A logic model is a visual representation of a program or project that outlines its goals, activities, outputs, and outcomes. It provides a roadmap for the program, detailing how resources will be used to achieve desired results and impact.
The logic model is an effective tool for communication and planning, as it clearly outlines the relationship between program activities, outputs, and outcomes, making it easy for stakeholders to understand and follow. Whether for a non-profit organization, government agency, or for-profit business, a well-constructed logic model can serve as a valuable tool in measuring progress and ensuring program success.
Table of Contents
Logic Model Templates
A Logic Model Template is a visual representation or framework that outlines the key components and logical connections of a program, project, or intervention. It provides a structured and systematic approach to planning, implementing, and evaluating initiatives by clearly illustrating the inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impacts of the program. Logic Model Templates help individuals and organizations clarify their goals, strategies, and expected results, and enable effective communication and coordination among stakeholders.
Logic Model Templates are flexible tools that can be adapted to various program types and sectors, including education, healthcare, nonprofit organizations, government initiatives, and community development projects. By using these templates, individuals and organizations can enhance their program planning, implementation, and evaluation processes. Logic Model Templates promote clarity, alignment, and shared understanding among stakeholders, helping to ensure that program goals, activities, and outcomes are effectively communicated and achieved. They are valuable tools for program managers, evaluators, funders, and other stakeholders seeking a comprehensive and structured approach to program design and evaluation.
Benefits of Using Logic Models

Using a logic model has numerous benefits that can improve the effectiveness and efficiency of a program or project. Some of the key benefits include:
Clarity and Understanding: A logic model provides a clear and concise visual representation of the program’s goals, activities, outputs, and outcomes, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and follow.
Improved Planning and Implementation: The logic model provides a roadmap for the program, allowing for more effective planning and implementation of activities. It helps to ensure that resources are being used in the most efficient and effective way possible.
Better Evaluation and Assessment: A logic model helps to establish a clear connection between program activities, outputs, and outcomes, making it easier to evaluate and assess the program’s success. This information can then be used to improve future program design and implementation.
Improved Communication: The logic model is a valuable tool for communicating the program’s goals, activities, and expected outcomes to stakeholders. It helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
Increased Funding Opportunities: A well-constructed logic model can help to demonstrate the value and impact of the program to potential funders, making it more likely to secure additional funding.
Evidence-Based Decision Making: A logic model helps to ensure that program decisions are based on evidence and data, rather than assumptions or gut instincts. This can lead to more effective and efficient program implementation, and a better understanding of what works and what doesn’t.
Increased Transparency: The logic model provides a clear and concise representation of the program’s goals, activities, outputs, and outcomes, making it easier to understand and communicate program activities to stakeholders. This increased transparency can help to build trust with stakeholders, and improve support for the program.
Improved Sustainability: A well-constructed logic model can help to ensure that a program is sustainable, by identifying potential challenges and limitations, and developing strategies to overcome them. This can help to ensure that the program continues to have a positive impact over the long term.
Better Resource Allocation: The logic model provides a clear understanding of the resources needed to achieve desired outcomes, allowing for more effective resource allocation and management.
Improved Collaboration: The logic model can help to foster collaboration and coordination among program stakeholders, by ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals, and using resources in the most efficient and effective way possible.
The Uses of Logic Models
Logic models are widely used in various fields to help organizations and individuals clarify their goals, objectives, and strategies. Here are some of the most common uses of logic models:
Program Planning and Evaluation: Logic models help organizations plan and evaluate their programs by providing a clear visual representation of their goals, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact.
Grant Writing: Logic models can be used to develop grant proposals by highlighting the expected outcomes of a program and demonstrating how the proposed activities will lead to these outcomes.
Communication: Logic models can be used as a communication tool to help stakeholders understand the purpose and objectives of a program.
Strategic Planning: Logic models can be used in strategic planning to help organizations align their resources and activities with their mission and goals.
Decision Making: Logic models can be used to inform decision making by providing a comprehensive overview of a program and its potential impact.
Performance Management: Logic models can be used to monitor and assess the performance of a program and make adjustments as needed to improve outcomes.
Collaboration: Logic models can be used to promote collaboration and coordination between different organizations and stakeholders by establishing a shared understanding of goals and objectives.
Overall, the use of logic models can help organizations and individuals clarify their thoughts, communicate effectively, and achieve their goals in a more efficient and effective manner.
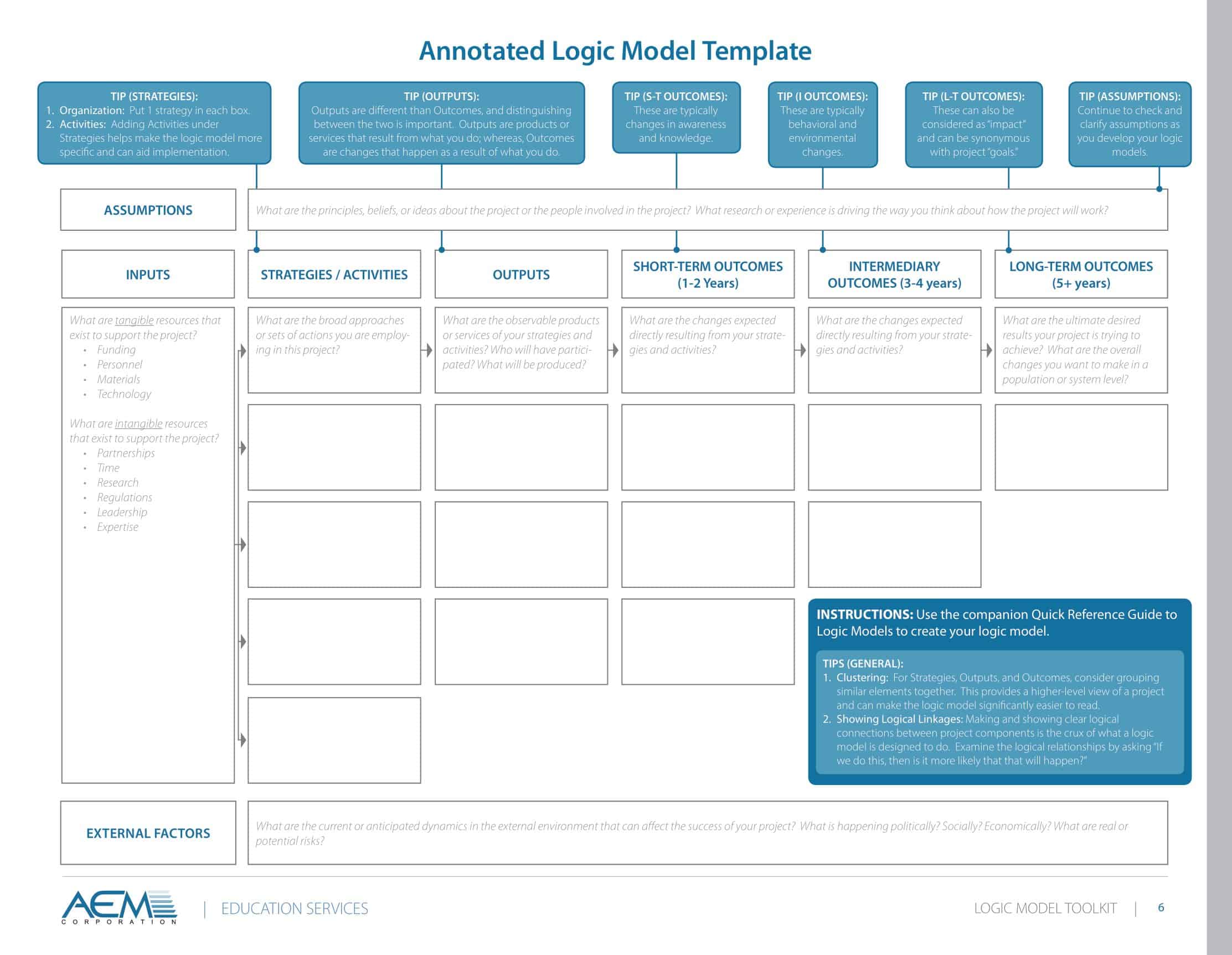
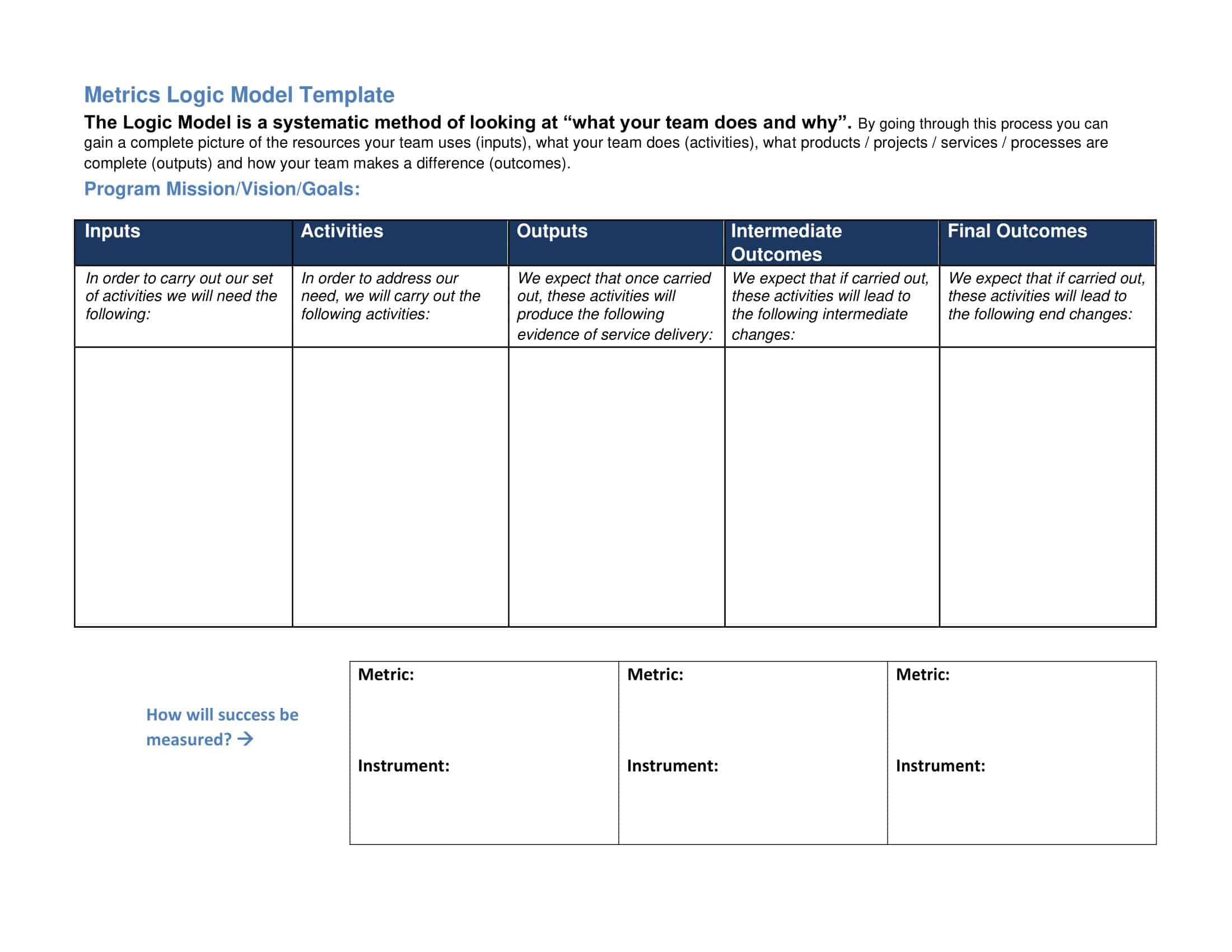
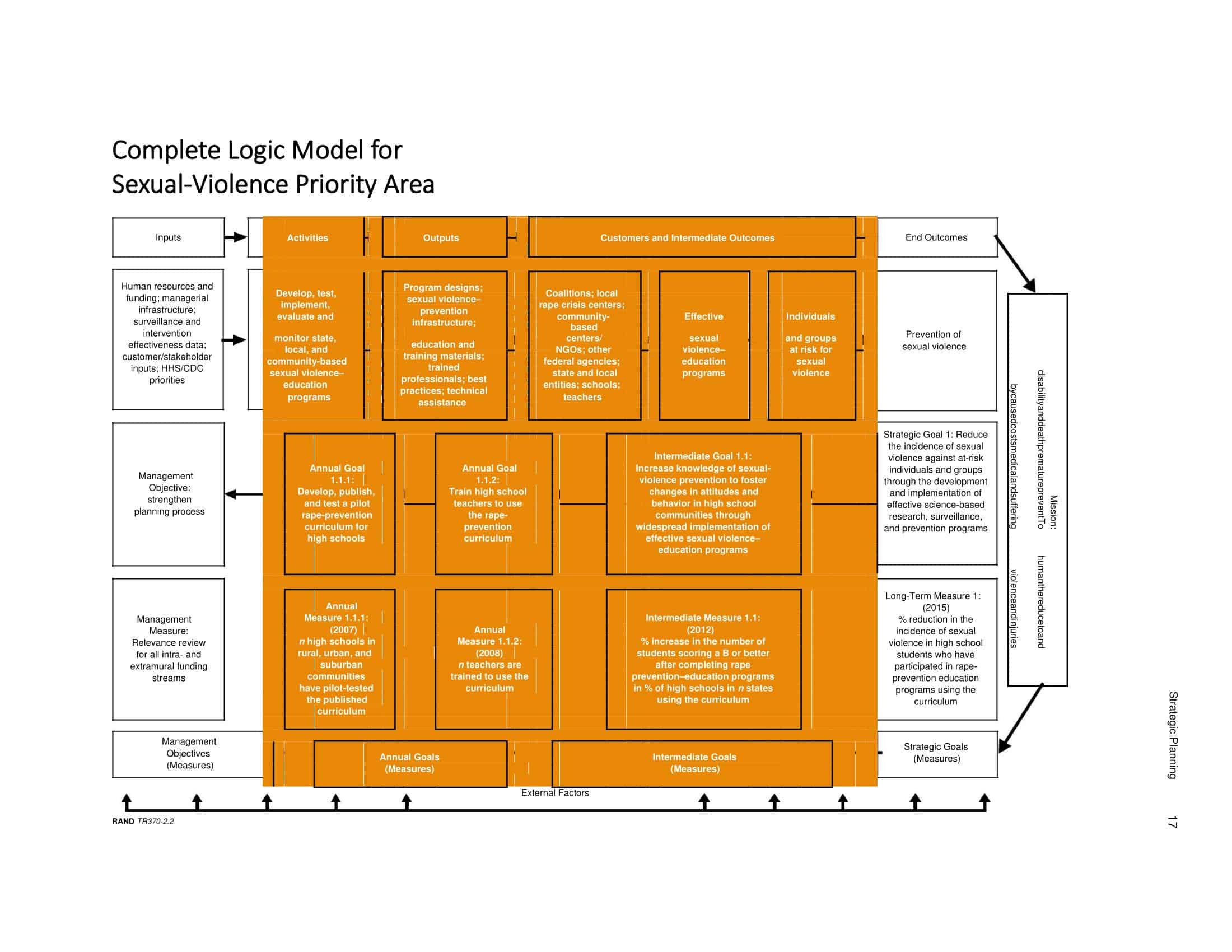
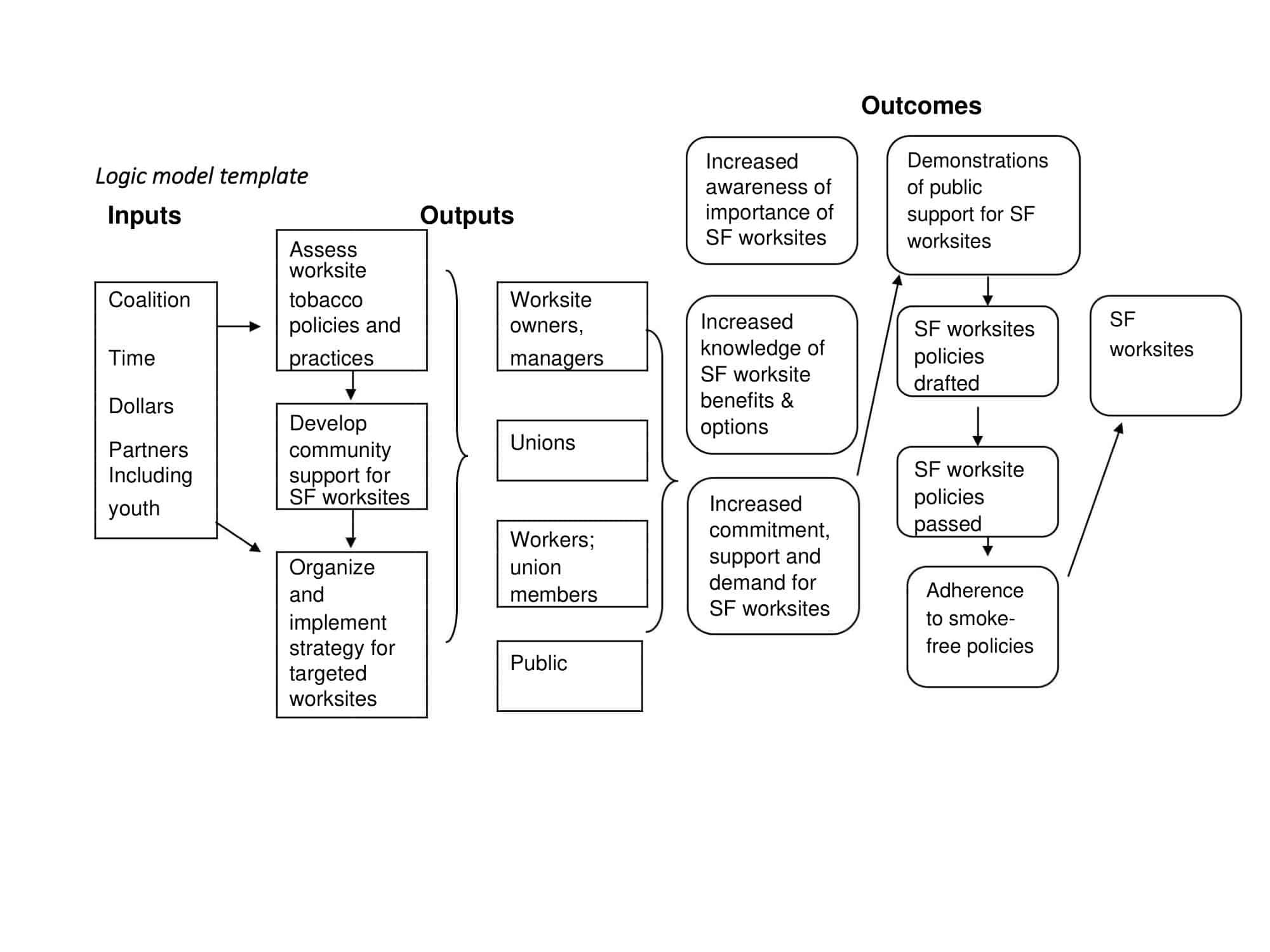
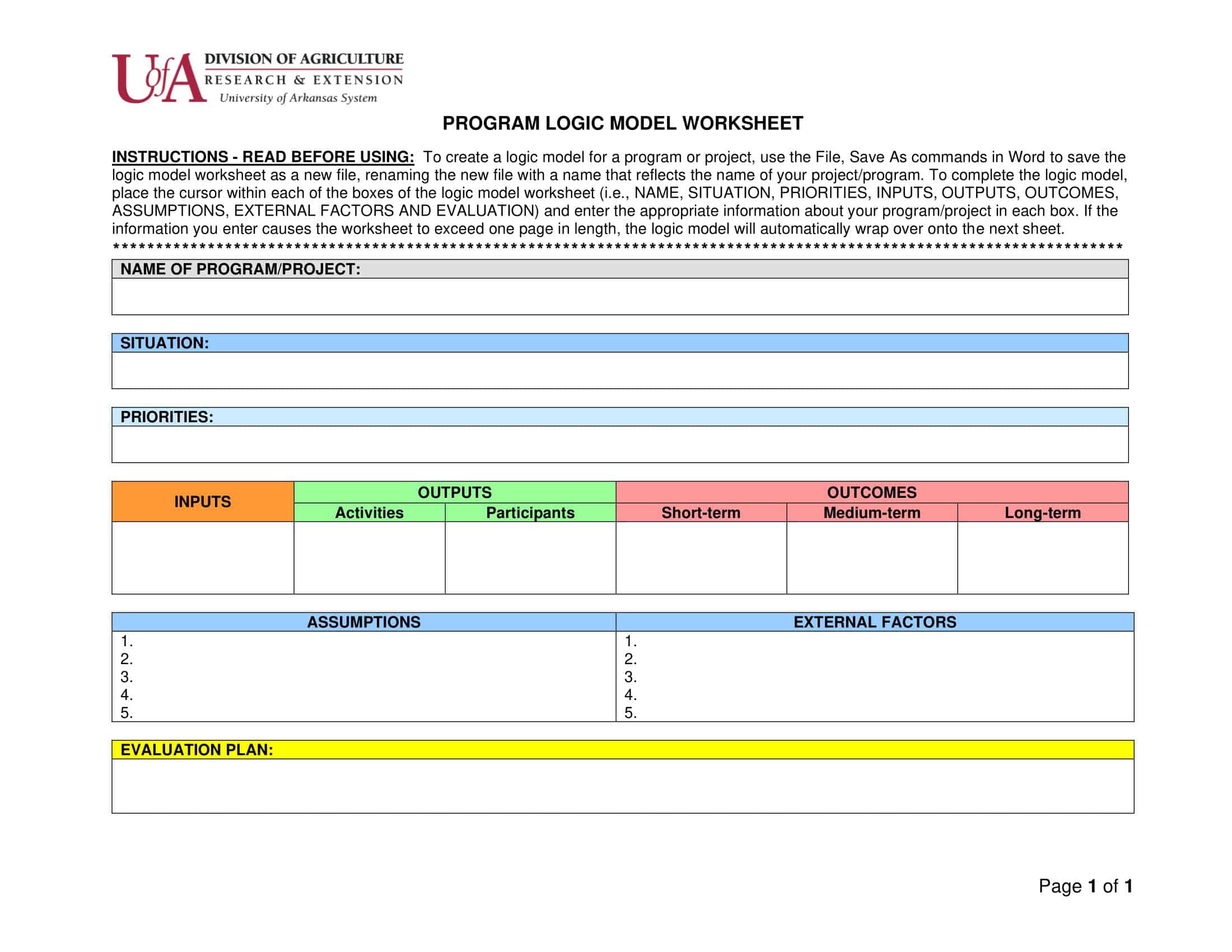
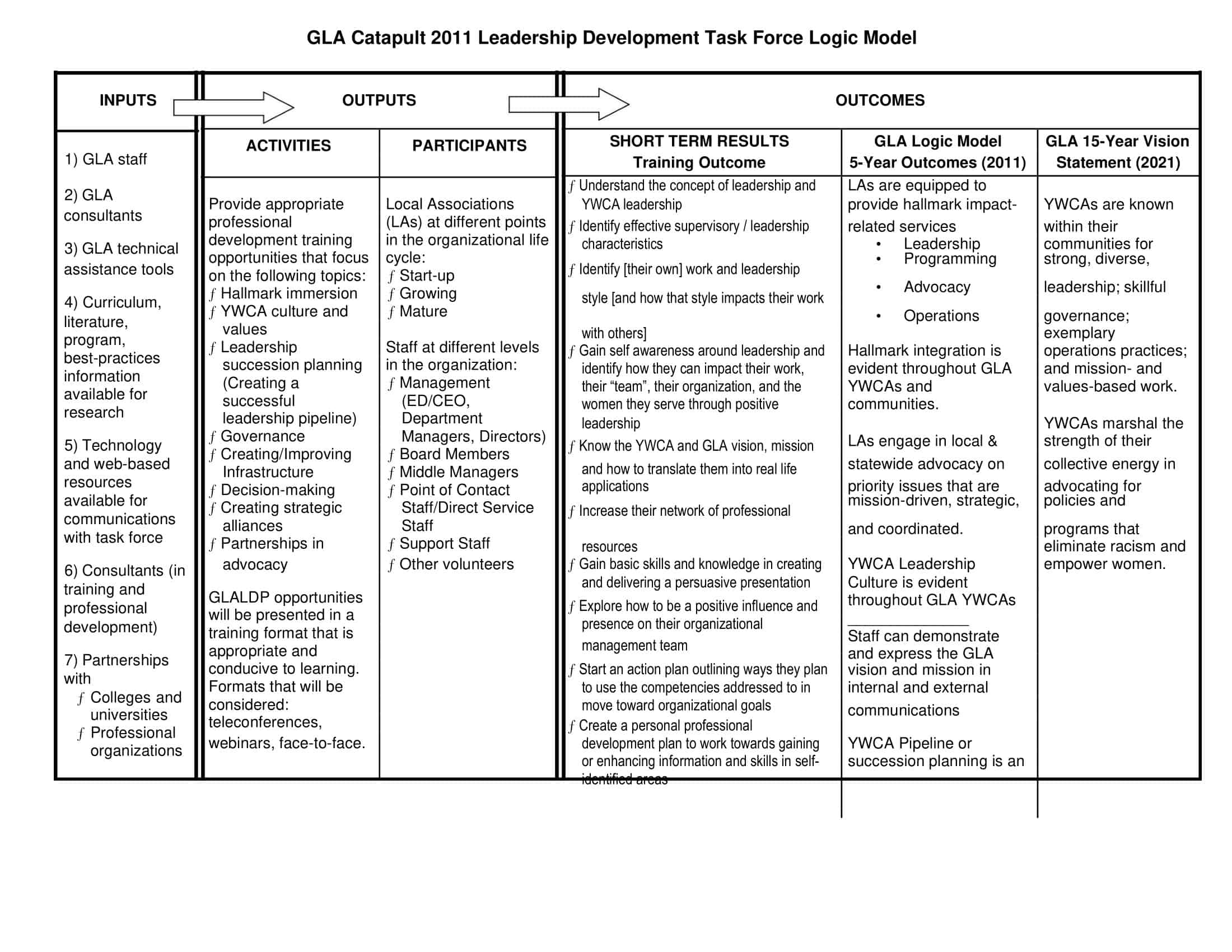
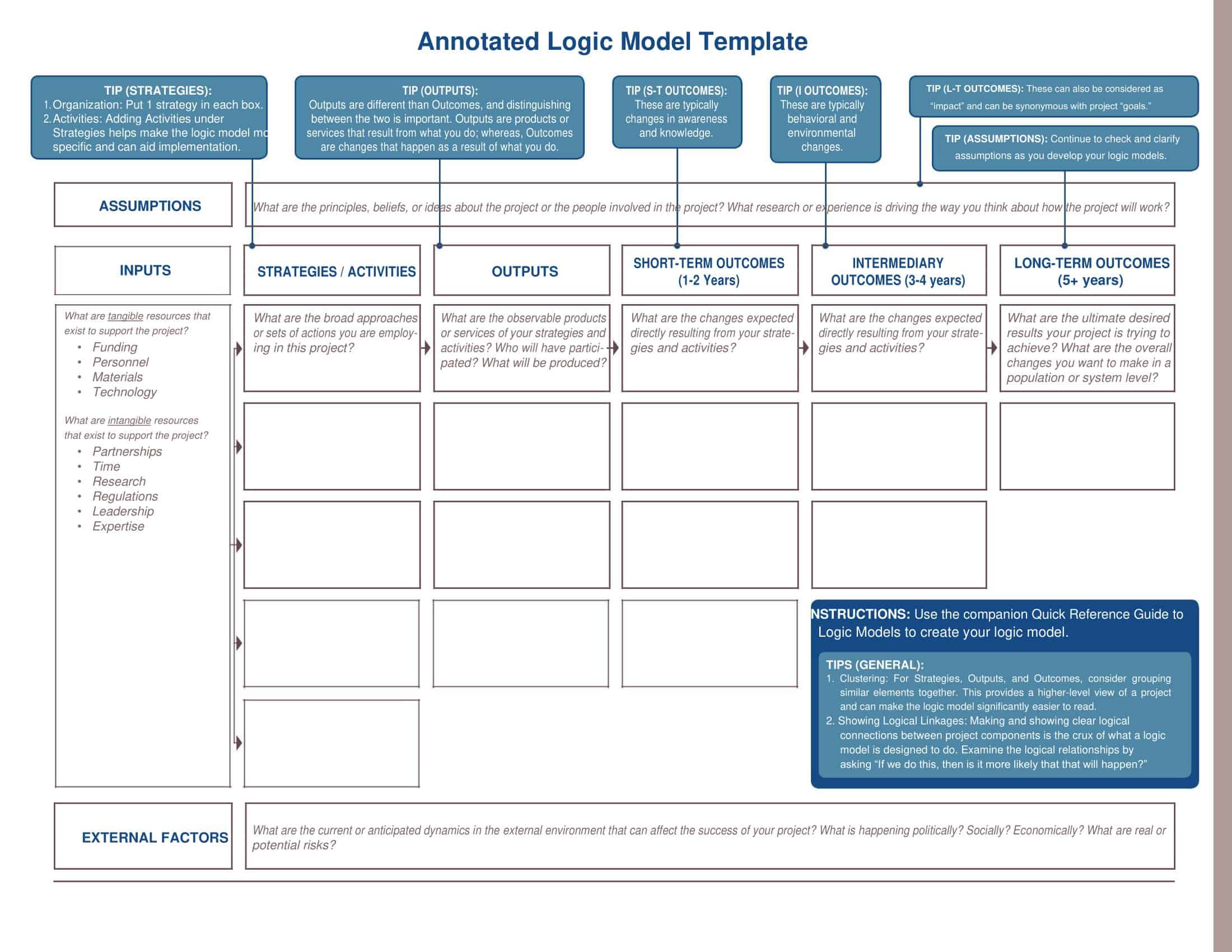
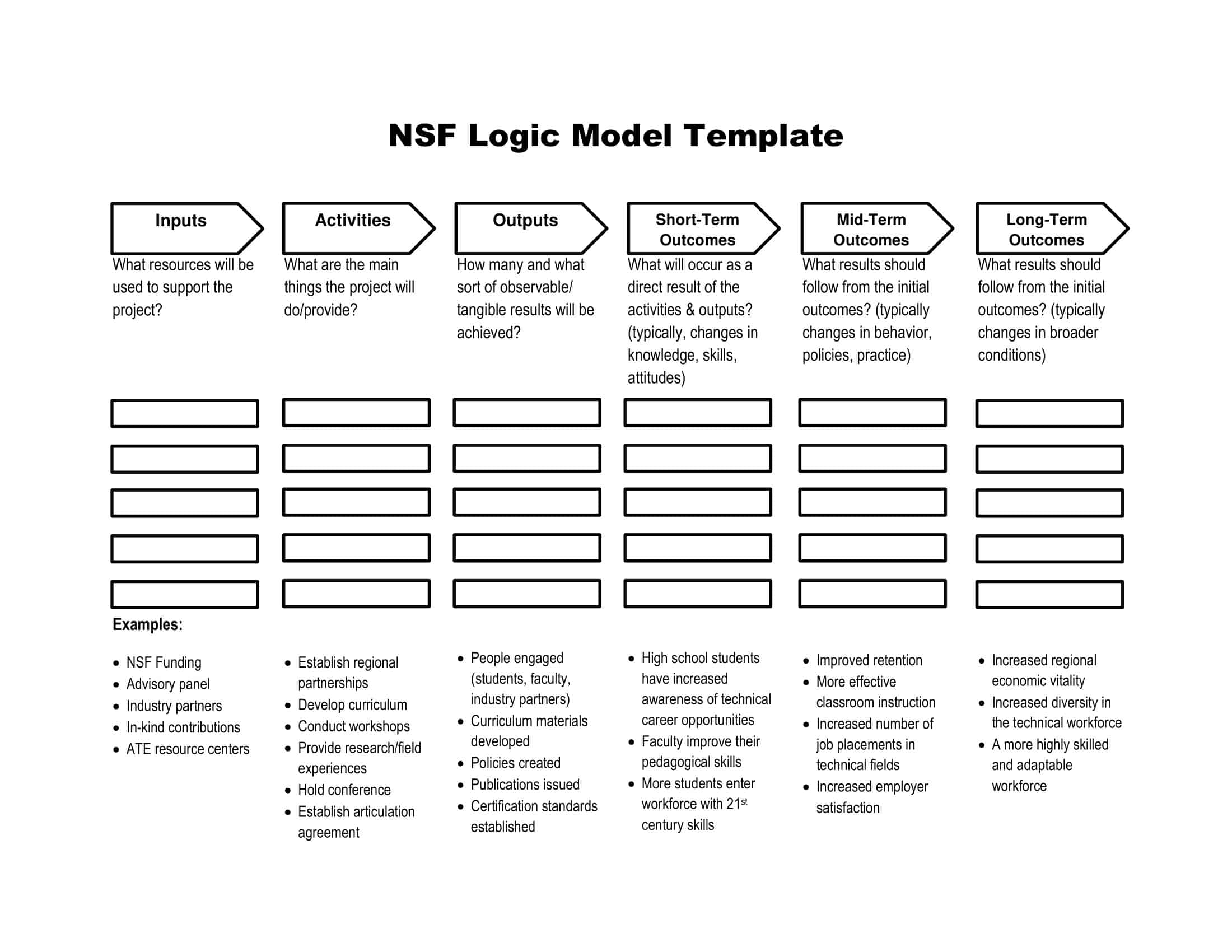
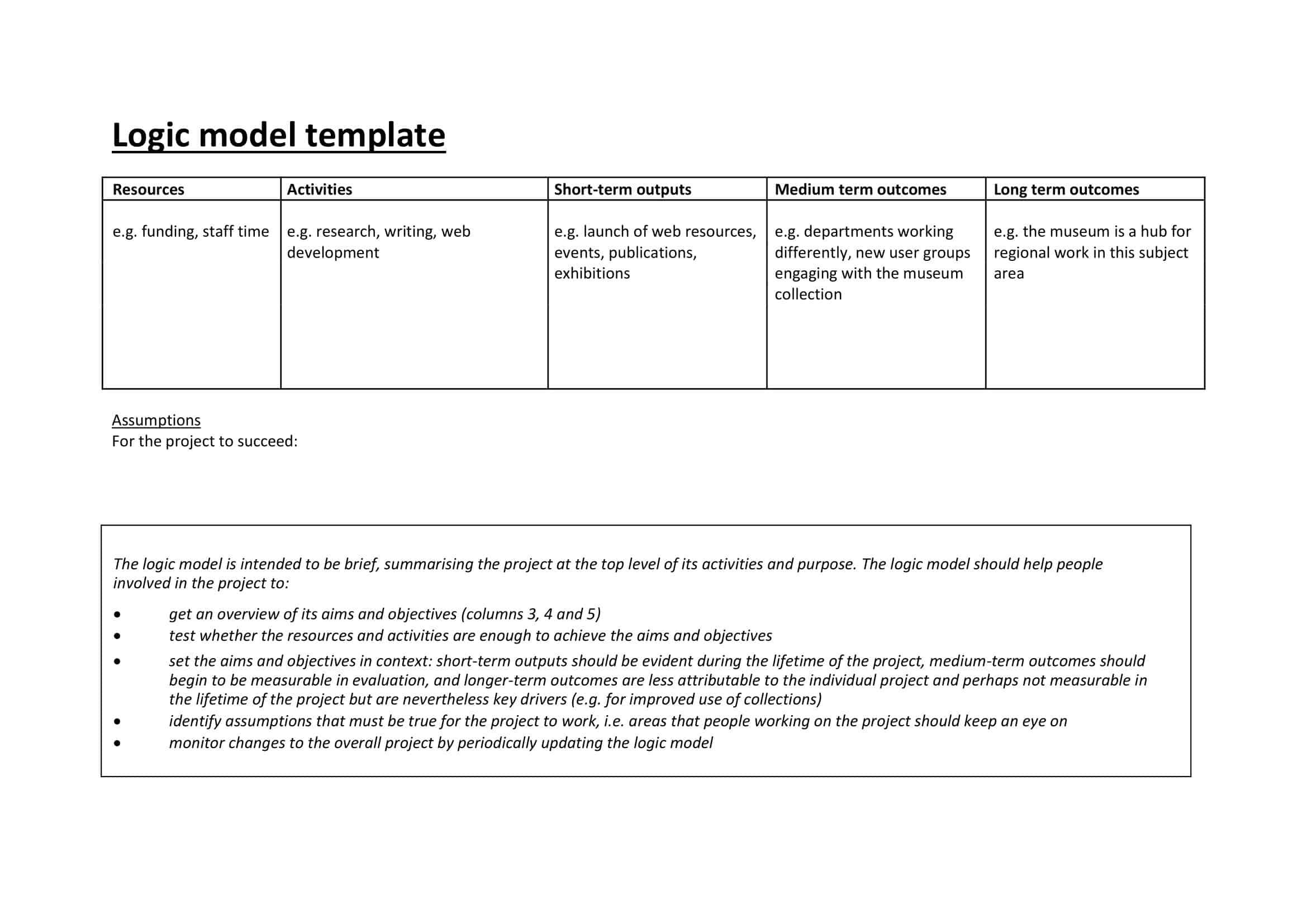
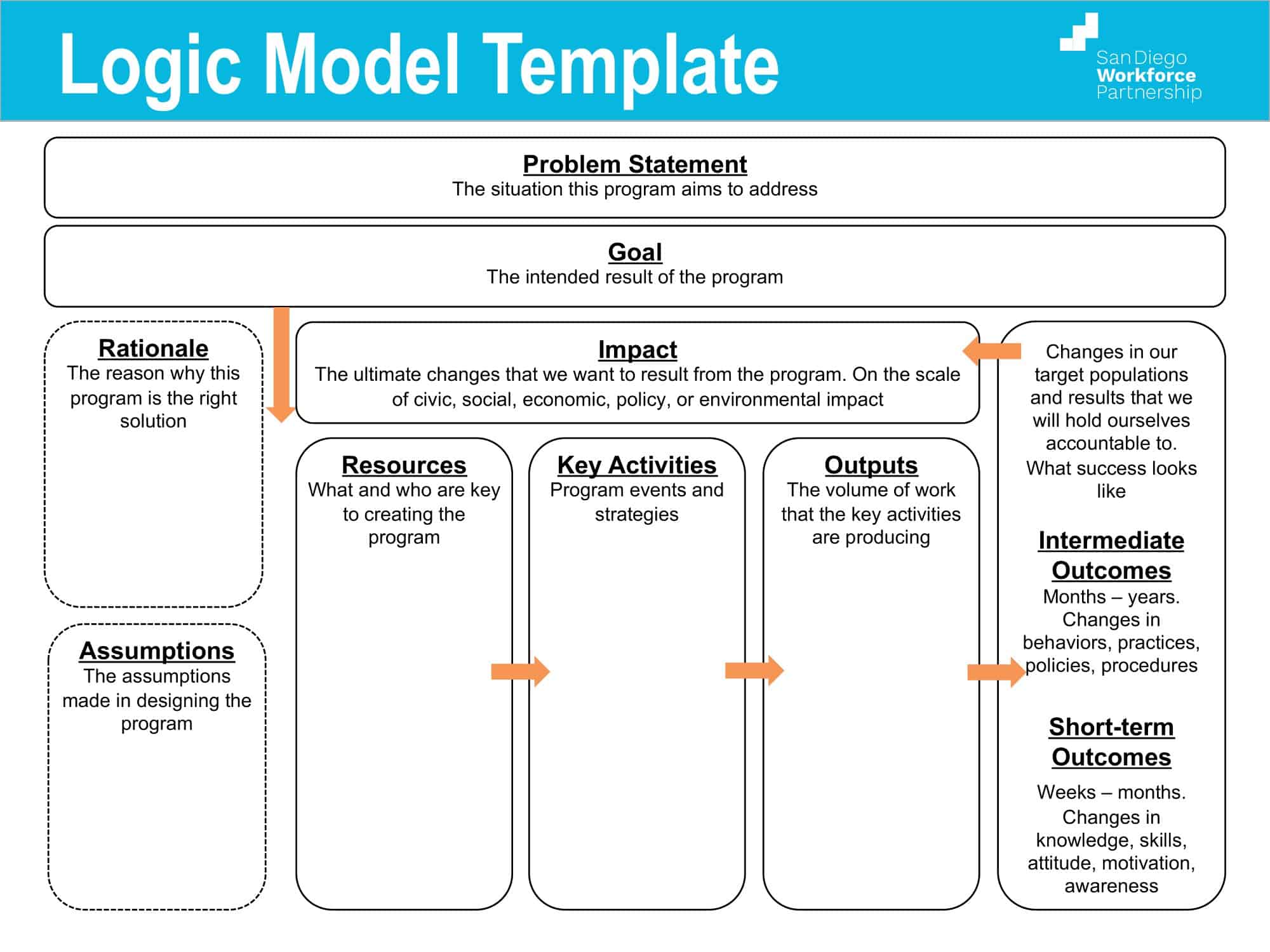
Elements of Logic Models
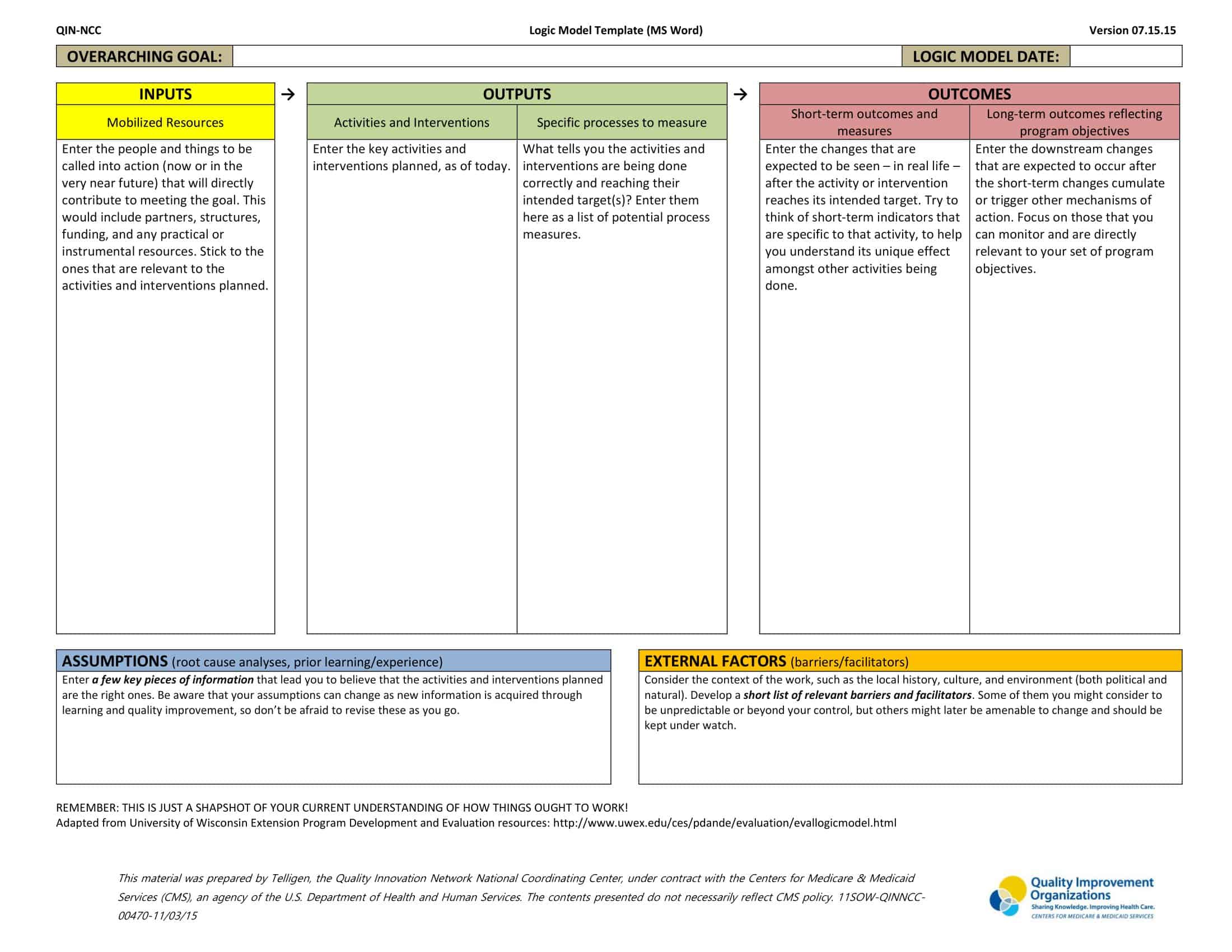
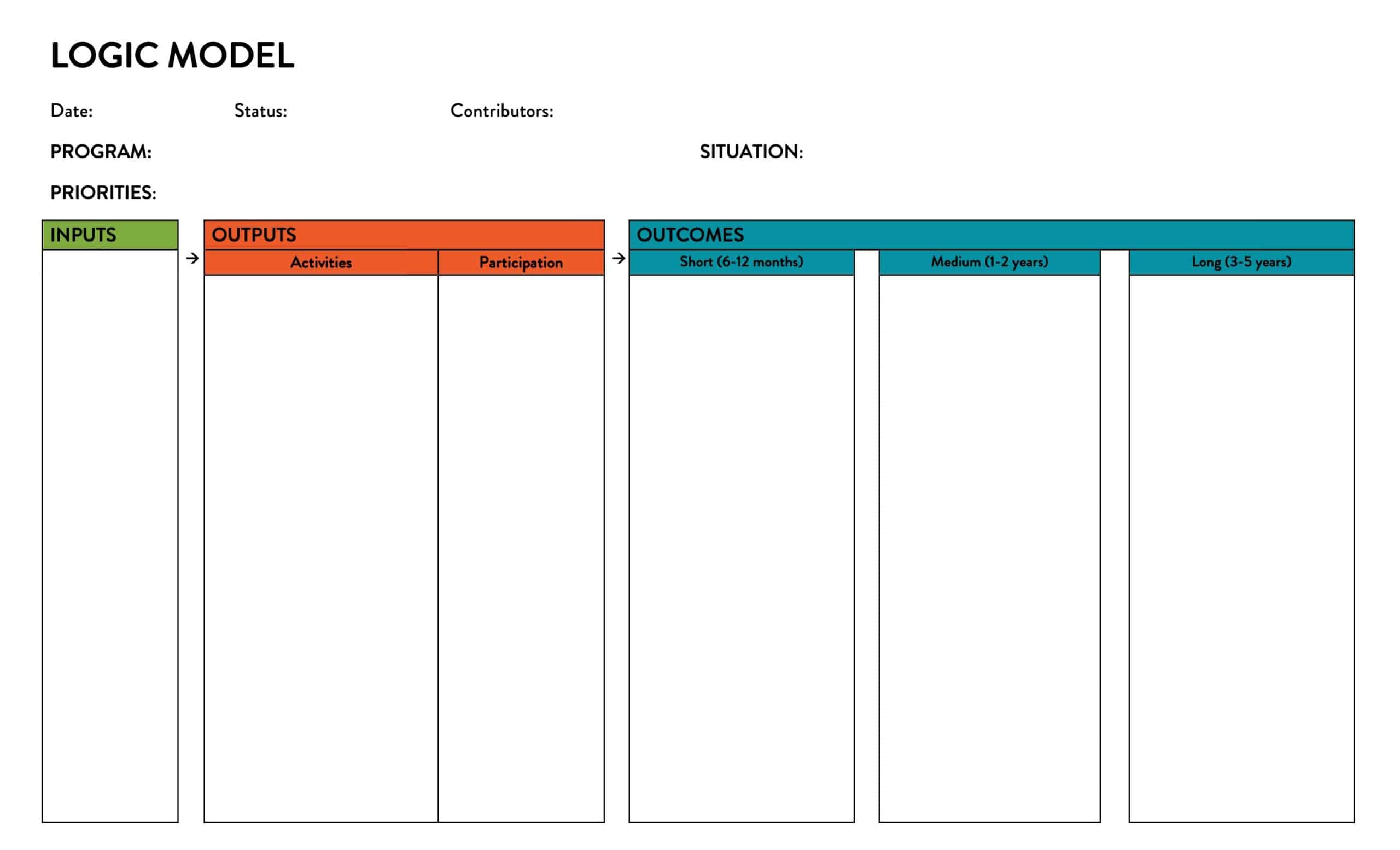
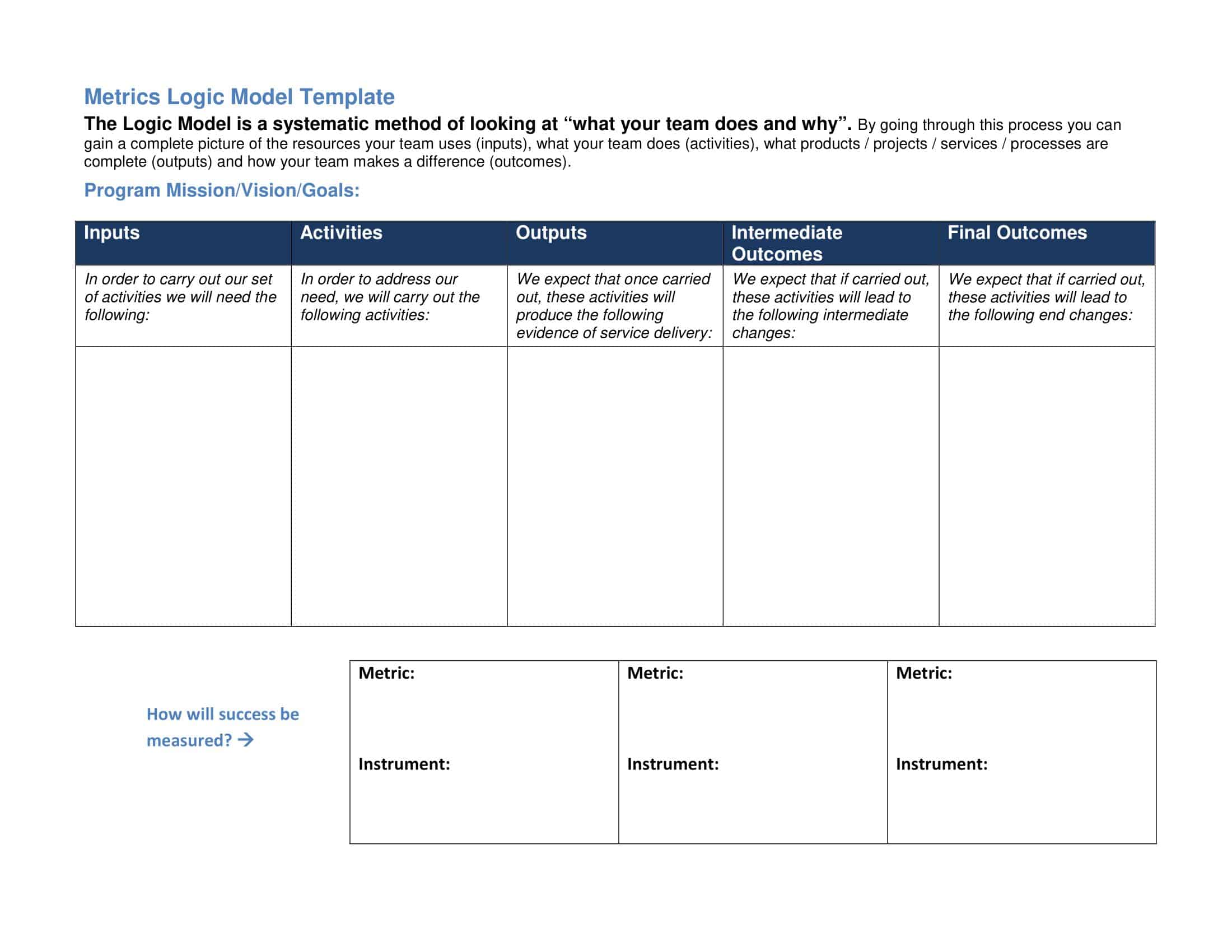
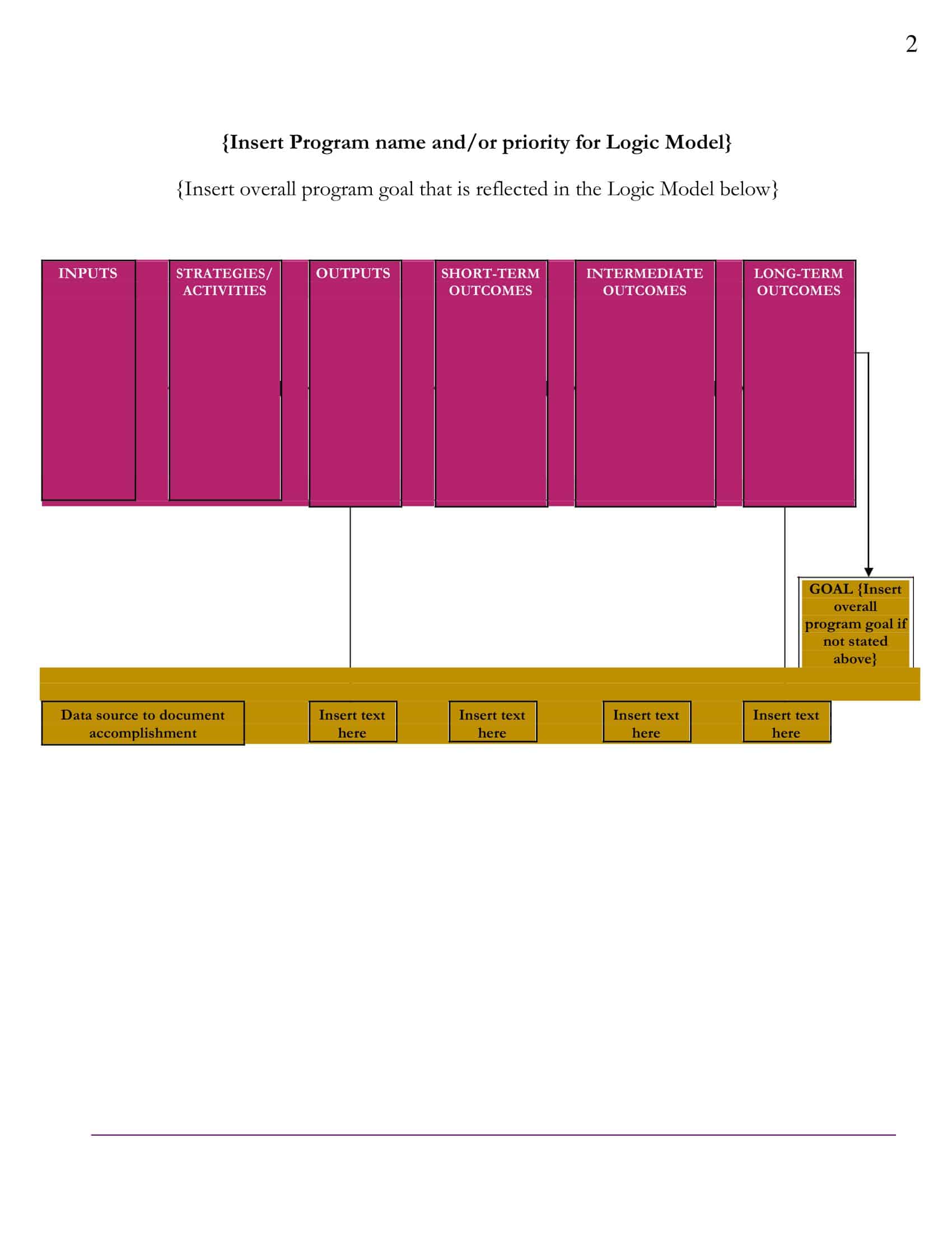
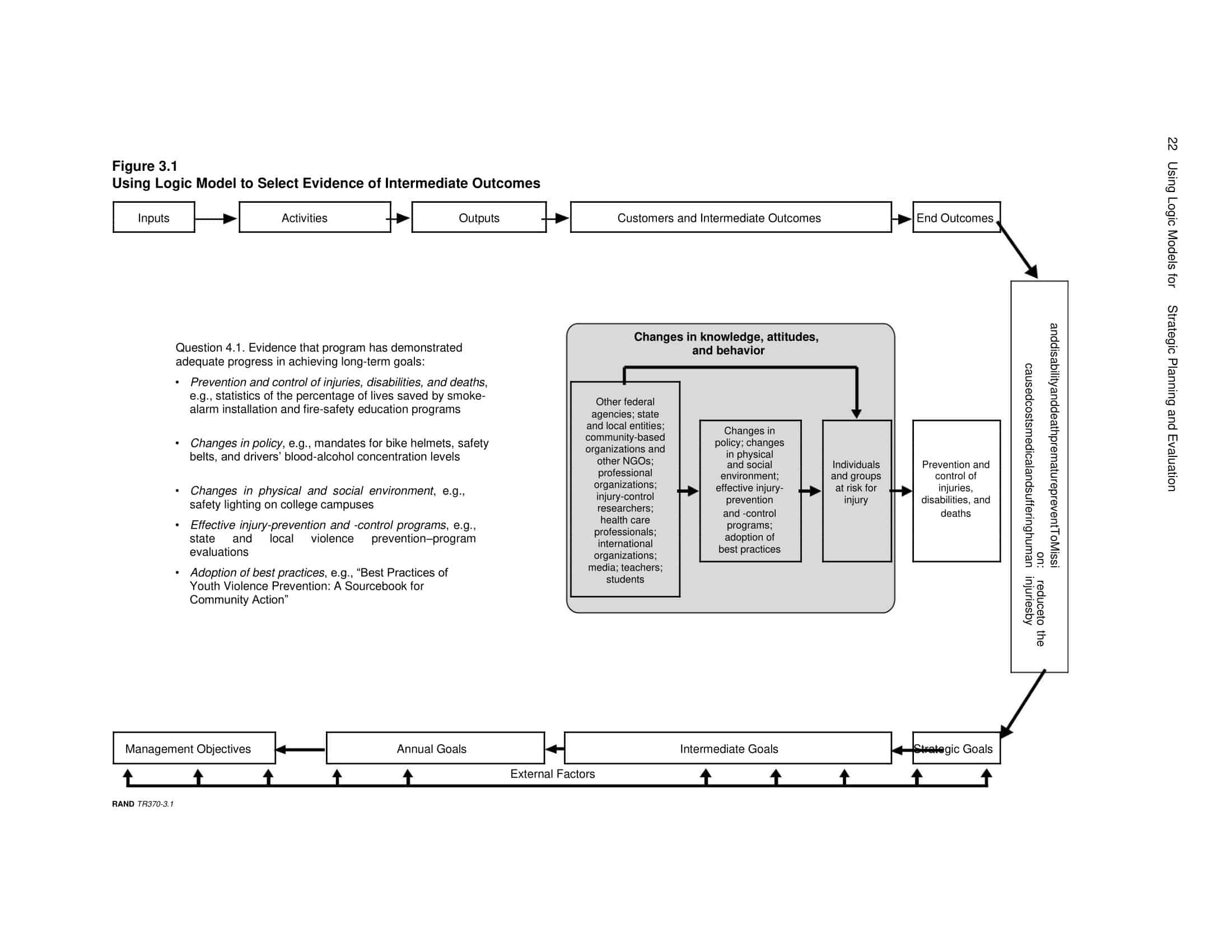
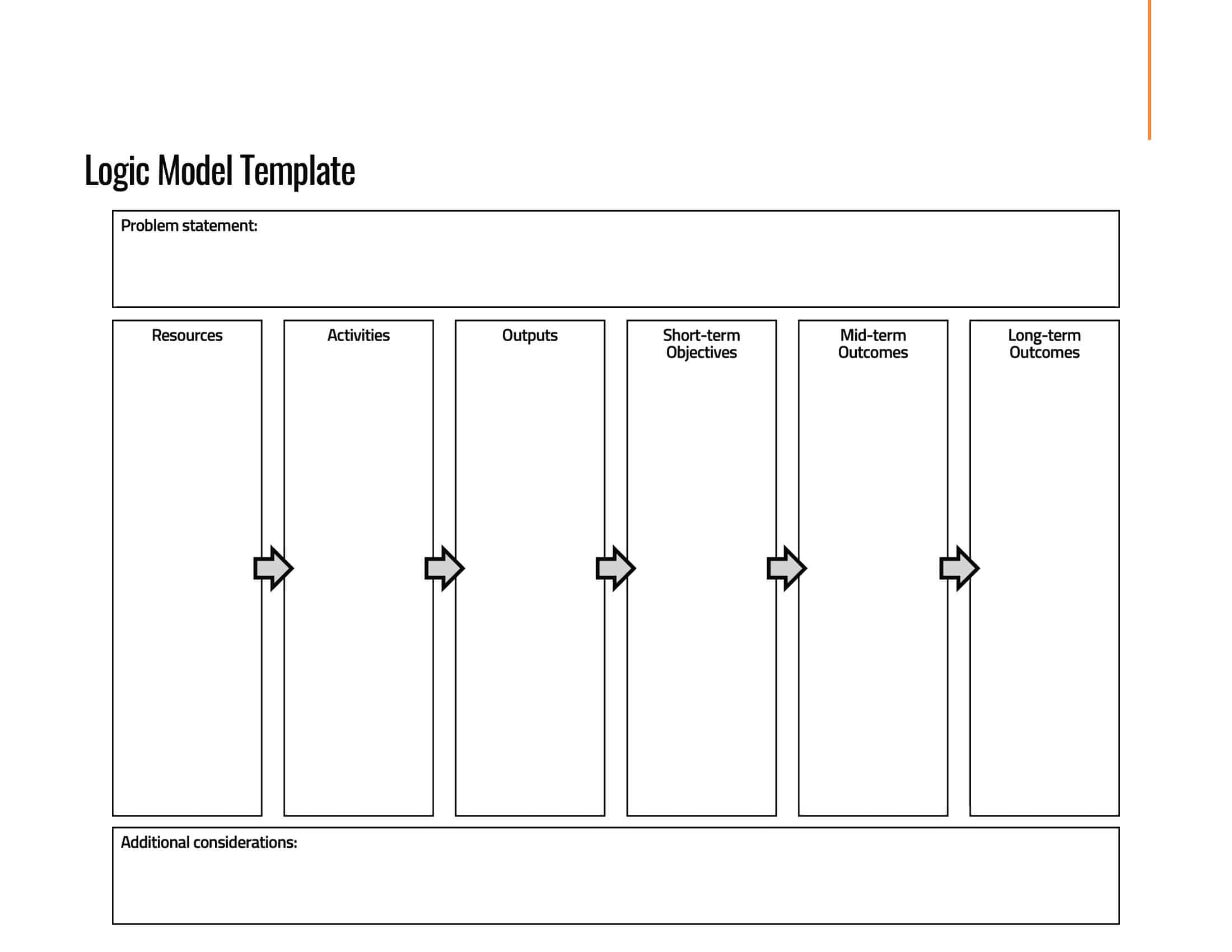
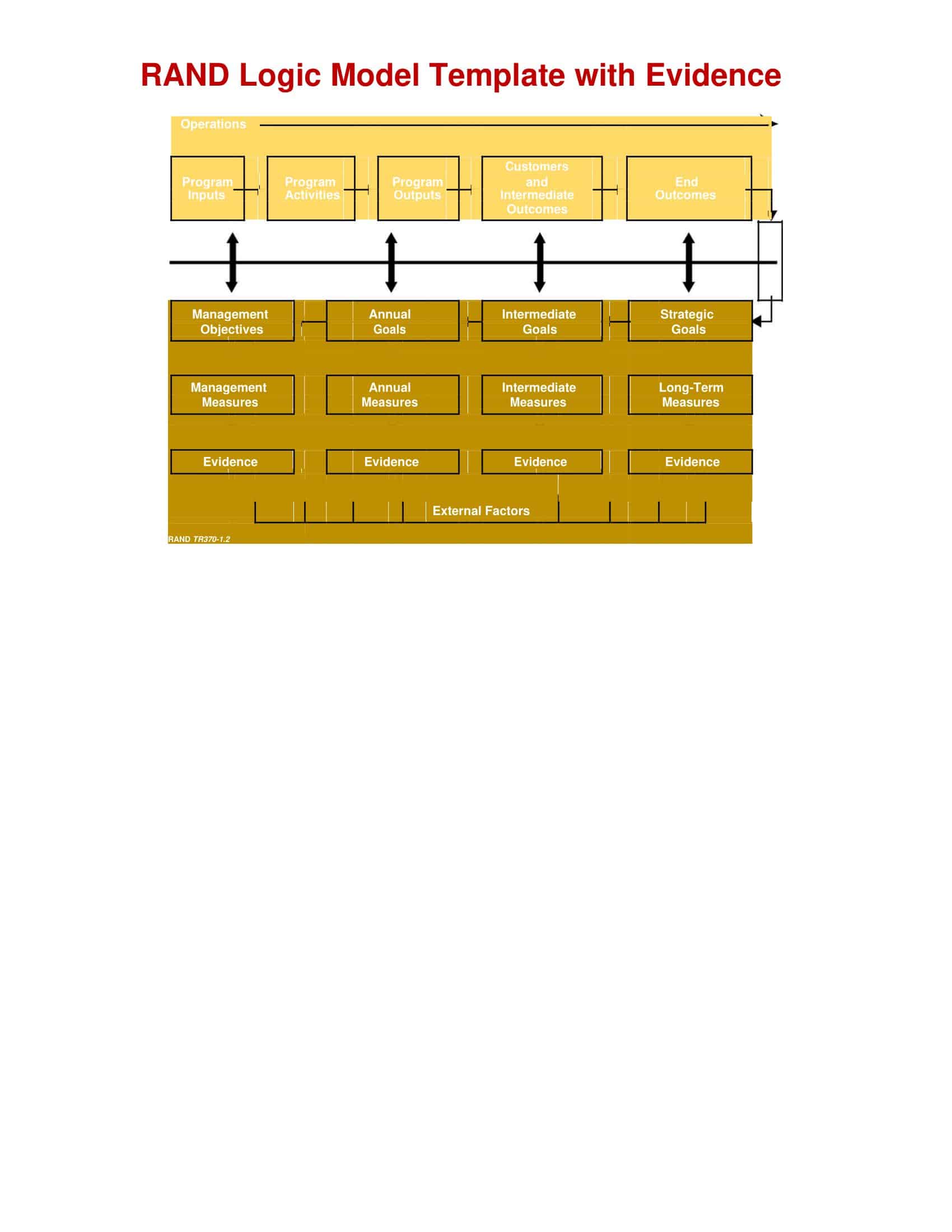
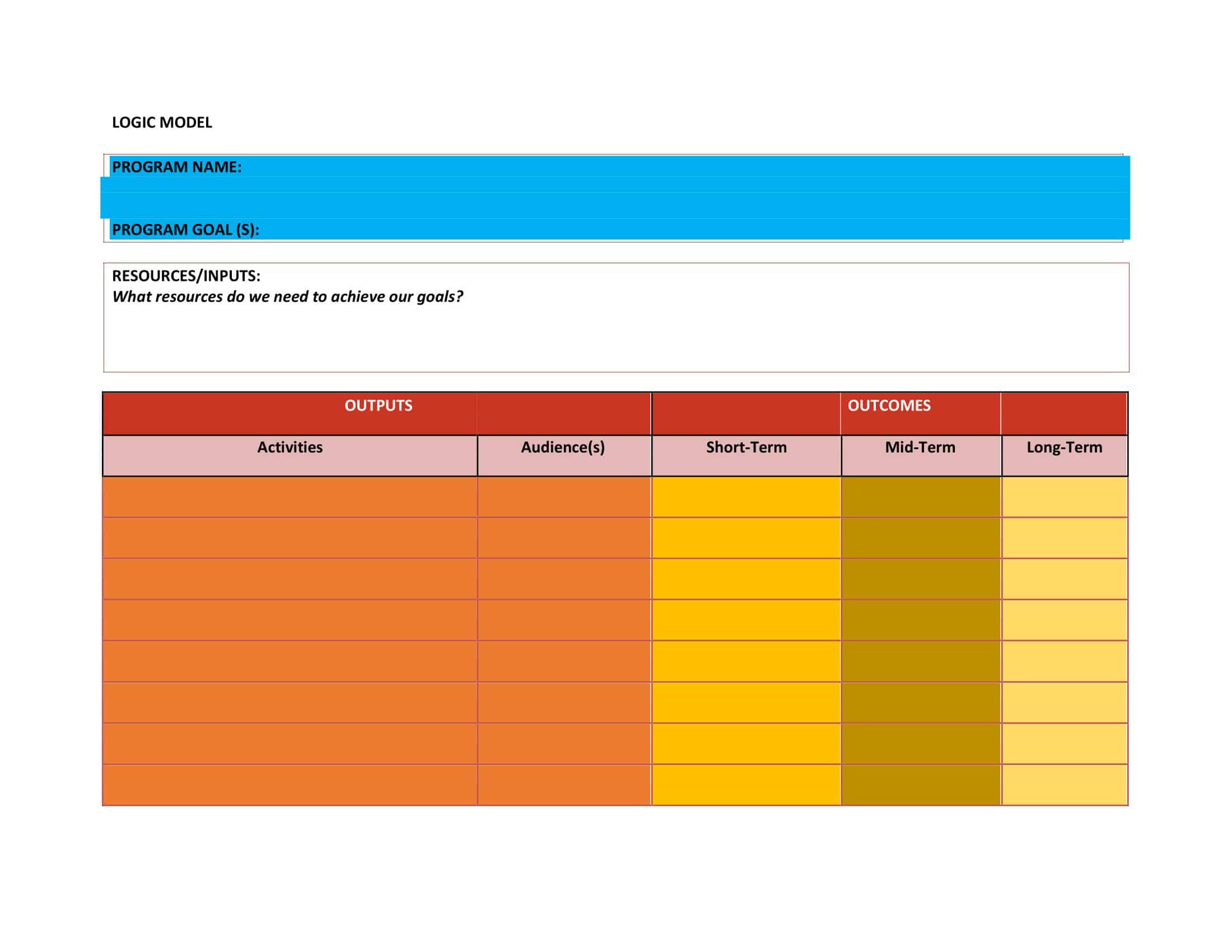
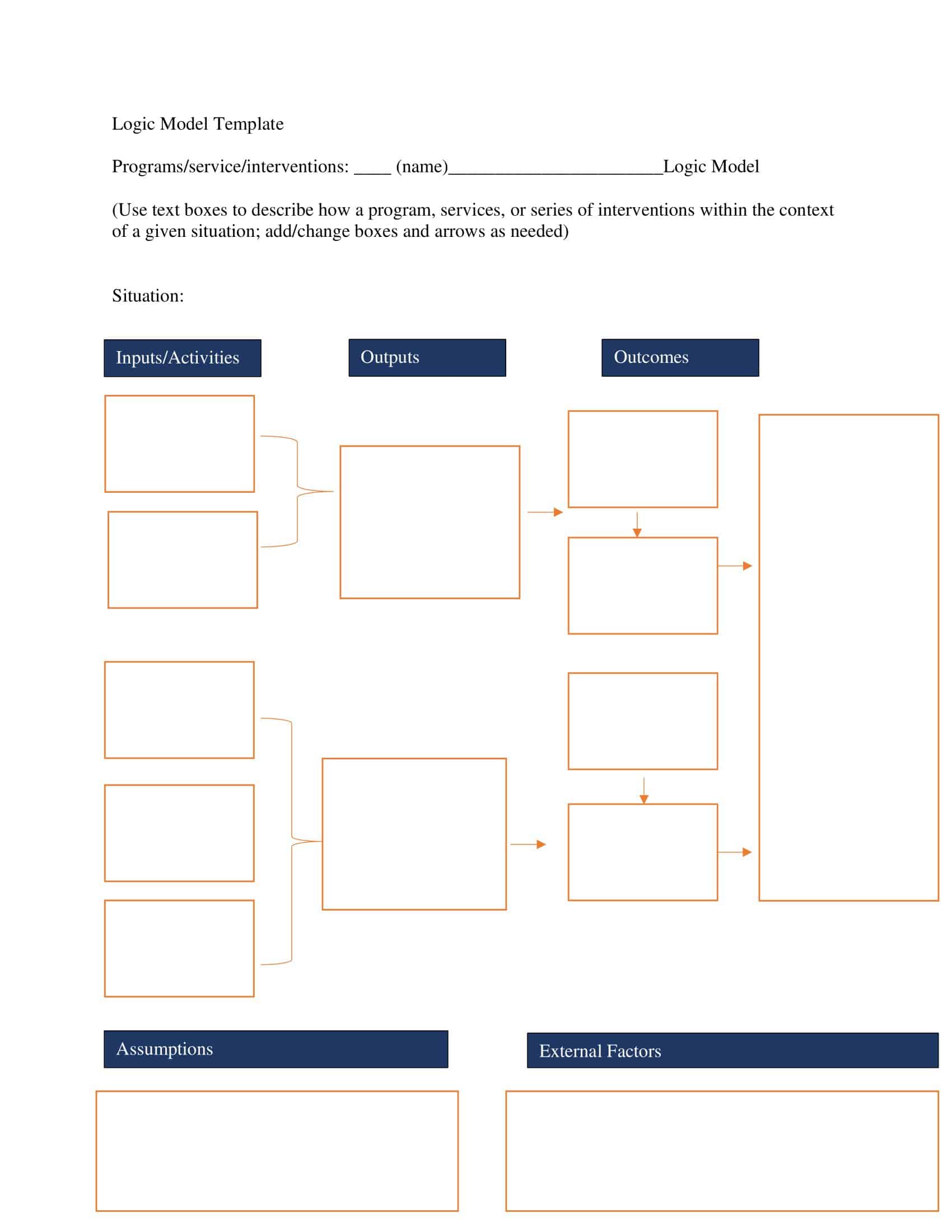
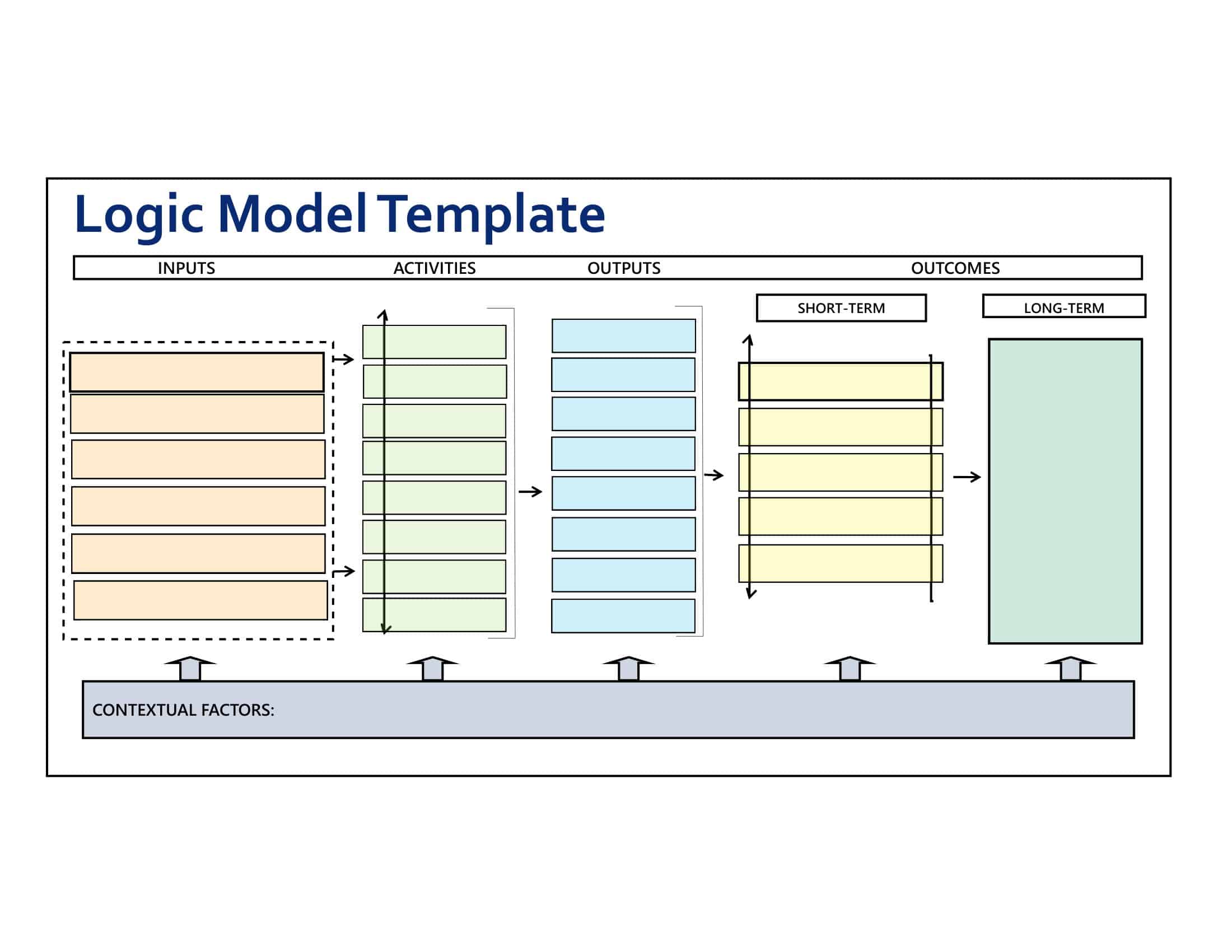
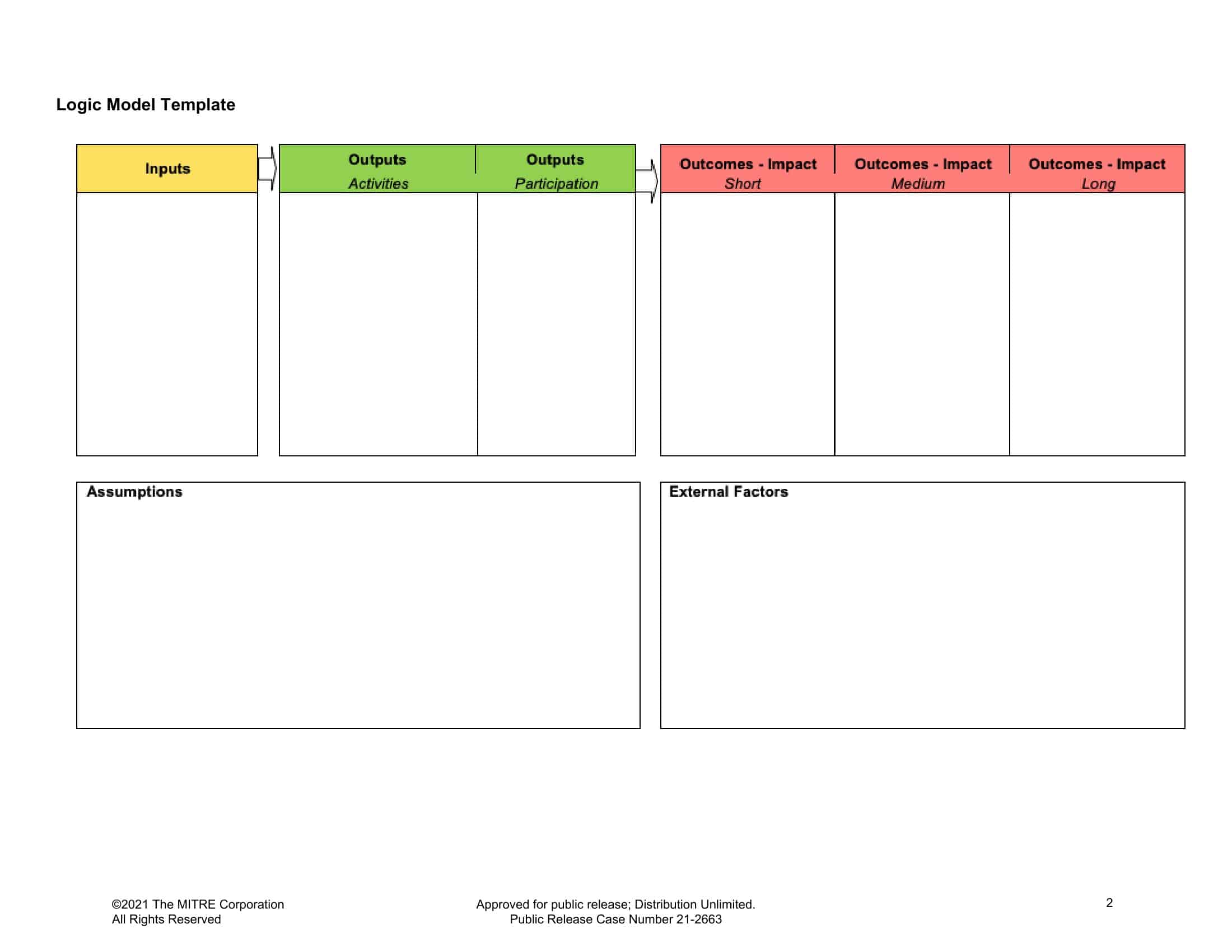
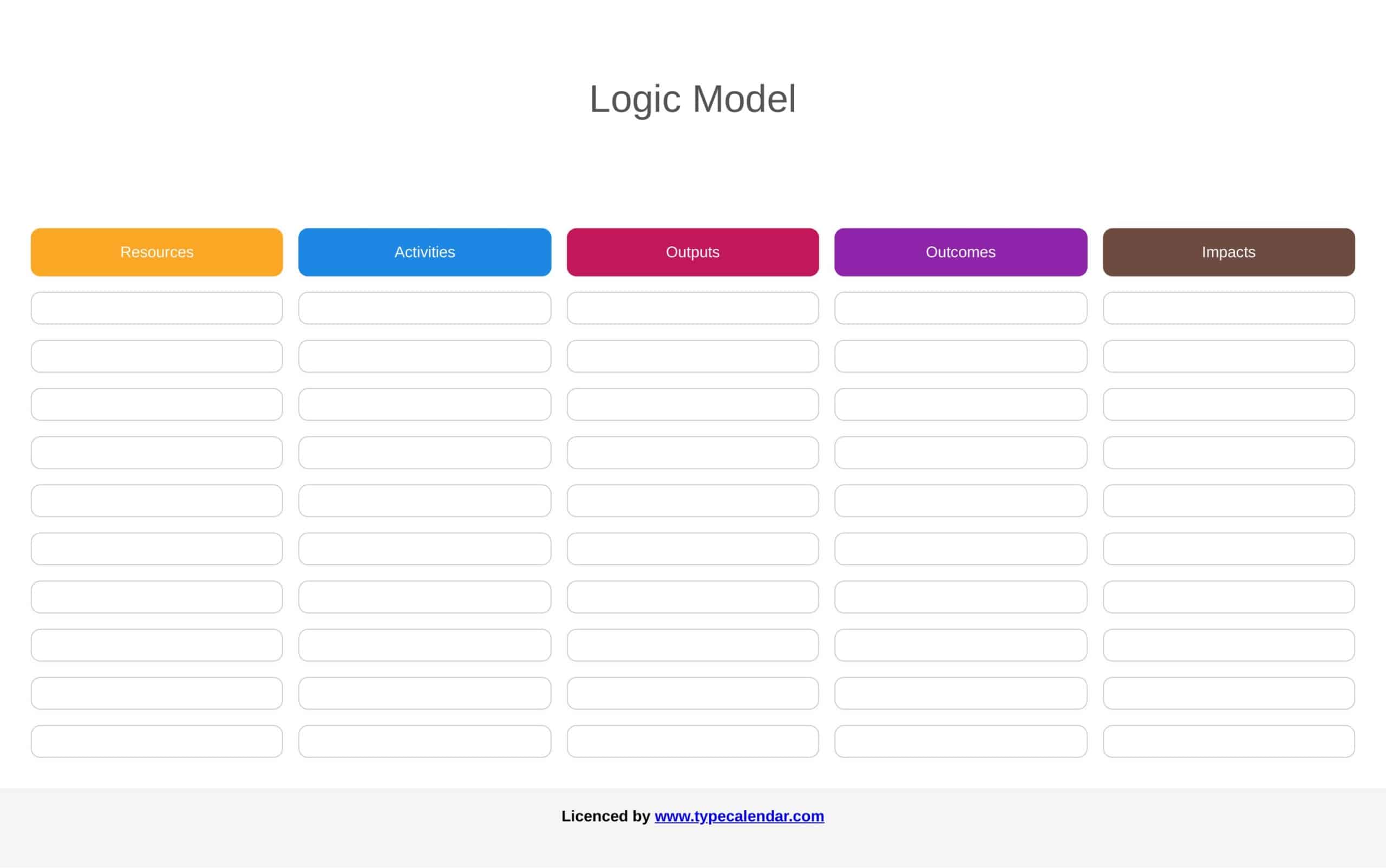
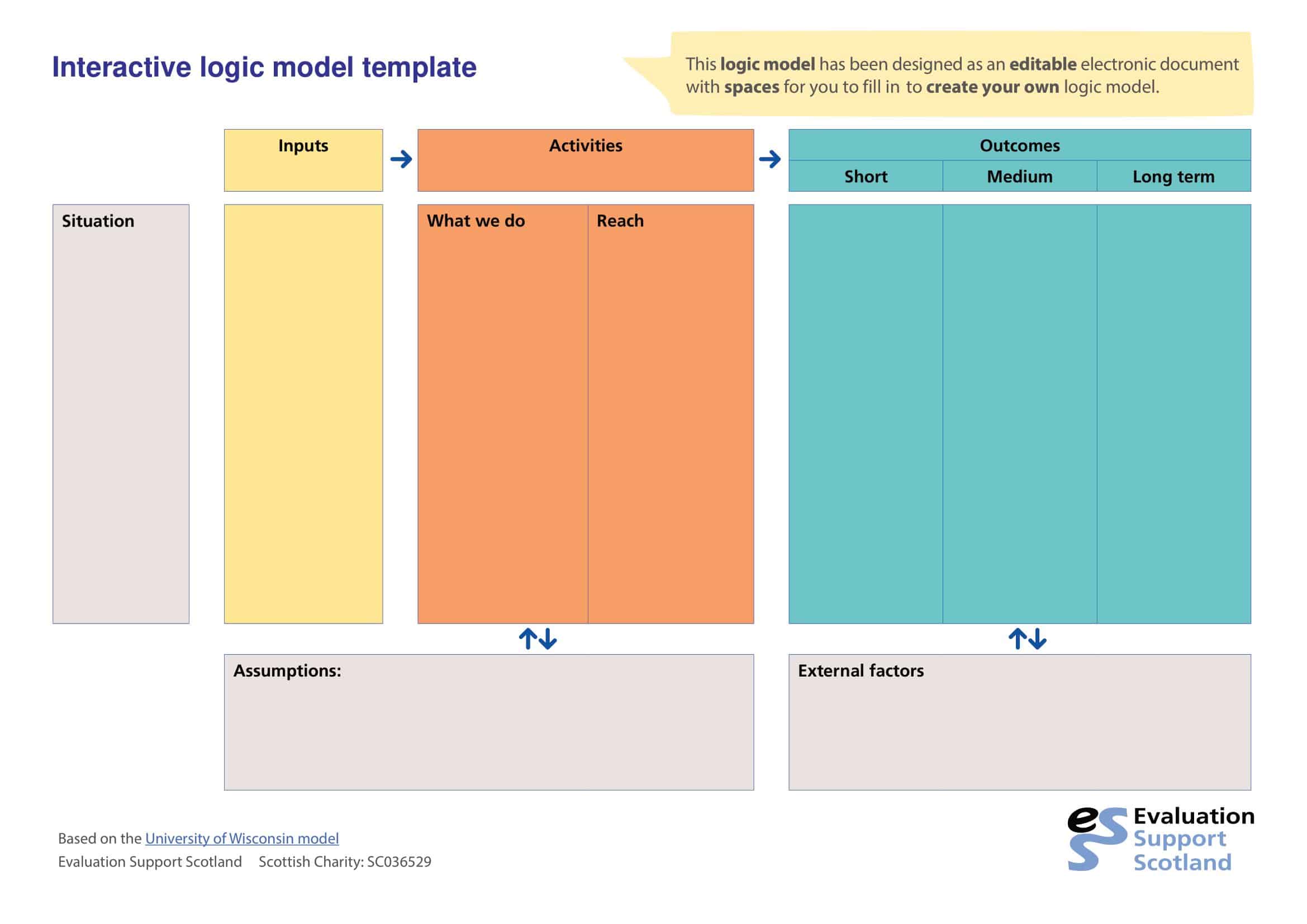
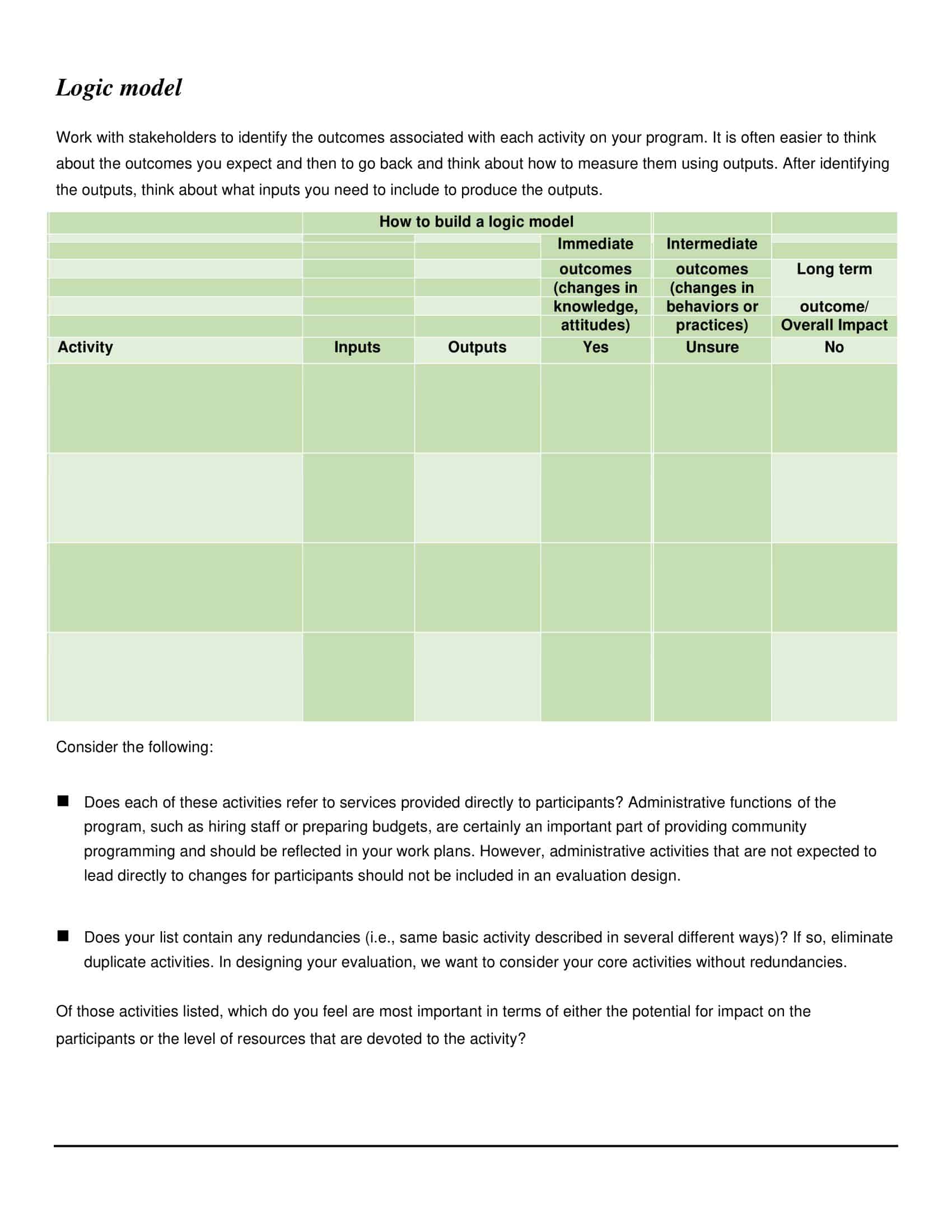
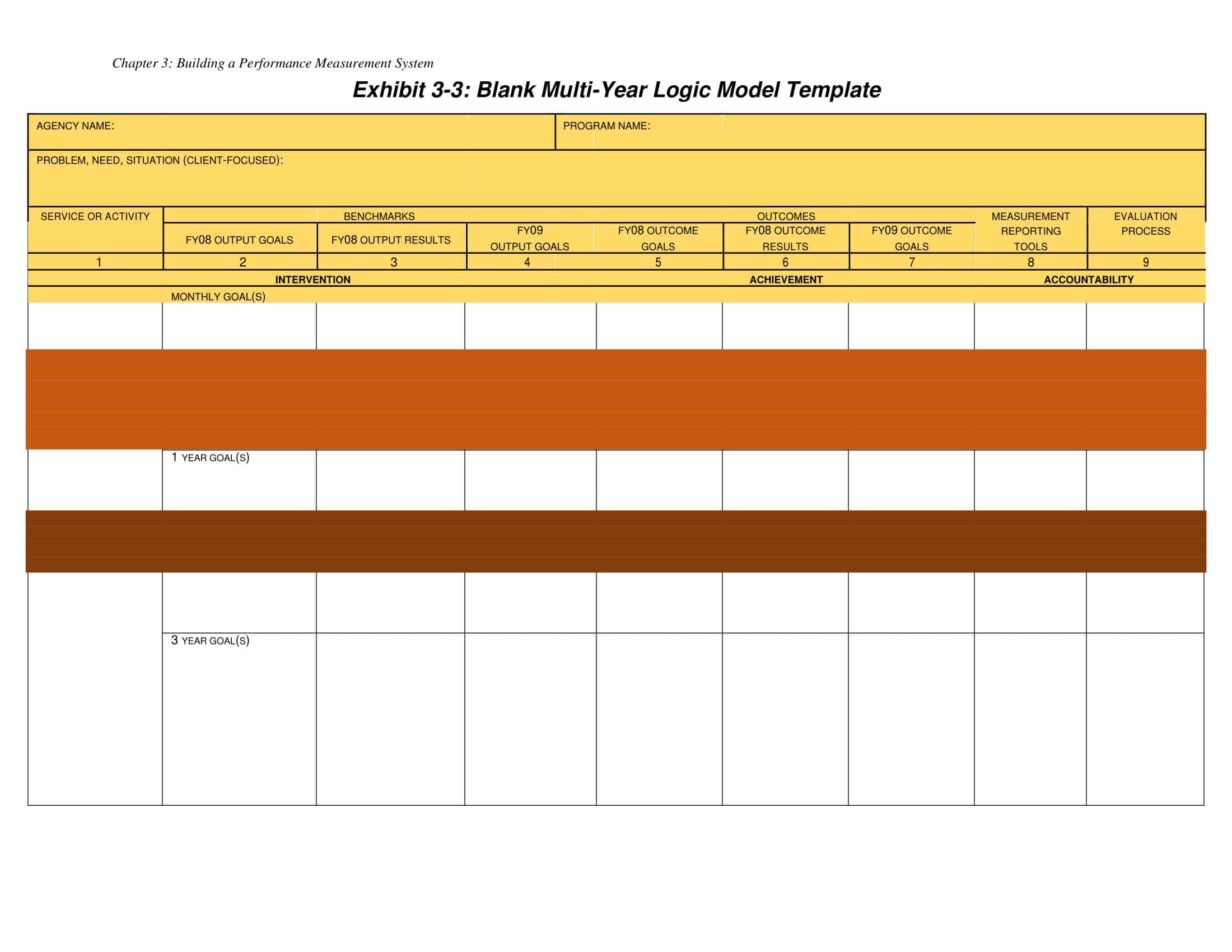
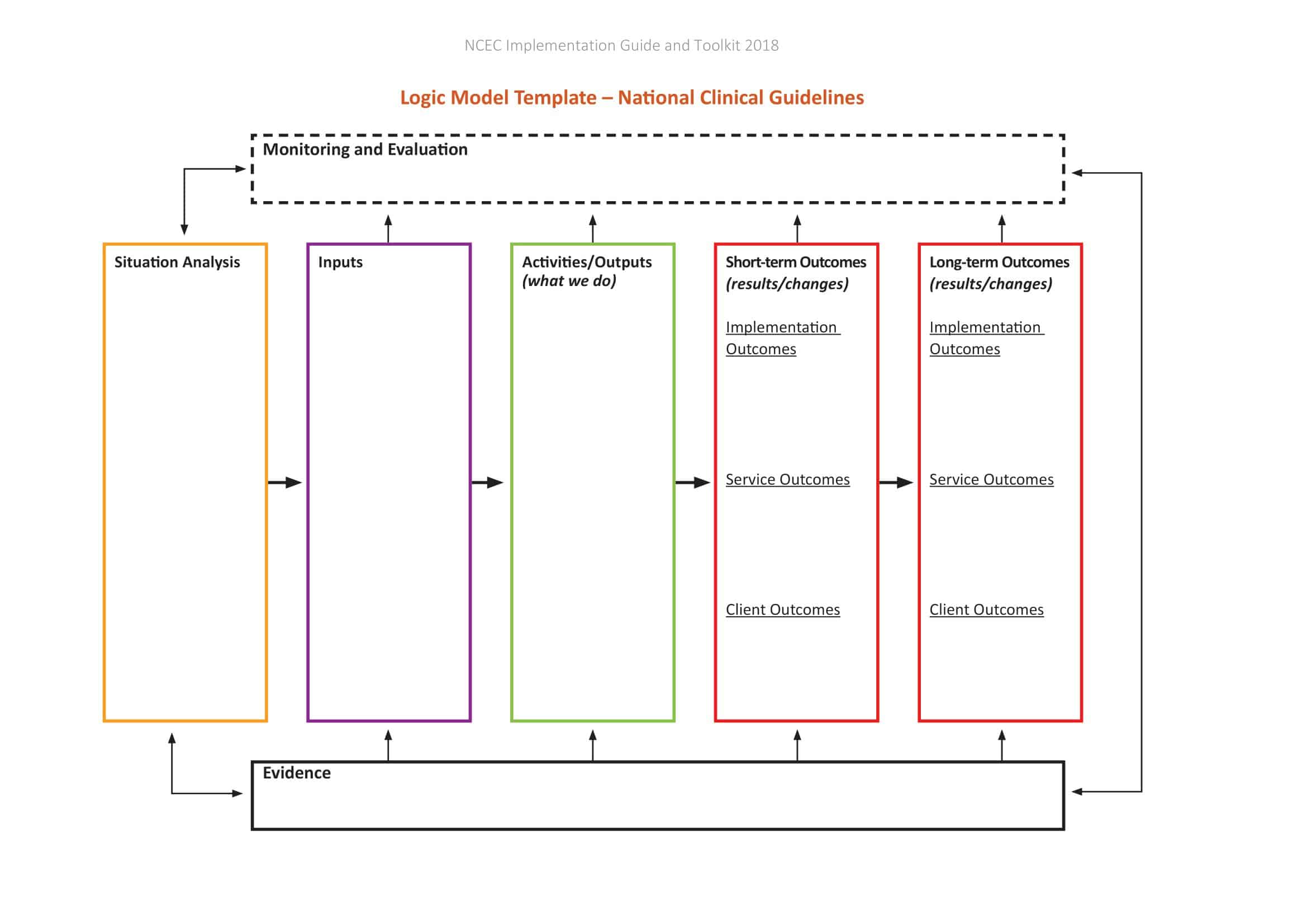
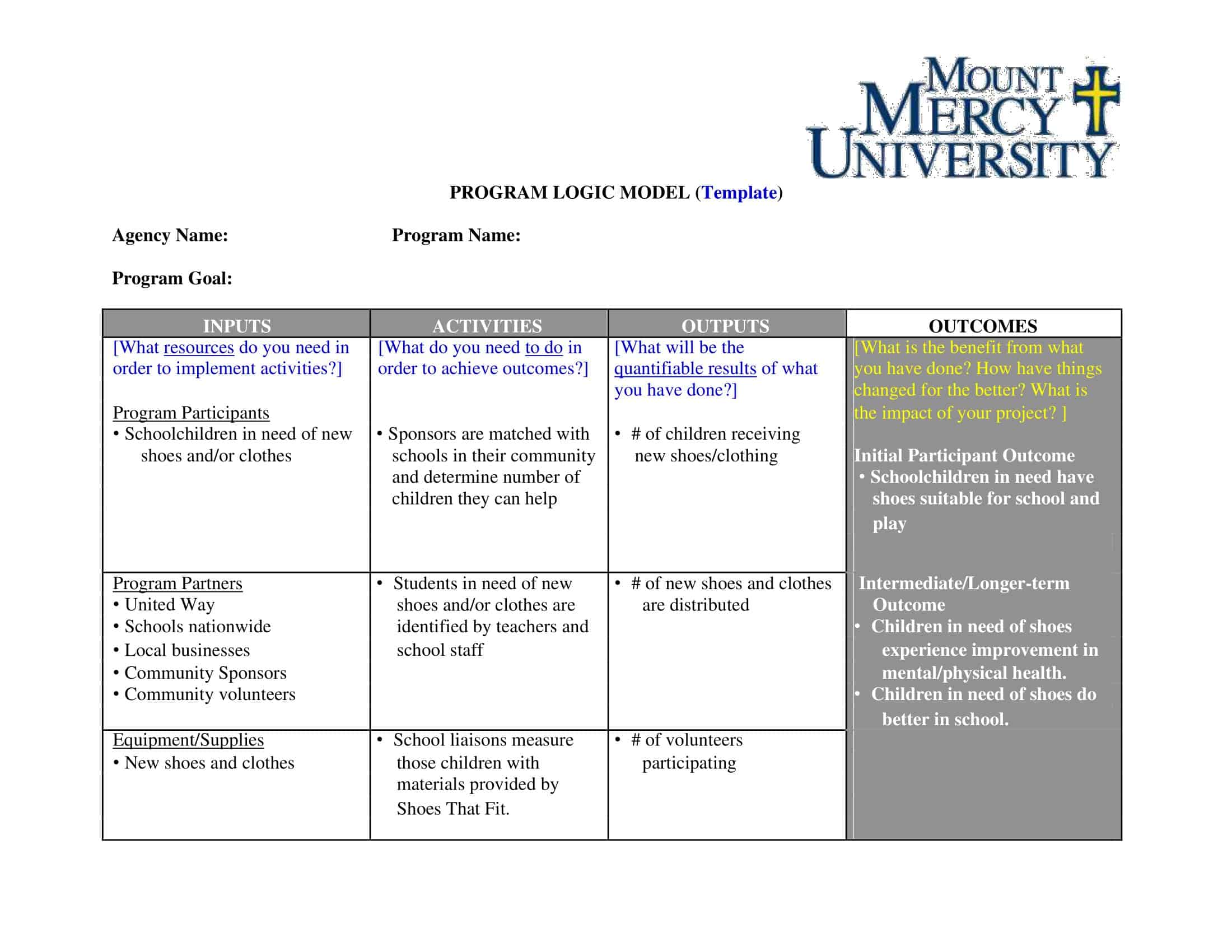
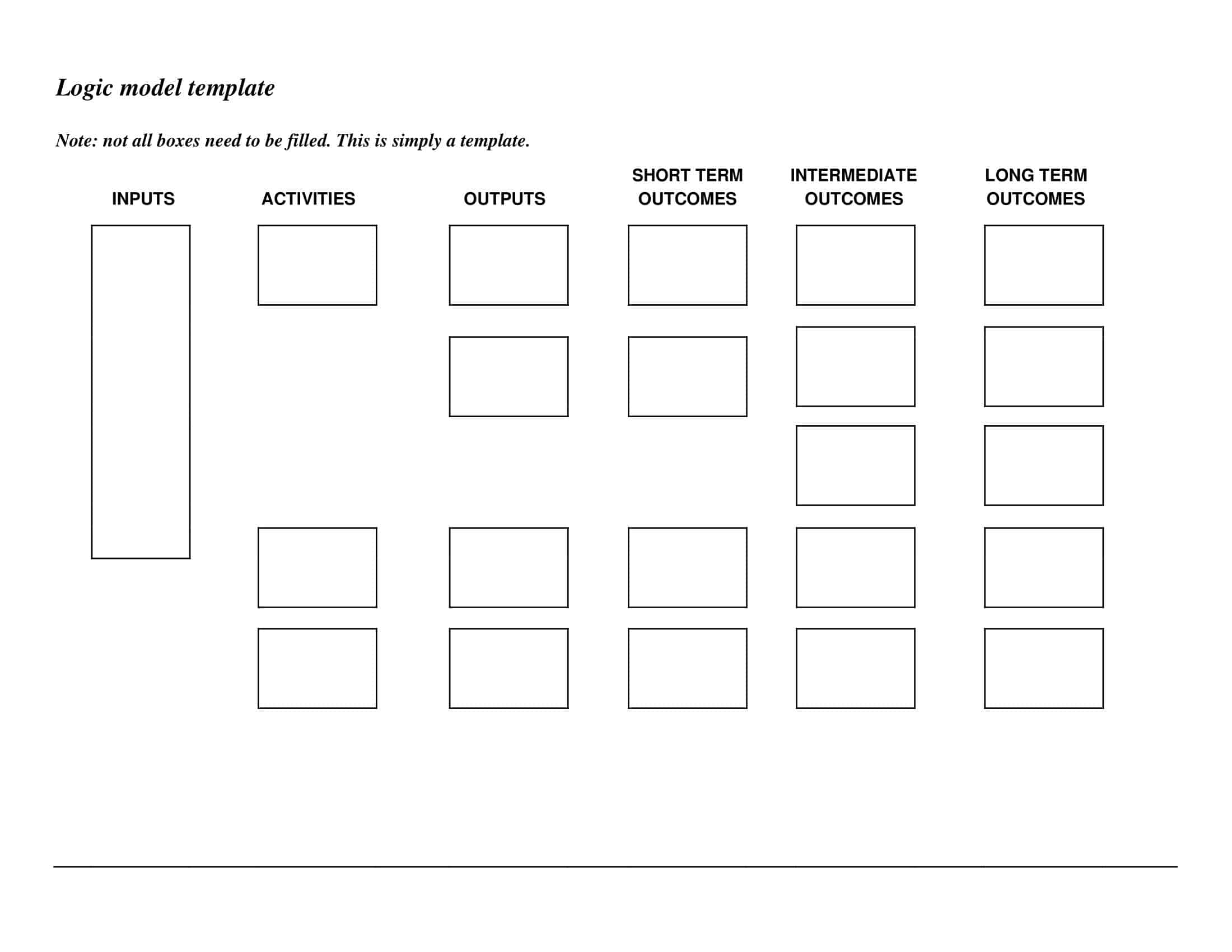
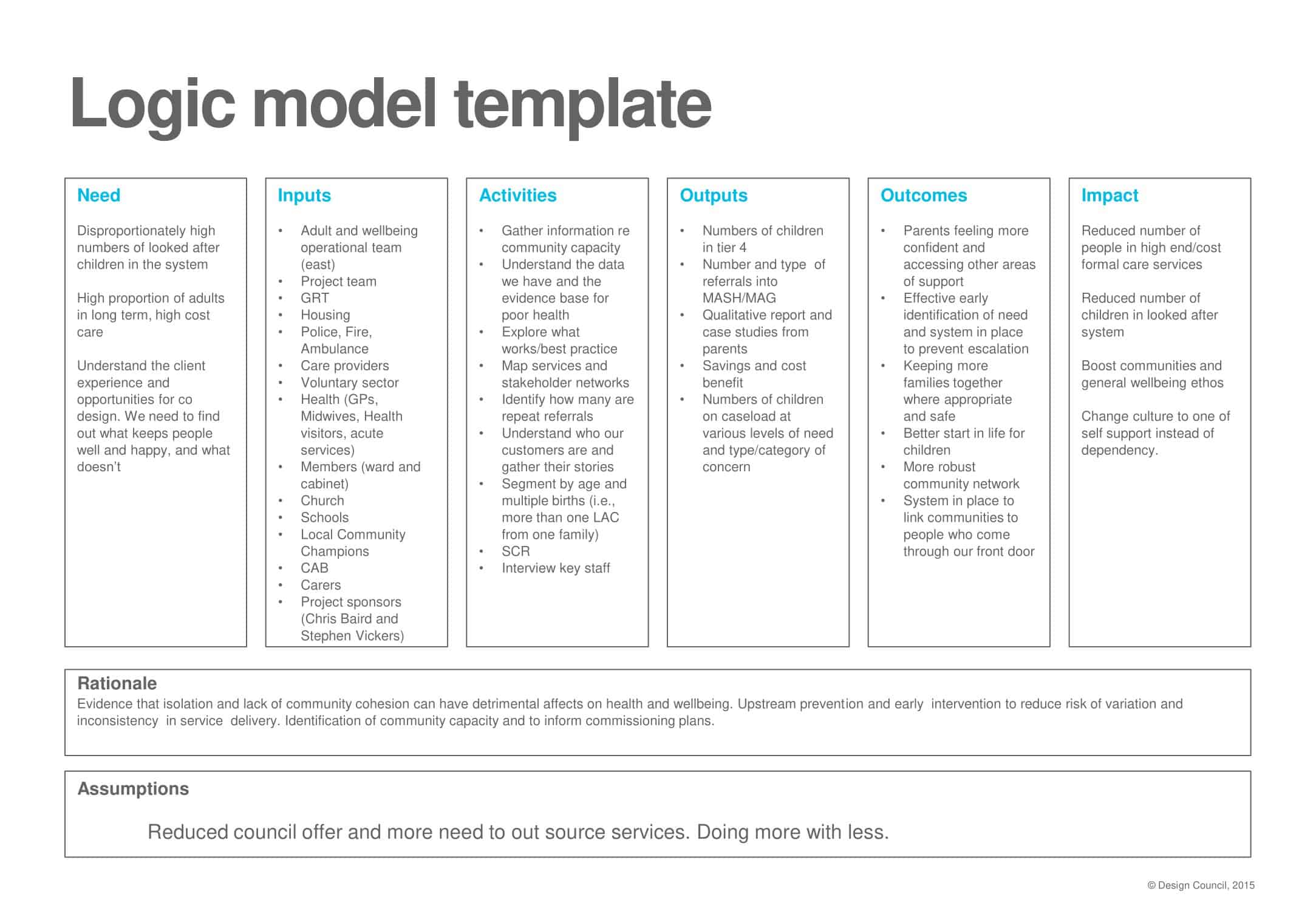
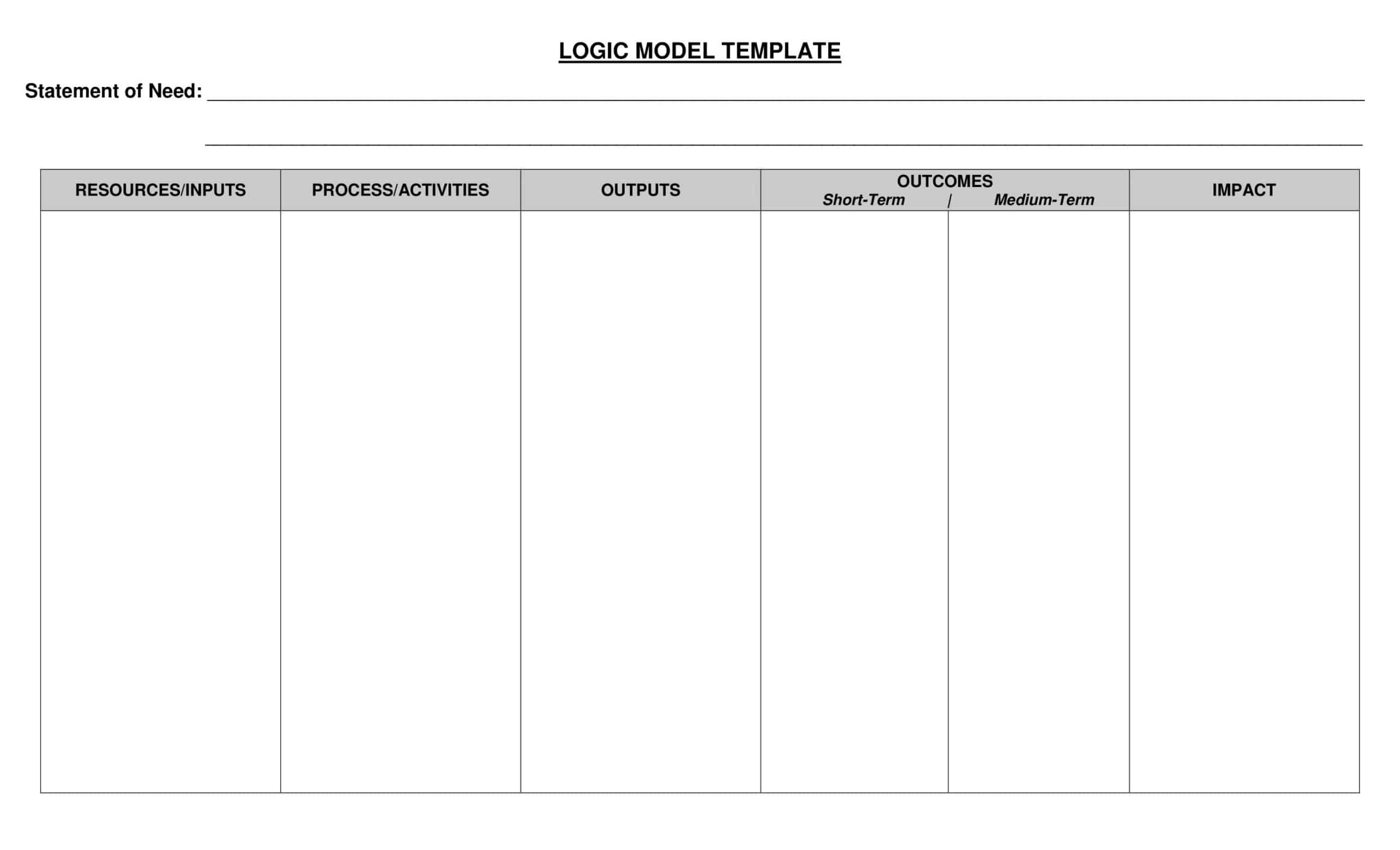
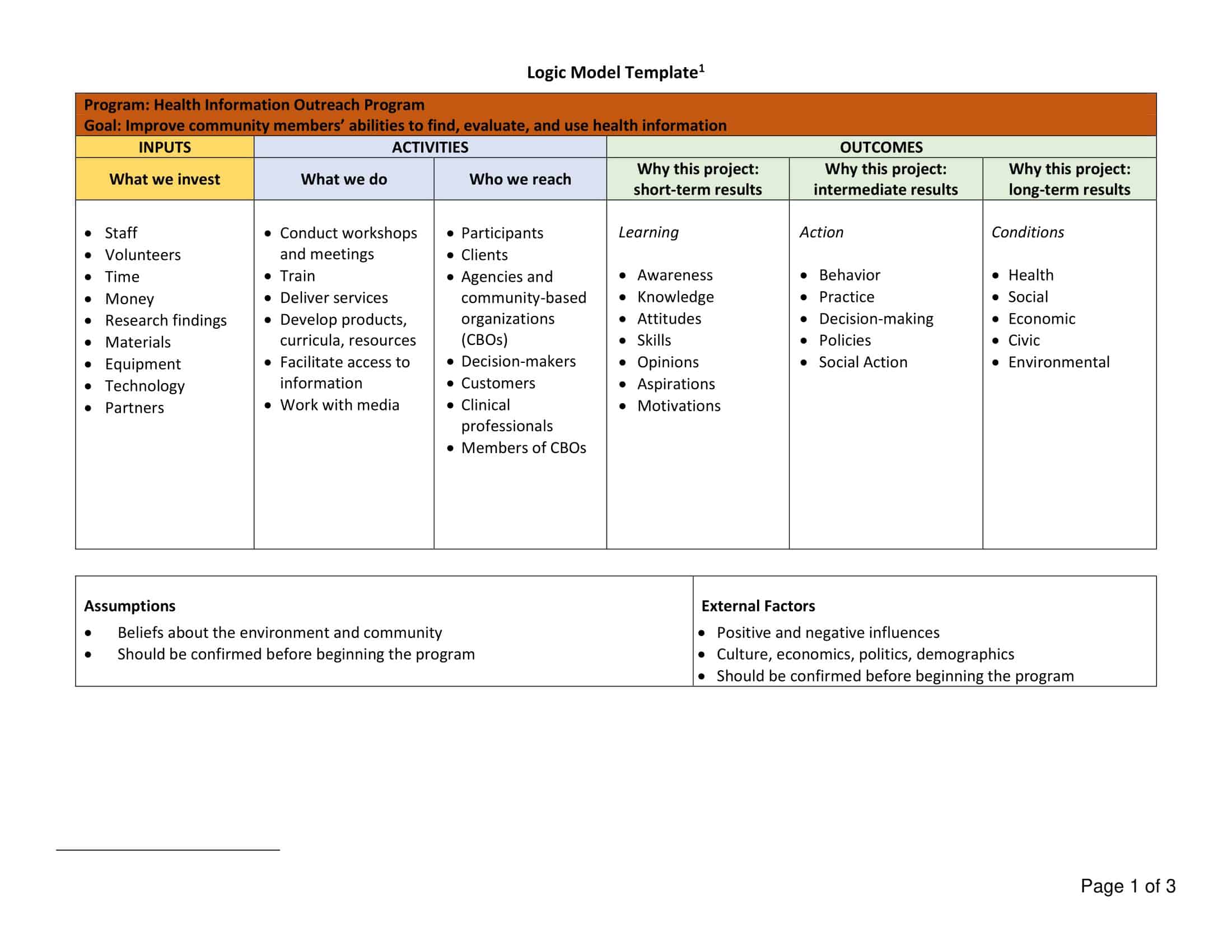
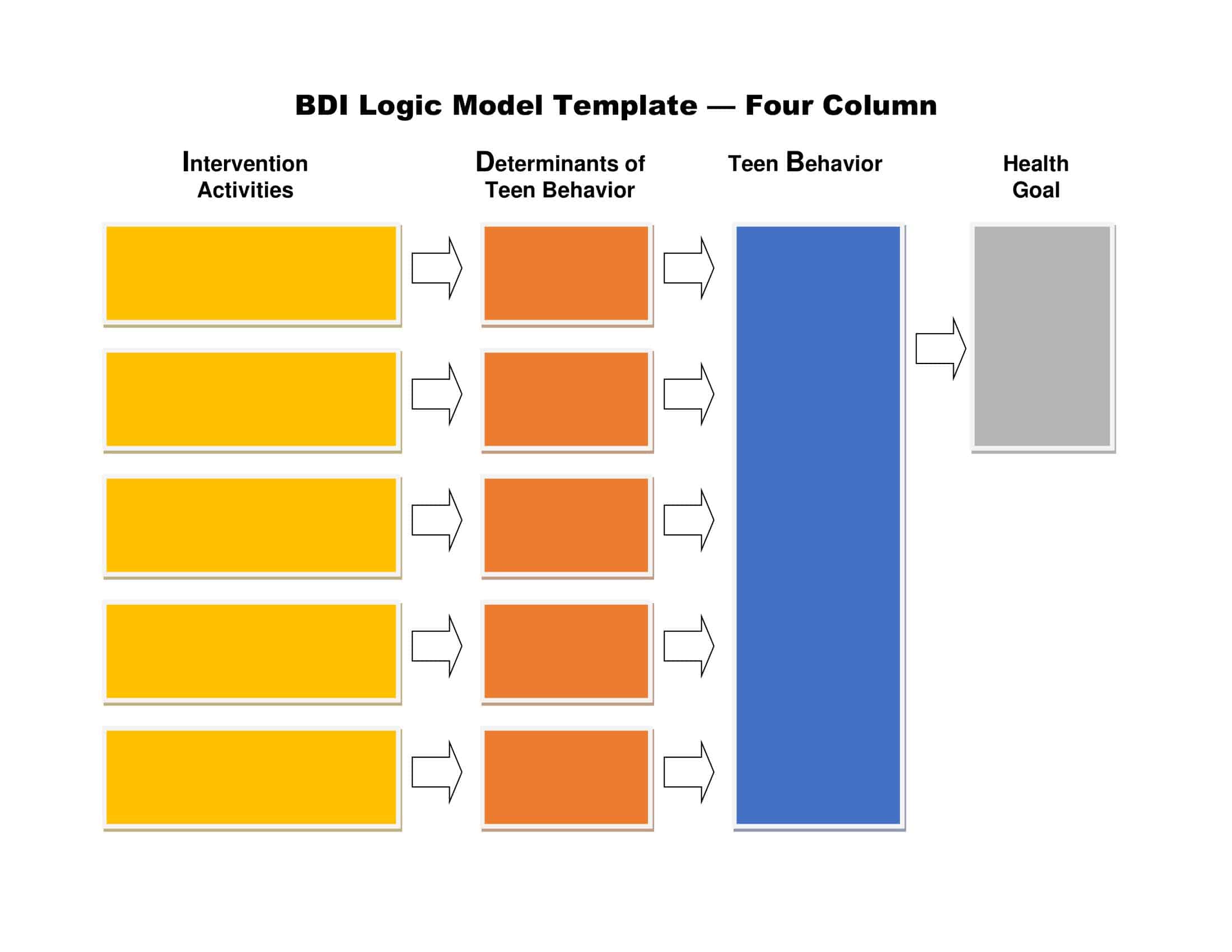
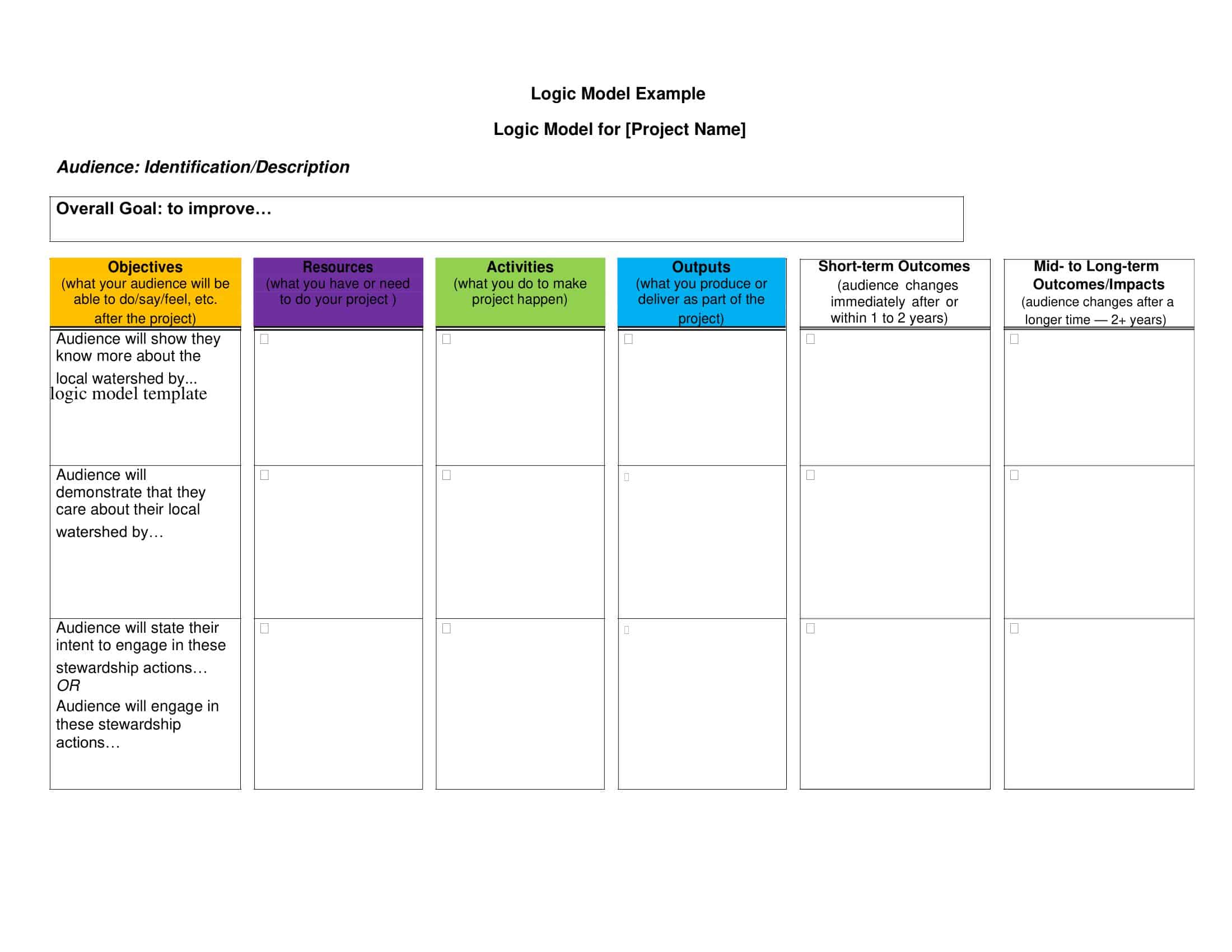
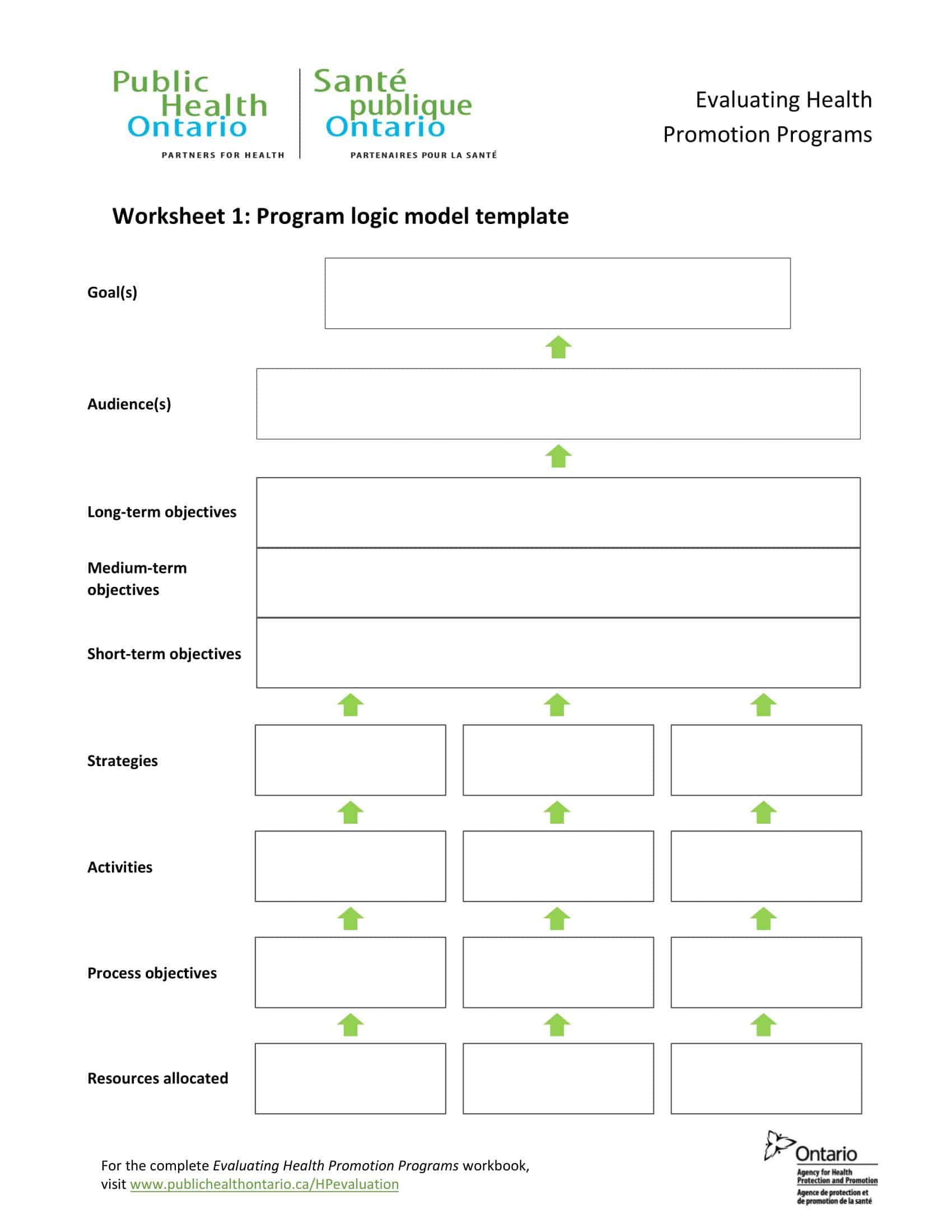
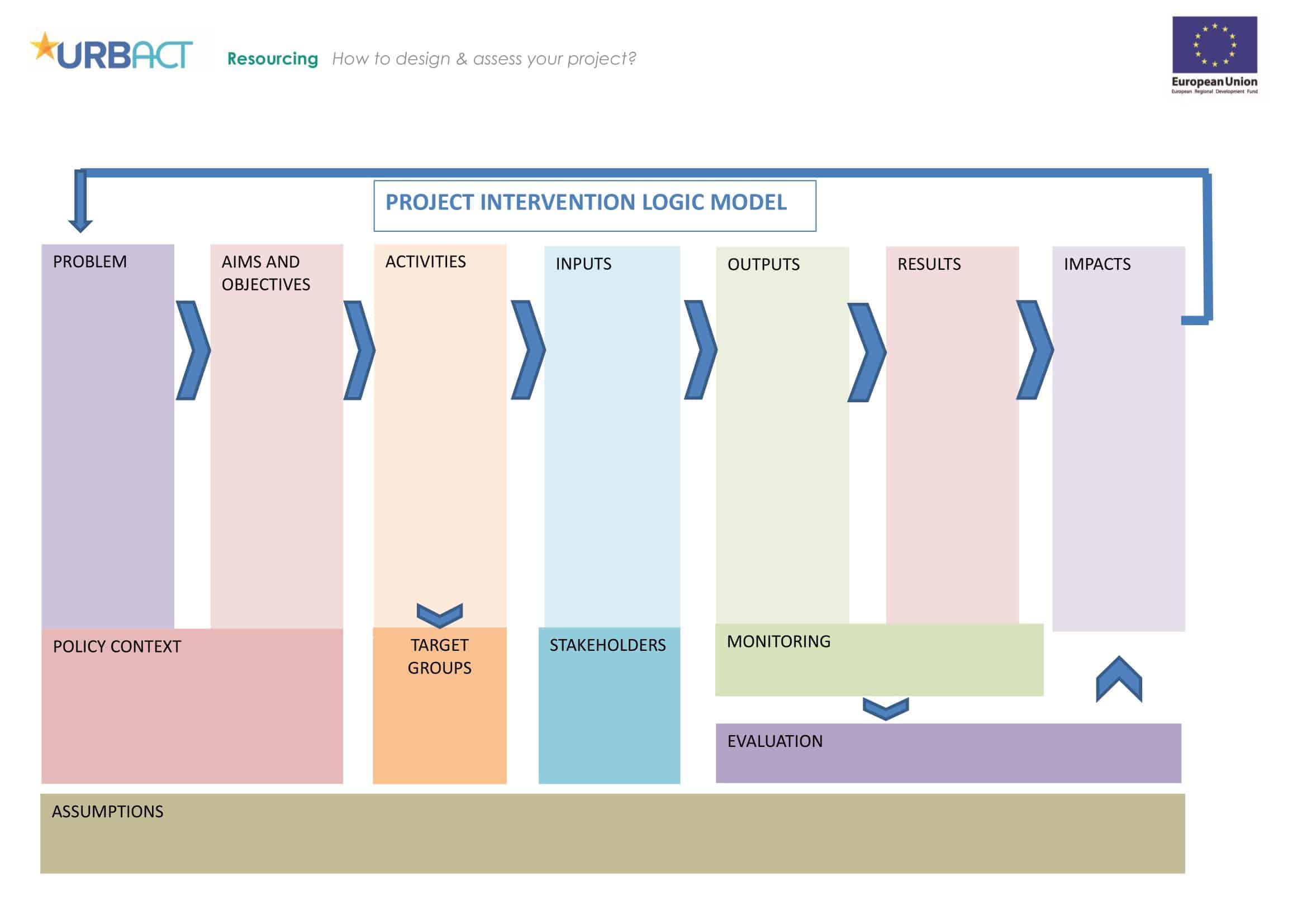
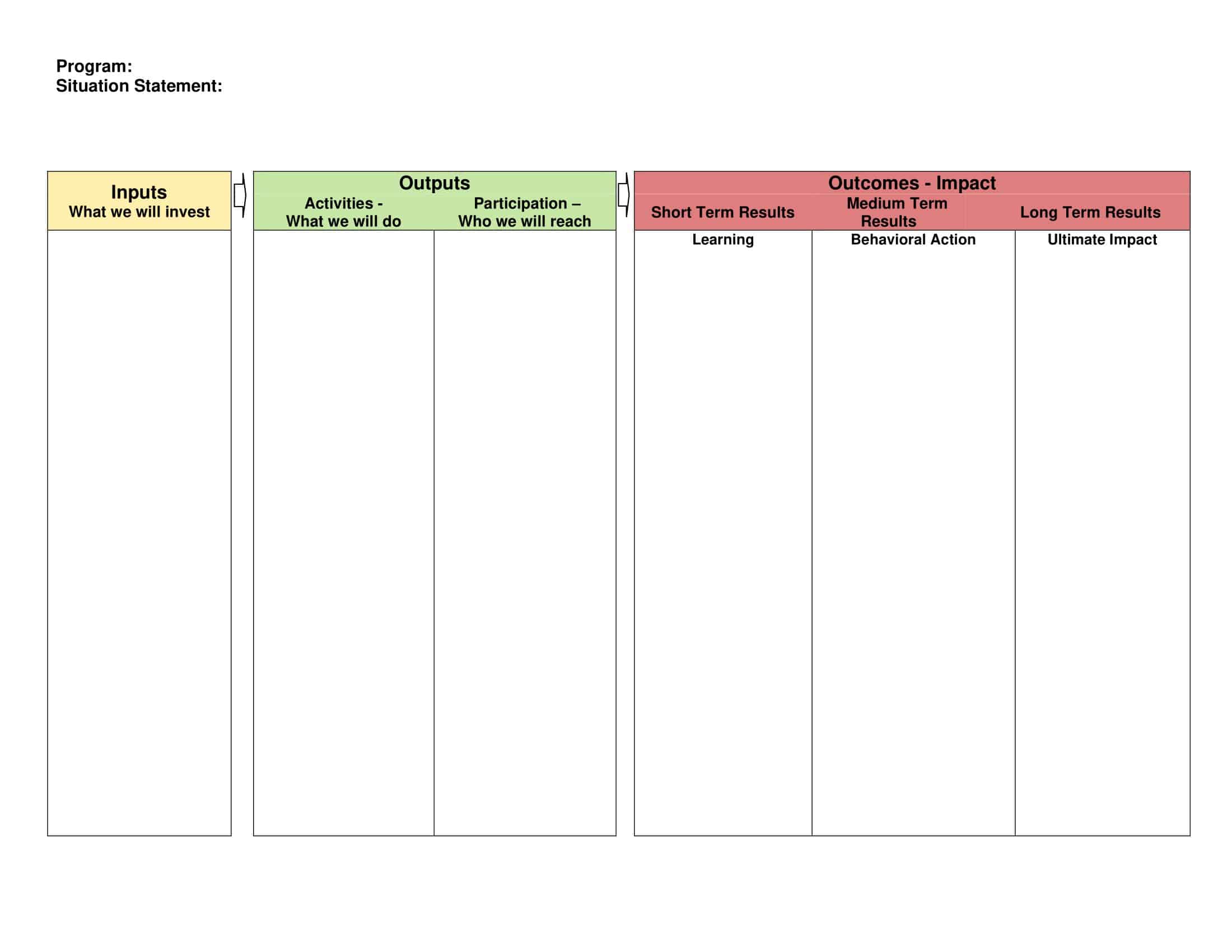
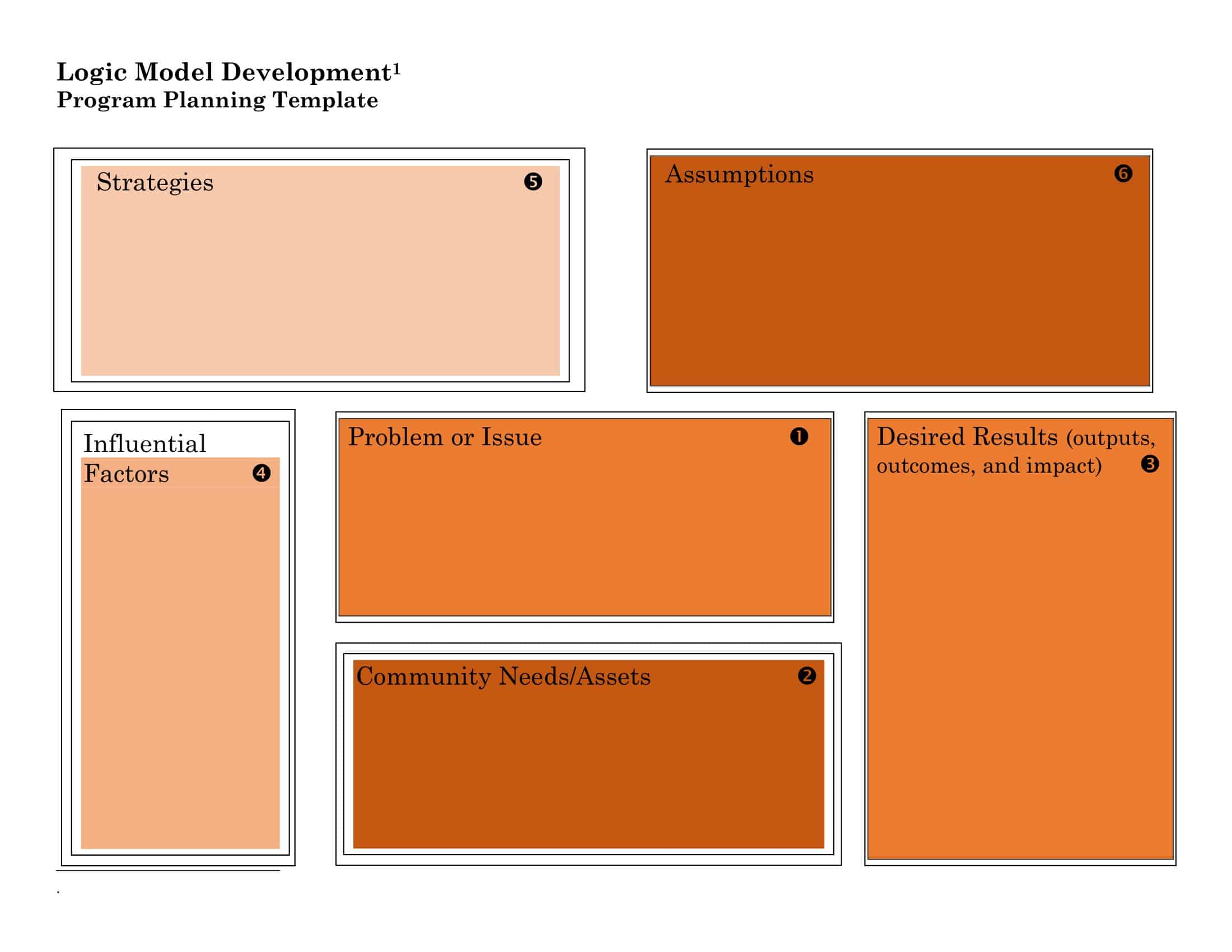
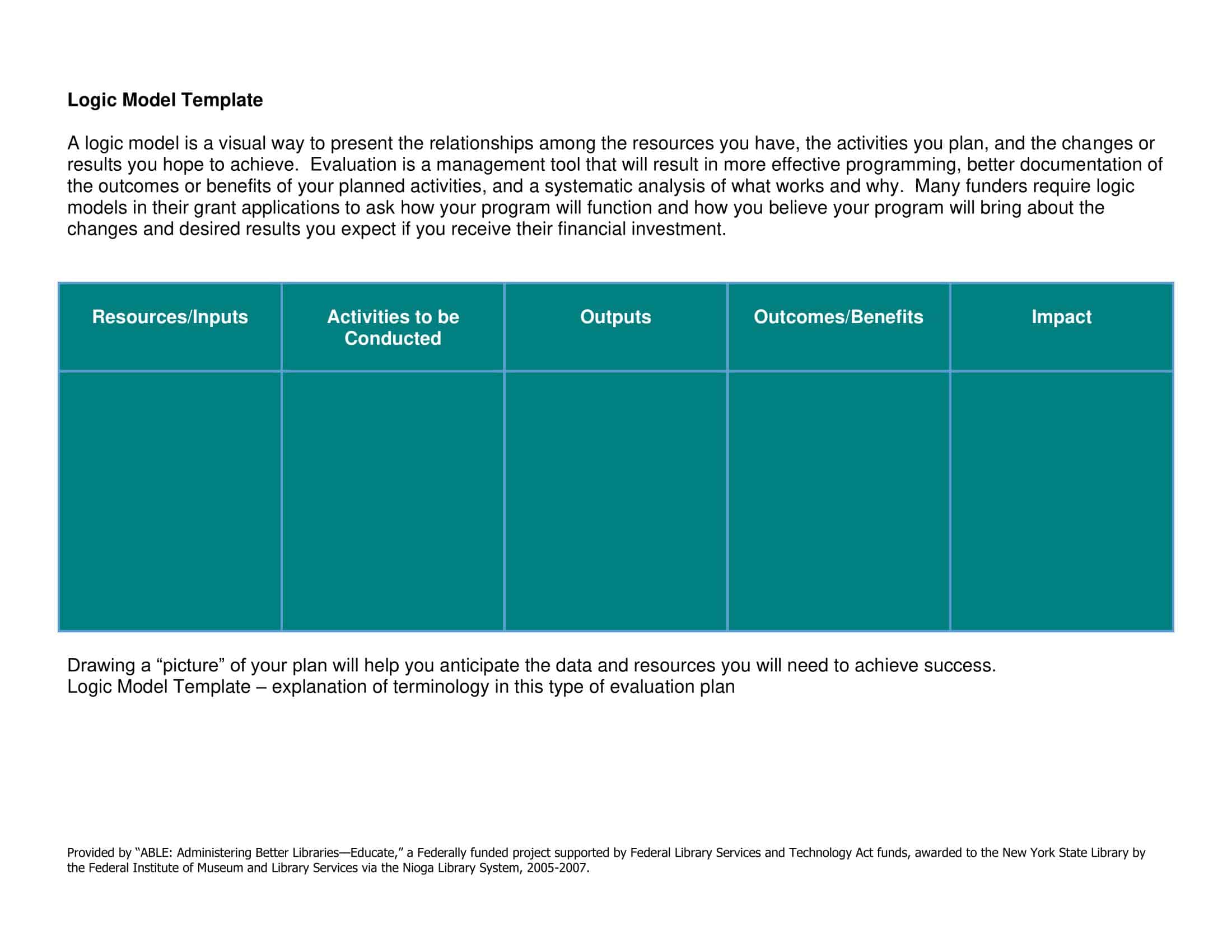
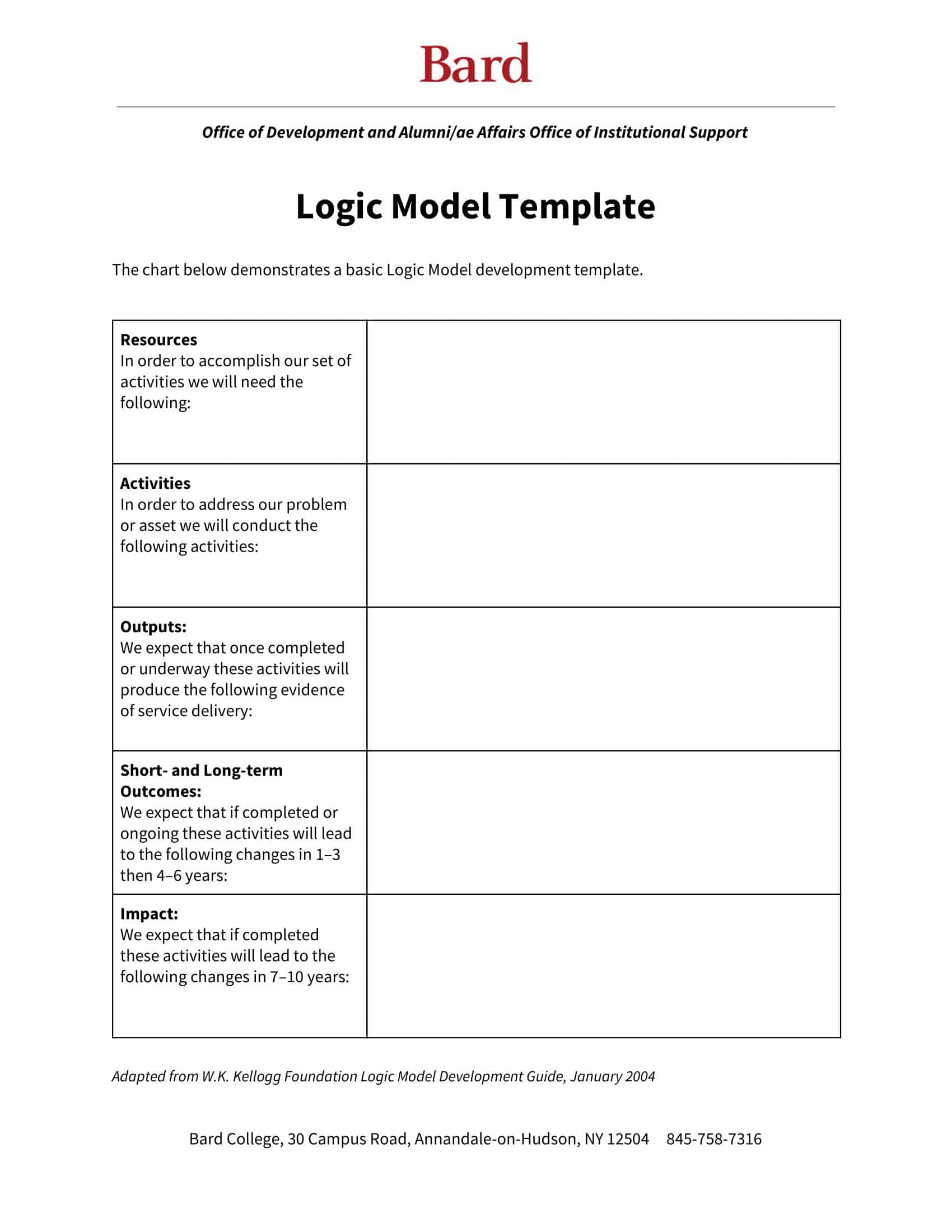
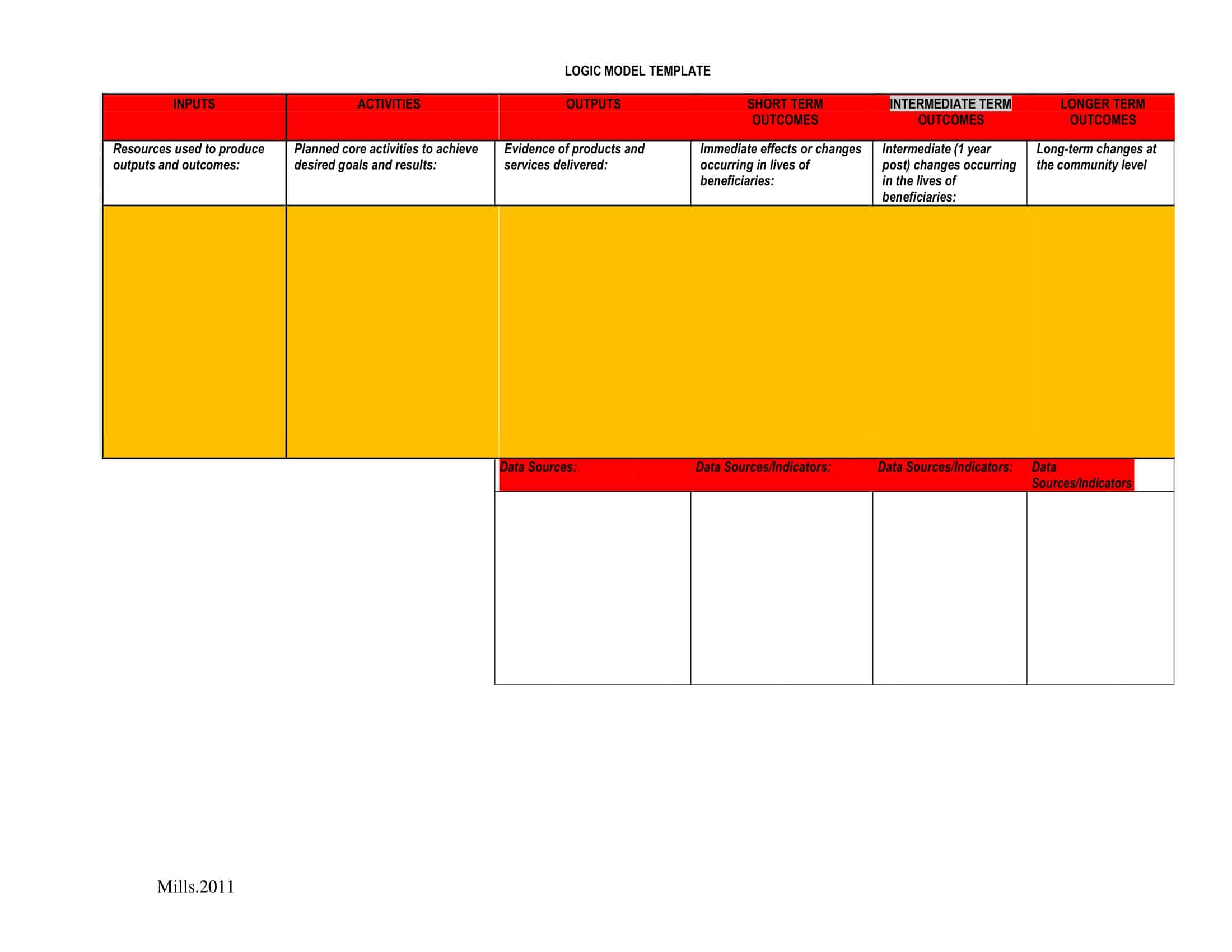
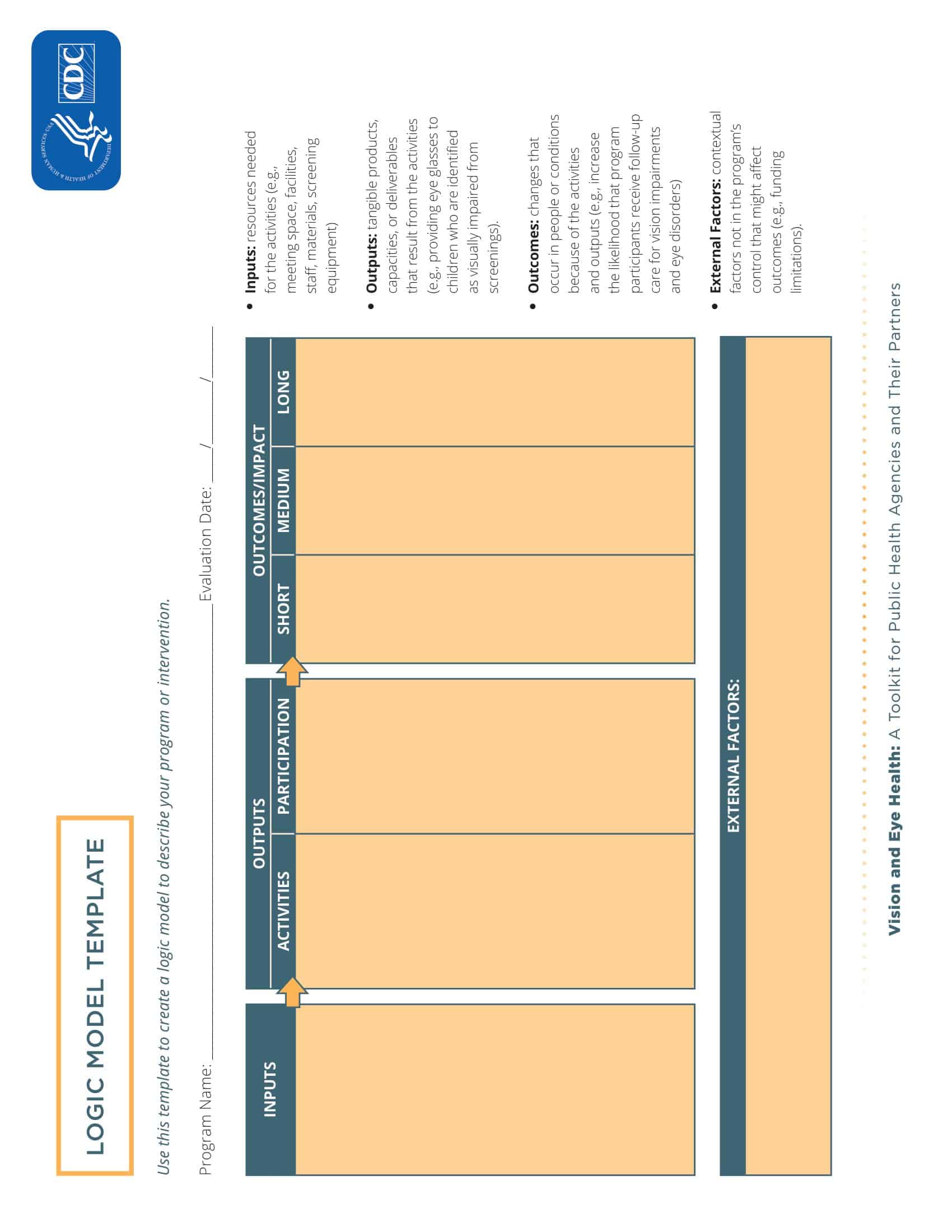
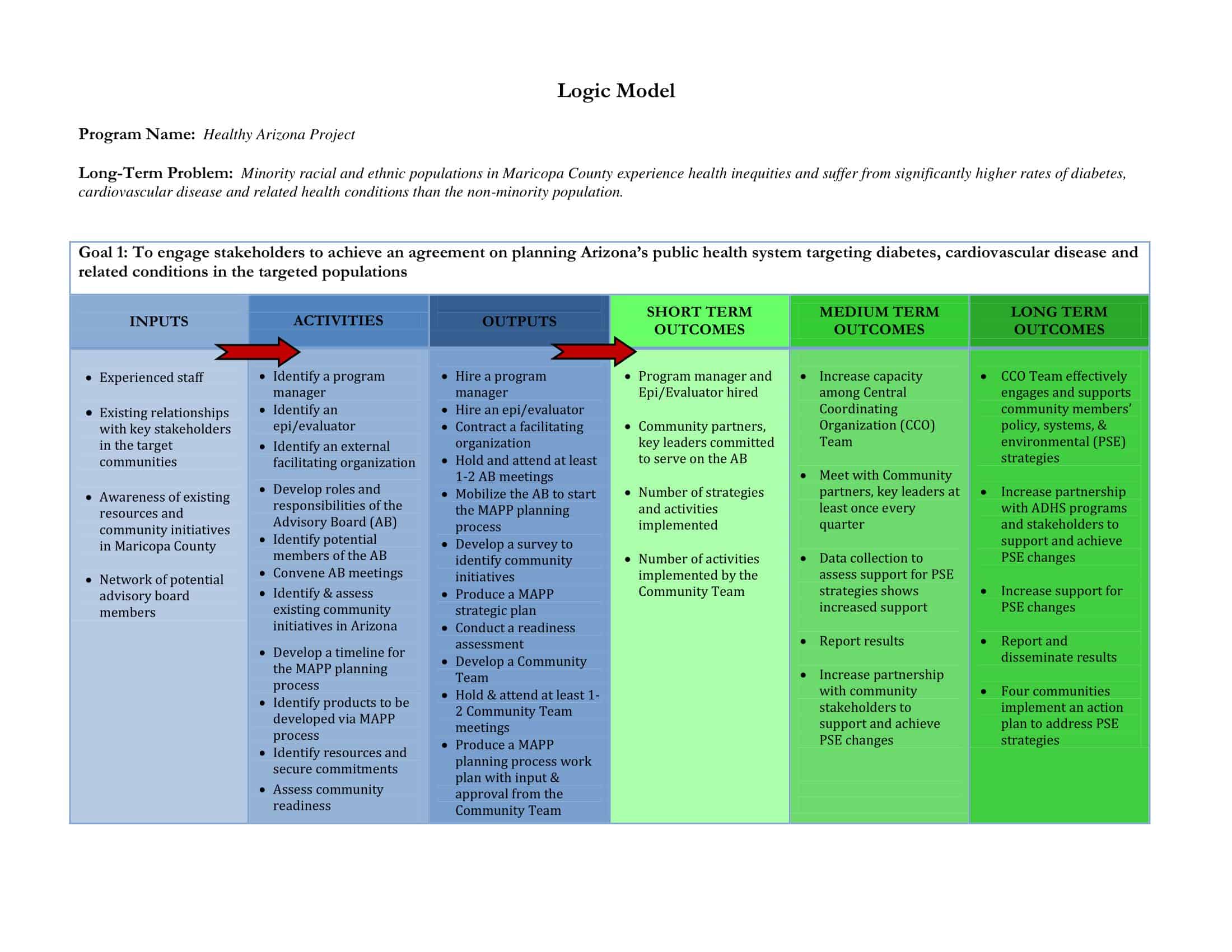
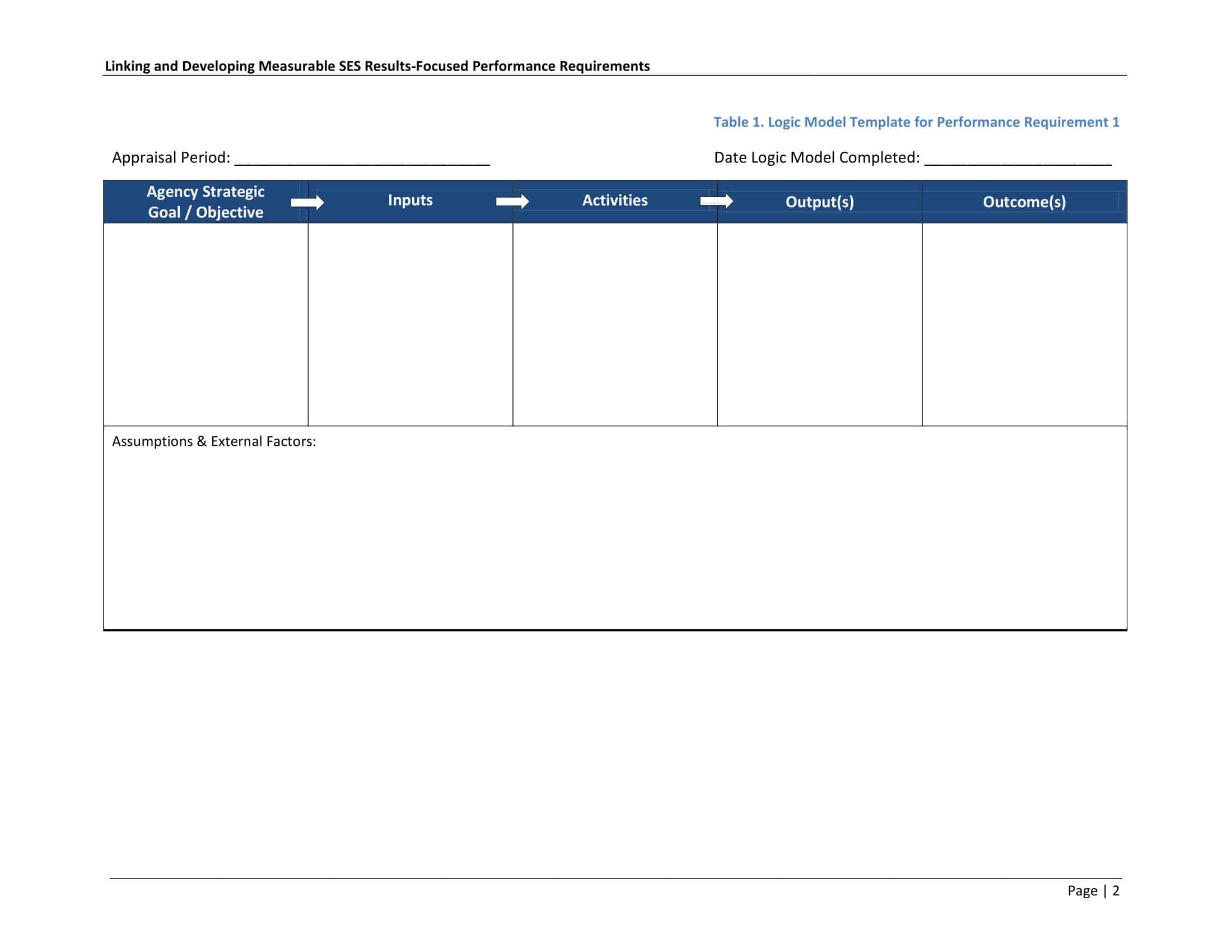
Logic models are graphical representations of the relationships between inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact. The following are the components of a typical logic model:
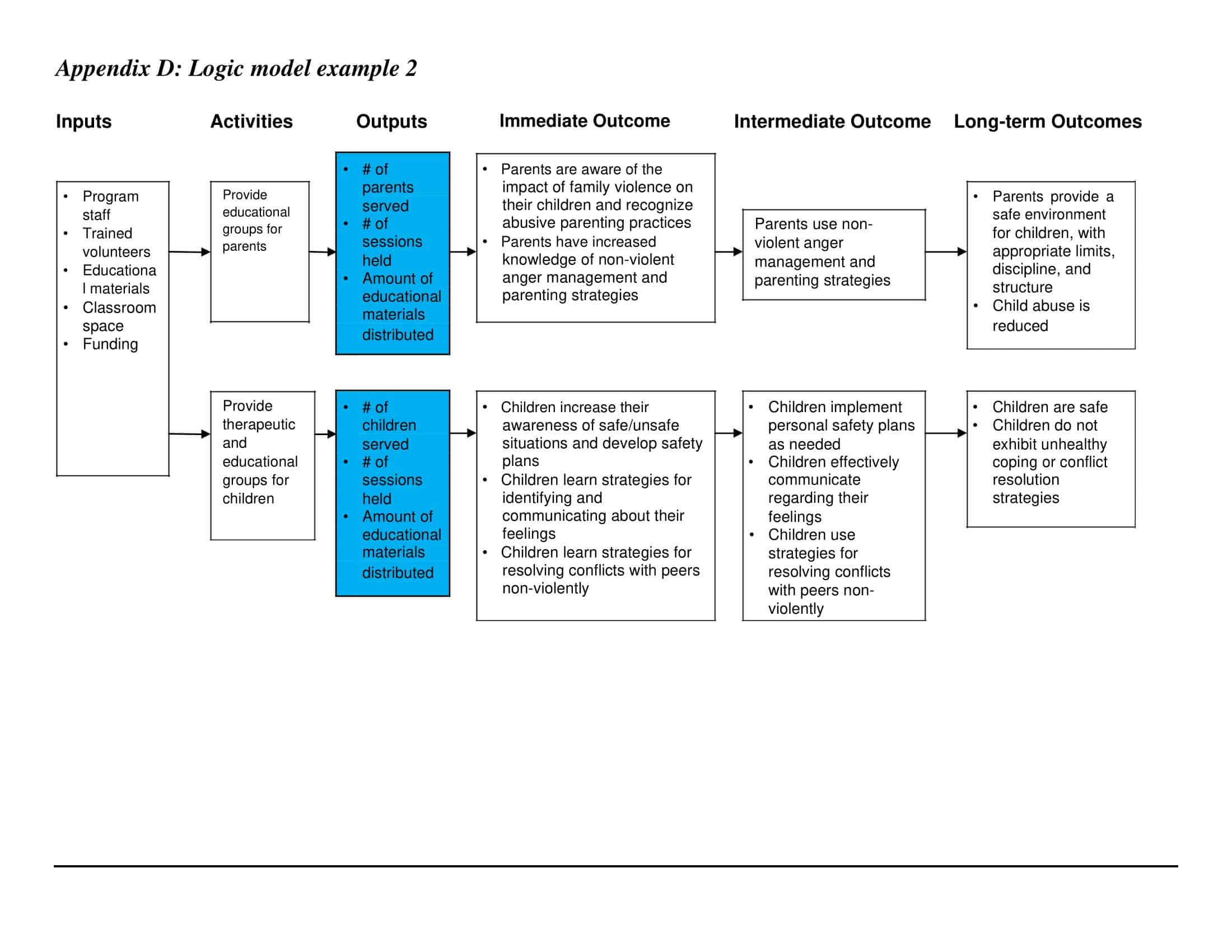
Inputs: This component includes the resources, such as financial, human, and material, needed to carry out the program activities.
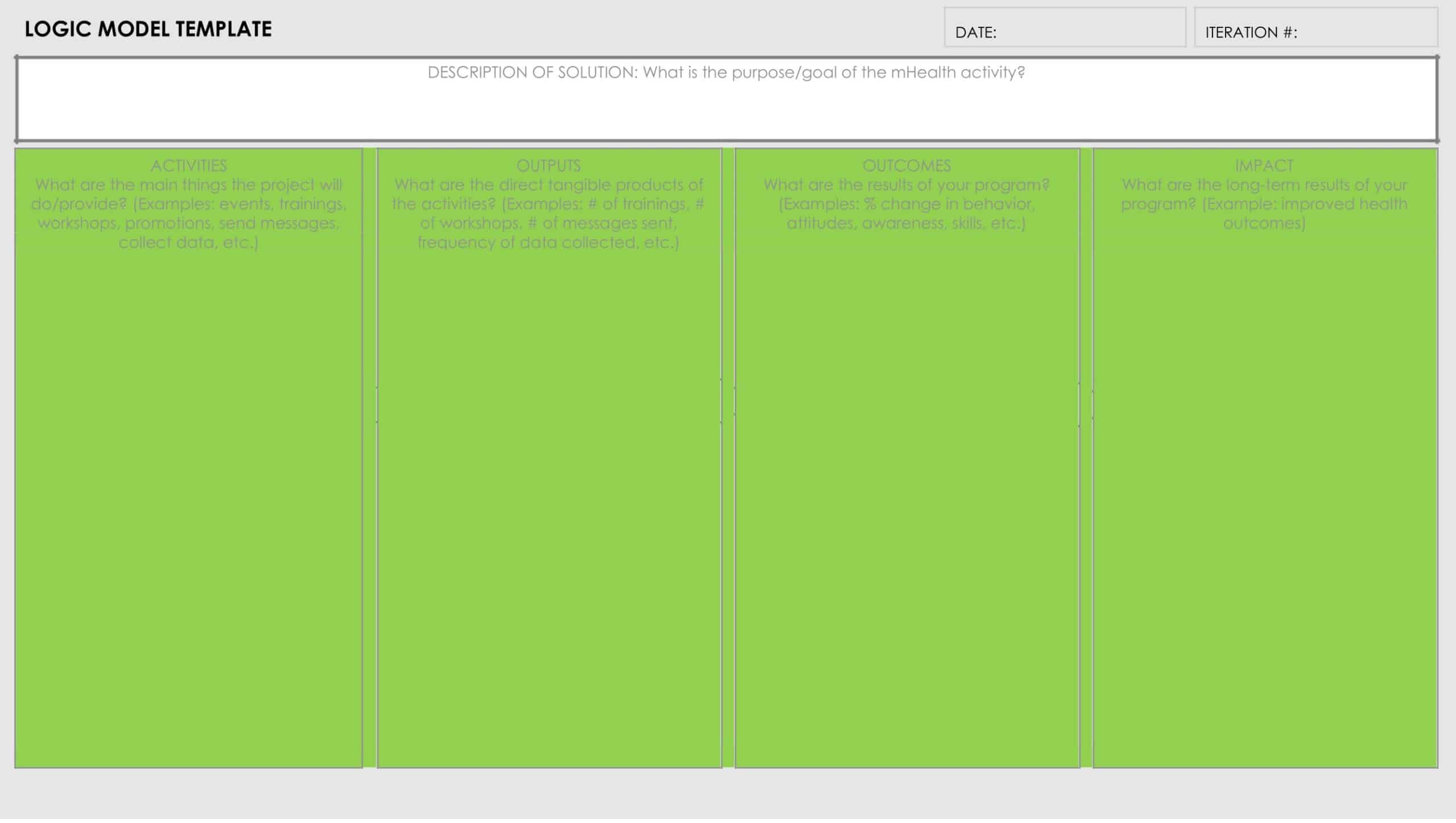
Activities: This component includes the specific actions or steps taken to achieve the program’s goals and objectives.
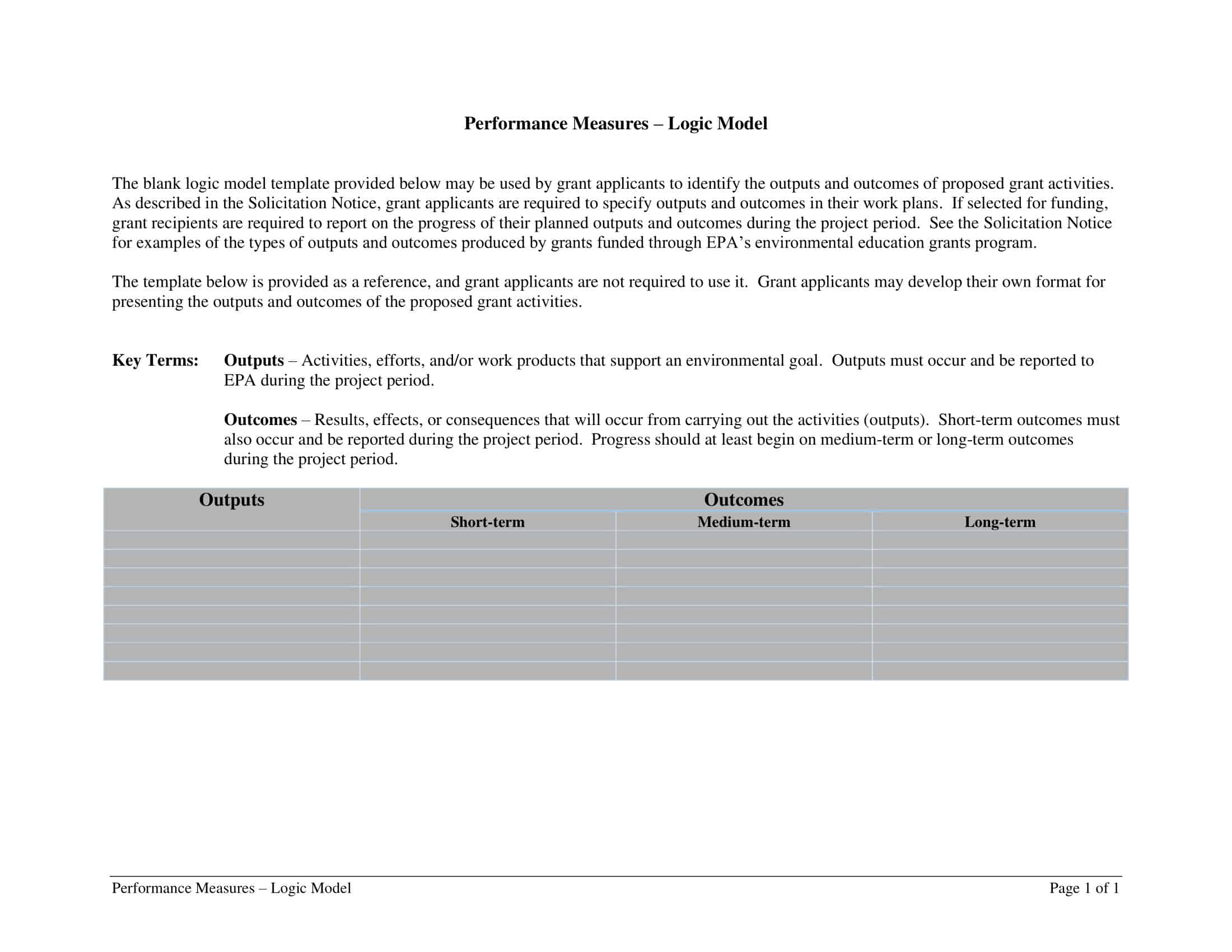
Outputs: This component includes the direct results or products of the program activities, such as the number of individuals served or the number of training sessions provided.
Outcomes: This component includes the changes or effects that result from the program, such as improved health or increased knowledge.
Impact: This component includes the long-term effects of the program, such as systemic change or a reduction in the prevalence of a specific problem.
Assumptions: This component includes the underlying assumptions about how the program will operate and the factors that could affect its success.
It’s worth noting that not all logic models are structured exactly the same way and that some may include additional components or levels of detail. However, the inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact components are the most common elements in a logic model.
How to Create a Logic Model
Creating a logic model is a valuable step in the planning and evaluation of a program or initiative. A logic model can help clarify program goals, objectives, and strategies and provide a clear visual representation of the relationships between inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a logic model:
Step 1: Define the Problem or Need
The first step in creating a logic model is to clearly define the problem or need that the program or initiative is intended to address. This could be a social issue, a gap in services, or an identified need for a particular population.
Step 2: Identify Program Goals and Objectives
Once the problem or need has been defined, the next step is to identify the program goals and objectives. These should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) and should reflect the intended impact of the program.
Step 3: Gather Information
The next step is to gather information about the program. This may include data on the population being served, current programs and services available, best practices in the field, and available resources. This information will be used to inform the development of the program activities and strategies.
Step 4: Develop Program Activities
Based on the information gathered, the next step is to develop a list of program activities. These activities should be specific, measurable, and directly related to the program goals and objectives. It’s also important to consider the resources required to carry out each activity, such as personnel, funding, and materials.
Step 5: Identify Outputs
Once the program activities have been identified, the next step is to identify the outputs. Outputs are the direct results or products of the program activities, such as the number of individuals served or the number of training sessions provided. Outputs should be specific and measurable and should reflect the direct impact of the program activities.
Step 6: Identify Outcomes
The next step is to identify the outcomes of the program. Outcomes are the changes or effects that result from the program and should be directly related to the program goals and objectives. Outcomes should be specific and measurable and should reflect the desired impact of the program.
Step 7: Identify Impact
The final step is to identify the long-term impact of the program. This should reflect the systemic change or reduction in the prevalence of a specific problem that the program is intended to achieve. The impact should be specific and measurable and should reflect the ultimate goal of the program.
Step 8: Create the Logic Model
Once the components of the logic model have been identified, it’s time to create the visual representation of the model. The logic model should be clear, concise, and easy to understand, and should include all of the components discussed above. The inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact should be represented in a clear and logical manner, showing the relationships between each component.
Step 9: Review and Revise the Logic Model
Once the logic model has been created, it’s important to review and revise it as needed. This may involve refining the program activities, adjusting the outputs, or reassessing the outcomes and impact. The logic model should be a living document that is reviewed and revised as the program evolves and changes.
In conclusion, creating a logic model is an important step in the planning and evaluation of a program or initiative. It can help clarify program goals, objectives, and strategies and provide a clear visual representation of the relationships between inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact. By following the steps outlined above, organizations and individuals can create a logic model that is effective, efficient, and results-oriented.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a logic model?
The purpose of a logic model is to provide a clear and concise overview of a program or initiative, including its goals, objectives, strategies, and intended impact. It is also used to plan, implement, and evaluate the program, ensuring that it is effective, efficient, and results-oriented.
How is a logic model used in program planning and evaluation?
In program planning, a logic model is used to identify and prioritize program activities, allocate resources, and determine the expected outcomes and impact. In evaluation, a logic model is used to measure the effectiveness of the program and assess whether it has achieved its goals and objectives.
What is the difference between inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact in a logic model?
Inputs are the resources needed to carry out the program activities. Activities are the specific actions or steps taken to achieve the program’s goals and objectives. Outputs are the direct results or products of the program activities. Outcomes are the changes or effects that result from the program. Impact is the long-term effect of the program, such as systemic change or a reduction in the prevalence of a specific problem.
How often should a logic model be reviewed and revised?
A logic model should be a living document that is reviewed and revised as needed. This may occur as the program evolves and changes, as new information becomes available, or as the goals and objectives of the program change. Regular review and revision of the logic model helps ensure that the program remains effective, efficient, and results-oriented.
Who uses logic models?
Logic models are used by a variety of stakeholders, including program managers, evaluators, funders, policy makers, and practitioners. They are useful for clarifying the program’s goals, objectives, and intended impact, and for guiding program planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Can a logic model be used for any type of program or initiative?
Yes, a logic model can be used for any type of program or initiative, regardless of size, scope, or focus. It is a versatile tool that can be adapted to a wide range of programs, including health, education, social services, community development, and more.
What is the role of logic models in program evaluation?
In program evaluation, logic models are used to measure the effectiveness of the program and assess whether it has achieved its goals and objectives. They help evaluators identify the program’s strengths and weaknesses, and suggest ways to improve the program in the future.
How does a logic model support evidence-based decision making?
A logic model supports evidence-based decision making by providing a clear and concise overview of the program’s goals, objectives, and intended impact. It helps stakeholders understand the program’s logic and structure, and provides a basis for evaluating program effectiveness and making informed decisions about program design and implementation.
Can a logic model be used to compare different programs or initiatives?
Yes, a logic model can be used to compare different programs or initiatives by highlighting similarities and differences in their goals, objectives, activities, outputs, outcomes, and impact. This information can be used to inform decision making about program design, implementation, and evaluation.
What are the limitations of logic models?
The limitations of logic models include the complexity of program design and implementation, the difficulty of predicting outcomes and impact, and the need for regular review and revision of the logic model. Additionally, logic models are only as effective as the data and information used to create them, so it is important to ensure that the information used is accurate, relevant, and up-to-date.
How can a logic model be used to improve program performance?
A logic model can be used to improve program performance by providing a clear and concise overview of the program’s goals, objectives, and intended impact. It helps program managers identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about program design and implementation. By using a logic model, program managers can ensure that the program remains focused, efficient, and results-oriented.






















![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
