Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic problem-solving process used to identify and address the underlying cause of an issue or problem. This method involves analyzing data, events, and information related to a problem to understand what went wrong and why it happened.
The goal of RCA is to prevent similar issues from happening in the future by addressing the root cause and implementing permanent solutions. This process can be applied in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and software development, and can help organizations improve processes, reduce errors, and increase overall efficiency.
Table of Contents
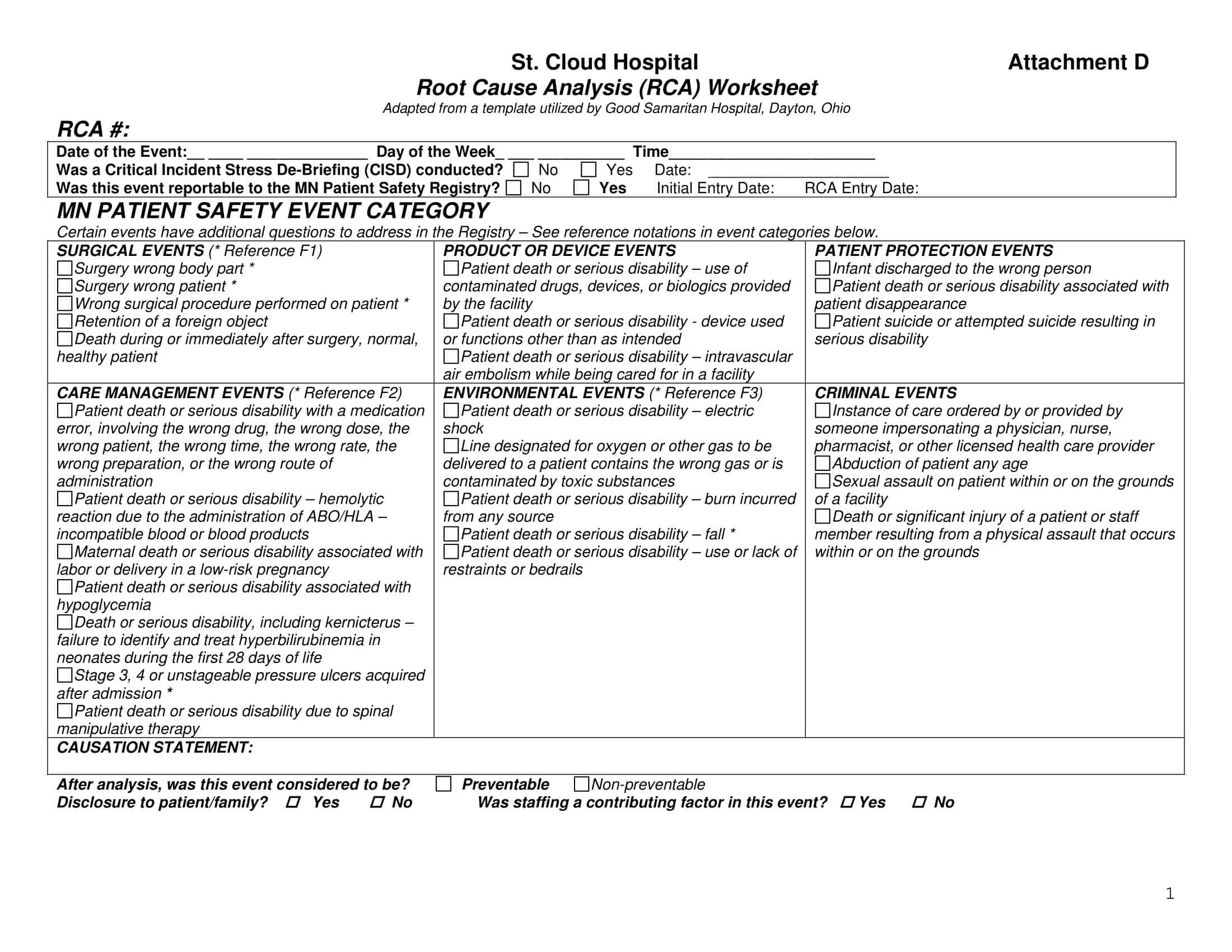
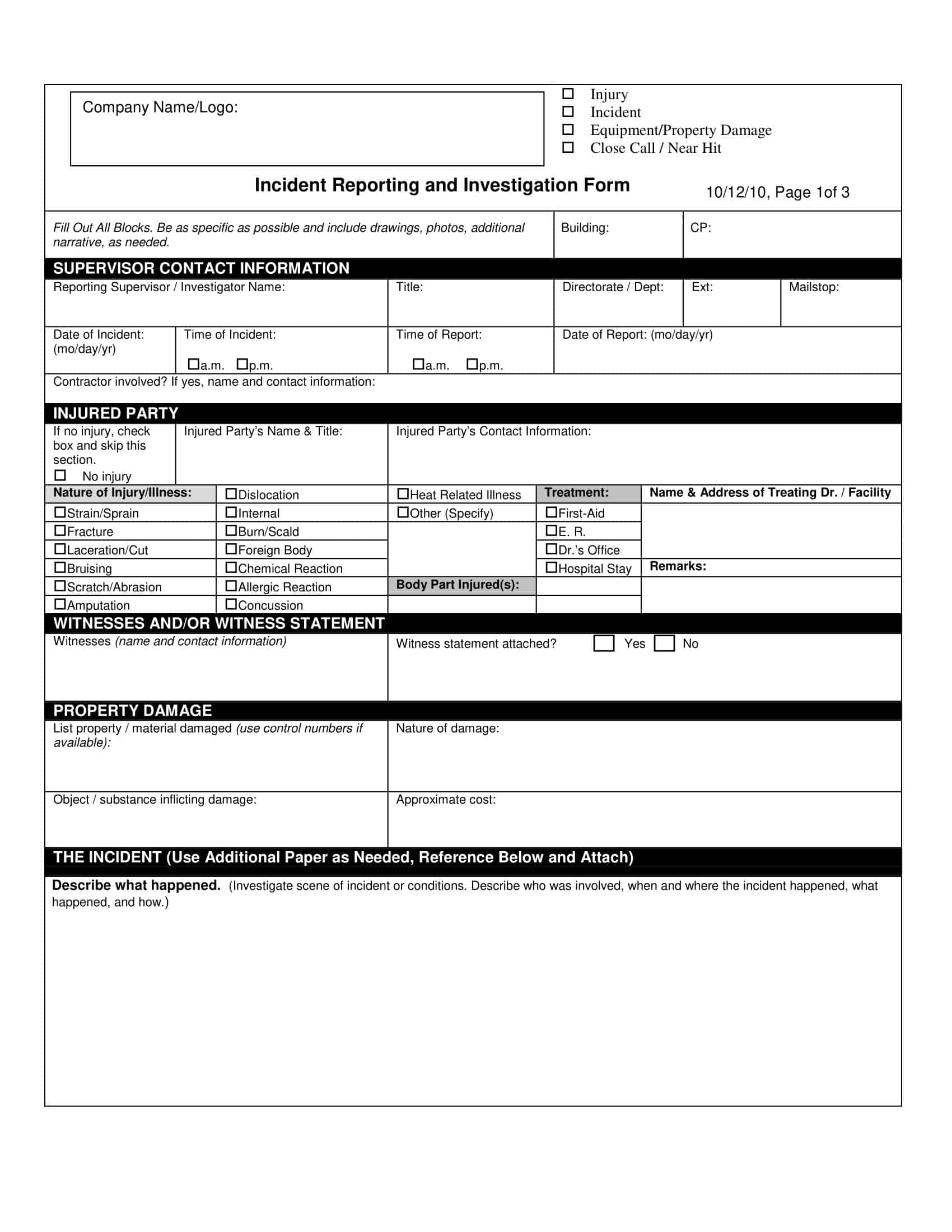
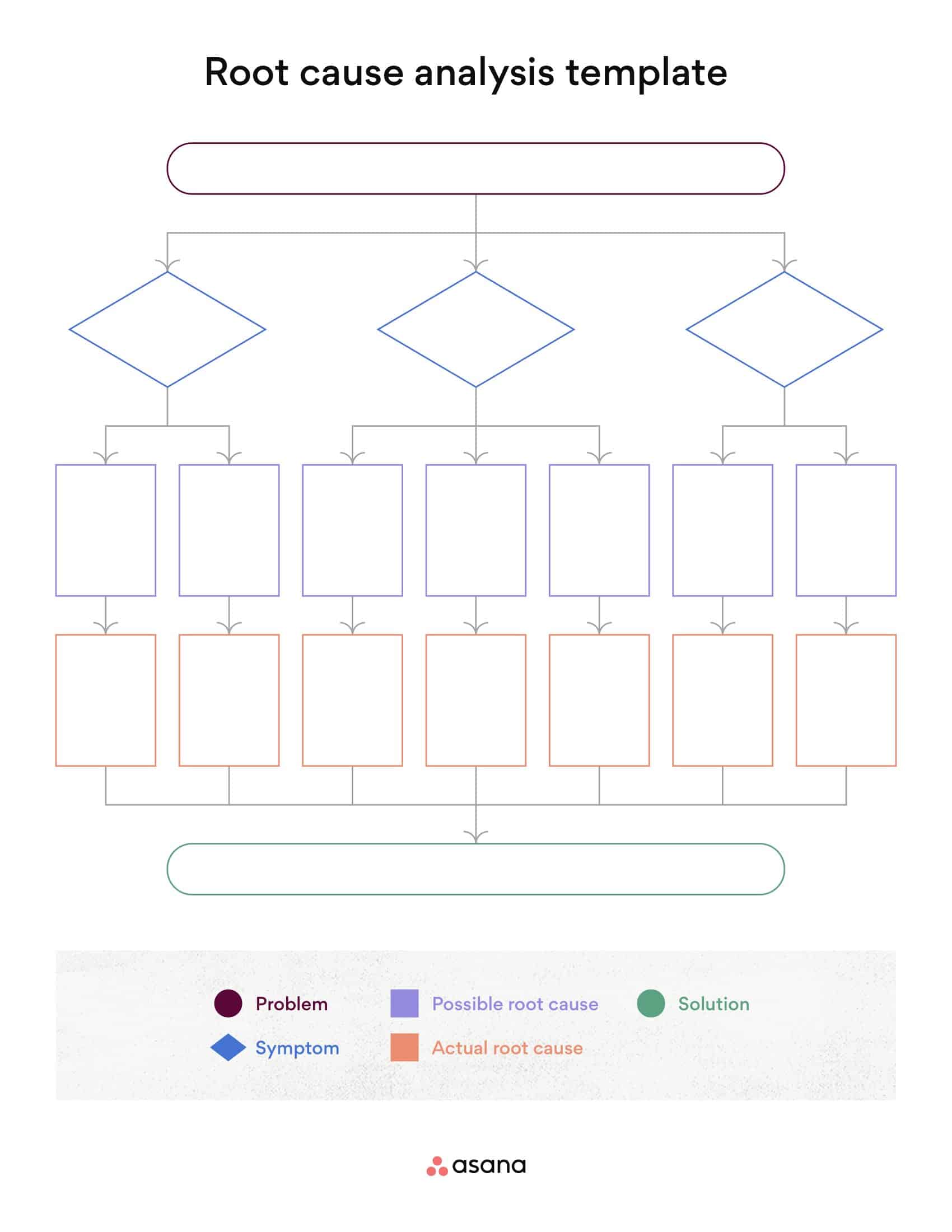
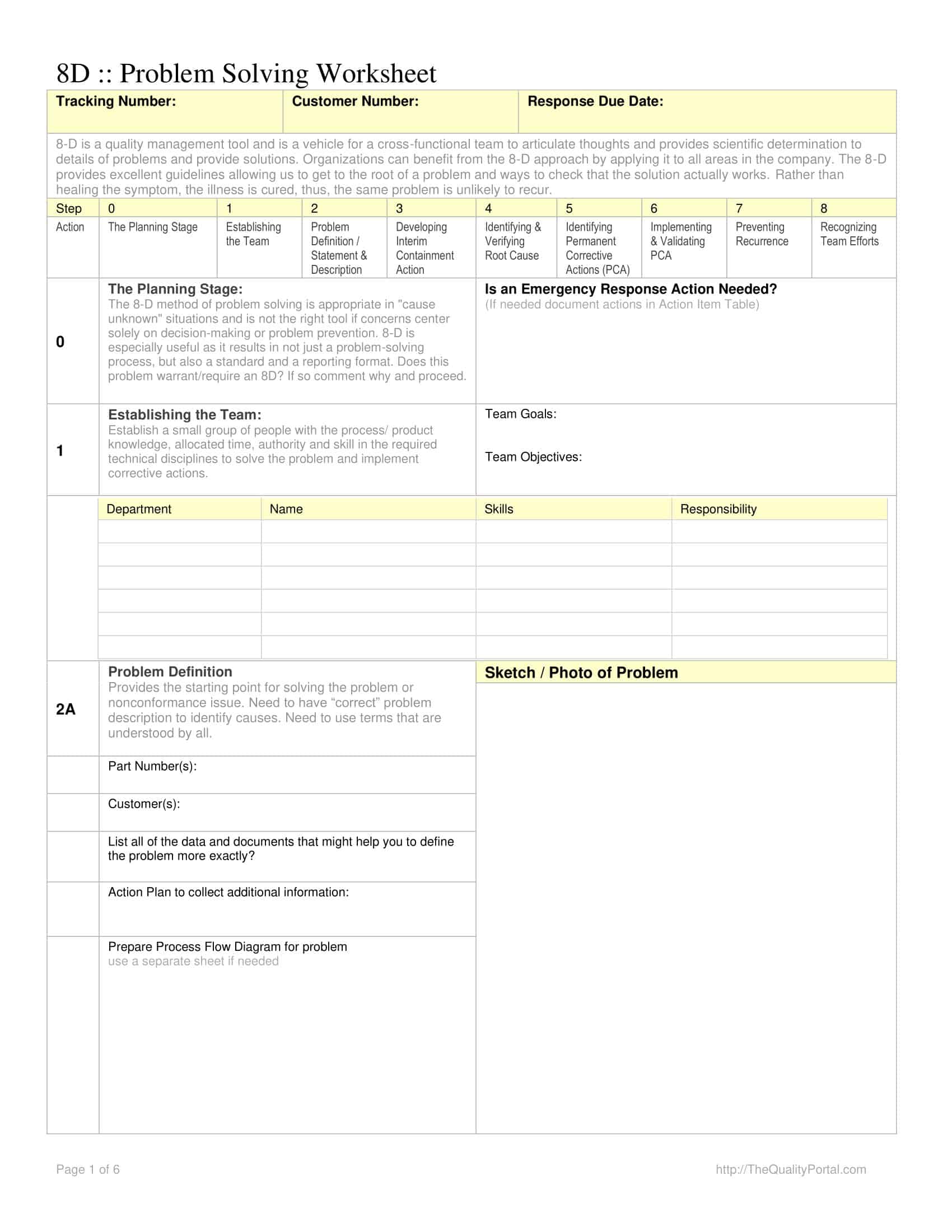
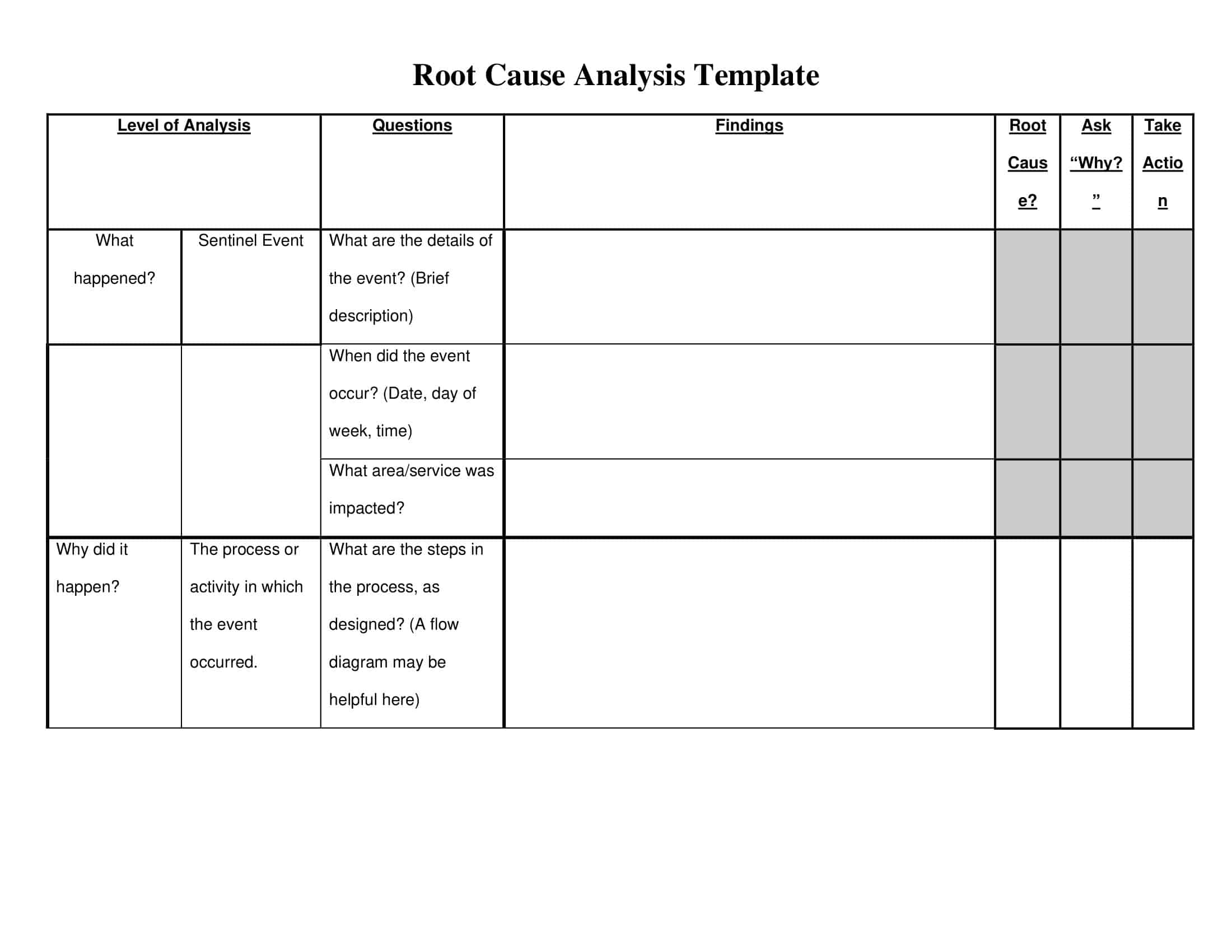
Root Cause Analysis Templates
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Templates are pre-designed formats used to systematically investigate and analyze the underlying causes of problems, incidents, or failures within an organization. These templates provide a structured framework for identifying the root causes of an issue, understanding the contributing factors, and developing effective solutions to prevent similar problems from recurring in the future. Root Cause Analysis Templates ensure consistency, thoroughness, and documentation of the analysis process, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the problem and enabling informed decision-making.
Root Cause Analysis Templates offer a structured and systematic approach to analyzing and addressing organizational problems. By using these templates, organizations can thoroughly investigate problems, identify their underlying causes, and develop targeted solutions to prevent recurrence. These templates facilitate consistency, documentation, and collaboration among team members, leading to more effective problem-solving and decision-making processes.
Root Cause Analysis Templates serve as valuable tools in continuous improvement efforts, enabling organizations to learn from past issues, optimize processes, and enhance overall performance.
What Is Root Cause Analysis Used For?

Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is used for a variety of purposes, including:
Problem Solving: RCA is primarily used to identify the underlying cause of a problem, issue, or malfunction. By addressing the root cause, organizations can effectively solve the problem and prevent it from happening again in the future.
Quality Improvement: RCA helps organizations identify areas of weakness in their processes and improve the quality of their products and services.
Incident Investigation: RCA is often used to investigate incidents, such as accidents, safety incidents, and equipment failures, to determine what went wrong and why.
Compliance: RCA can be used to help organizations comply with regulations and standards, such as ISO 9001 or the FDA.
Risk Management: RCA is a key tool for managing risk in an organization by helping to identify potential hazards and potential causes of problems, and taking steps to mitigate them.
Overall, RCA is an effective method for improving processes, reducing errors, and increasing efficiency in organizations of all types and sizes.
When to Use Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) should be used when an organization needs to identify and address the underlying cause of a problem. Here are some common situations in which RCA is used:
Reoccurring problems: If a problem keeps happening, RCA can help determine why and how to prevent it from happening again.
Significant incidents or failures: RCA can be used to investigate serious incidents or failures, such as accidents, equipment malfunctions, or data breaches.
Quality or performance issues: RCA can be used to identify and address the root cause of quality or performance issues, such as high error rates, long turnaround times, or customer complaints.
Process improvement initiatives: RCA can be used to identify areas of improvement in a process, such as bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas where errors are most likely to occur.
Regulatory compliance: RCA can be used to ensure that an organization is in compliance with relevant regulations and standards, such as ISO 9001 or the FDA.
Overall, RCA should be used whenever an organization needs to understand the root cause of a problem and implement effective solutions to prevent it from happening again.
Root Cause Analysis Methods, Tools & Techniques
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic problem-solving process used to identify and address the underlying cause of an issue or problem. The goal of RCA is to prevent similar issues from happening in the future by addressing the root cause and implementing permanent solutions. The following is a comprehensive guide to RCA methods, tools, and techniques.
Methods:
Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a group problem-solving technique that can be used to generate a large number of ideas about the possible causes of a problem. Participants in a brainstorming session are encouraged to share their thoughts and ideas freely and to build upon each other’s suggestions.
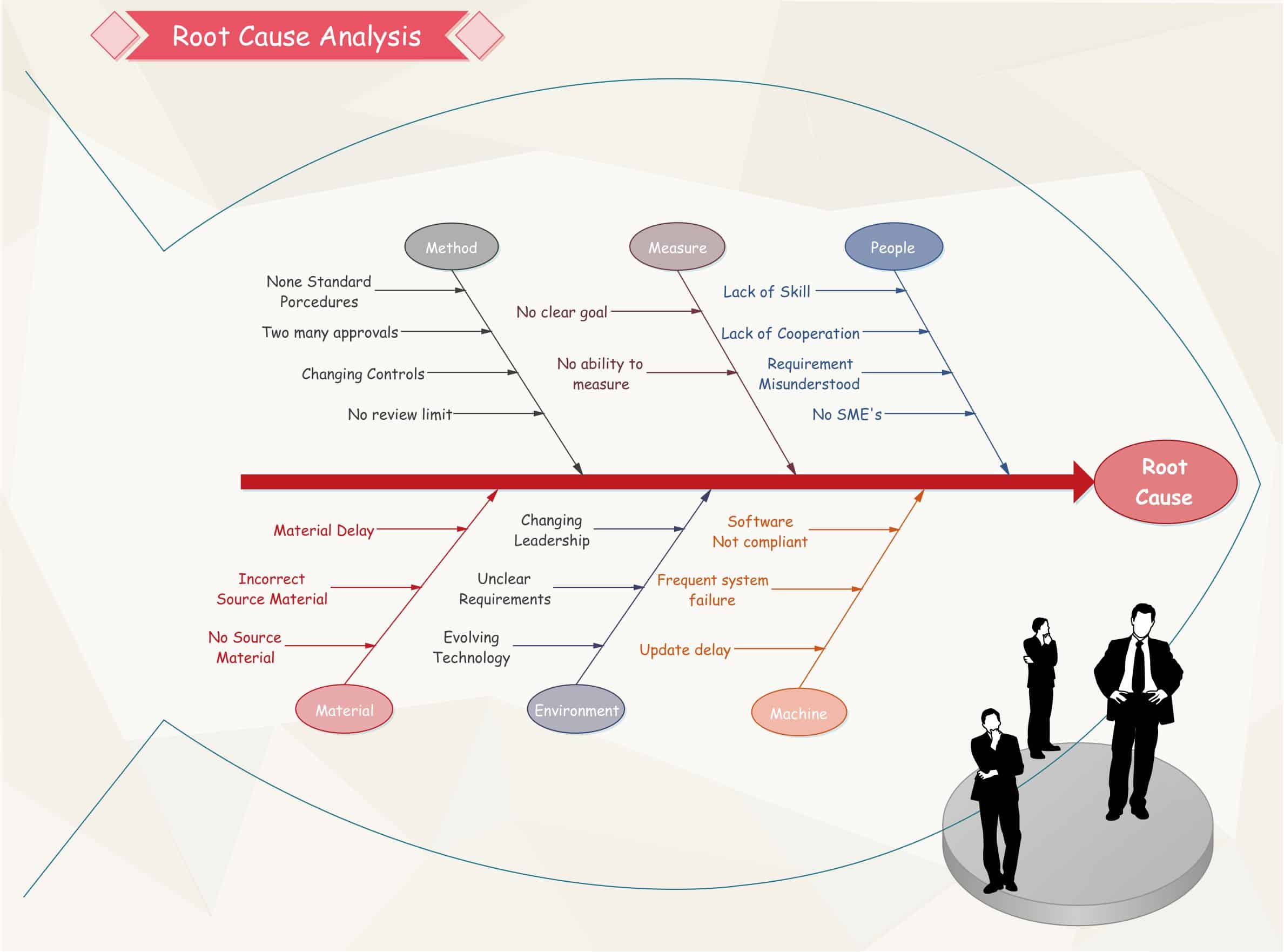
Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram: The Fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa diagram, is a visual tool used to identify the potential causes of a problem. The diagram is organized like the spine of a fish, with the problem at the head and the potential causes branching out from the spine.
Pareto Analysis: Pareto Analysis is a statistical method used to identify the most significant causes of a problem. It is based on the principle that 80% of the effects of a problem are caused by 20% of its causes. Pareto Analysis can help organizations prioritize their efforts and focus on the most important causes of a problem.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): FMEA is a systematic, proactive method used to identify potential failure modes in a process, system, or product and evaluate their impact on the system. FMEA is often used in the design phase of a product or process to identify potential problems before they occur.
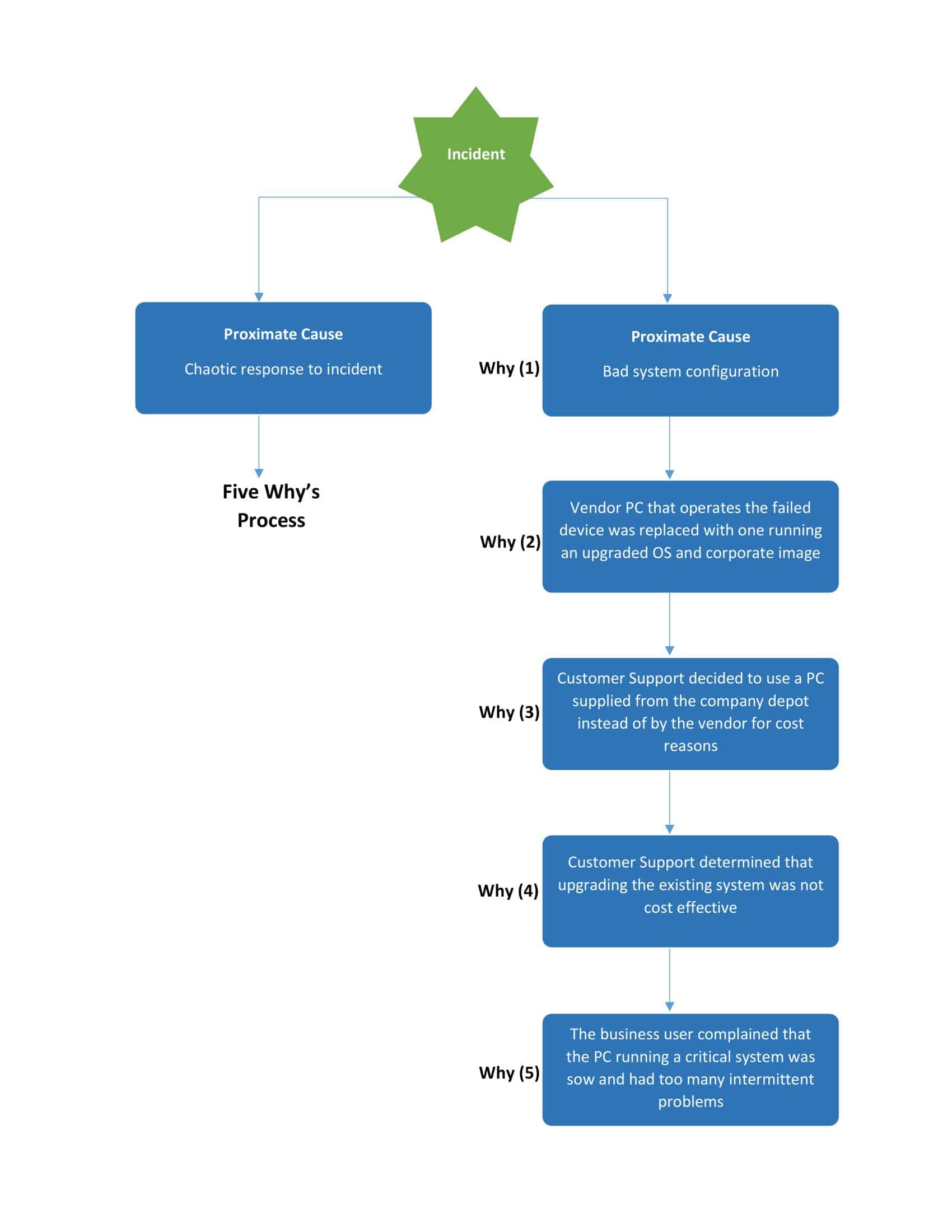
5 Whys: The 5 Whys is a simple but effective problem-solving technique used to get to the root cause of a problem. The process involves asking “why” five times to drill down to the underlying cause of a problem.
Tools:
Flowchart: A flowchart is a visual representation of a process, showing the flow of steps and decision points. Flowcharts can be useful in RCA because they help to identify where a problem occurred in the process and can help to identify potential causes of the problem.
Checklists: Checklists are lists of items or steps that must be completed in order to achieve a specific goal. Checklists can be useful in RCA because they help to ensure that all potential causes of a problem are considered.
Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns and relationships in data that may be related to a problem. This type of analysis can be useful in RCA because it can help to identify the root cause of a problem by looking for correlations and trends in data.
Data Collection and Management Tools: Data collection and management tools, such as spreadsheets, databases, and project management software, can be useful in RCA because they allow organizations to collect, store, and analyze data related to a problem.
Techniques:
Root Cause Tree Analysis: Root Cause Tree Analysis is a visual method used to identify the root cause of a problem by mapping out the relationships between potential causes and effects.
Root Cause Mapping: Root Cause Mapping is a visual method used to identify the root cause of a problem by mapping out the relationships between potential causes and effects.
Root Cause Identification Worksheet: The Root Cause Identification Worksheet is a structured tool used to identify the root cause of a problem by breaking the problem down into smaller components and asking questions to identify the underlying causes.
Root Cause Analysis Matrix: The Root Cause Analysis Matrix is a tool used to identify the root cause of a problem by grouping potential causes into categories and rating the likelihood and impact of each cause. The matrix allows organizations to prioritize their efforts by focusing on the most likely and significant causes of a problem.
Root Cause Interviews: Root Cause Interviews are structured interviews with individuals who are directly involved with the problem or have knowledge about the issue. The goal of these interviews is to gather information and perspectives about the problem, and to identify potential causes.
Root Cause Analysis Workshops: Root Cause Analysis Workshops are structured meetings in which a team of individuals comes together to identify the root cause of a problem. The workshop typically involves a facilitator, a group of experts, and a structured problem-solving process.
Root Cause Simulation: Root Cause Simulation is a technique used to identify the root cause of a problem by simulating the conditions and events leading up to the problem. This technique can be used to test different scenarios and identify the most likely cause of a problem.
It is important to note that RCA is not a one-time event, but rather a continuous process of improvement. Organizations should regularly review their processes and systems, and use RCA when needed to identify and address any issues or problems.
In conclusion, Root Cause Analysis is a powerful tool for organizations looking to improve the quality of their products and services, increase efficiency, and reduce the likelihood of incidents and failures. By using a combination of methods, tools, and techniques, organizations can identify the root cause of a problem, implement effective solutions, and prevent similar issues from happening in the future.
Root Cause Analysis Steps (How to Perform a Root Cause Analysis)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic problem-solving process used to identify and address the underlying cause of an issue or problem. The goal of RCA is to prevent similar issues from happening in the future by addressing the root cause and implementing permanent solutions. The following is a step-by-step guide to conducting a Root Cause Analysis.
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in conducting an RCA is to clearly define the problem that you are trying to solve. This includes identifying the problem, its impact, and its scope. It is important to ensure that everyone involved in the RCA process understands the problem that is being addressed.
Step 2: Gather Information
The next step is to gather information about the problem. This includes data and facts about the problem, as well as the opinions and perspectives of individuals who are directly involved with the issue or have knowledge about it. Data collection tools such as checklists, questionnaires, and interviews can be used to gather this information.
Step 3: Analyze the Data
Once you have gathered all the relevant information, the next step is to analyze the data. This includes reviewing the data, identifying patterns and trends, and looking for relationships between the data and the problem. Data analysis tools such as flow charts, fishbone diagrams, and statistical analysis can be used to help you better understand the data.
Step 4: Identify Possible Causes
Using the information and data gathered in the previous steps, the next step is to identify possible causes of the problem. This can involve brainstorming sessions, Root Cause Identification Worksheets, or Root Cause Analysis Workshops. The goal of this step is to generate a comprehensive list of possible causes of the problem.
Step 5: Evaluate Possible Causes
Once you have identified the possible causes of the problem, the next step is to evaluate each one to determine which is the most likely root cause. This can involve rating each possible cause based on its likelihood and impact, or using tools such as the Root Cause Analysis Matrix to prioritize your efforts.
Step 6: Verify the Root Cause
The next step is to verify the root cause by conducting additional testing and analysis. This may involve simulating the conditions and events leading up to the problem, or conducting Root Cause Interviews with individuals who were directly involved with the issue.
Step 7: Implement a Solution
Once the root cause has been identified and verified, the next step is to implement a solution to address the issue. This may involve making changes to processes, systems, or products, or training employees to prevent similar issues from happening in the future.
Step 8: Monitor and Evaluate
The final step in the RCA process is to monitor and evaluate the solution to ensure that it is effective and to prevent similar issues from happening in the future. This includes regularly reviewing processes, systems, and products, and using RCA when needed to identify and address any issues or problems that may arise.
It is important to note that RCA is not a one-time event, but rather a continuous process of improvement. Organizations should regularly review their processes and systems, and use RCA when needed to identify and address any issues or problems.
In conclusion, Root Cause Analysis is a powerful tool for organizations looking to improve the quality of their products and services, increase efficiency, and reduce the likelihood of incidents and failures. By following the steps outlined in this guide, organizations can conduct a comprehensive Root Cause Analysis and identify the root cause of a problem, implement effective solutions, and prevent similar issues from happening in the future.
FAQs
Why is RCA important?
RCA is important because it helps organizations improve the quality of their products and services, increase efficiency, and reduce the likelihood of incidents and failures. By identifying and addressing the root cause of a problem, organizations can prevent similar issues from happening in the future and improve overall performance.
What is the difference between RCA and problem-solving?
Problem-solving is a broad term that refers to the process of identifying and addressing a problem. RCA is a specific type of problem-solving process that focuses on identifying and addressing the root cause of a problem. The goal of RCA is to prevent similar issues from happening in the future by addressing the root cause, whereas problem-solving may focus on finding a quick fix for the immediate issue.
How does RCA differ from cause-and-effect analysis?
Cause-and-effect analysis is a tool used in RCA to identify the relationship between an event (the effect) and its potential causes. RCA is a comprehensive problem-solving process that includes cause-and-effect analysis, but also includes other steps such as data collection, data analysis, and solution implementation.
How can RCA be used in a continuous improvement program?
RCA can be used in a continuous improvement program by regularly reviewing processes and systems, and using RCA when needed to identify and address any issues or problems. By continuously improving processes and systems, organizations can reduce the likelihood of incidents and failures and improve overall performance.
Who should be involved in the RCA process?
Individuals who should be involved in the RCA process include those who are directly involved with the problem, those who have knowledge about the issue, and experts in the relevant fields. The RCA team should also include a facilitator to guide the process.
How long does the RCA process take?
The time required for the RCA process can vary depending on the complexity of the problem, the amount of data that needs to be collected and analyzed, and the number of individuals involved in the process. In general, the RCA process can take several days to several weeks to complete.













































![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)
