.
- Insert Sparklines: Sparklines are mini charts placed in single cells, each representing a row of data in your selection. They provide a quick way to see patterns and trends.
- In Excel, select an empty cell where you want the sparkline to be, go to “Insert”, and then “Sparklines”. Select your data and click “OK”.
- In Google Sheets, use the =SPARKLINE() function.
- Freeze Rows or Columns: If your gradebook is large, freeze the top row with the assignment names and the first column with the student names. This way, as you scroll through your gradebook, you’ll always have a reference point.
- In both Excel and Google Sheets, you can do this by selecting a cell, then going to “View”, and then “Freeze”.
FAQs
Why should I use a gradebook template?
A gradebook template saves time and effort, as you don’t have to design a gradebook from scratch. It provides a structured, organized way to record and manage grades, and many templates have features to automatically calculate total scores, averages, or convert raw scores into letter grades.
How do I handle extra credit in a gradebook?
Extra credit can be added to the total points a student has earned, or you could add the extra credit points to both the total points earned and the total possible points, depending on your grading policies.
Can parents and students view the digital gradebook?
Most digital gradebooks or learning management systems allow parents and students to view grades, often in real-time. This accessibility promotes transparency and allows students and parents to keep track of academic progress.
How can I secure the data in a digital gradebook?
Digital gradebooks should be secured with passwords and user permissions to protect student data. Regular backups are also recommended to prevent data loss. Cloud-based gradebooks often have security measures in place and automatically backup data.
What should I do if a student disputes a grade in the gradebook?
If a grade dispute arises, refer back to the graded assignment and the established grading criteria. It’s important to have clear and consistent grading policies to reference in such situations. Some digital gradebooks allow for comments or notes on each grade, which can provide context for the grade given.





























![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)
