In the dynamic landscape of today’s business world, the ability to predict the future has become more vital than ever. Sales forecasting, at its core, is an indispensable tool that helps businesses to anticipate their future sales and revenue.
This predictive process, if executed effectively, can unveil key insights for strategic planning, risk management, and resource allocation. While it might not offer a perfect picture of the future, it equips decision-makers with valuable foresight, allowing them to prepare for potential market fluctuations and adapt accordingly.
In this article, we’ll delve into the complexities of sales forecasting, exploring its methodologies, benefits, challenges, and how the integration of technology can enhance its accuracy and efficiency.
Table of Contents
What is sales forecasting?

Sales forecasting is a process used by companies to estimate future sales. It plays a key role in managing virtually all aspects of a business, from making informed decisions about managing costs, to planning for growth and assessing future profitability.
Forecasts can be based on historical sales data, industry comparisons, and economic trends. It often involves a combination of quantitative data analysis and qualitative judgments. Companies typically develop sales forecasts on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly.
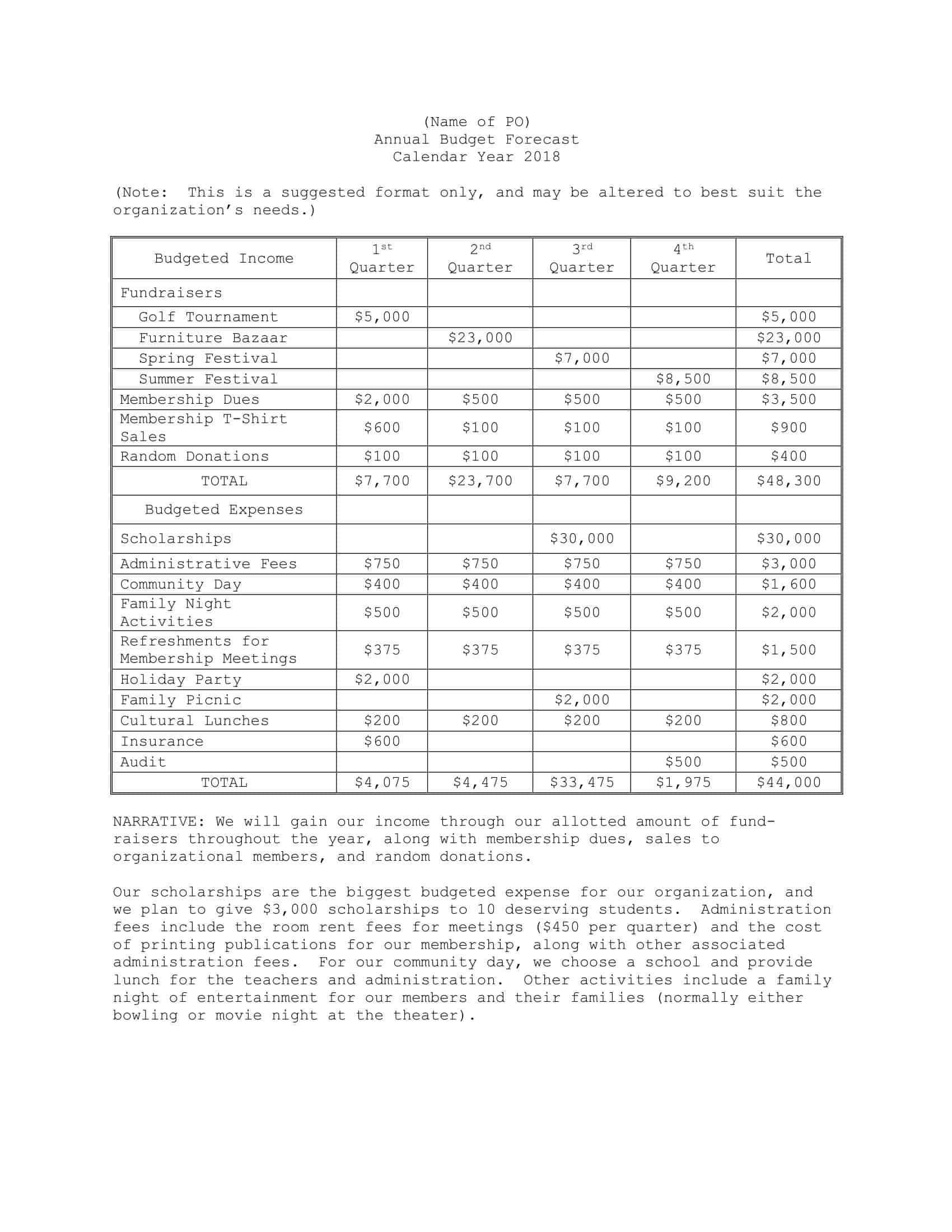
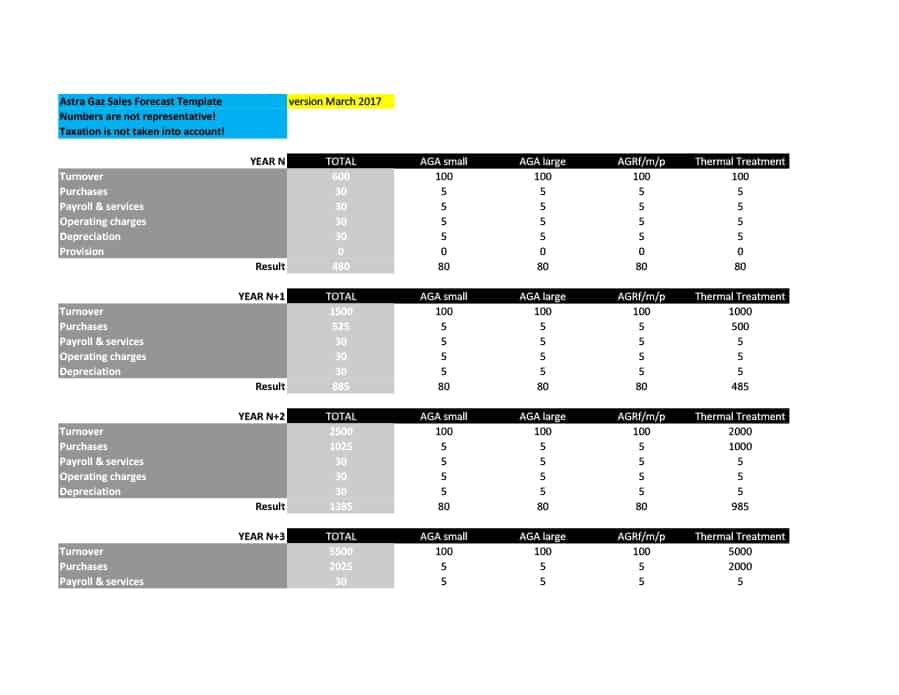
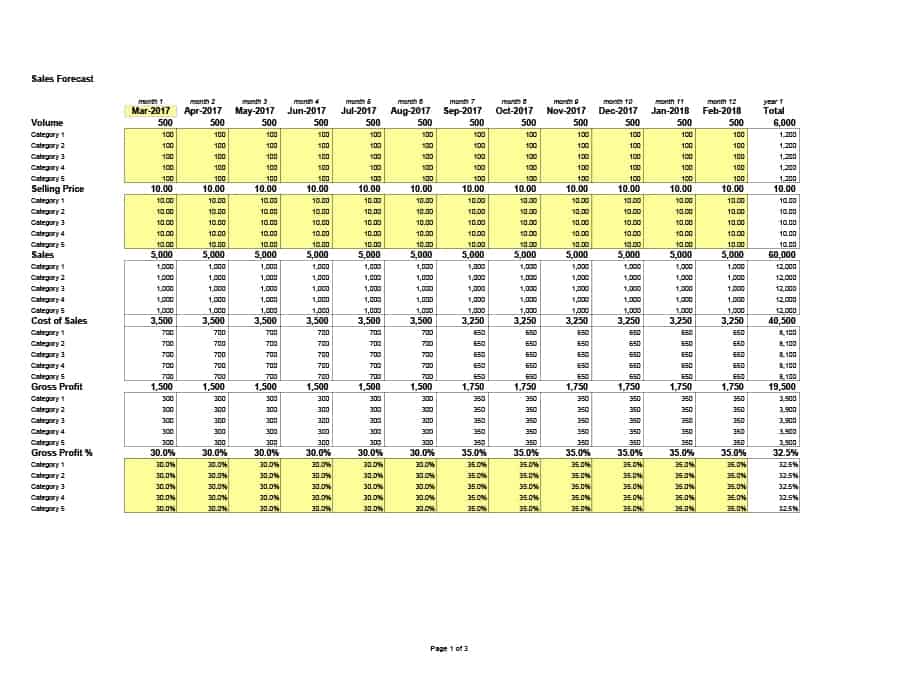
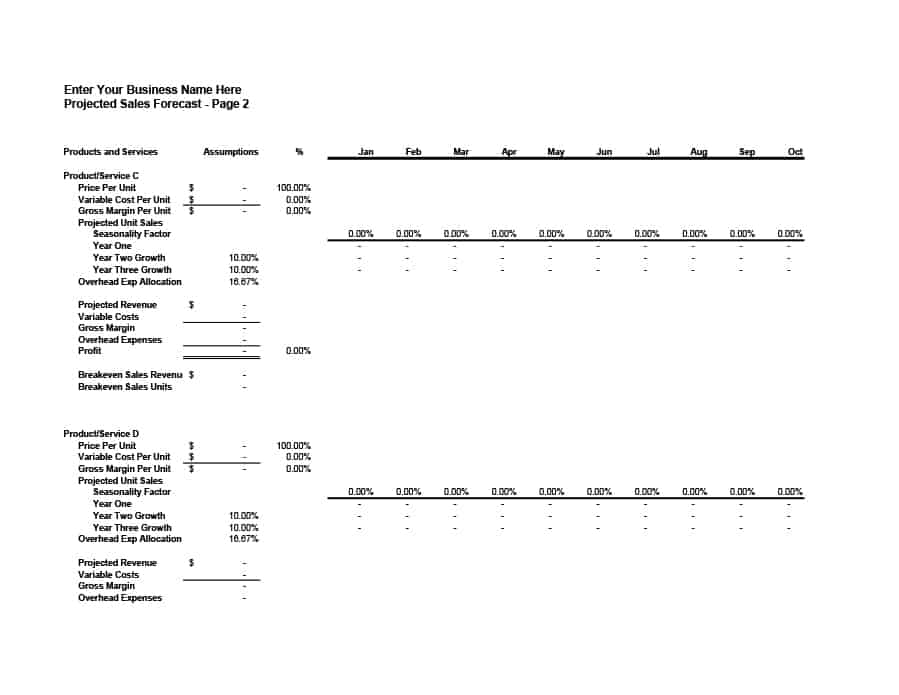
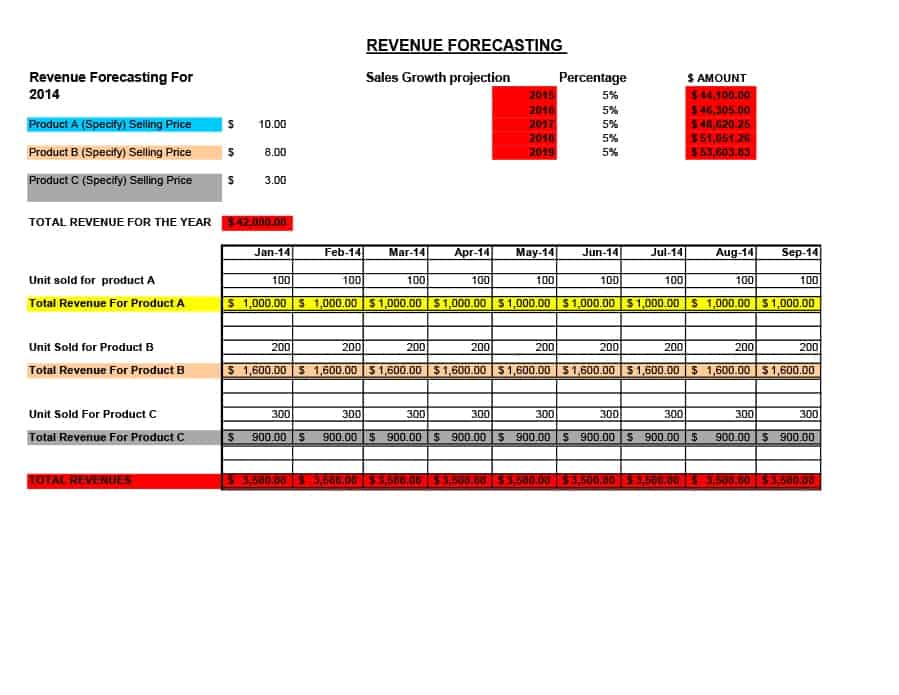
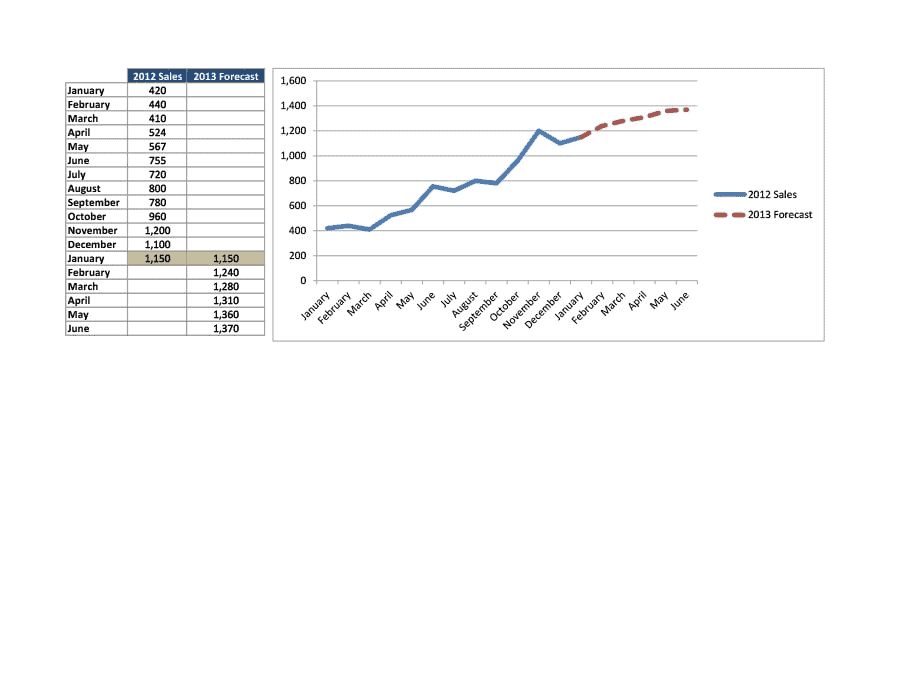
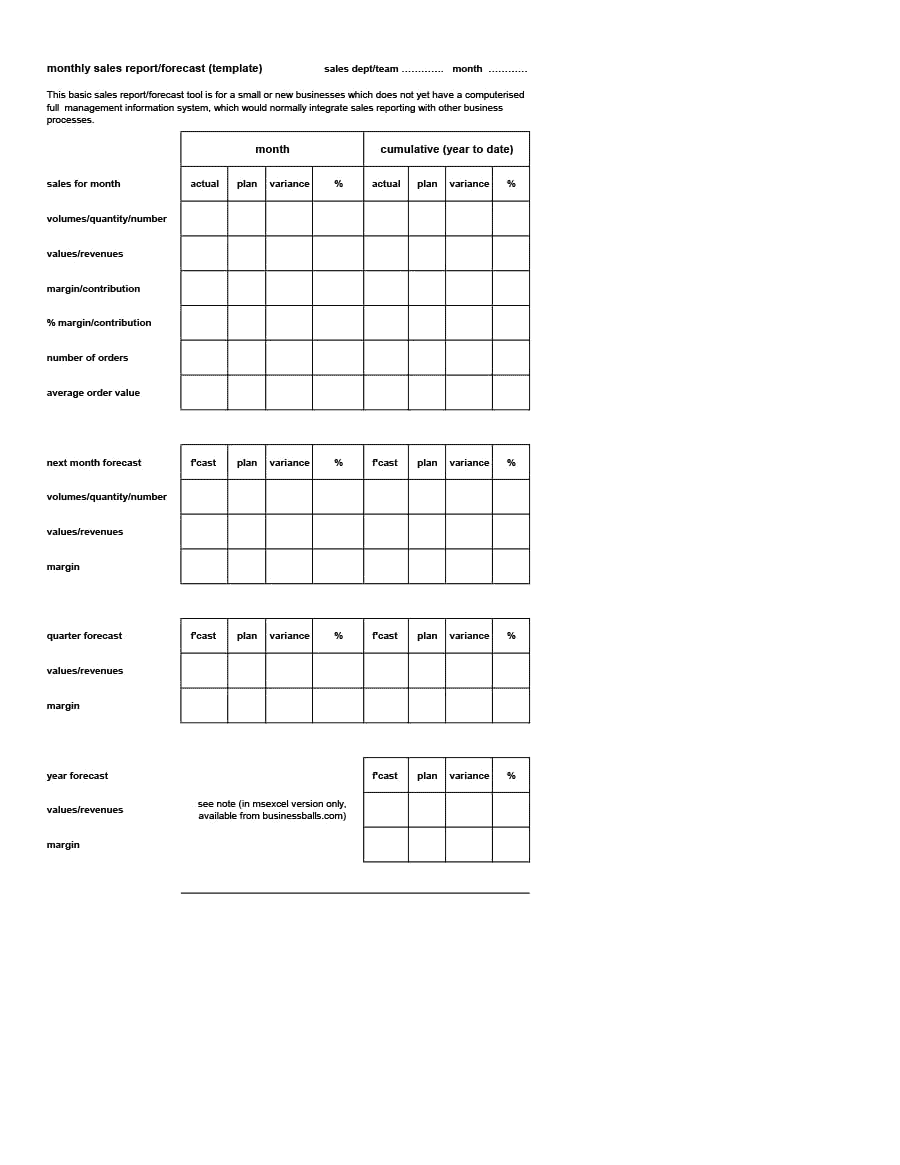
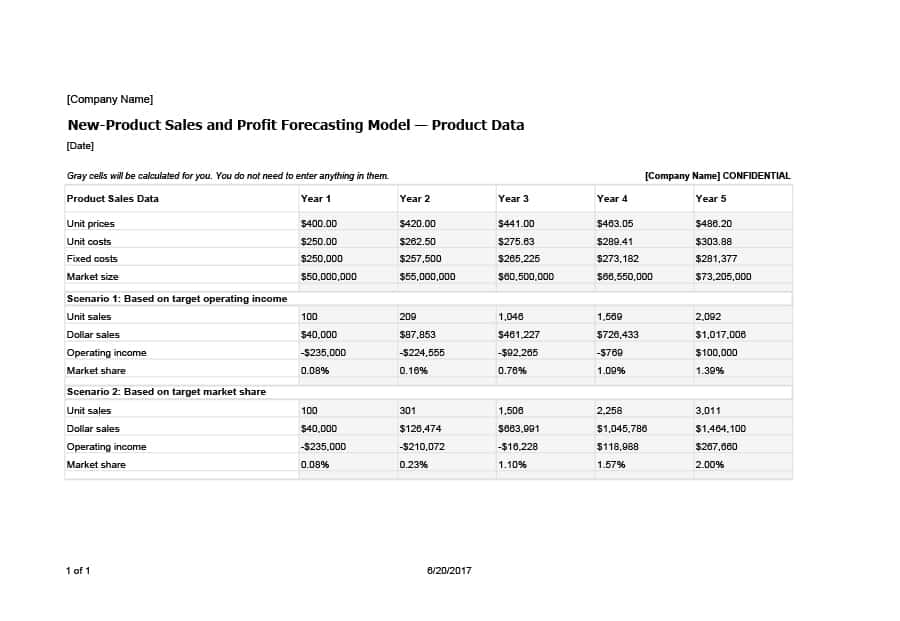
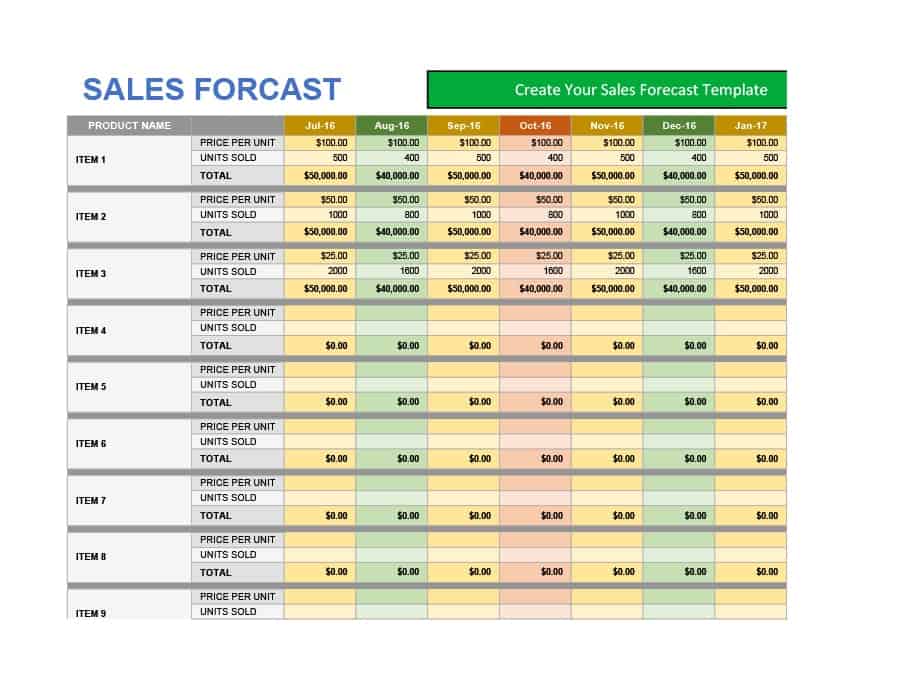
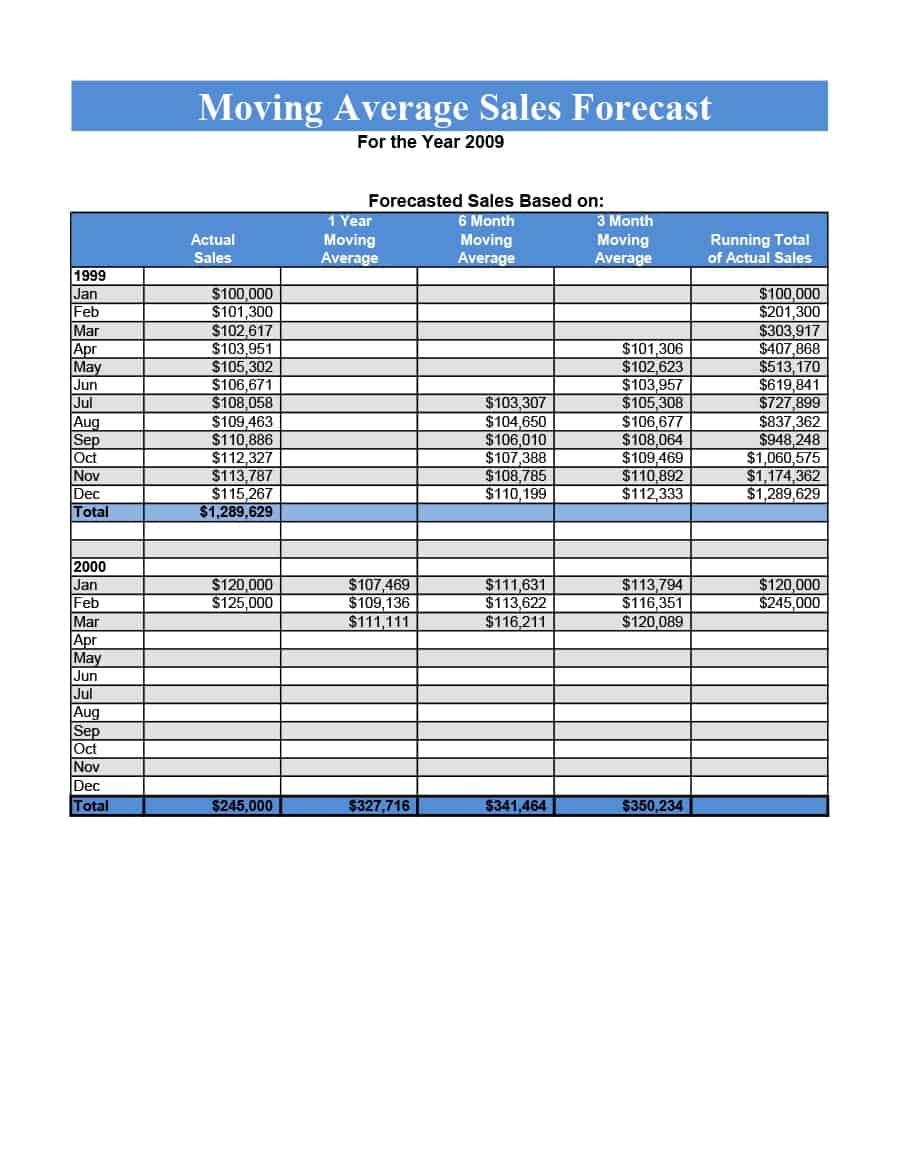
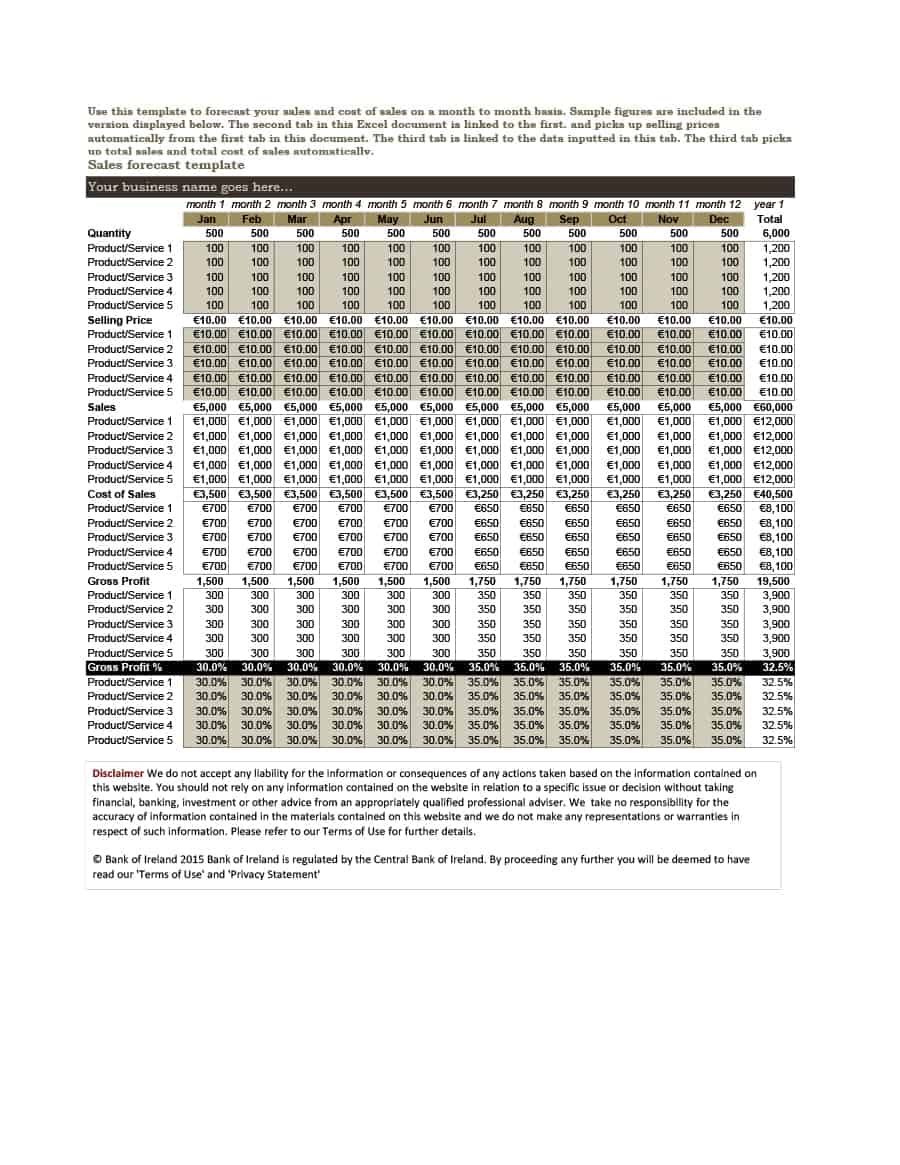
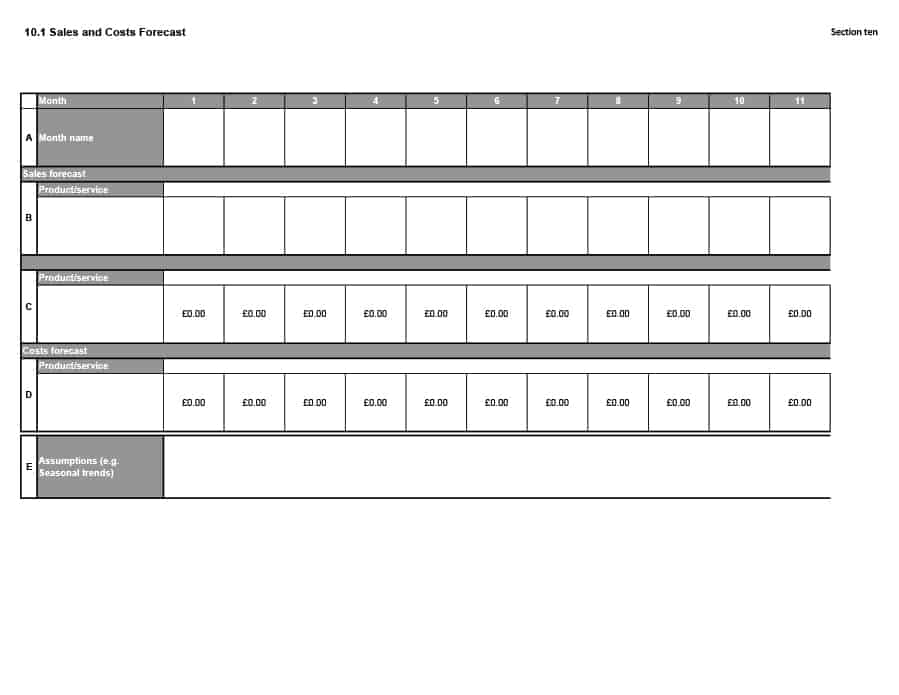
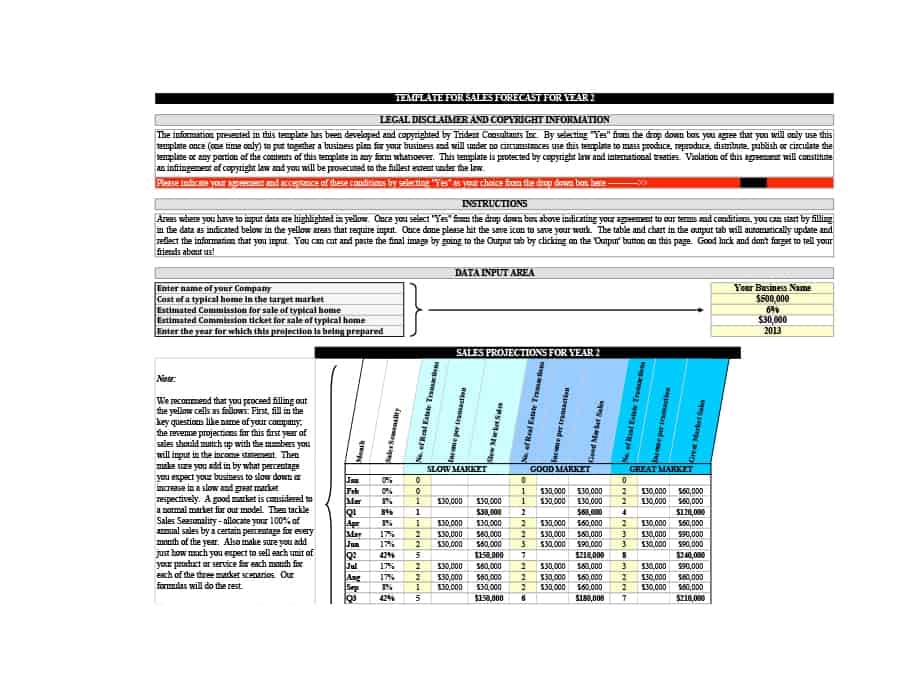
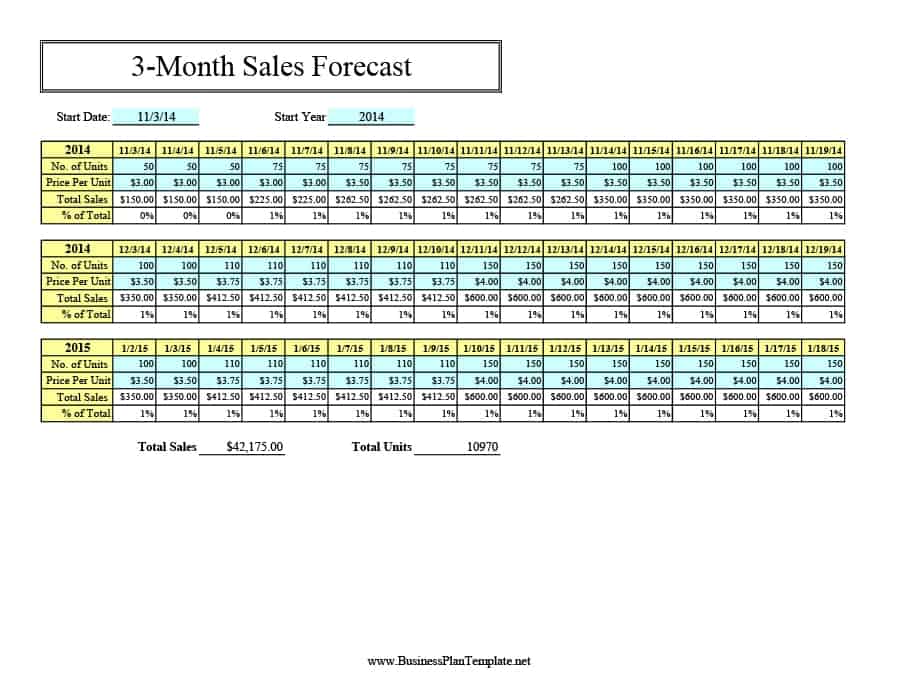
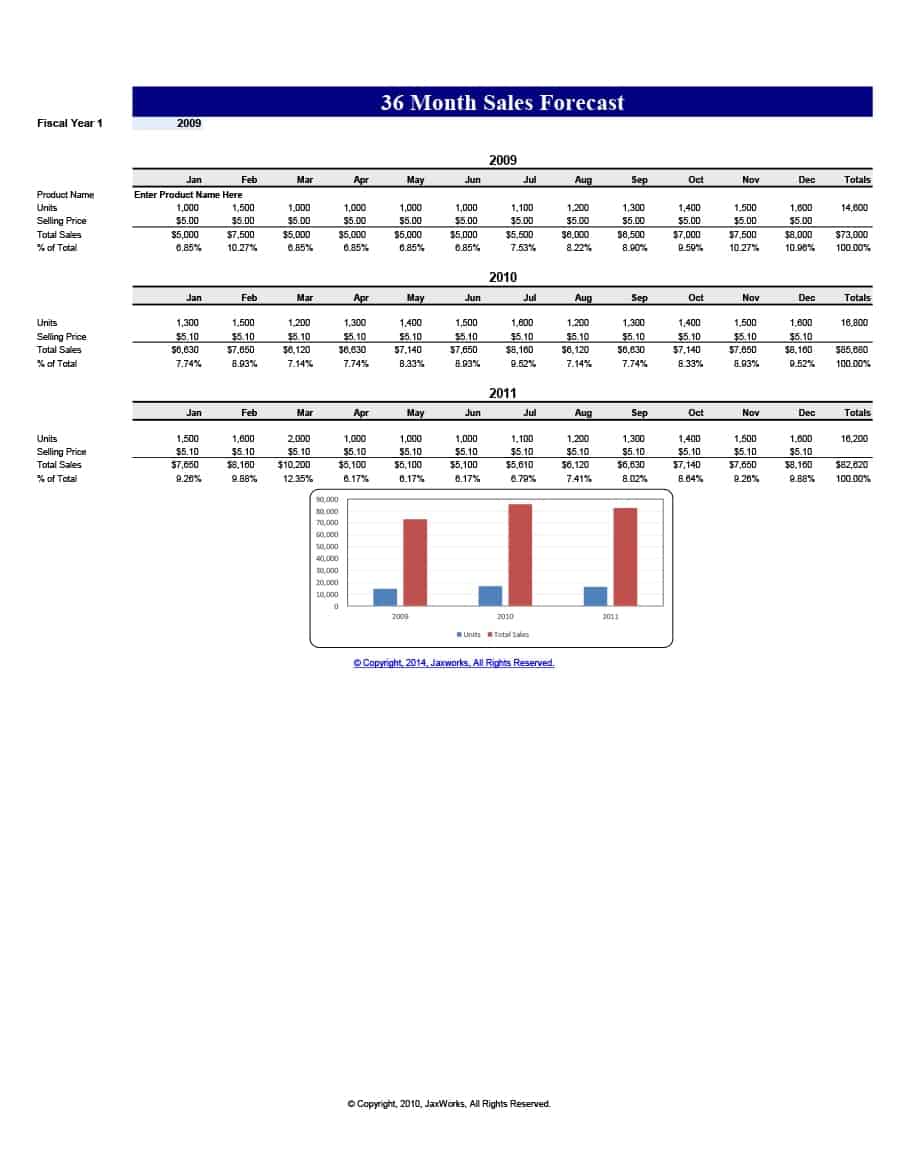
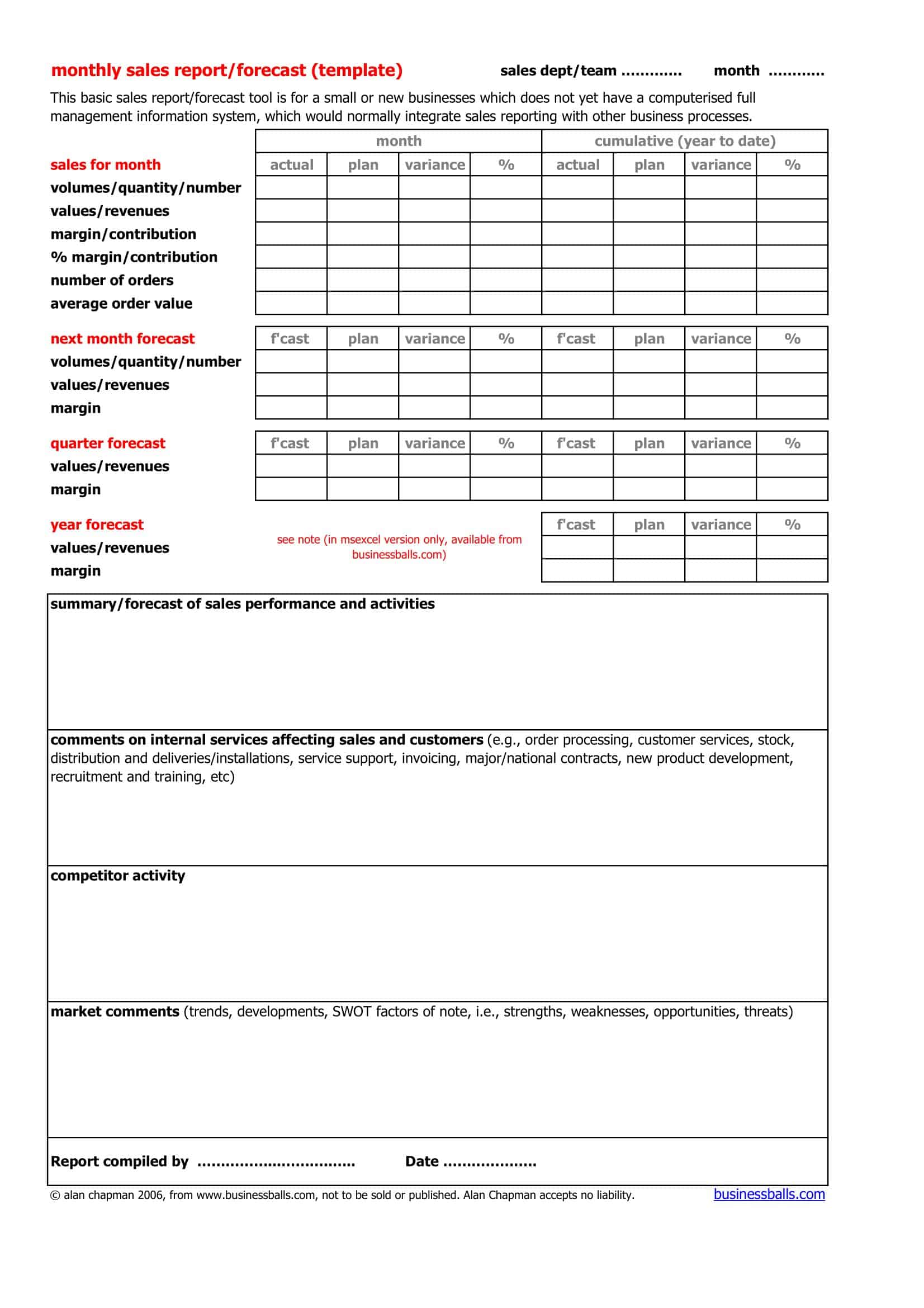
Sales Forecast Templates
Sales Forecast Templates are prestructured formats designed to assist businesses in projecting future sales. These templates provide an organized way to predict revenue, which is crucial for planning business operations, financial management, and strategic planning.
Common elements of these templates include fields for product or service names, units sold, unit price, projected sales volume, and total revenue. Some may also include sections for different market segments, seasonal variations, and historical sales data for comparison.
Sales Forecast Templates are indispensable in business planning. They allow businesses to anticipate future sales trends, which informs decisions on production, inventory management, budgeting, and setting sales goals.
Importance of sales forecasting
Sales forecasting is critically important for businesses for a myriad of reasons, some of which include:
Financial Planning
An accurate sales forecast provides insights into how much revenue a business can expect to generate in the future, enabling it to budget accordingly. Companies can plan their expenditures on marketing, product development, and other operational aspects with a clear understanding of their expected revenue.
Inventory Management
Sales forecasts help businesses manage their inventory more effectively. By predicting the number of products or services they will sell, companies can ensure they have sufficient inventory to meet demand, without overspending on excess stock. This reduces the risk of stockouts and overstocking, both of which can impact profitability and customer satisfaction.
Production Planning
In manufacturing contexts, sales forecasts guide the production schedule. They help determine how much of a particular product to produce based on the projected demand, reducing waste and optimizing the use of resources.
Cash Flow Management
Accurate sales forecasts help manage cash flow. Understanding the anticipated income helps businesses plan for both routine expenses and unexpected costs.
Strategic Planning
Sales forecasting is a critical input in strategic planning. Businesses use these forecasts to set goals, plan for growth, assess risks, and make informed decisions about market expansion, diversification, and other long-term strategies.
Resource Allocation
Sales forecasting helps in managing human and capital resources. By predicting which products or services will be in demand, businesses can allocate their resources more effectively.
Performance Evaluation
Sales forecasts are not only essential for future planning, but they also provide benchmarks against which actual performance can be compared. This comparison helps in evaluating the effectiveness of sales strategies and identifying areas for improvement.
Investor Relations and Financing
Reliable sales forecasts can demonstrate a business’s potential to investors, lenders, and other stakeholders, and can play a pivotal role in securing funding or attracting investment.
Who uses sales forecast?
Sales forecasting is an essential process that spans across various departments within a business organization, each utilizing these forecasts for different purposes. Here’s a detailed guide on who uses sales forecasts and how they utilize them:
Sales Department
The primary user of sales forecasts is the sales department. Sales teams use forecasting to set targets, track progress, and plan their selling activities. Forecasting helps them identify which products are likely to sell, in what quantities, and in which markets. Salespeople can use these insights to prioritize their efforts, target their most promising leads, and manage their sales pipelines more effectively.
Marketing Department
Marketing teams use sales forecasts to plan their campaigns and activities. They can gauge which products will be in high demand and therefore, need more marketing support. Moreover, they can use these forecasts to determine the potential return on investment for different marketing strategies.
Finance Department
Finance teams use sales forecasts for budgeting, cash flow management, and financial reporting. They use these forecasts to plan budgets for various departments, manage company expenses, and estimate future revenue. In addition, sales forecasts can also guide investment decisions and risk assessments.
Operations and Production Departments
For businesses that manufacture products or manage large supply chains, sales forecasts are critical for efficient operations. These departments use forecasts to plan production schedules, manage inventory, and organize logistics to ensure that products are available when and where they’re expected by customers.
Human Resources Department
HR departments use sales forecasts to plan for staffing needs. If sales forecasts predict growth, HR may need to recruit additional staff or arrange for additional training. Conversely, if a downturn is expected, HR might need to consider downsizing or reassigning staff.
Executive Management
The executive team uses sales forecasts to make strategic decisions about the company’s direction. They can use these forecasts to assess market opportunities, identify potential risks, and make decisions about business expansion, product development, or other strategic initiatives.
Investors and External Stakeholders
While not directly involved in creating or implementing sales forecasts, investors, lenders, and other external stakeholders use these forecasts to evaluate the company’s financial health and future potential. Accurate sales forecasts can help a company attract investment or secure loans.
Types of sales forecasting
Sales forecasting is a crucial process in every organization, and there are several methods for predicting future sales. The type of sales forecasting used often depends on the nature of the business, its stage of growth, the available data, and the specific goals of the forecast. Here are some of the most common types of sales forecasting:
Historical Forecasting
This is one of the simplest methods of sales forecasting, which involves using a company’s past sales data as the basis for predicting future sales. The assumption is that history will repeat itself. For example, if a clothing retailer sold 500 jackets last winter, it might forecast the sale of a similar number for the next winter. This type of forecasting is straightforward but fails to account for changes in market conditions or business operations.
Length of Sales Cycle Forecasting
This method takes into account the average length of the sales cycle and the current opportunities in the pipeline. For instance, if a software company knows that their average sales cycle is six months and they currently have potential deals worth $1 million in their pipeline, they might forecast $1 million in sales over the next six months.
Opportunity Stage Forecasting
This approach involves assigning a probability to each stage of the sales pipeline, and predicting revenue based on the value of opportunities at each stage. For instance, a company might determine that prospects who request a demo have a 40% chance of buying. If they have 10 prospects at the demo stage, each representing $10,000 in potential sales, they could forecast $4,000 in sales from these prospects.
Intuitive Forecasting
Sometimes, especially in new businesses or rapidly changing markets, there’s little historical data available, so sales leaders have to rely on their intuition or judgement. For example, a sales manager might forecast higher sales for a revolutionary new product, despite having no past data, because they believe it will resonate with customers.
Multivariable Analysis Forecasting
Also known as predictive analysis, this method uses advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to predict sales. It takes into account multiple variables, including historical sales data, economic indicators, market trends, and more. For instance, a car manufacturer might use this type of forecasting to predict sales based on variables like consumer confidence, GDP growth, and fuel prices.
Time Series Analysis Forecasting
This forecasting method involves analyzing sales data collected over time to identify trends, patterns, and seasonal fluctuations. For instance, an ice-cream shop might forecast higher sales in summer months based on the previous years’ sales patterns.
Extrapolation Forecasting
This technique involves using statistical methods to extrapolate trends from historical data. For example, if a company’s sales have been growing at 10% per year, it might forecast a similar growth rate for the next year.
What factors influence the accuracy of sales forecasting?
The accuracy of sales forecasting is pivotal for strategic planning and business operations. However, the forecasting process can be influenced by numerous factors which can lead to either accurate or inaccurate predictions. Understanding these factors is crucial for improving the reliability of your sales forecasts. Here are some of the key influencing factors:
Quality of Data
The accuracy of a sales forecast heavily relies on the quality of the data used. If the data is outdated, incorrect, or incomplete, the forecast is likely to be inaccurate. This highlights the importance of maintaining a clean, organized, and up-to-date database.
Sales Cycle Length
The length of the sales cycle can impact the accuracy of a forecast. Longer sales cycles can lead to more uncertainty and higher chances of a deal falling through, thus making accurate forecasting more challenging.
Economic Conditions
Changes in the economy, such as periods of recession or growth, can significantly influence customer purchasing behavior, and thus, sales forecasts. For instance, an economic downturn might cause consumers to reduce spending, affecting the accuracy of forecasts based on data from periods of economic growth.
Market Trends and Consumer Behavior
Trends in the marketplace and changes in consumer behavior can greatly impact sales. New technologies, shifts in consumer preferences, or changes in demographic trends can either boost or hinder sales, influencing the accuracy of the forecast.
Competitive Landscape
Changes in the competitive landscape can also impact sales forecasts. The introduction of new competitors, changes in competitors’ pricing strategies, or innovative offerings from competitors can alter the market dynamics and affect sales.
Historical Sales Data
While historical sales data is often used to predict future sales, it may not always be an accurate predictor. Past performance doesn’t guarantee future results, especially in rapidly changing industries. However, it can provide a good baseline for forecasts if used in conjunction with other factors.
Seasonality
Many businesses experience seasonality in their sales, such as increased sales during the holiday season for retail businesses. Failing to account for seasonality can lead to inaccurate forecasts.
Product Lifecycle
The stage of a product’s lifecycle can greatly influence sales. New products might see rapid sales growth, while mature products may have stable or declining sales.
Sales Team Input
The input of the sales team can influence the accuracy of a forecast. Their insights from direct interactions with customers can provide valuable information about likely future sales. However, this can also introduce bias into the forecast if not balanced with objective data.
Political and Regulatory Environment
Changes in laws, regulations, or political climate can also impact sales. For instance, new environmental regulations might affect sales of certain products, or political instability could disrupt supply chains.
Understanding these factors and how they can impact your sales forecast is crucial. By considering these factors, you can make more accurate predictions, adjust your business strategies accordingly, and drive your business growth.
Popular Free Sales Forecasting Software Solutions
Sales forecasting software can be a game-changer when it comes to predicting future sales trends. These tools automate the forecasting process, improve accuracy, and help businesses make data-driven decisions. Here are details about 10 sales forecasting software solutions that are popular in the market:
Salesforce
Salesforce is a comprehensive CRM platform that includes robust sales forecasting capabilities. It provides real-time visibility into the sales pipeline, generates accurate sales forecasts using AI, and offers customizable forecast categories. Salesforce’s forecasting tool can handle multiple currencies and is designed for collaborative forecasting, allowing for adjustments and comments from team members.
HubSpot Sales Hub
HubSpot offers a powerful sales forecasting tool as part of its Sales Hub. It allows you to generate sales forecasts based on deals in your sales pipeline, and you can filter forecasts by team, individual sales reps, or deal stage. HubSpot also provides detailed reports to track your progress towards sales goals.
Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM provides predictive sales forecasting that helps businesses plan effectively. It offers a variety of forecasting options, including territory-based forecasting, hierarchical forecasting, and overlay forecasting. Zoho also allows you to set quotas for sales teams and track their performance against the forecast.
Pipedrive
Pipedrive is a sales CRM with a visual sales pipeline that’s designed to be user-friendly. Its sales forecasting features include the ability to project revenues from ongoing deals, generate detailed sales reports, and identify deals that require attention. Pipedrive also supports customizing the stages of your sales pipeline to match your sales process.
Insightly
Insightly is a CRM and project management tool that provides sales forecasting capabilities. It allows you to forecast sales based on opportunities in your pipeline, track progress towards sales targets, and generate detailed sales reports. Insightly’s forecasts can be broken down by team, territory, or sales rep.
Clari
Clari is an AI-driven sales forecasting platform that offers predictive insights and detailed analysis of your sales pipeline. Clari provides real-time forecasts, risk analysis, and opportunity management. Its AI algorithms analyze historical data and current deals to predict future revenue.
Anaplan
Anaplan is a connected planning platform that provides advanced sales forecasting capabilities. It offers real-time forecasts, quota planning, territory management, and predictive modeling. Anaplan’s platform is designed to be collaborative and scalable, making it suitable for large organizations.
IBM Planning Analytics
IBM Planning Analytics is an AI-infused planning and forecasting tool that offers powerful sales forecasting capabilities. It provides real-time insights, scenario modeling, and predictive analytics. IBM’s tool is designed for large-scale, complex forecasting scenarios.
Aviso
Aviso is an AI-powered sales forecasting and analytics platform. It offers real-time pipeline visibility, predictive forecasting, and deal-level insights. Aviso’s AI models learn from your sales data to improve forecast accuracy over time.
DataRobot
DataRobot is an automated machine learning platform that includes sales forecasting capabilities. It provides AI-driven forecasts, real-time insights, and advanced analytics. DataRobot supports a wide range of forecasting models and is designed to handle large data sets.
How to Create a Sales Forecast
Creating a sales forecast involves careful analysis, informed estimation, and a deep understanding of your business. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to create a sales forecast:
Step 1: Define the Time Period
Decide the time period for your sales forecast. This could be monthly, quarterly, or annually depending on your business needs and the level of detail you want. The time frame of your sales forecast should align with your business planning cycle.
Step 2: Identify Your Sales Units
Sales units are the products or services you sell. Break down your sales by product or service line. This provides a more detailed and accurate forecast as different products might have different sales trends and growth rates.
Step 3: Gather Historical Data
Collect past sales data for the period equivalent to the one you’re forecasting. If you’re predicting the next quarter’s sales, look at the past few quarters, or even years if the data is available. This data will form the baseline of your forecast.
Step 4: Account for Market Trends and Conditions
Examine market trends, industry reports, and economic indicators to understand the bigger picture. If your industry is growing rapidly or if there’s a new trend that could impact your sales, factor this into your forecast.
Step 5: Factor in Sales and Marketing Efforts
Consider the impact of your marketing campaigns, product launches, and sales initiatives on the forecast. If you plan to ramp up marketing efforts or launch a new product, it’s likely to increase sales.
Step 6: Account for Seasonality
If your business experiences seasonal fluctuations, be sure to factor these into your forecast. Look at sales data from the equivalent period in previous years to understand the seasonal trends in your sales.
Step 7: Consult with Sales Team
Your sales team can provide valuable insights from the frontlines. They can offer information on the pipeline status, potential deals, customer feedback, and market conditions. This can add another layer of information to your forecast.
Step 8: Draft Your Initial Forecast
Using all the data and information gathered, create your initial sales forecast. It can be as simple as projecting past sales forward, adjusting for factors like market growth, seasonality, and sales initiatives, or it might involve more complex statistical analysis.
Step 9: Review and Adjust Regularly
A sales forecast is not a static document. It should be reviewed and updated regularly to incorporate actual sales results and changing market conditions. This allows you to adjust your predictions and make informed decisions about your business strategy.
Step 10: Use Sales Forecasting Tools
There are numerous sales forecasting tools that can automate much of the forecasting process. These tools can handle large amounts of data and complex calculations, making the forecasting process more efficient and accurate.
FAQs
How Can I Improve Sales Forecast Accuracy?
Sales forecast accuracy can be improved by maintaining high-quality data, accounting for market conditions, consulting with your sales team, regularly reviewing and adjusting forecasts, and using sales forecasting software. Incorporating multiple forecasting methods can also enhance accuracy.
How Often Should Sales Forecasts Be Updated?
The frequency of updating sales forecasts depends on your business size, type, and the volatility of your industry. However, it’s generally advisable to update your forecast regularly – monthly or even weekly in some industries – to keep them aligned with current market conditions and business situations.
What is the Difference Between a Sales Forecast and a Sales Budget?
A sales forecast is an estimate of future sales, whereas a sales budget is a plan for future sales. The sales forecast informs the sales budget. A sales forecast is typically based on past data, market analysis, and predictions, while a sales budget is what the company aims to achieve.
What Factors Influence Sales Forecasts?
Several factors can influence sales forecasts, including economic conditions, market trends, competitive landscape, quality of data, sales cycle length, seasonality, and political and regulatory changes.
What Role Does Sales Forecasting Play in Supply Chain Management?
Sales forecasting plays a vital role in supply chain management as it helps predict demand for products. This information is crucial for inventory management, production planning, and logistics. Accurate sales forecasting can help prevent stockouts or overstocks, thus optimizing the supply chain.
What are Some Common Sales Forecasting Mistakes?
Common sales forecasting mistakes include relying solely on intuition, not using historical data, failing to consider market trends, not adjusting forecasts regularly, and failing to involve the sales team in the forecasting process. All these can lead to inaccurate sales forecasts.





























![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)
