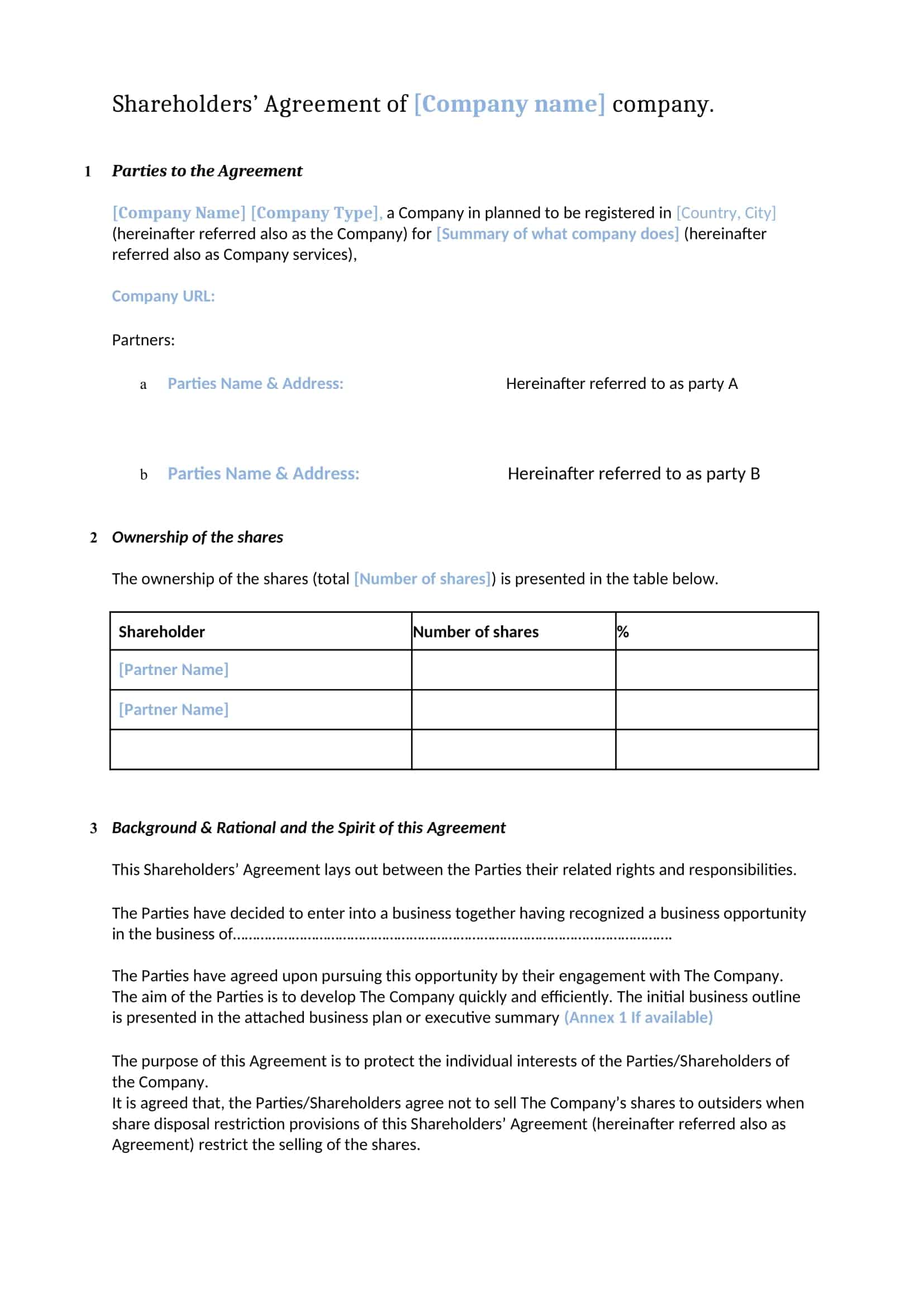
A Shareholder Agreement is a legal document that outlines the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of the shareholders in a company. This type of agreement is typically used when a company has multiple shareholders, and it serves as a way to ensure that all parties are on the same page when it comes to the management and operation of the company.
The agreement can cover a wide range of issues, including the distribution of profits, the appointment of directors, and the process for making major business decisions. In this article, we will discuss the key elements of a Shareholder Agreement and why it is important for a company to have one in place.
Table of Contents
Shareholder Agreement Templates
Establish clear guidelines and protect the interests of shareholders with our comprehensive collection of Shareholder Agreement Templates. These customizable and printable templates provide a legally binding framework for shareholders in a company to define their rights, responsibilities, and ownership stakes. Our templates cover essential aspects such as voting rights, dividend distribution, decision-making processes, transfer of shares, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
By utilizing our Shareholder Agreement Templates, you can ensure a fair and harmonious relationship among shareholders, prevent conflicts, and maintain the stability and growth of your company. Streamline the process of shareholder agreements, protect the rights and investments of all parties involved, and foster a positive and productive shareholder environment with our user-friendly templates. Download now and establish a solid foundation for shareholder collaboration and success.
Shareholder Agreements: Why is it so important?

A Shareholder Agreement is important for a company because it establishes a clear set of rules and guidelines for the shareholders to follow. It helps to prevent disputes and misunderstandings by clearly outlining the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of each shareholder. The agreement can also provide a framework for making important business decisions, such as the appointment of directors and the distribution of profits.
It can also include provisions for resolving disputes or deadlocks that may arise between shareholders. Additionally, having a Shareholder Agreement in place can help to protect the company’s assets and interests by establishing clear ownership rights and responsibilities. Overall, having a Shareholder Agreement can help to ensure that a company runs smoothly and that the shareholders’ interests are protected.
Advantages of a Shareholders’ Agreement
A Shareholder Agreement can provide a number of advantages for a company and its shareholders. Some of these advantages include:
Clarity and certainty: A Shareholder Agreement can provide clarity and certainty for all parties involved, outlining the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of the shareholders in a clear and concise manner.
Protection of shareholders’ rights: A Shareholder Agreement can protect the rights of shareholders by outlining clear ownership rights and procedures for the transfer of shares.
Resolving disputes: A Shareholder Agreement can provide a framework for resolving disputes that may arise between shareholders.
Managing change: A Shareholder Agreement can help to manage change within a company, such as the addition or removal of shareholders, by outlining clear procedures for these changes.
Flexibility: A Shareholder Agreement can be tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the company and its shareholders, allowing for a level of flexibility that may not be possible with standard legal documents.
Preparing for future events: A Shareholder Agreement can be used to prepare for potential future events such as a buyout, merger, or an exit of one or more shareholders.
Maintaining control: A Shareholder Agreement can be used to ensure that the management of the company remains in the hands of the shareholders, and not outside investors or other third parties.
Compliance: A Shareholder Agreement can help to ensure that the company and its shareholders are in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Key Elements of a Shareholder Agreement
A Shareholder Agreement typically includes a variety of information to ensure that all shareholders are aware of their rights and responsibilities. Some key information that should be included in a Shareholder Agreement includes:
Ownership rights
The agreement should clearly outline the percentage of ownership for each shareholder, as well as any restrictions on the transfer of shares.
Management and control
The agreement should specify how the company will be managed and controlled, including the process for appointing directors and making major business decisions.
Profit and loss distribution
The agreement should outline how profits and losses will be distributed among shareholders.
Voting rights
The agreement should specify the voting rights of each shareholder, including the percentage of ownership needed to pass a vote.
Shareholder meetings
The agreement should specify how and when meetings will be held, as well as the notice required for shareholders to attend.
Dispute resolution
The agreement should provide a framework for resolving disputes that may arise between shareholders.
Exit provisions
The agreement should include provisions for what happens when a shareholder wants to sell their shares or leave the company.
Restrictions
It should include any restrictions on the shareholders, such as non-compete and confidentiality clauses.
Compliance
The agreement should outline the compliance requirements of the company and shareholders.
When to use a shareholder agreement?
A Shareholder Agreement is typically used when a company has multiple shareholders, as it serves as a way to ensure that all parties are on the same page when it comes to the management and operation of the company. Some common situations when a Shareholder Agreement is used include:
Starting a new company: When a new company is formed, it is important to establish a clear set of rules and guidelines for the shareholders to follow.
Adding new shareholders: When new shareholders are added to a company, a Shareholder Agreement can help to ensure that they are aware of their rights and responsibilities.
Changing the structure of the company: If the structure of a company changes, such as the addition of new shareholders or the removal of existing shareholders, a Shareholder Agreement can help to ensure that all parties are aware of the changes.
Addressing disputes: If disputes arise between shareholders, a Shareholder Agreement can provide a framework for resolving them.
Protecting company’s assets and interests: A Shareholder Agreement can help to protect the company’s assets and interests by establishing clear ownership rights and responsibilities.
Preparing for potential future events: A Shareholder Agreement can also be used to prepare for potential future events such as a buyout, merger or an exit of one or more shareholders.
Key terms of a Shareholders Agreement
A Shareholder Agreement is a legal document that outlines the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of the shareholders in a company. Some key terms that may be included in a Shareholder Agreement include:
Shareholders: The individuals or entities that own shares in the company.
Shares: The units of ownership in a company.
Share Capital: The total value of the company’s issued shares.
Directors: The individuals who manage and control the company.
Quorum: The minimum number of shareholders required to be present at a meeting to make decisions.
Voting rights: The right of shareholders to vote on important business decisions.
Dividends: The distribution of profits to shareholders.
Preemptive rights: The right of existing shareholders to maintain their percentage of ownership by purchasing new shares before they are offered to others.
Tag Along rights: The right of minority shareholders to join in the sale of shares of the majority shareholders.
Drag Along rights: The right of majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to sell their shares in the event of a sale of the company.
Buy-Sell provisions: Provisions that govern how shares can be bought, sold or transferred.
Exit Provisions: Provisions that govern how a shareholder can exit the company and the procedures for the transfer of shares.
Non-compete clauses: Restrictions on shareholders from competing with the company after they leave.
Confidentiality clauses: Restrictions on shareholders from disclosing the company’s confidential information.
Compliance provisions: Requirements for the shareholders and the company to comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
How to Draft a Shareholders Agreement
Drafting a Shareholder Agreement is an important step in establishing and protecting the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of the shareholders in a company. A well-drafted Shareholder Agreement can provide clarity and certainty for all parties involved, as well as helping to manage change within the company and resolve disputes that may arise.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to draft a Shareholder Agreement:
Step 1: Identify the shareholders.
The first step in drafting a Shareholder Agreement is to identify all of the shareholders in the company. This includes individuals and entities that own shares in the company. It is important to include the names and contact information for each shareholder, as well as the number of shares they own.
Step 2: Define the company’s capital structure.
The next step is to define the company’s capital structure, which includes the total number of shares that have been issued and the percentage of ownership that each shareholder holds. This information should be included in the Shareholder Agreement to ensure that all parties are aware of their ownership stakes in the company.
Step 3: Outline the rights and responsibilities of the shareholders.
The Shareholder Agreement should outline the rights and responsibilities of the shareholders, including their rights to vote on important business decisions, the right to receive dividends, and the right to participate in the management of the company. It should also include any restrictions on the transfer of shares or other ownership rights.
Step 4: Establish procedures for resolving disputes.
Disputes may arise between shareholders, and it is important to have a clear and fair procedure in place for resolving these disputes. The Shareholder Agreement should include a mechanism for resolving disputes, such as mediation or arbitration, to ensure that disputes are handled in a timely and efficient manner.
Step 5: Include provisions for managing change.
The Shareholder Agreement should include provisions for managing change within the company, such as the addition or removal of shareholders, the issuance of new shares, or the sale of the company. These provisions should outline the procedures for these changes and any restrictions that may apply.
Step 6: Include provisions for the protection of confidential information.
The Shareholder Agreement should include provisions for the protection of confidential information, including restrictions on shareholders from disclosing the company’s confidential information.
Step 7: Include provisions for compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
The Shareholder Agreement should include provisions for compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, including requirements for the shareholders and the company to comply with laws and regulations that apply to the company.
Step 8: Review and update the agreement regularly.
It is important to review and update the Shareholder Agreement regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This includes reviewing the agreement in the event of any significant changes to the company or its shareholders.
Step 9: Consult with legal professional
It is highly recommended to consult with a legal professional while drafting the Shareholder Agreement, as they can ensure that the terms used in the agreement are legally enforceable and that the agreement complies with all relevant laws and regulations.
FAQs
Who should be included in a Shareholder Agreement?
A Shareholder Agreement should include all individuals and entities that own shares in the company, along with their names and contact information and the number of shares they own.
When should a Shareholder Agreement be reviewed and updated?
A Shareholder Agreement should be reviewed and updated regularly, especially in the event of any significant changes to the company or its shareholders.
Can a Shareholder Agreement be changed?
Yes, a Shareholder Agreement can be changed, but it requires the agreement of all shareholders or as per the provision stated in the agreement.
What happens if a shareholder breaches the terms of the Shareholder Agreement?
The specific consequences for a breach of the Shareholder Agreement will depend on the terms of the agreement. Typically, a breach of the agreement may result in the imposition of fines, penalties, or other remedies specified in the agreement. In some cases, it may also result in the termination of the shareholder’s rights and interests in the company.
Can a Shareholder Agreement be used to limit the rights of shareholders?
Yes, a Shareholder Agreement can be used to limit the rights of shareholders, such as by restricting their ability to transfer their shares or by requiring them to obtain the approval of other shareholders before taking certain actions. However, it is important to ensure that any limitations imposed on shareholders are reasonable and do not violate any laws or regulations.
How is a Shareholder Agreement enforced?
A Shareholder Agreement can be enforced through legal action in court. If a dispute arises between shareholders, a court may be asked to interpret the terms of the agreement and to enforce the rights and obligations of the parties.
What is the difference between a Shareholder Agreement and a Stock Purchase Agreement?
A Shareholder Agreement is a legal document that outlines the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of the shareholders in a company, while a Stock Purchase Agreement is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions of the sale of shares in a company. The Stock Purchase Agreement typically comes after the Shareholder Agreement


















































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Payment Agreement Templates [PDF, Word] 2 Payment Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Payment-Agreement-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Separation Agreement Templates [PDF, Word] 3 Separation Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Separation-Agreement-1-150x150.jpg)
