Keeping track of business expenses is a key responsibility in any organization. Creating clear, organized expense reports allows employees to document costs for reimbursement and helps companies monitor spending. However, developing expense reports from scratch can be complex and time-consuming. Using pre-made templates allows for easy expense reporting that follows company guidelines.
In this article, we will look at key information to include in expense reports and provide downloadable expense report templates to simplify the process. With the right templates, employees can quickly submit expenses, managers can approve or deny reimbursement, and accounting can categorize costs. Well-designed expense report templates make the process seamless while ensuring documentation for company records.
Table of Contents
What is an Expense Report?

An expense report is a document that employees submit to their employer to record and get reimbursed for business-related costs. The report lists any expenditures the employee has incurred as part of their job duties, like travel, meals, supplies, etc. Good expense reports contain detailed information on each expense including date, amount, description, receipt, and expense category or type.
The main purpose of expense reports is to create a record and documentation of costs that can be repaid to the employee. Companies require employees to use expense reports in order to reimburse work-related spending. The reports allow managers to review and approve or deny requests based on company policy.
Accounting can then categorize expenses appropriately for accurate financial reporting. Standardized expense reporting improves compliance, creates transparency into spending, and provides documentation for audits and taxes. Well-organized, complete expense reports are vital for smooth reimbursement processes in any organization.
Expense Report Templates
For businesses, properly tracking employee expenses is crucial for taxation and reimbursement purposes. An expense report template streamlines the processing and organization of these costs.
The template consolidates expenses by category such as travel, meals, supplies, etc. Employees provide receipts validating each expense. Important details are captured including vendor name, purchase date, description and amount. Excel templates allow for automatic calculations and totals.
A well-designed expense report template benefits both employer and employee. Employers have documentation needed to write-off business expenses come tax season. For employees, the standardized template takes the guesswork out of reporting costs for reimbursement. Having an efficient system saves time and hassle on both sides. Expense templates promote proper record keeping and transparent reporting of employee spend.
Why Expense Report is Important?
Expense reports are crucial components in the financial and operational management of any business or organization. They provide detailed records of the expenditures incurred during business operations, especially those by employees. Here’s why expense reports are important:
Budgeting & Financial Planning
Expense reports allow businesses to track and categorize their expenditures, helping them understand where their money is going. This understanding is vital for setting budgets for future periods, making financial forecasts, and planning for growth or cost-cutting.
Reimbursement
When employees pay out-of-pocket for business-related expenses, they need a formal system to claim reimbursements. An accurate expense report ensures that employees are compensated fairly and timely for any business-related expenditures they’ve made.
Financial Transparency
Expense reports promote transparency within an organization. They provide a clear view of the costs associated with business operations, which can be reviewed by managers, auditors, and stakeholders.
Tax Deductions
For many businesses, especially those in countries with a detailed tax code, certain business expenses are tax-deductible. However, to claim these deductions, a company must have clear, detailed records of these expenses. An organized expense report system ensures that these records are available when needed.
Auditing & Compliance
If a company’s financial statements are audited, auditors will want to see records of expenses to ensure they’ve been recorded and accounted for correctly. Furthermore, certain industries have specific compliance standards related to expenses, and detailed reporting helps in adhering to these regulations.
Cost Control & Management
By regularly reviewing expense reports, businesses can identify areas where they might be overspending or where costs are unexpectedly rising. This can lead to more informed decision-making and opportunities to negotiate better rates with suppliers or cut unnecessary expenses.
Fraud Prevention
A consistent and transparent expense reporting process can deter fraudulent activities. When employees know that their expenses are being scrutinized, they’re less likely to submit fraudulent or inflated claims. Additionally, a robust system can identify anomalies or suspicious activities that might indicate fraud.
Operational Insights
Beyond mere financial implications, expense reports can provide insights into business operations. For example, if travel expenses are high, it might indicate that remote communication tools could be a better investment. Alternatively, high expenses in a particular department could indicate inefficiencies that need addressing.
Decision Making
Detailed expense reports help business leaders make informed decisions. When considering areas for expansion or cutbacks, having a clear understanding of where money is being spent and why it’s crucial.
Cash Flow Management
Businesses, especially small ones, need to keep a close eye on their cash flows. Expense reports give them insights into outgoing cash, helping them manage liquidity and ensuring they have enough resources to cover their short-term obligations.
Stakeholder Trust
For businesses with external stakeholders or investors, transparency in financial dealings, including detailed expense reports, can build trust. It shows that the company is being managed responsibly and that there’s oversight on how funds are spent.
What Should An Expense Report Include?
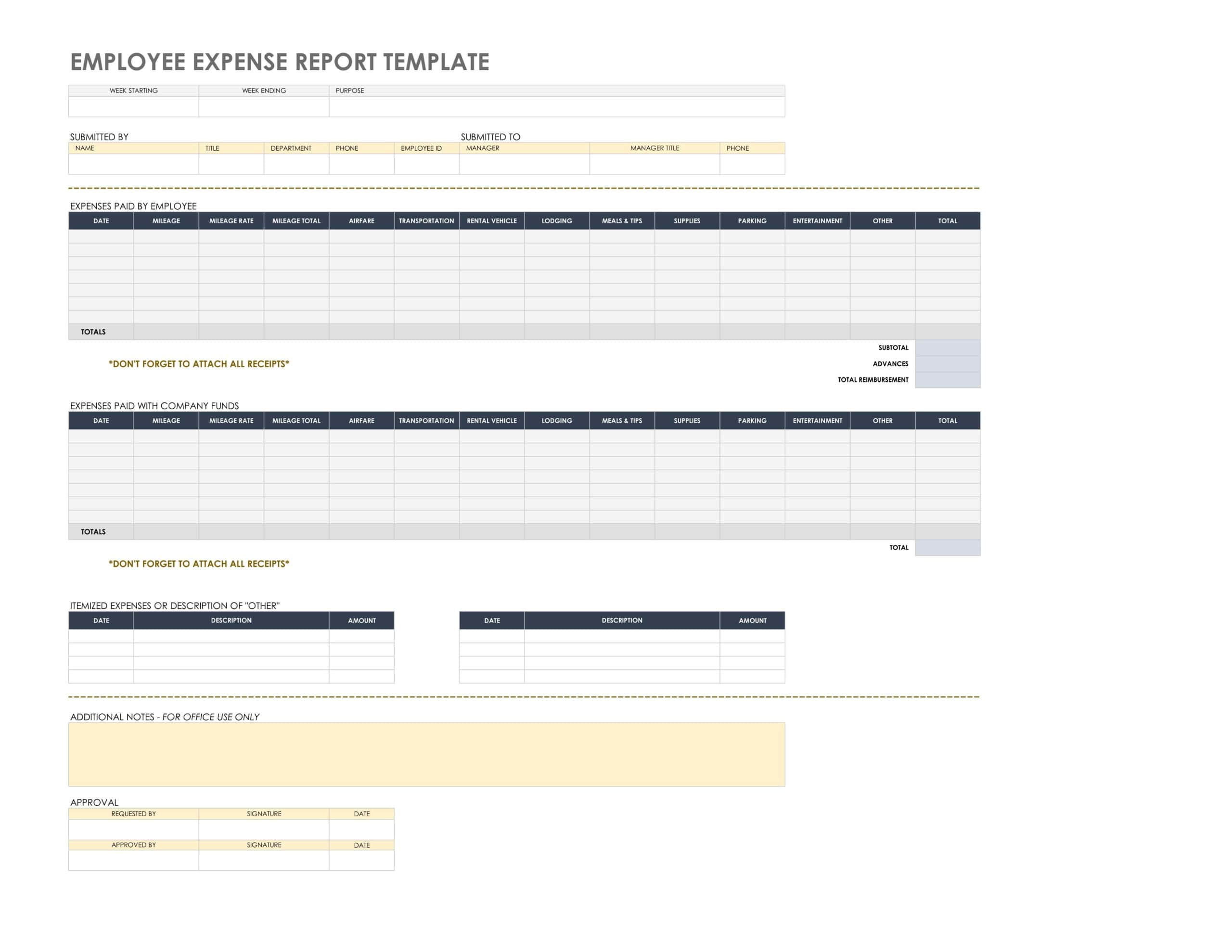
Submitting complete, accurate expense reports is important for prompt reimbursement and financial tracking. However, determining what key information to include can be confusing. Expense reports that lack important details can get rejected and delay repayments. So what should an expense report include? There are several core elements that every expense report needs to contain – the date, amount, description, category, receipt, and approvals for each expenditure.
Providing these details gives accounting and management the information they need to process reimbursements and maintain records. In this article, we will outline the essential components of a well-formatted expense report. Understanding the key pieces to incorporate makes it easier for employees to compile reports and get repaid quickly. Here are the main elements every expense report should include:
- Header Information:
- Report Name/Title: Clearly state that the document is an expense report.
- Employee Information: Name, employee ID, department, and position.
- Report Period: Specify the date range for which the expenses were incurred, such as “January 1, 2023, to January 31, 2023.”
- Report ID or Number: For tracking and reference purposes.
- Expense Details:
- Date of Expense: The date the expense was incurred.
- Expense Category: E.g., travel, meals, accommodation, office supplies, etc.
- Description: A brief description of the expense. For instance, if it’s a meal expense, it could include details like “Lunch with client at XYZ Restaurant.”
- Vendor/Supplier Name: The entity where the expense was incurred, e.g., a specific hotel, restaurant, airline, or store.
- Receipt Number: If applicable.
- Amount: The cost of the expense. Ideally, list this in both the original currency (if foreign) and the company’s home currency.
- Payment Method: E.g., cash, credit card, company card, etc.
- Receipts & Documentation:
- Attach original receipts, invoices, or other relevant documentation to support each expense. Digital systems often allow for electronic attachments or scans.
- Some companies use mobile apps that allow employees to snap photos of their receipts, which are then automatically added to the expense report.
- Total Amount:
- A clear and bold summation of all the expenses listed.
- If there were advances given to the employee, these should be mentioned, and the net amount to be reimbursed (or returned) should be calculated.
- Notes or Comments:
- A section for any additional notes, explanations, or comments regarding the expenses.
- Approval Workflow:
- Submitted By: The name and signature (or digital confirmation) of the employee submitting the report.
- Approved By: Space for the signatures (or digital confirmation) of the relevant department heads, managers, or finance personnel who review and approve the report.
- Date of Approval: The date when the report was approved.
- Reimbursement Details (if applicable):
- Reimbursement Method: E.g., check, direct deposit, cash, etc.
- Reimbursement Date: When the employee was reimbursed.
- Reimbursement ID/Reference: For tracking purposes.
- Miscellaneous:
- Exchange Rate: If the report includes expenses in a foreign currency, mention the exchange rate used.
- Tax Information: If certain expenses are taxed differently or if the tax amount needs to be mentioned separately.
- Footer:
- Company’s name, address, contact details, and any other relevant company information.
Types of Expense Report Template
Expense report templates can vary based on the type of organization, the nature of the expenses, and the specific requirements of each department or function. Here are some common types of expense report templates:
- Travel Expense Report Template:
Travel expense reports are essential for employees who travel for business purposes. They allow businesses to track and manage costs associated with trips, including airfare, lodging, meals, and other incidental expenses.
- Features: This template typically includes fields for dates of travel, destinations, the purpose of the trip, transportation costs (airfare, train tickets, car rentals), accommodations (hotel costs, taxes, fees), meals and entertainment expenses, and any other miscellaneous expenses related to the trip, such as tips or business center costs.
- Benefits: Such templates help in ensuring that travel expenses comply with company policies and IRS (or equivalent in other countries) guidelines for reimbursements. They also assist in budgeting for future trips and can offer insights into potential cost-saving opportunities in travel arrangements.
- Usage: Often used by sales teams, executives, consultants, and other professionals who need to travel for work.
- Employee Reimbursement Template:
This template is used when employees make out-of-pocket purchases for the company. While it can include travel-related expenses, it’s more generalized and can encompass any work-related expense.
- Features: Includes fields for the date of purchase, vendor or supplier name, expense category (like office supplies, software, training materials), amount, and a section for attaching or referencing receipts.
- Benefits: It streamlines the process of reimbursing employees, ensuring that they are paid back promptly and accurately. It also provides a way to track these miscellaneous expenses, ensuring they are legitimate business expenses and are recorded correctly in financial statements.
- Usage: Common in almost all organizations, especially where employees might need to make quick purchases for office supplies, software, or any other materials required for their work.
- Monthly Departmental Expense Template:
Designed for department heads or managers, this template provides a summary of all expenses incurred by a specific department in a month.
- Features: It breaks down expenses by category (like salaries, equipment, software subscriptions), and typically includes a section for recurring vs. one-time expenses. There might also be fields for budgeted vs. actual expenses to track variance.
- Benefits: This helps department heads manage their budgets effectively, understand where funds are being spent, and make necessary adjustments in the future. It also aids upper management in gauging the financial efficiency of each department.
- Usage: Used by department heads or managers in larger organizations to manage and track their department’s finances.
- Project-Based Expense Report Template:
For businesses that work on specific projects, like construction or consulting, tracking expenses at the project level is crucial.
- Features: This template will include fields specific to the project, such as project name, client name, start and end dates, and categories related to the specific type of project (like material costs, labor costs, licensing fees).
- Benefits: It allows for accurate billing to clients and ensures that the project remains within budget. It also provides insights into the profitability of individual projects, which can inform future project bids and proposals.
- Usage: Commonly used by project managers, contractors, consultants, and other professionals working on specific, time-bound projects.
- Training and Development Expense Report Template:
For companies investing in employee training and development, a separate report template can ensure a detailed breakdown of associated expenses.
- Features: The template might cover registration fees, material costs, accommodation and travel for off-site training, expenses for trainers or consultants, and other relevant expenditures like venue rental or online platform costs.
- Benefits: Monitoring training costs can offer insights into the ROI of development programs, ensuring that resources are used effectively. It can also help HR and training departments plan budgets and prioritize development initiatives.
- Usage: Commonly used by HR departments, training coordinators, and team leads responsible for employee development.
- Entertainment and Client Meeting Expense Report Template:
When businesses host clients or have entertainment expenses, it’s essential to separate these from other costs for clarity and compliance reasons.
- Features: This would detail the date, client’s name, purpose of the meeting, venue, total amount, and any other specifics, such as the number of attendees. It would often be used for meals, events, or gifts given to clients.
- Benefits: Separating client-related expenses ensures clarity in accounting, helps in understanding the costs associated with client acquisition and retention, and ensures compliance with taxation and business policies.
- Usage: Typically used by sales, business development, and client relationship teams.
- Capital Expenditure Report Template:
This is used for expenses related to the purchase or upgrade of long-term assets like equipment, property, or technology infrastructure.
- Features: Details about the asset, its lifespan, vendor or supplier details, date of purchase, installation costs, and any associated fees or maintenance plans.
- Benefits: Tracking capital expenditures separately helps in depreciation calculations, long-term financial planning, and understanding the company’s investment in assets.
- Usage: Often managed by the finance department or asset management teams in conjunction with department heads making the purchase.
- Event or Conference Expense Report Template:
For businesses that host or attend conferences, exhibitions, or events, having a tailored template can be beneficial.
- Features: It might encompass registration fees, stall or booth setup costs, promotional material expenses, travel and accommodation for attendees, and any other related expenditure like advertising or sponsorships.
- Benefits: This provides clarity on the ROI of participating in or hosting such events. It aids in budgeting for future events and ensures that all costs, even smaller ones, are accounted for.
- Usage: Marketing teams, event organizers, and professionals responsible for attending or hosting industry events.
How to Create an Expense Report
Submitting accurate, timely expense reports is key to getting reimbursed for employee spending. However, for many, creating expense reports can seem complicated, resulting in delayed or denied repayments. Following a clear, defined process makes it easier to produce complete reports that contain all required information.
In this article, we provide a step-by-step guide on how to create an expense report. We will outline the key steps involved, including saving receipts, filling out report forms, adding descriptions, categorizing expenses, submitting for approval, and more. With these steps, employees can simplify the expense report process and avoid common mistakes. Here are the main steps we will cover in this guide for creating accurate expense reports:
Step 1: Understand the Purpose
Before you start creating an expense report, it’s crucial to understand its primary purpose. An expense report is typically used by businesses and professionals to track and report expenses incurred during a specific period, often related to business operations like travel, meals, or office supplies. Recognizing the importance of accuracy is key. A well-maintained expense report not only helps in ensuring reimbursements are accurate but also assists businesses in financial forecasting and budgeting.
Step 2: Gather All Necessary Receipts and Documents
Start by collecting all the receipts, invoices, and any other documents related to the expenses you’re reporting. This is important for two reasons. First, it helps to ensure that you don’t miss out on any expenditure. Second, in most professional settings, receipts serve as a validation for your claims, and without them, you might not get reimbursed. It’s a good practice to organize these receipts chronologically or categorically, as this will make the actual reporting process smoother.
Step 3: Choose a Reporting Format or Tool
There are various formats and tools available for creating expense reports. Some organizations might provide their employees with specific software or templates for this purpose. If you’re working independently, you can use spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or specialized software like Expensify or Concur. Whichever tool or format you choose, ensure it allows for detailed entries and categorization of expenses.
Step 4: Categorize Your Expenses
Start by dividing your expenses into broad categories. Common categories include travel, meals, accommodation, office supplies, and miscellaneous. After classifying, break them down further if necessary. For instance, under travel, you might have expenses related to airfare, taxis, public transportation, and fuel. By categorizing, you make your report more organized and easier for approvers or accountants to understand and process.
Step 5: Input Expense Details
For each expense, enter specifics like date, vendor or merchant name, description of the expense, and the amount. If you’re working with foreign currency, ensure to note the currency type and conversion rate if it’s already converted. In digital tools or spreadsheet programs, you can use formulas to automatically total each category and provide a grand total at the end.
Step 6: Attach Supporting Documents
If you’re submitting your report digitally, scan or take clear pictures of your receipts and attach them to your expense report. Some software allows for direct attachment to each entry, which can be useful for reviewers. If you’re submitting a paper report, consider attaching photocopies of the receipts or using a pocket folder to keep all supporting documents together.
Step 7: Review and Verify
Before finalizing your report, take a moment to review each entry. Ensure that all amounts are correctly inputted, and there are no duplications or missing entries. This step is crucial because errors can delay reimbursements or create complications in financial records.
Step 8: Submit the Report
Once you’re satisfied with the accuracy and completeness of your report, submit it to the appropriate person or department in your organization. This could be a manager, an accounting department, or another relevant party. Make sure to keep a copy, digital or physical, for your records.
Step 9: Track and Follow Up
After submission, keep track of your report’s status. Some companies might have a specified timeframe for processing expense reports. If you don’t receive feedback or reimbursement within that period, consider following up. This ensures that your report doesn’t get lost in the shuffle and that you receive the reimbursements you’re entitled to.
Conclusion
Using an expense report template can save employees time and simplify the reimbursement process. In this article, we’ve covered the key information that should be included in expense reports, like dates, descriptions, categories, and receipts. We also walked through the steps involved in properly completing these reports. With the understanding of what makes a complete, compliant expense report, employees can now utilize the free editable expense report template attached.
This template in Excel and Word formats allows for easy expense reporting that follows recommended guidelines. All the needed columns and sections are provided – just plug in your spending details. With this expense report template, employees can quickly compile their expenses for reimbursement, managers have the details needed to approve spending, and accounting gets standardized data for recording. The template eliminates the need to build expense reports from scratch, making the process seamless.
FAQs
Are receipts always required for expense reports?
While the necessity for receipts can vary by company policy or the amount of the expense, they are generally required for validation and audit purposes. Some businesses might have a threshold below which a receipt isn’t mandatory, but for transparency and accuracy, it’s always a good practice to attach supporting documents.
Can I use digital tools or apps for my expense reports?
Yes, there are many digital tools and apps like Expensify, Concur, and QuickBooks that are specifically designed to help streamline the process of creating, submitting, and approving expense reports. These tools often allow for direct receipt scanning, automatic categorization, and easy report generation.
Are personal expenses allowed on an expense report?
Generally, personal expenses are not allowed on a business expense report and should not be submitted for reimbursement. However, unintentional inclusion can happen. If personal expenses are found on a report, they are typically deducted or not reimbursed.
Can I claim expenses without an expense report?
Typically, no. An expense report provides a structured way to claim expenses and ensures there’s a record for every claim made. Without such a report, it becomes challenging for businesses to track, validate, and reimburse expenses.
Why are expense reports necessary?
Expense reports serve multiple purposes:
- They ensure employees are reimbursed accurately for out-of-pocket expenses.
- They help businesses track and manage costs.
- They provide a clear record for tax purposes, ensuring allowable deductions are claimed.
- They aid in financial forecasting and budgeting.





































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
