Mastering the symphony of operations in manufacturing is a formidable challenge, yet one that brims with opportunities. The heart that beats in rhythm with every stage of this complex dance is the production schedule. This vital tool, when wielded effectively, can orchestrate material flow, labor allocation, and machine utilization, paving the way for improved efficiency and profitability. This article will unravel the intricate aspects of production scheduling, highlight its strategic significance, and provide insights into the methods that industry leaders employ to optimize this crucial process.
Table of Contents
What is Production Scheduling?

Production scheduling is the allocation of resources, timing, and order of operations to create goods or services in a manufacturing or service-oriented business. This involves determining the sequence of operations, specifying who will carry out each task, and when these tasks will occur, while also considering available resources such as labor, equipment, and raw materials.
It serves as a roadmap for the production process, setting the pace for manufacturing activities to meet demand while optimizing resource use, minimizing waste, and maximizing efficiency and productivity. The scope of production scheduling ranges from short-term daily tasks to long-term strategic planning, with the ultimate goal of ensuring a smooth and cost-effective production process.
Production Schedule Templates
Manufacturing operations require detailed production schedules for efficiency and on-time delivery. Production schedules optimize workflows and resources. Production schedule templates provide valuable frameworks to build comprehensive schedules.
The templates contain sections for each phase of production. This includes raw material delivery, batch processing times, quality checks, equipment maintenance, final assembly, and packaging. Templates enable scheduling by product, machine, employee, or facility area. Calendar views provide at-a-glance overviews of plant activity.
With production schedule templates, managers can develop schedules faster than starting from scratch. Templates prompt inclusion of all relevant manufacturing processes and constraints. Completed schedules coordinate workflows, resources, and inventory. They identify bottlenecks or constraints for improvement. Templates increase plant productivity and on-time order fulfillment. Whether planning a week, month, or full year, production schedule templates drive efficient, optimized manufacturing operations.
What is a production schedule used for?
A production schedule serves multiple purposes, all of which combine to ensure efficient operations, optimal resource allocation, and the fulfillment of customer orders in a timely manner. Here are some of the primary uses:
Order Prioritization
It aids in sequencing production orders based on factors such as demand, deadlines, and the importance of clients. This helps to minimize late deliveries and maintain strong customer relationships.
Resource Allocation
The schedule assists in allocating resources, including manpower, machinery, and raw materials. It helps to reduce idle time and avoid resource conflicts by coordinating who is doing what, where, and when.
Inventory Management
By integrating with supply chain and inventory management systems, a production schedule helps maintain optimal levels of inventory – reducing holding costs and preventing stockouts.
Productivity Optimization
By ensuring efficient use of resources and minimizing downtime, a well-managed production schedule increases overall productivity and throughput.
Cost Management
Effective production scheduling can reduce production costs by minimizing waste, reducing overtime expenses, and identifying and mitigating bottlenecks.
Forecasting
Production schedules can aid in predicting future production capabilities and capacities, which can influence strategic planning, including market commitments, resource procurement, and infrastructure investments.
Risk Management
With a clear view of operations, potential issues and bottlenecks can be identified and addressed early, reducing the impact of unexpected events on the production process.
Quality Control
By enabling consistent workflow, production schedules can help maintain the quality of the end product. Fluctuations in workflow can result in quality issues; a consistent schedule helps mitigate this.
Regulatory Compliance
In regulated industries, maintaining a precise production schedule is crucial for compliance. It provides a documented trail of activities for audits and can help validate that all necessary steps were followed in the production process.
Improvement Initiatives
The data derived from a production schedule can be used to drive continuous improvement efforts, such as Lean or Six Sigma initiatives. It provides a basis for identifying areas of waste or inefficiency and a way to measure the impact of changes.
Film and Television Production
In this industry, a production schedule outlines what scenes are to be shot, when, where, and who is involved (actors, directors, crews). It helps coordinate the availability of cast and crew, the use of sets, props, and costumes, and the allocation of budgets. This is critical in ensuring a smooth filming process, on-time completion, and staying within the budget.
Event Management
Production schedules in event management detail the timeline of activities leading up to and during the event, such as setup, rehearsals, performances, and teardown. It helps coordinate vendors, staff, performers, and venue usage to ensure the event runs smoothly.
Construction
For construction projects, a production schedule, often referred to as a construction schedule, outlines the timeline for each phase of construction, including who is responsible for each task. It ensures resources are efficiently utilized and projects are completed on time and within budget.
Publishing
In publishing, a production schedule might outline manuscript deadlines, editing, design, proofreading, printing, and distribution tasks. It ensures the timely publication of books, magazines, newspapers, or online content.
Software Development
In this field, a production schedule, often part of a project management plan, outlines the timeline for development tasks, testing, debugging, and deployment. It helps coordinate team members and ensures the project stays on track and meets release deadlines.
Research & Development (R&D)
In an R&D setting, a production schedule might involve the coordination of experimental tasks, resource allocation, data collection, and analysis periods, guiding the project towards its completion and objective realization within the stipulated timeframe.
Importance of Production Scheduling
Production scheduling is a crucial aspect of any manufacturing or production-oriented business. Here are the key reasons why it is so important:
Efficiency in Resource Allocation: Production scheduling ensures optimal utilization of resources, including machinery, materials, and labor. It helps in allocating these resources effectively to various processes and tasks to avoid any idleness or overuse, leading to reduced operational costs and maximized output.
Minimizes Production Time: With effective scheduling, the total time taken for production can be reduced significantly. It outlines the sequence of tasks, thereby streamlining operations and minimizing delays, enhancing overall productivity.
Improves Delivery Performance: Production scheduling helps in planning and tracking the production process accurately. This means products can be delivered to customers on time, improving customer satisfaction and the company’s reputation.
Reduces Inventory Costs: Efficient production scheduling can lead to a decrease in unnecessary inventory stockpiling. With a well-planned schedule, raw materials and finished goods are not stored longer than necessary, reducing inventory holding costs.
Increases Flexibility: A detailed production schedule offers a clear view of all operations, allowing managers to respond to changes or disruptions more flexibly. This can include adjusting to sudden increases or decreases in demand, machine breakdowns, or delays from suppliers.
Enhances Quality Control: Regular scheduling of production activities allows for consistent quality checks and adjustments. This ensures the final product meets quality standards, reducing waste and rework costs.
Predictability and Transparency: Production schedules provide a clear overview of when tasks are supposed to begin and end, allowing for better predictability of the production process. This transparency can help in aligning all stakeholders, including workers, managers, and suppliers, on the expected output and timelines.
Improved Worker Morale: Production scheduling helps in eliminating confusion about what needs to be done and when. Workers know their exact tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities, leading to reduced stress and increased job satisfaction.
Strategic Decision-Making: Production scheduling can provide valuable data for management to make strategic decisions. Understanding the capacity and efficiency of the production process can guide decisions about scaling up operations, investing in new equipment, or hiring additional staff.
Sustainability: Effective production scheduling can lead to a reduction in waste production, energy consumption, and raw material usage, contributing to more sustainable business practices.
Production Planning vs. Production Scheduling
Production planning and production scheduling are two closely related aspects of manufacturing and production management, and both are vital for smooth and efficient operations. Despite their interrelatedness, they have different focuses and carry out distinct roles within the production process.
Production Planning
Production planning is a strategic process that occurs before production begins. It involves determining what products will be produced, the quantity of each product, and when the production will start and finish.
Here are some key features of production planning:
- Scope: Production planning looks at the bigger picture. It is concerned with the overall production goals and the strategies required to achieve these goals.
- Time Horizon: Production planning is typically done for a long-term horizon, often for months or even years into the future.
- Activities: It involves activities such as demand forecasting, capacity planning, determination of production objectives, and resource allocation. It also includes identifying potential bottlenecks or issues that might arise during production and developing solutions or alternatives.
- Objective: The main goal of production planning is to optimize resource utilization, maximize production efficiency, minimize production costs, and ensure that customer demand can be met within the given time frame.
- Change Frequency: Production plans are generally not changed frequently as they represent long-term strategic decisions. However, they may be revised in response to significant changes in market conditions, customer demand, or resource availability.
Production Scheduling
Production scheduling, on the other hand, is a more detailed, tactical process. It involves specifying the sequence and timing of tasks that need to be carried out during production, based on the overall plan.
Here are some key features of production scheduling:
- Scope: Production scheduling focuses on the operational level, detailing the sequence of tasks and operations that need to be carried out to implement the production plan.
- Time Horizon: Scheduling typically focuses on the short-term horizon, often on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
- Activities: It involves determining task sequences, setting start and finish dates for each task, assigning resources to tasks, and setting up mechanisms for tracking progress and performance.
- Objective: The main goal of production scheduling is to ensure that production operations run smoothly and efficiently, with minimal delays and disruptions. It aims to meet the production deadlines while maintaining product quality.
- Change Frequency: Production schedules are more dynamic than production plans. They are reviewed and adjusted frequently to reflect actual progress, changes in task requirements, and any unexpected issues or disruptions.
Comparison
While production planning and production scheduling have distinct roles, they are closely linked. A well-developed production plan provides the foundation for an effective production schedule. Similarly, feedback from the production scheduling process can inform adjustments to the production plan. Both are crucial for effective production management: the plan provides the strategic direction, while the schedule manages the day-to-day operations to implement the plan.
For example, a furniture manufacturer’s production planning might involve deciding the types and quantities of furniture to produce over the next year based on market research and sales forecasts. The plan will also need to consider resource availability, including materials, labor, and machinery, and may involve strategic decisions such as purchasing new equipment or hiring additional staff.
Once the production plan is established, production scheduling comes into play. This might involve specifying the sequence of tasks for each piece of furniture, assigning workers to each task, setting start and finish dates, and determining quality control procedures. The schedule would be reviewed and adjusted regularly to reflect actual progress and any unexpected issues, such as delays in material delivery or machine breakdowns.
In summary, production planning and production scheduling are both vital components of production management. While they have different focuses and carry out distinct roles, they work together to ensure that production operations are efficient, cost-effective, and capable of meeting customer demand.
How to create a production scheduling
Creating a production schedule requires a keen understanding of your business operations, resources, and goals. It’s a detailed process involving careful planning and analysis. Let’s go through the steps involved in creating an effective production schedule:
Step 1: Define Your Objectives
The first step in creating a production schedule is to define your objectives. Your objective might be to increase production output, reduce downtime, streamline operations, improve resource allocation, or something else entirely. Having a clear goal provides a roadmap for your production schedule and helps you make strategic decisions.
For example, if your objective is to increase production output, you will focus on minimizing downtime, optimizing task sequences, and efficiently allocating resources to meet this goal.
Step 2: Identify Your Resources
Next, list all resources needed for the production process. This includes raw materials, equipment, machinery, and workforce. Knowing the availability and capacity of your resources helps in effective task scheduling and prevents overuse or idleness.
In our continuing example, you would identify all the machines needed in the production process, the raw materials required for the product, and the workforce available to carry out the tasks.
Step 3: Breakdown the Production Process into Tasks
The production process should be broken down into a list of tasks to be accomplished. This involves identifying all the steps involved in your manufacturing process from start to finish.
In the context of our example, the tasks might include procuring raw materials, preparing the machines, processing the materials, assembling the products, quality control, packaging, and shipping.
Step 4: Estimate Task Duration and Dependencies
For each task, estimate how long it will take to complete. If possible, use historical data for more accurate estimates. Also, identify any dependencies between tasks. Some tasks can’t start until others have been completed.
For example, in a production line, the assembly of the product can’t begin until all the parts have been manufactured. Also, quality control can’t start until the assembly is complete.
Step 5: Assign Responsibilities
Assign each task to a person or a team. Clear delegation of duties ensures accountability and smooth execution.
In our example, certain teams might be responsible for machine preparation, while others handle assembly or quality control.
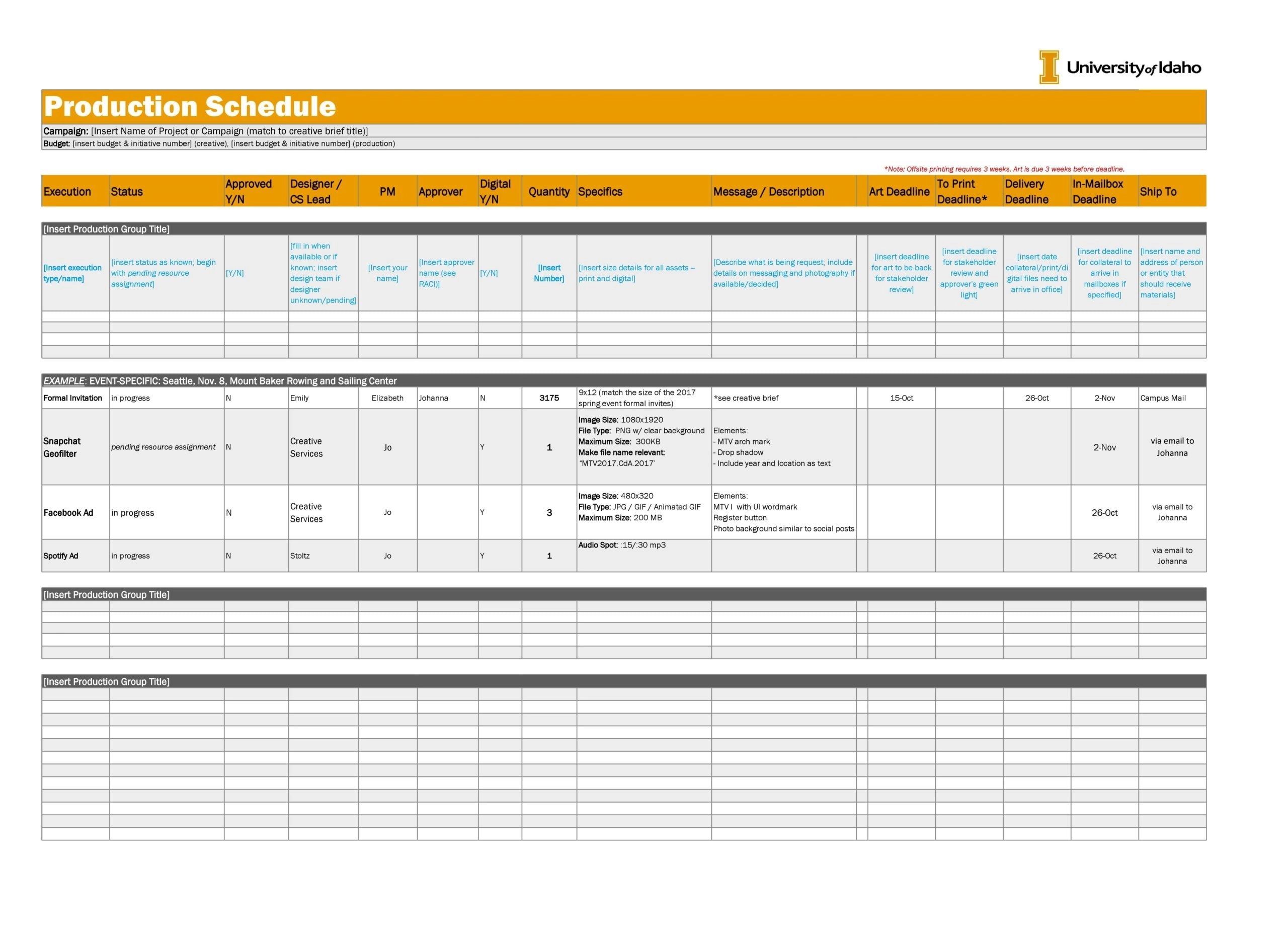
Step 6: Create the Schedule
Arrange the tasks on a timeline based on their estimated duration and dependencies. Software tools can be very helpful in visualizing and adjusting the schedule. The result is a production schedule that shows when each task will start and finish.
In our example, you might use a Gantt chart to visualize the schedule. The chart would show that machine preparation starts on day one, raw material processing starts as soon as machine preparation is complete, and so forth.
Step 7: Implement Quality Control Measures
Plan for regular quality checks throughout the production process to ensure the final product meets the required standards.
In our example, quality checks might occur after raw material processing, after assembly, and before shipping.
Step 8: Review and Adjust the Schedule Regularly
The final step is to regularly review the schedule and adjust it as necessary. Unexpected issues can arise that disrupt the original plan. Regular reviews ensure you catch these issues early and adjust the schedule accordingly.
- Continuing our example, suppose a key piece of machinery breaks down. You would need to adjust the schedule to account for the delay in production, possibly shifting tasks around or temporarily increasing the workforce in other areas to maintain output levels.
- Creating a production schedule is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. It requires regular reviews and updates to reflect the actual progress and changes in the production process. By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive production schedule that optimizes your operations and helps achieve your business objectives.
FAQs
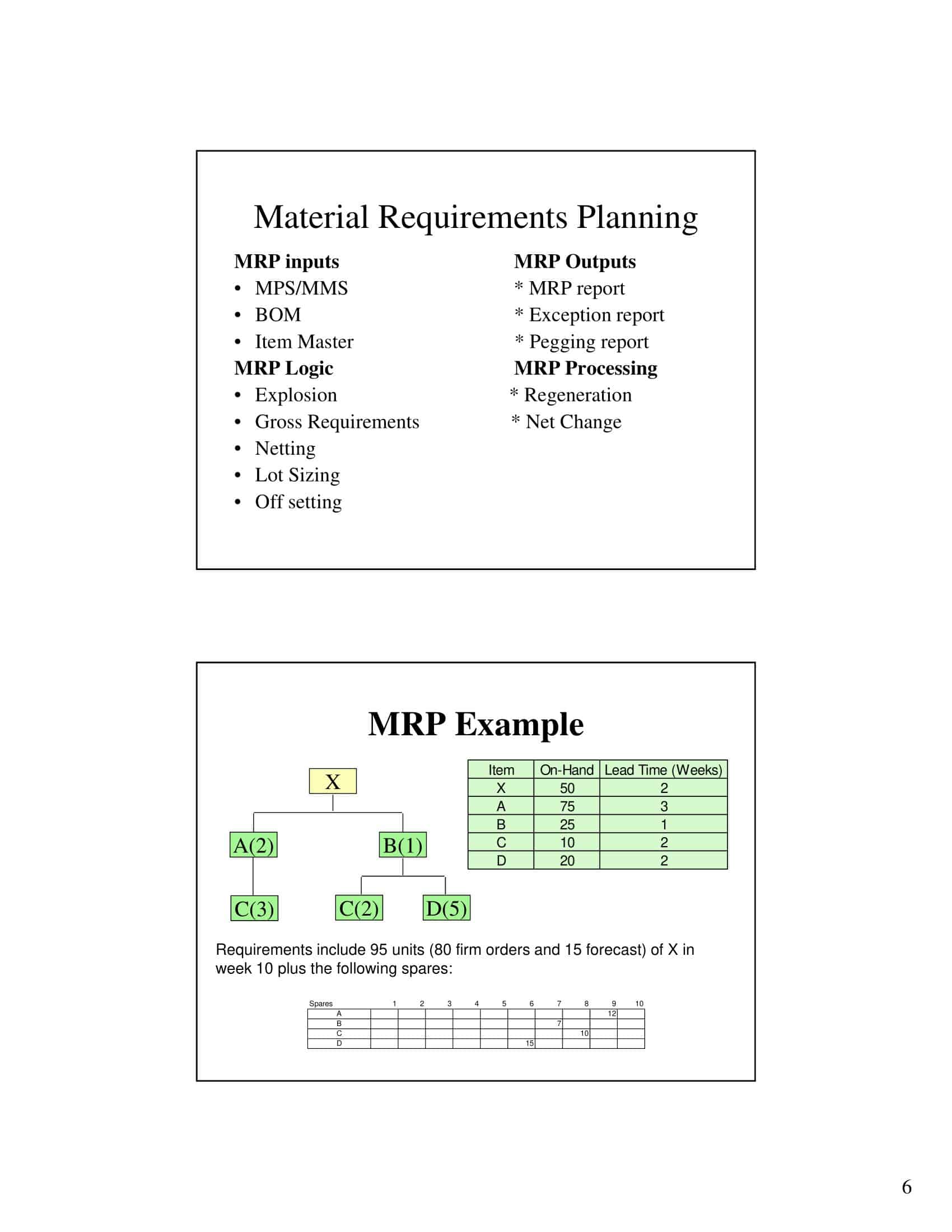
What is a master production schedule?
A master production schedule (MPS) is a plan for individual commodities to be produced in each time period such as production, staffing, inventory, etc. It is usually linked to manufacturing where the plan indicates when and how much of each product will be produced.
What software is used for production scheduling?
There are many software tools available for production scheduling. Some of the more popular ones include SAP Production Planning, Microsoft Project, Oracle NetSuite, and Workfront.
What is Just-In-Time (JIT) production scheduling?
Just-In-Time (JIT) production scheduling is a strategy where production is closely aligned with customer demand to minimize inventory holding costs. The aim is to produce exactly what is needed, when it’s needed, and in the quantity needed.
What is meant by lean production scheduling?
Lean production scheduling is a concept from the Lean Manufacturing philosophy which aims to eliminate waste and increase efficiency. It focuses on producing only what is needed, reducing inventory, and aligning production closely with demand.
How does production scheduling help in reducing costs?
Production scheduling helps in reducing costs by optimizing resource utilization, minimizing downtime, reducing inventory holding costs, and increasing overall efficiency. This leads to cost savings and improved profitability.
How often should a production schedule be updated?
The frequency of updating a production schedule depends on the nature of the business and industry. For some, it may be necessary to update schedules daily due to fast-paced environments, while others might update them weekly or monthly.
How does technology aid in production scheduling?
Technology aids in production scheduling by automating many scheduling tasks, providing real-time data for decision making, simulating different scheduling scenarios, and providing tools for collaboration and communication.
What is the role of a production scheduler?
A production scheduler is responsible for planning and organizing production schedules, assessing project and resource requirements, estimating, negotiating, and agreeing budgets and timescales with clients and managers, and ensuring that health and safety regulations are met.













































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
