You have decided to set up some goals for yourself, either to improve your life or achieve something in your professional capacity. You know the importance of setting goals, but how to choose the proper goal-setting techniques is a big question. SMART is a popular approach used by most professionals while setting their goals, but like all other things, you need to know some important facts and limitations involved with it.
Table of Contents
SMART Goals Templates
Smart Goals Templates are valuable tools used to set clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals. These templates provide a structured framework for individuals, teams, or organizations to define and track their objectives in a smart and systematic manner. Smart Goals, an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, help ensure that goals are well-defined, realistic, and aligned with overall objectives.
Smart Goals Templates provide a structured and systematic approach to goal setting and tracking. By utilizing these templates, individuals, teams, or organizations can clarify their objectives, establish measurable targets, and enhance their focus and productivity.
Smart Goals Templates can be customized to fit various contexts, such as personal development, project management, performance evaluation, or strategic planning. Whether used by individuals for personal goal setting, teams for project management, or organizations for strategic planning, Smart Goals Templates serve as effective tools for setting, monitoring, and achieving goals in a smart and organized manner.
What are SMART Goals?

SMART can be explained as an acronym that can be used in goal setting. SMART is a term formed by combining the words “Specific, Measurable, Accepted, Relevant, Time” and defines the objectives in project management, which is named after the initials of these words.
The first known use of the term SMART was made in George T. Doran’s Management Review in November 1981.
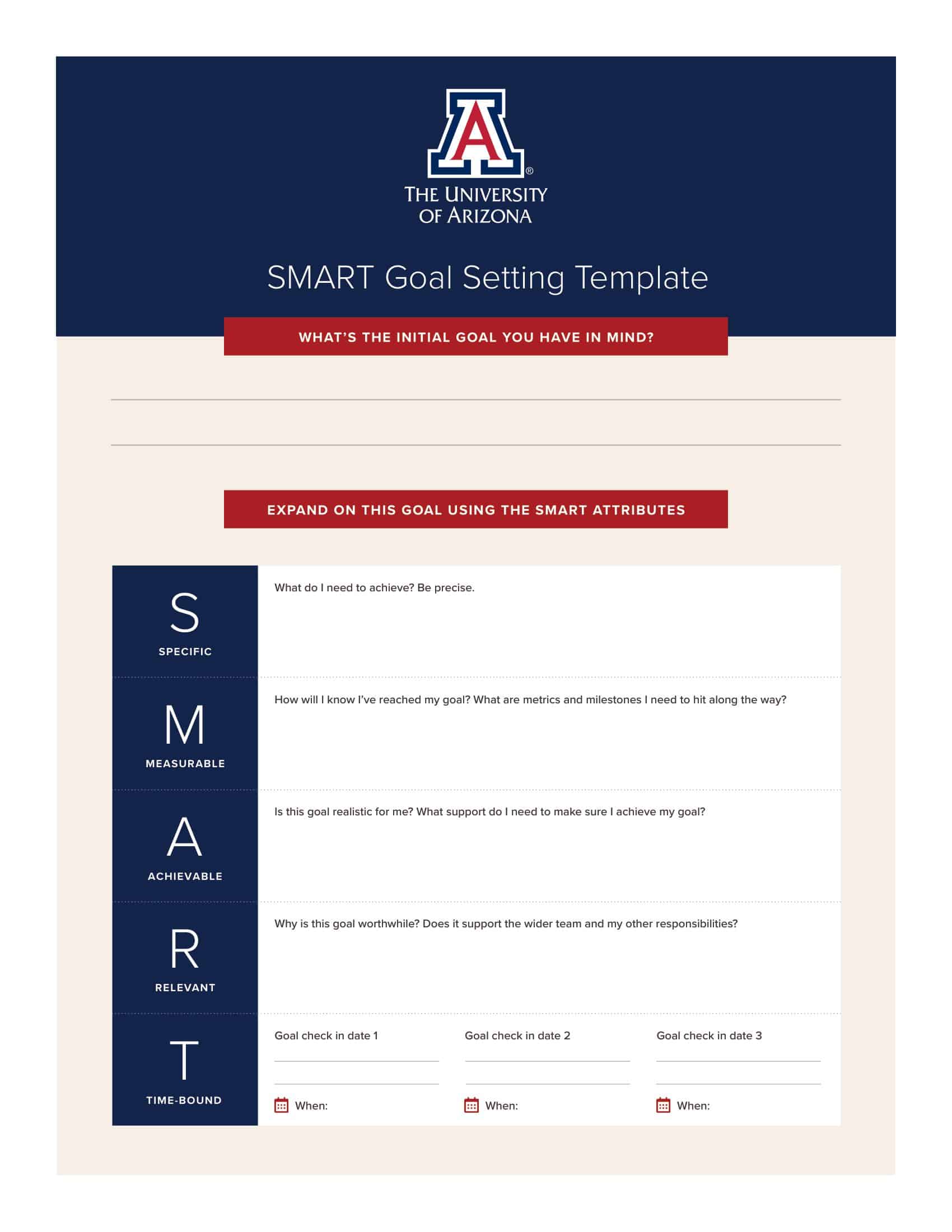
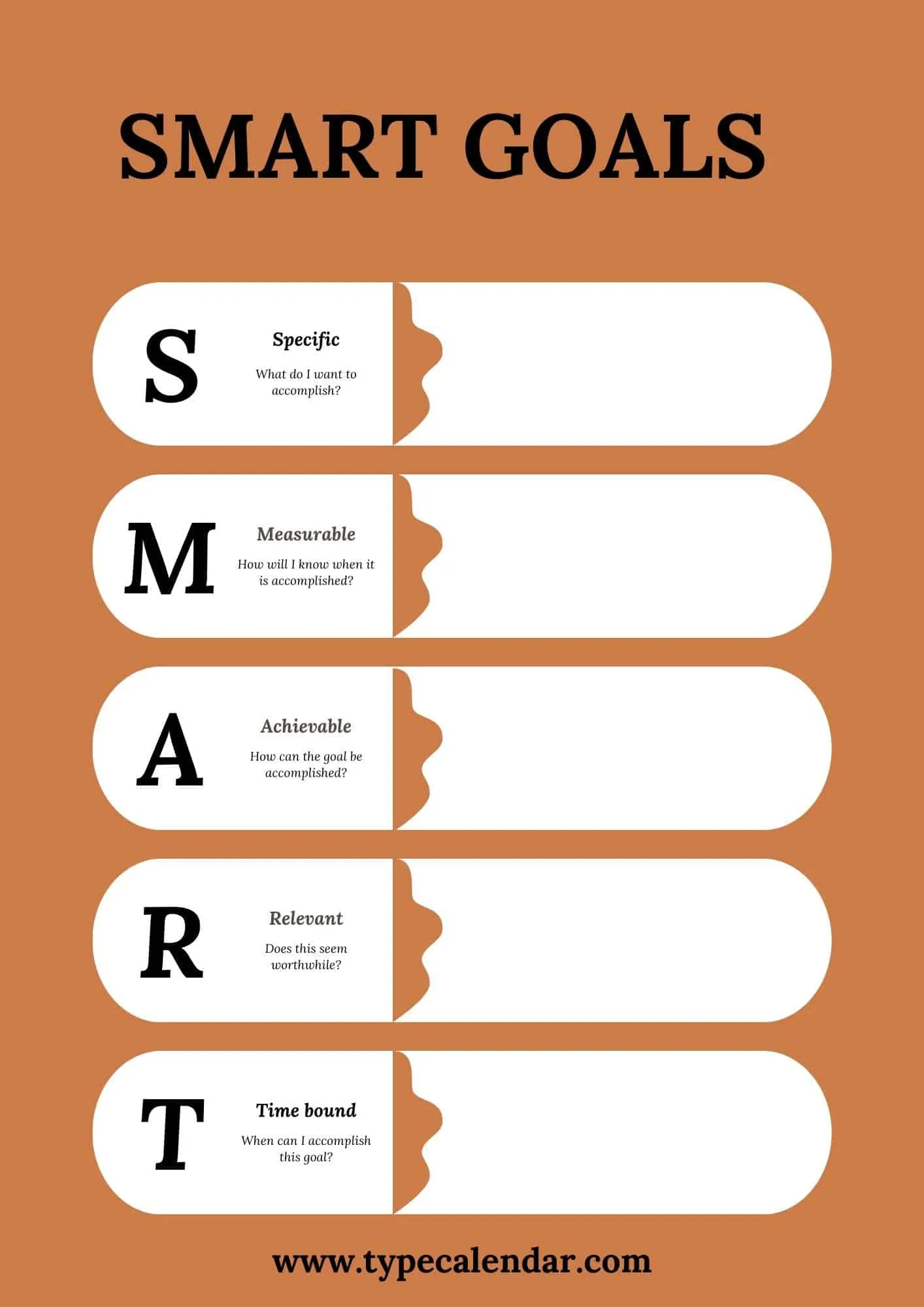
- S = Specific: The target must be defined precisely and clearly
- M = Measurable: The target must be measurable
- A = Accepted: Target must be acceptable to recipients
- R = Reasonable: The target must be attainable.
- T = Time-bound: The target’s schedule, beginning, and end should be clear
If a goal meets all these criteria, it now becomes a SMART goal. If SMART is applied correctly, it demonstrates verifiable and measurable goals.
Let’s examine these five elements that makeup SMART. Let’s take a look at the roadmap on how to create a SMART goal.
S = Specific
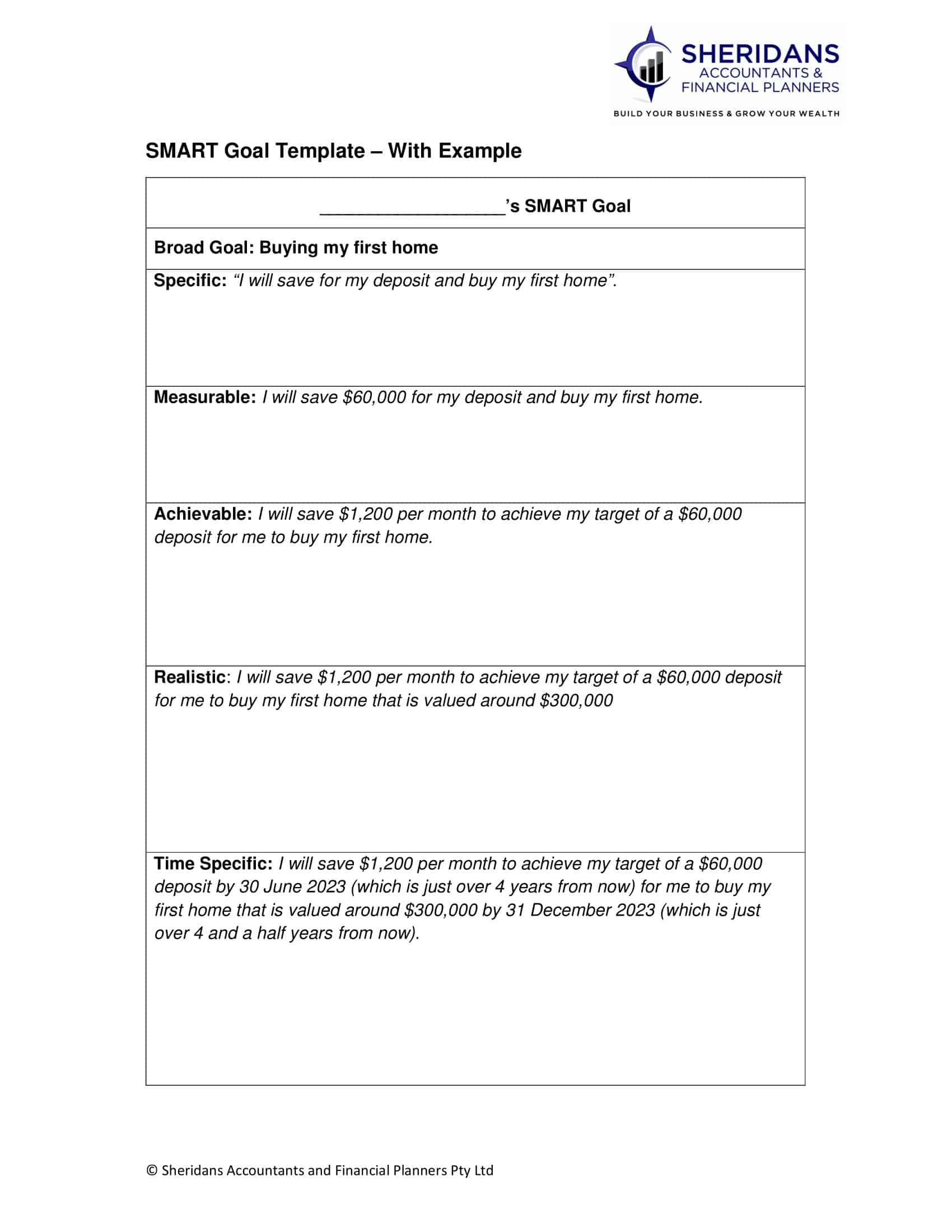
First of all, the characteristics of the target should be defined as clearly as possible. The goal should be concrete, and there should be no undefined details. To determine these details, “what do I want to do, why is it important, how should it be, where, when?” questions should be asked.
Smart goals should be clearly stated first. For example, “I have to practice a foreign language for at least half an hour every day to move to a higher position at my workplace. Thus, thanks to the foreign language that I developed well during my promotion period, I could reach my goal and be promoted.”
M = Measurable
If the goal is to be transformed into a smart goal, it must be measurable. By using numbers, progress towards the goal can be tracked, and motivation can be maintained. “How many, how many, how will I know when I am a success?” questions should be asked.
Let’s exemplify measurability; “I will move to a higher position by doing the necessary work in 1 year at my workplace.”
A = Accepted
It must be attainable for a goal to be counted among smart goals. Capacity needs to be challenged, but it is still a rational and realistic approach to see that the target is within reach and to set a target in this way. “How do I reach my goal? Is my goal realistic?” questions should be asked.
Let’s exemplify accessibility; “I have to work hard to get promoted. Do I have time for this? Can I put my social life on the back burner and focus entirely on work?”
R = Reasonable :
Is the specified target really appropriate for the person or institution that is declaring it or not? The answer to the question must be determined. If the target is not suitable for the person or the institution, the motivation will decrease, making it very difficult to reach the target. “Is it the right time, is it needed, are we the right person/institution, is this valuable, is it applicable in the current environment?” questions should be asked. If the answers are yes, it means that there is one more step behind for the target to be among the smart targets.
Let’s exemplify conformity; “Is it the right time for extra training to help me get promoted? If I take this position, will I be able to handle it?”
T = Time-bound
Smart goals must have a time limit and deadline. Smart goals should include a calendar. A target with an uncertain end date may cause permanent delay. Compliance with a strict schedule makes a goal more rational. A target calendar should be created by answering questions such as “When, where am I in two months, what stage will I be at next week, what should I do today?”
Let’s exemplify the timing: “There is exactly one year until the promotion time. I have to complete my studies exactly one month before that time, within 11 months and repeat it in the last month. I will test my foreign language once a month.”
A Brief History of SMART Goals
The first contextual event in the history of SMART goals occurred in 1968. Dr. Edwin Locke published a seminal article, “Towards a Theory of Task Motivation and Incentives.” Locke found that properly set goals result in superior corporate performance in the paper.
Edwin Locke began his research on the power of goal setting and organizational performance in the late 1960s. George T. Doran published an article in 1981 called “Management has a SMART way to write down goals and objectives” and laid out the main principles of SMART goals.
What are five reasons why people would set goals?
Focus
Goal setting is the starting point of all the achievement and success in any field. It is the main reason some people become what they want, and some don’t. You need to set goals for you to be able to achieve any success in your life. Goal setting will help you stay on top of things. When you become a part of any organization, a company, or a team, certain tasks will be assigned to you; it will be quite hard for you to balance everything in your personal life with all that is asked of you at work. One good thing about goal setting is that it makes your life simpler; all the distractions and time-wasting activities have no place in your life anymore after you set up goals.
Direction
Goals give direction. Before setting your goals, you should know that two types of goals are audacious goals and incremental goals. An audacious goal is a long-term goal or one that entails a huge task to be achieved within a certain time frame. It may take years before you can achieve them, and it also requires deep commitment on your part. On the other hand, an incremental goal is a short-term one that doesn’t take long to accomplish but requires consistency over time for continuous improvement. It’s important to note both kinds of goals to reach your full potential in life. The journey towards success lies in the hands of the person who has decided what he wants, knows where he’s going, and has already chosen his path.
Priorities
There are goals and priorities. Priorities play a very crucial role in success. When you set a goal, chances are you’re going to follow through with it and not deviate from your course when you have priorities in mind. With a clear and written description of what is important to you, you’ll never forget to stay on top of those essential parts of your life.
Managing Time
You can be successful in managing your time if you set SMART goals. If an employee is late for work every day, it makes his employer wonder about his work ethic. On the other hand, if an employee arrives on time every day and regularly performs his job duties to the employer’s satisfaction, that says good things about him. This is true in any job: whether you are a teacher, doctor, sales representative, or IT professional.
Fulfillment
People who set goals and achieve them promptly get a feeling of fulfillment. They are happy and motivated to set more goals, which ultimately become a part of the path to success. In this ever-changing world, one might sometimes feel completely lost. However, if you’ve already set yourself clear goals and established an achievable plan to reach them, it’s much easier to wade through the unpredictability and ride on the steady journey to your childhood dreams. To help you identify your own goals and set up your way to success, below is a list of factors that will help you achieve your life’s objectives successfully.
Conclusion
Goal setting is important to accomplish tasks in a focused manner. Goals are necessary to give a direction to achieve results. They stress the importance of what you want to achieve and why it is important for you. Typecalendar.com says that goal setting helps employees do their job better and motivates them to work in a target-oriented and result-driven way.
Goal setting makes sense for both individuals and teams because performance is directly linked with the expectations of people or targets set for them. Goals help you organize your thoughts, prioritize your work better, and can really help you move forward.
FAQs
How to make smart goals worksheet?
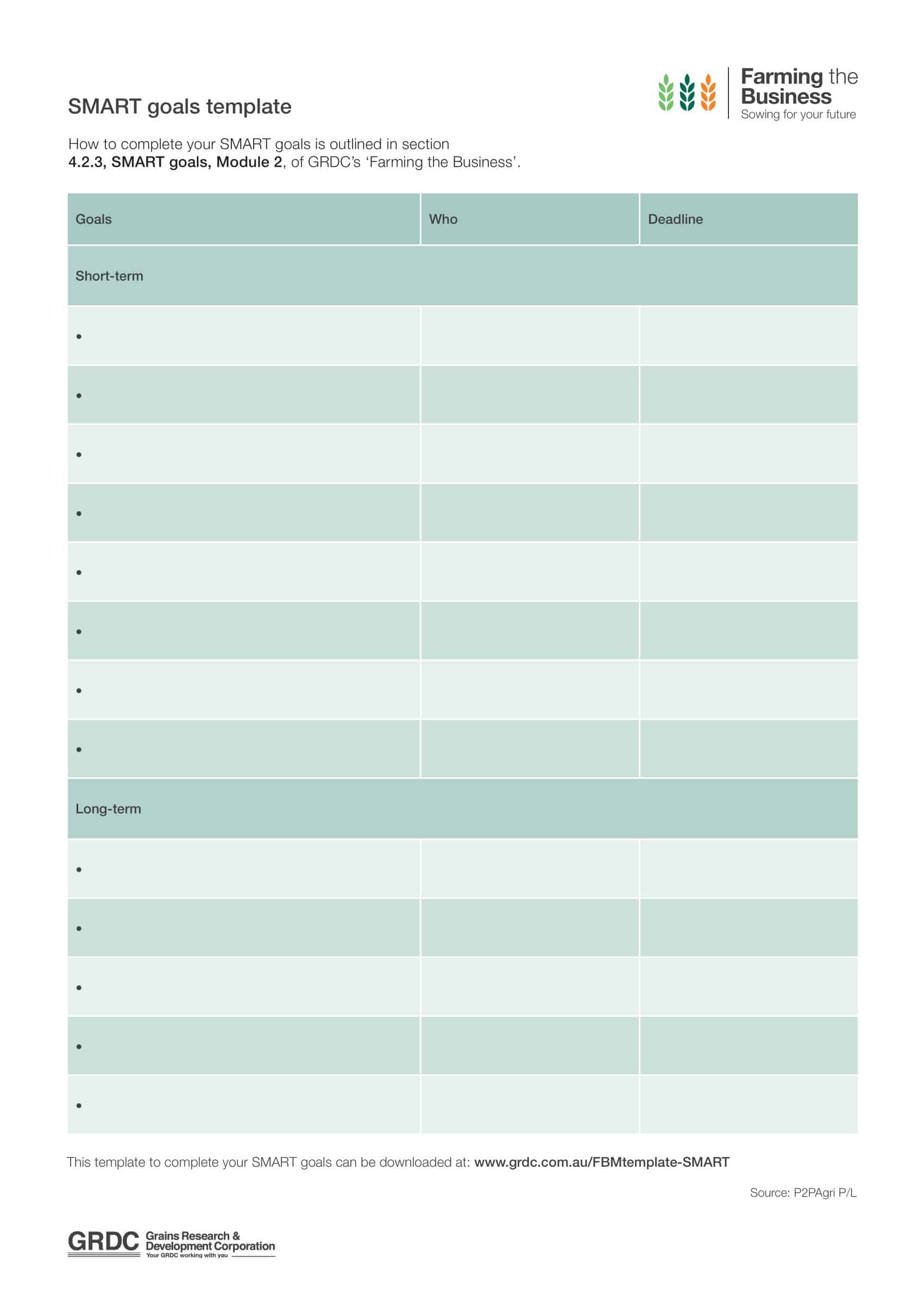
Create a table with columns for the 5 sections of SMART goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For each goal the student or employee is working on, have them fill out details for each component. This focuses them on setting goals that meet SMART criteria by articulating precise actions, metrics, and deadlines.
What are 5 smart goals examples?
- Increase revenue by 10% in the next 6 months through launching a new marketing campaign.
- Lose 15 pounds in the next 3 months through daily exercise and adopting a low-carb diet.
- Improve presentation skills by 25% in 1 month by taking a course and practicing twice per week.
- Read one self-improvement book per month this year to expand leadership skills.
- Learn to play 5 new songs on the guitar in the next 2 months through 30 minutes of practice 5 times per week.
What do you write in smart goals?
SMART goals contain:
- The Specific actions needed to accomplish the goal
- Measurable targets to track progress
- Achievable skills and resources required
- Relevance to broader objectives
- Timeframes including deadlines and intervals
How to do a SMART goal table?
Make a table with 5 columns labeled S,M,A,R,T. The rows can be labeled with individual goals. Fill out the table by writing in:
- S – Precise actions to take
- M – Quantifiable metrics and measures
- A – Resources available, scope constraints
- R – Alignment with wider goals
- T – Target dates for milestones and final completion
This structure allows clear visualization of how each goal meets the SMART criteria.






















































![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 1 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
