Risk management is a vital aspect of any successful project, and the Risk Register Template is an essential tool for any project manager. The template allows project managers to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate or avoid them, ensuring the successful completion of the project.
Whether you’re working on a large-scale business venture or a small, internal project, having a clear understanding of the risks involved can mean the difference between success and failure. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the Risk Register Template and how it can help project managers navigate the ever-present threat of risk in any project.
Table of Contents
Risk Register Templates
Risk Register Templates are essential tools used in project management and risk management processes to systematically identify, assess, and track risks associated with a project or an organization. These templates provide a structured format for capturing and documenting key information about risks, enabling project teams to proactively manage and mitigate potential threats to project success.
Risk Register Templates can be customized based on the specific needs of the project, industry best practices, or organizational requirements. They can be designed as digital spreadsheets, project management software, or integrated into risk management systems. By utilizing Risk Register Templates, project teams can proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks, leading to improved project outcomes, reduced uncertainties, and increased overall project success. These templates serve as a vital tool for risk management, enabling project teams to stay on top of potential risks and make informed decisions to protect project objectives.
What Is a Risk Register?

A risk register is a document or tool used to identify, assess, and prioritize potential risks to an organization or project. It is used to help organizations plan for and respond to potential risks, and is often a key component of an overall risk management strategy.
A risk register typically includes a list of identified risks, along with information about the likelihood and potential impact of each risk. It may also include details about the mitigation measures that have been or will be put in place to address the risks, as well as information about who is responsible for monitoring and managing the risks.
Why is it important?
A risk register is an important tool for organizations of all sizes, as it helps them identify, assess, and prioritize potential risks that could impact their operations, reputation, or bottom line. Some of the key benefits of using a risk register include:
Increased awareness of potential risks: By identifying and documenting potential risks in a centralized location, organizations can increase their overall risk awareness and ensure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of the risks they face.
Prioritization of risks: By assessing the likelihood and potential impact of each risk, organizations can prioritize risks and allocate resources to those that pose the greatest threat.
Improved decision-making: By having a clear understanding of the risks an organization faces, decision makers can make more informed decisions about how to mitigate or prevent those risks.
Better communication: A risk register can help facilitate better communication between different departments and stakeholders by providing a clear, centralized location for risk information.
Compliance: Some industries require organizations to have a robust risk management process, and a risk register is an important element of that process. By having a risk register, organizations can demonstrate to regulators and auditors that they have taken steps to identify and manage risks.
Continual improvement: By regularly reviewing and updating the risk register, organizations can ensure that they are continually improving their risk management processes and are better prepared to handle new risks as they arise.
Overall, a risk register is a valuable tool that can help organizations make better decisions, allocate resources more effectively, and reduce the likelihood of negative impacts from risks.
Key Elements of a Risk Register
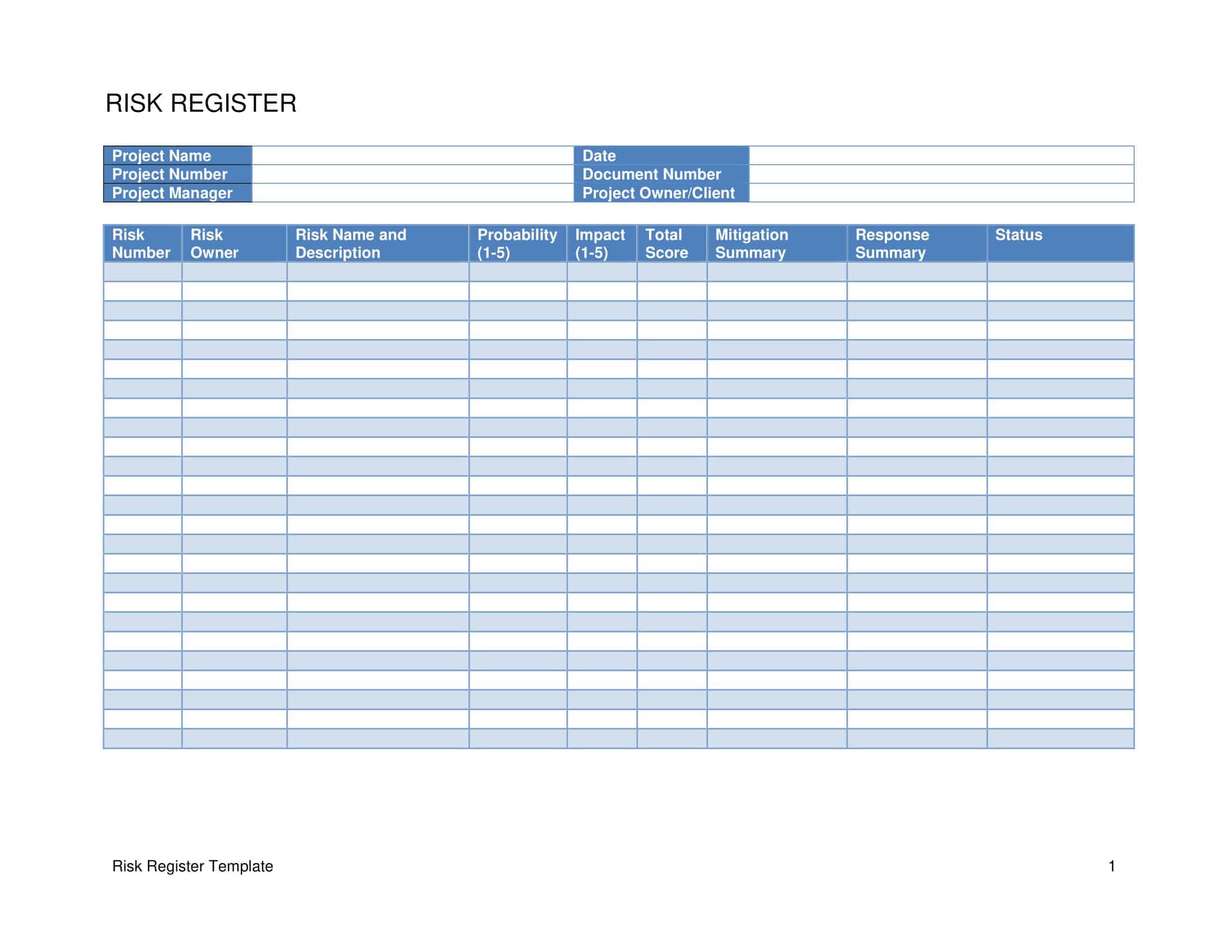
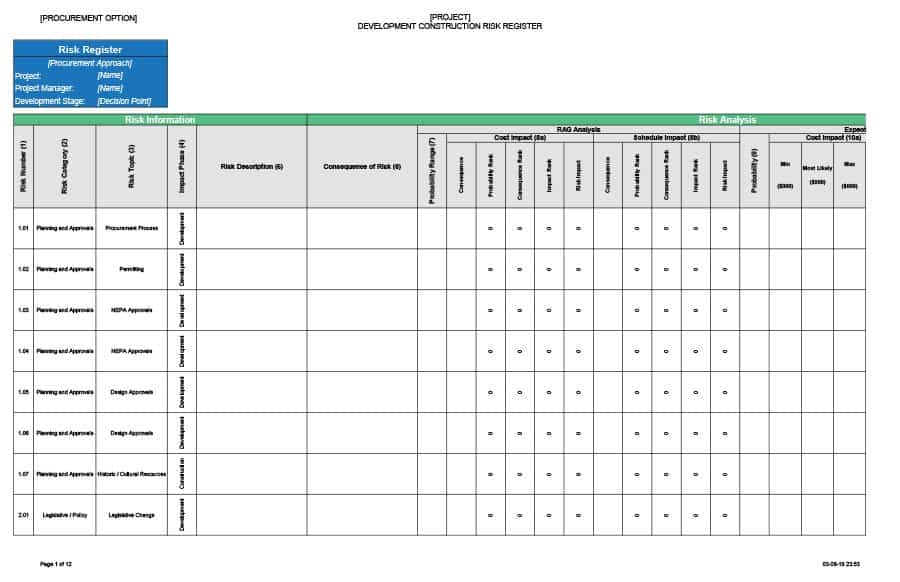
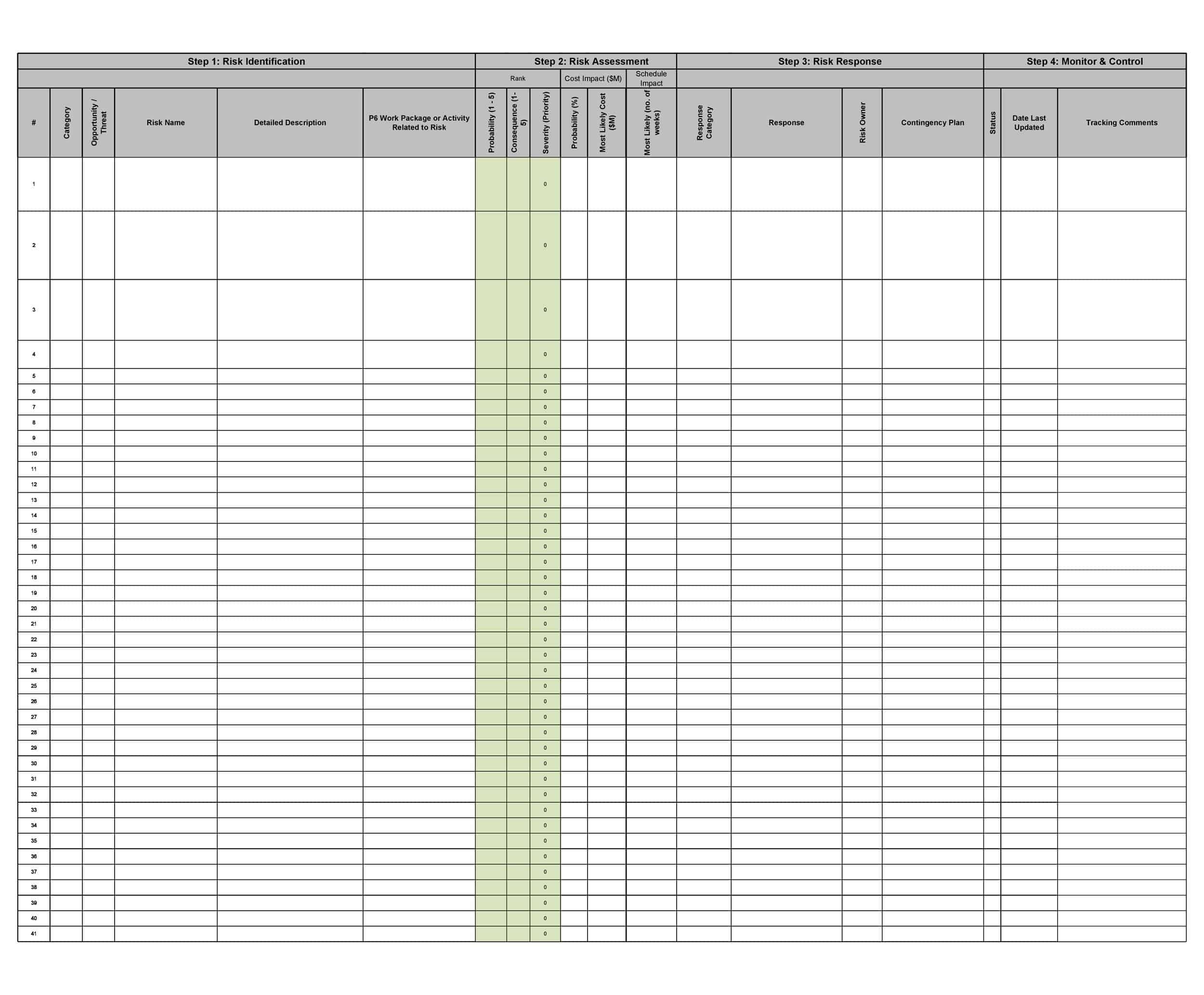
A risk register is a document or tool used to identify, assess, and track risks to a project, organization, or program. The essential elements of a risk register include:
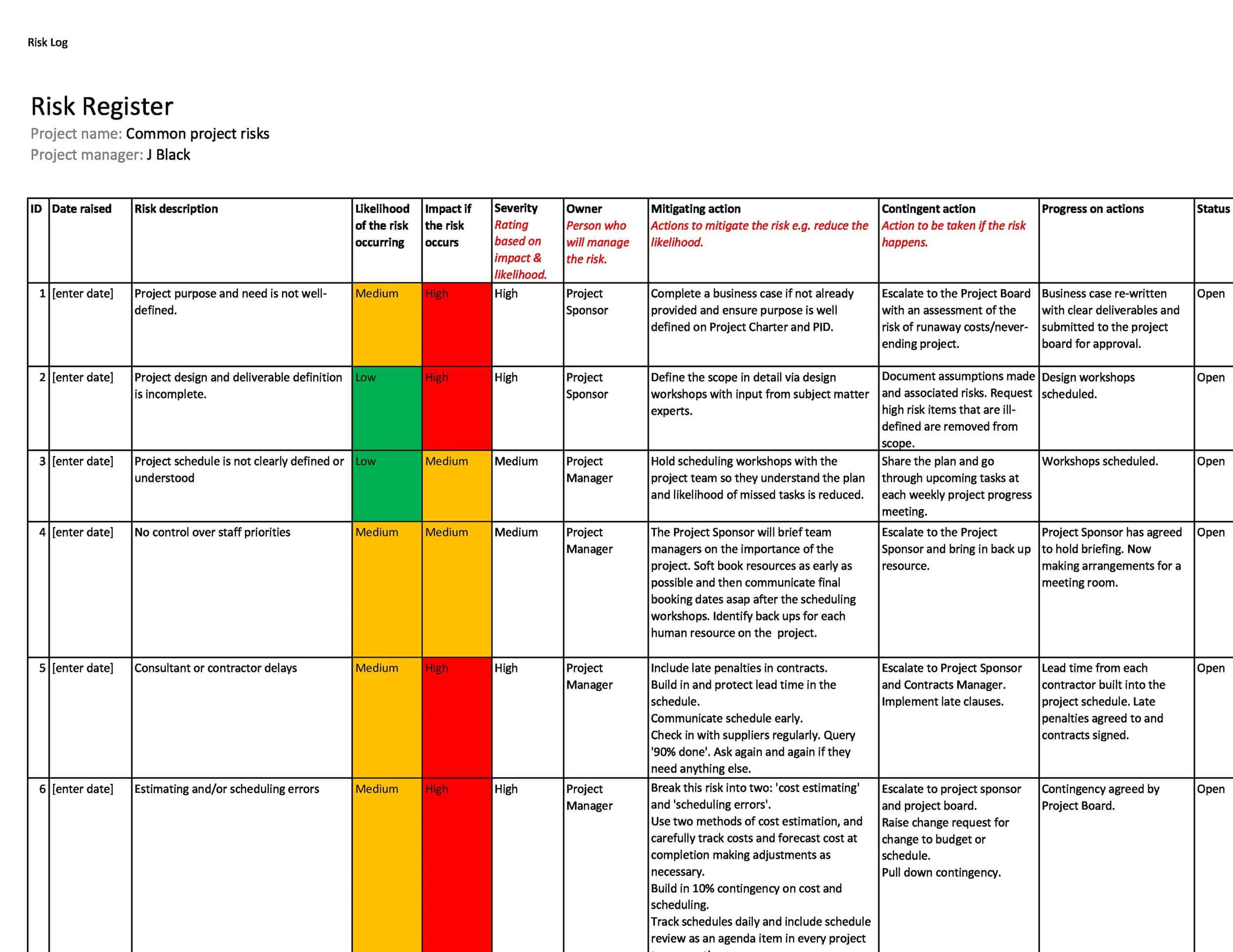
Risk ID: Each risk in the register should have a unique identification number or code to help with tracking and reference.
Risk Description: A clear and detailed description of the risk, including its cause, potential impact, and the assets or objectives it threatens.
Risk Probability and Impact: The likelihood of the risk occurring and the potential impact if it does occur. This can be represented numerically, using a scale such as low, medium, or high, or using a probability/impact matrix.
Risk Owner: The person or team responsible for managing the risk.
Risk Status: The current status of the risk, including whether it is open, closed, or mitigated.
Risk Response: The actions taken or planned to mitigate or manage the risk.
Risk Trigger: The event or condition that would indicate that the risk has occurred.
Mitigation Costs and Benefits: The cost and potential benefits of implementing a risk response.
Due Date: The date by which the risk response is planned to be implemented.
Review Date: The date by which the risk will be reviewed again to assess its continued relevance and impact.
Supporting Documents: Any related documents that would help in assessing or understanding the risk better
Historical Data: Any relevant historical data that have been available from similar project or organization, that would be beneficial in identifying and assessing the risk.
In addition to these elements, a good risk register should also be easily accessible to all stakeholders, easy to update and understand, and provide clear visibility into the risks facing the project, organization, or program.
It’s also important to keep in mind that risk register is not a one-time document, but a living document that need to be updated and reviewed regularly, especially as the project, organization, or program progresses and new information becomes available.
How to Create a Risk Register Template
Creating a risk register is an important step in identifying, assessing, and managing risks to a project, organization, or program. The process of creating a risk register involves several key steps, which include:
Identify Risks
The first step in creating a risk register is to identify all potential risks that may affect the project, organization, or program. Risks can come from a variety of sources, such as changes in requirements, external factors like natural disasters, or internal issues like delays or budget overruns. To identify risks, you can use a variety of techniques such as brainstorming, root cause analysis, or risk breakdown structures.
Assess Risks
Once potential risks have been identified, the next step is to assess each risk to determine its probability and impact. The assessment should include the likelihood of the risk occurring and the potential impact if it does occur. This can be represented numerically, using a scale such as low, medium, or high, or using a probability/impact matrix.
Prioritize Risks
After assessing the risks, the next step is to prioritize them based on their likelihood and impact. Risks with a high probability and high impact should be given the highest priority, while risks with a low probability and low impact can be given a lower priority. Prioritizing risks helps to focus risk management efforts on the most significant risks first.
Identify Risk Responses
Once risks have been prioritized, the next step is to identify appropriate risk responses for each risk. Risk responses can include avoiding the risk, transferring the risk, accepting the risk, or mitigating the risk. The appropriate response will depend on the specific risk, the resources available, and the organization’s risk tolerance.
Develop a Risk Management Plan
The final step in creating a risk register is to develop a risk management plan that outlines the specific actions that will be taken to mitigate or manage each identified risk. The plan should include details such as the responsible party, the timeline for implementation, and any required resources.
Maintain and Review the Risk Register
Once the risk register has been created, it’s important to maintain and review it regularly. This involves updating the register as new information becomes available, reassessing the risks as the project or organization evolves, and monitoring the risk management plan to ensure that actions are being taken as planned.
In addition to these steps, it’s also important to ensure that the risk register is easily accessible to all stakeholders, easy to update and understand, and provides clear visibility into the risks facing the project, organization, or program.
It’s also important to keep in mind that creating a risk register is an ongoing process. Your risk management plan should not be considered a one-time task, but a continuous process. It’s necessary to review the risks and update the register regularly. For example, new risks may arise as the project progresses, so it is necessary to be aware of potential new risks that may arise and adjust the risk management plan accordingly.
In order to create a Risk register, you can use a software or excel sheets for better tracking, monitoring and reporting of risks. This tool would assist the risk management team in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. It can also provide them with the necessary information to make informed decisions.
FAQs
How often should a risk register be reviewed and updated?
A risk register should be reviewed and updated regularly, especially as the project, organization, or program progresses and new information becomes available. The review and update should include reassessing the risks and monitoring the risk management plan to ensure that actions are being taken as planned.
Can a software be used to create a risk register?
Yes, software can be used to create a risk register. It can assist the risk management team in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, and provides them with the necessary information to make informed decisions. it also helps in better tracking, monitoring and reporting of risks
Can a risk register be shared with stakeholders?
Yes, a risk register can be shared with stakeholders such as project team members, senior management, and other relevant parties. Sharing the risk register with stakeholders helps to ensure that everyone is aware of the risks facing the project, organization, or program, and can provide input and feedback for risk management.
How do you create a risk register?
To create a risk register, make a table with columns for risk ID, category, description, causes, probability, impacts, mitigating actions, risk owners, status and review dates. Next, identify project risks, evaluate impact and likelihood, detail response plans, and assign owners. Update the log as needed.
What does a good risk register look like?
A good risk register clearly captures details like: Brief risk descriptions, risk causes and impacts, qualitative probability and severity ratings, mitigation actions, designated risk owners, target resolution dates, current status, and review dates to assess progress.
What is a risk register template?
A risk register template provides a pre-made table document to simply log risks in areas like columns for: Unique ID, risk description, probability rating, impact assessment, priority score, mitigation actions, owners, review status, status updates, and target closeout dates to resolution.
What is a sample risk register?
A sample risk could be: ID: 001 Risk: Supply delays from vendors Cause: COVID-related supplier shutdowns Likelihood: High Impact: Critical project delays
Mitigation: Dual source materials Owner: John Smith Status: Active













































![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)
