Running a business can be a daunting task, with multiple responsibilities and challenges to juggle simultaneously. From managing daily operations to planning for long-term growth, business owners often find themselves struggling to balance multiple priorities at once. To ensure success in a competitive marketplace, it’s crucial for businesses to keep a close eye on their finances, particularly their expenses.
Payroll expenses are one of the biggest categories of spending for most businesses, making it essential to monitor and manage them effectively. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of payroll reports as a valuable tool for analyzing and improving your business. We’ll discuss how to create and interpret these reports, providing insights and strategies that can help you optimize your payroll and improve your bottom line.
Table of Contents
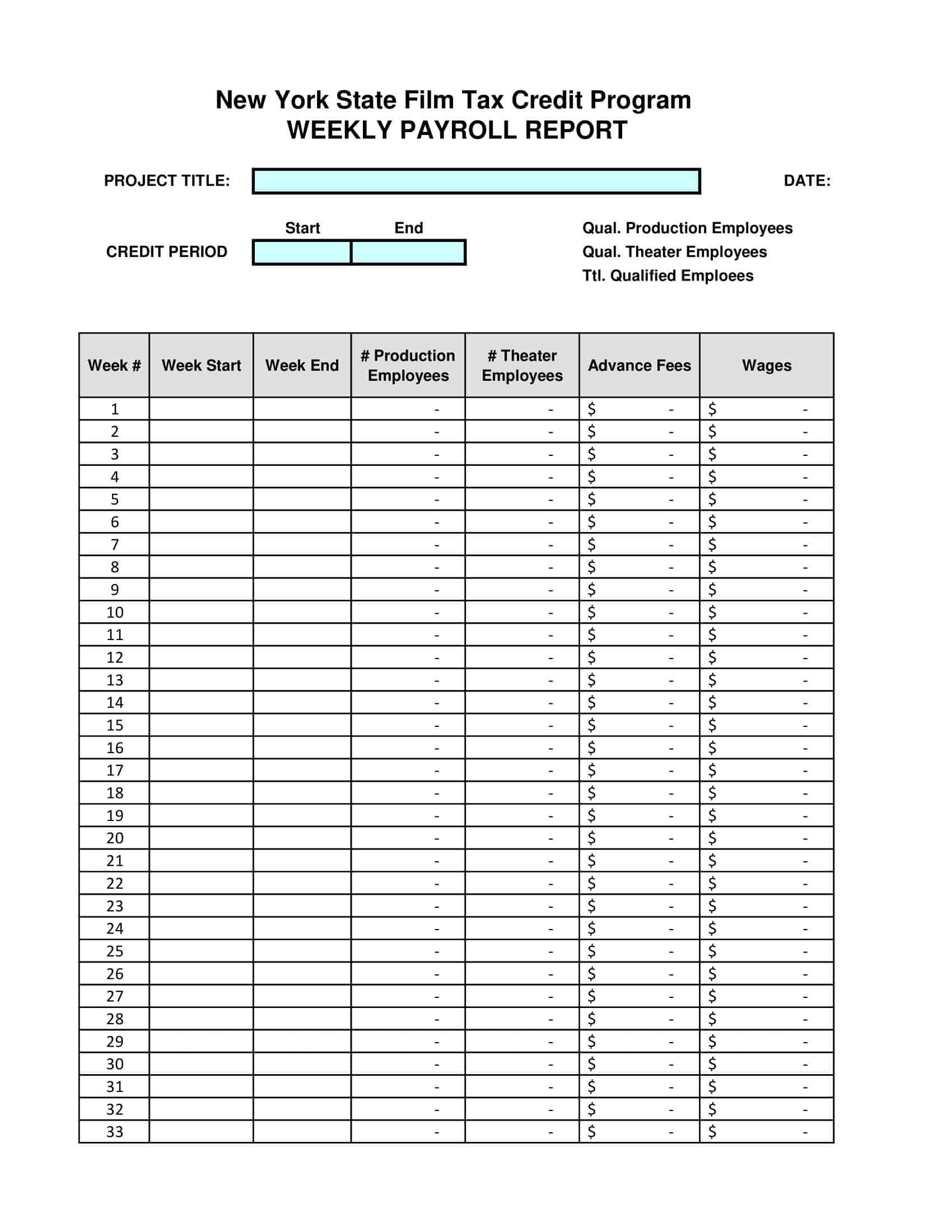
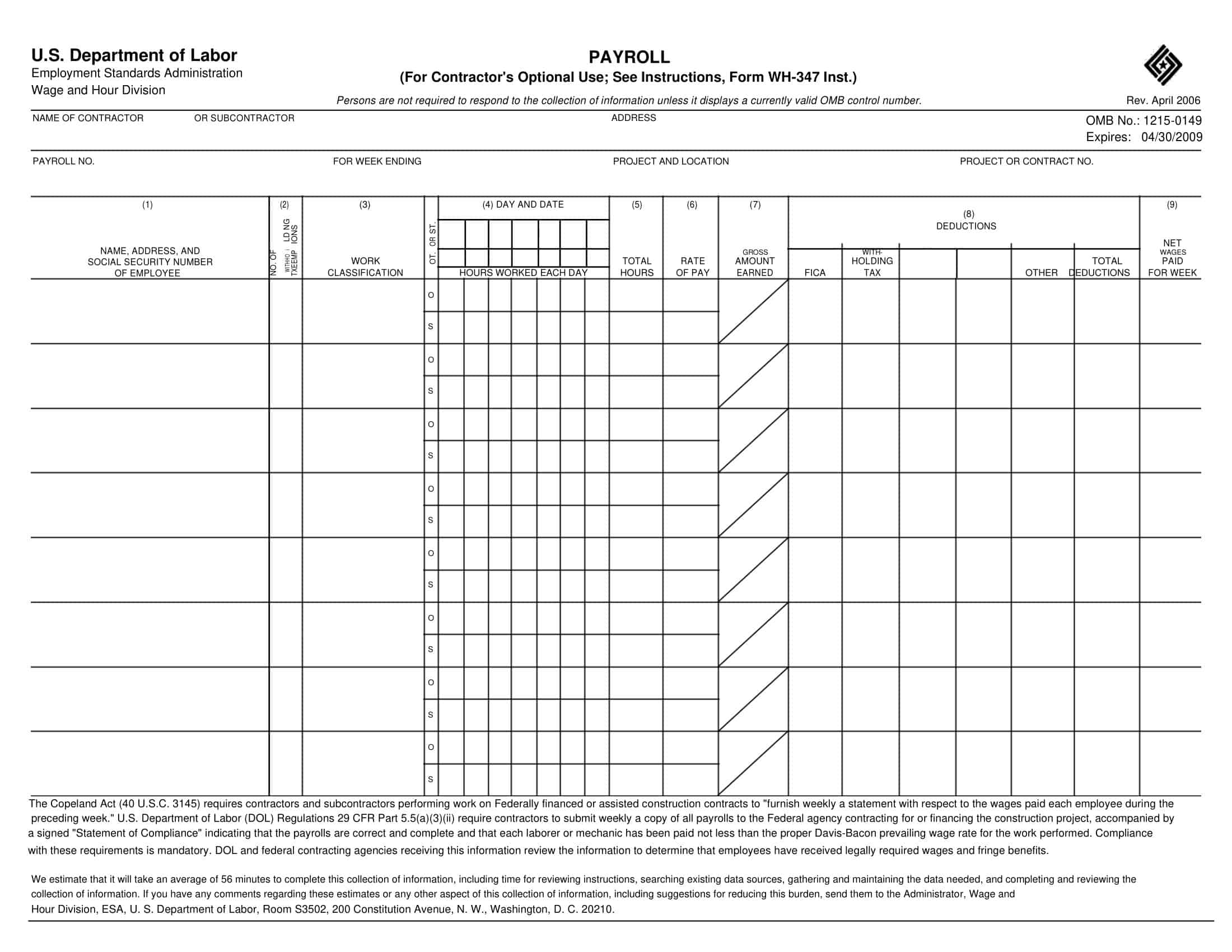
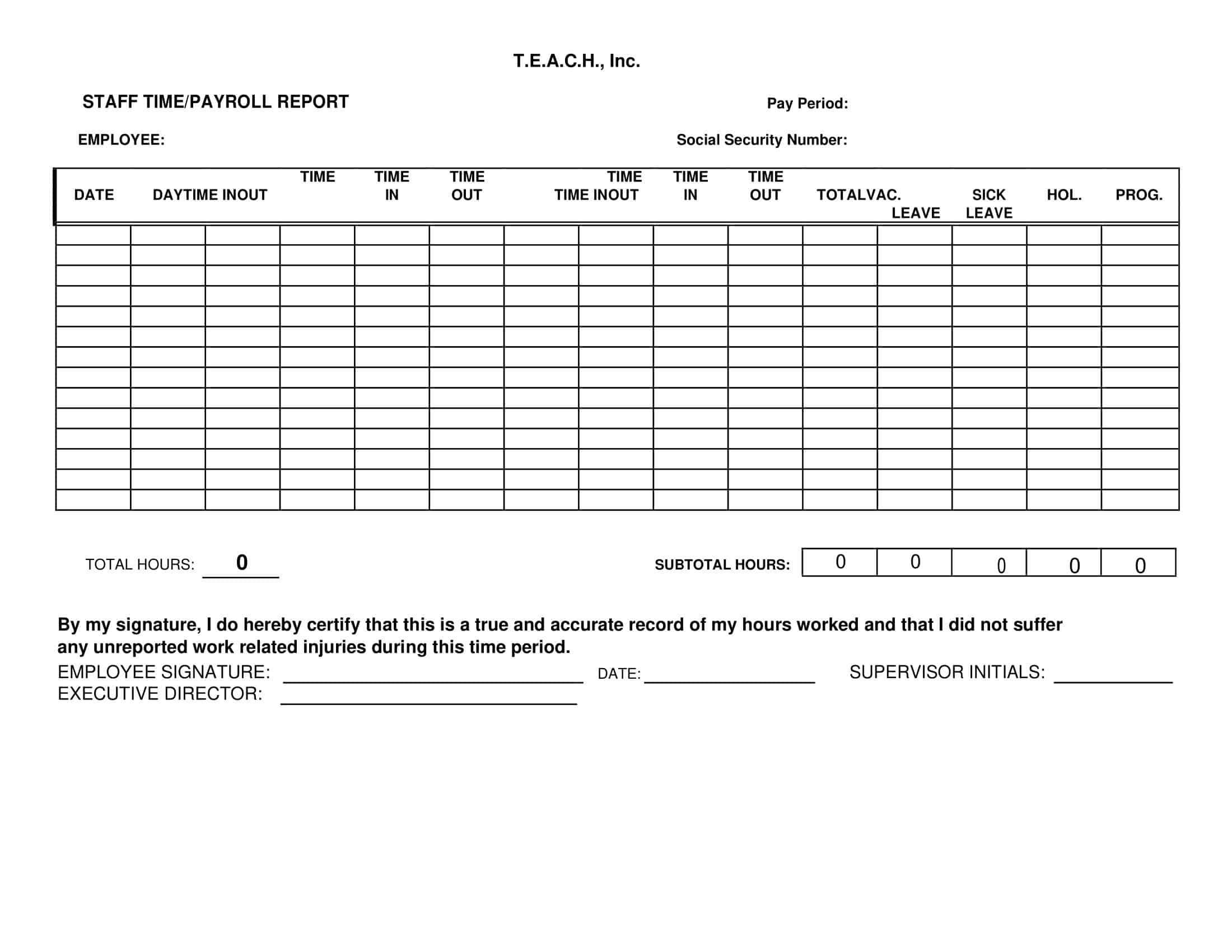
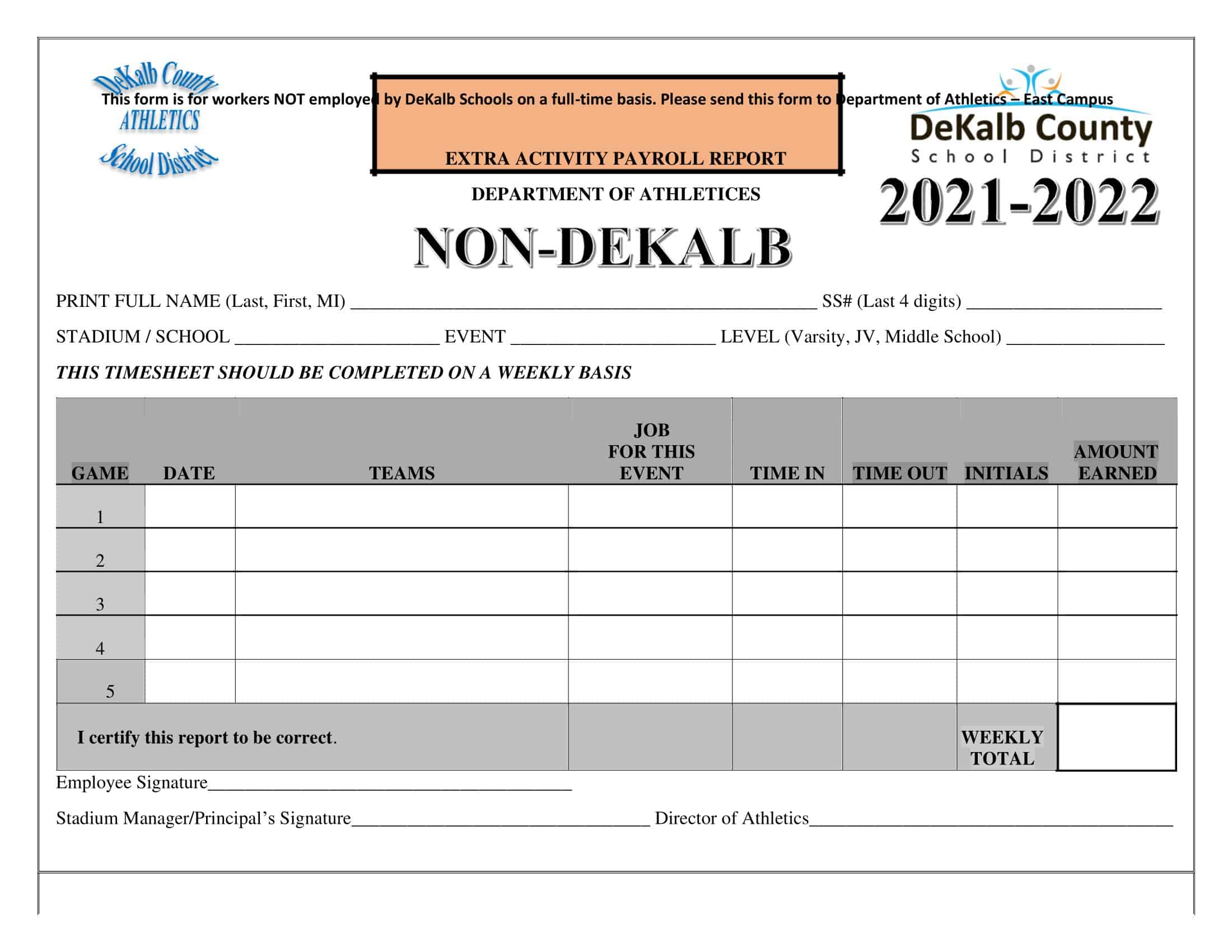
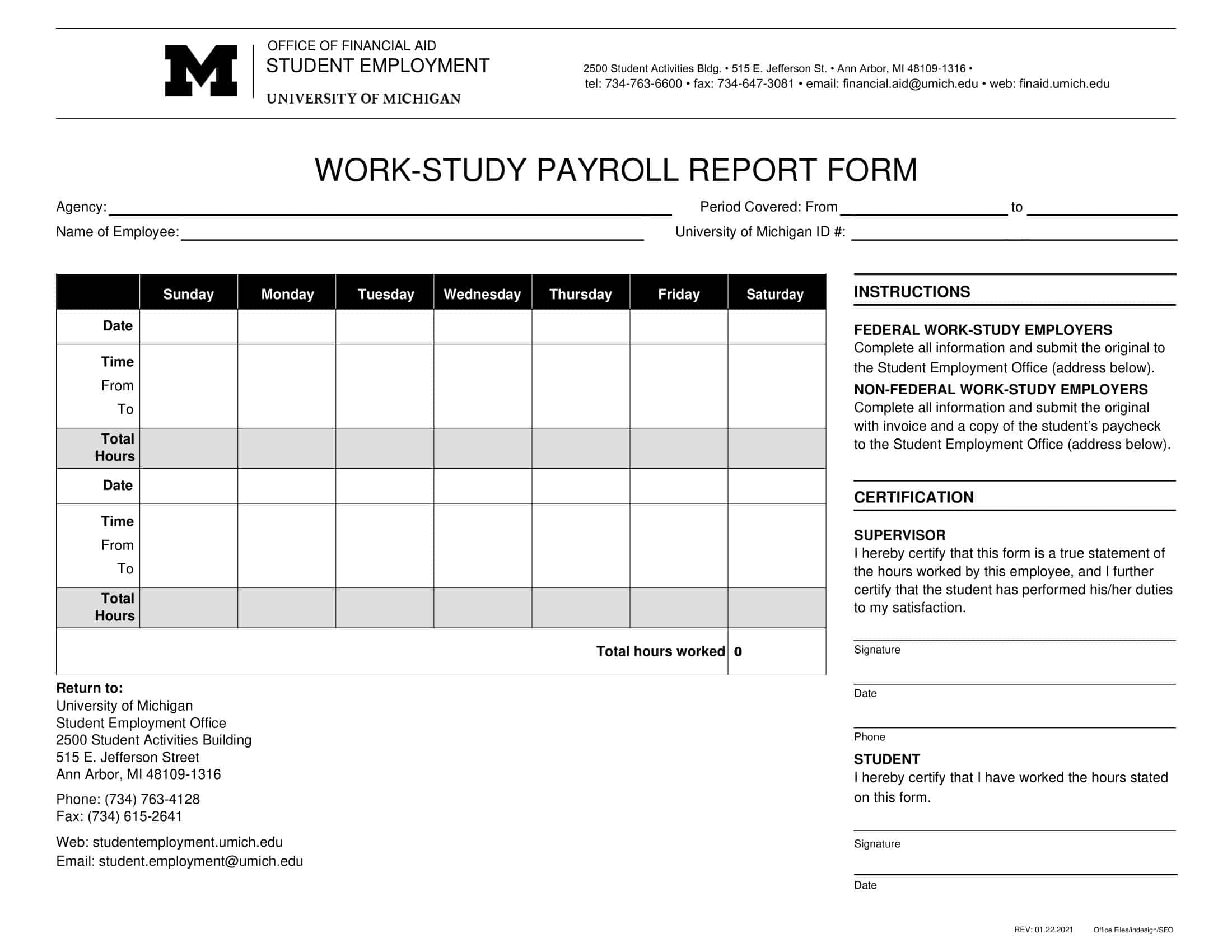
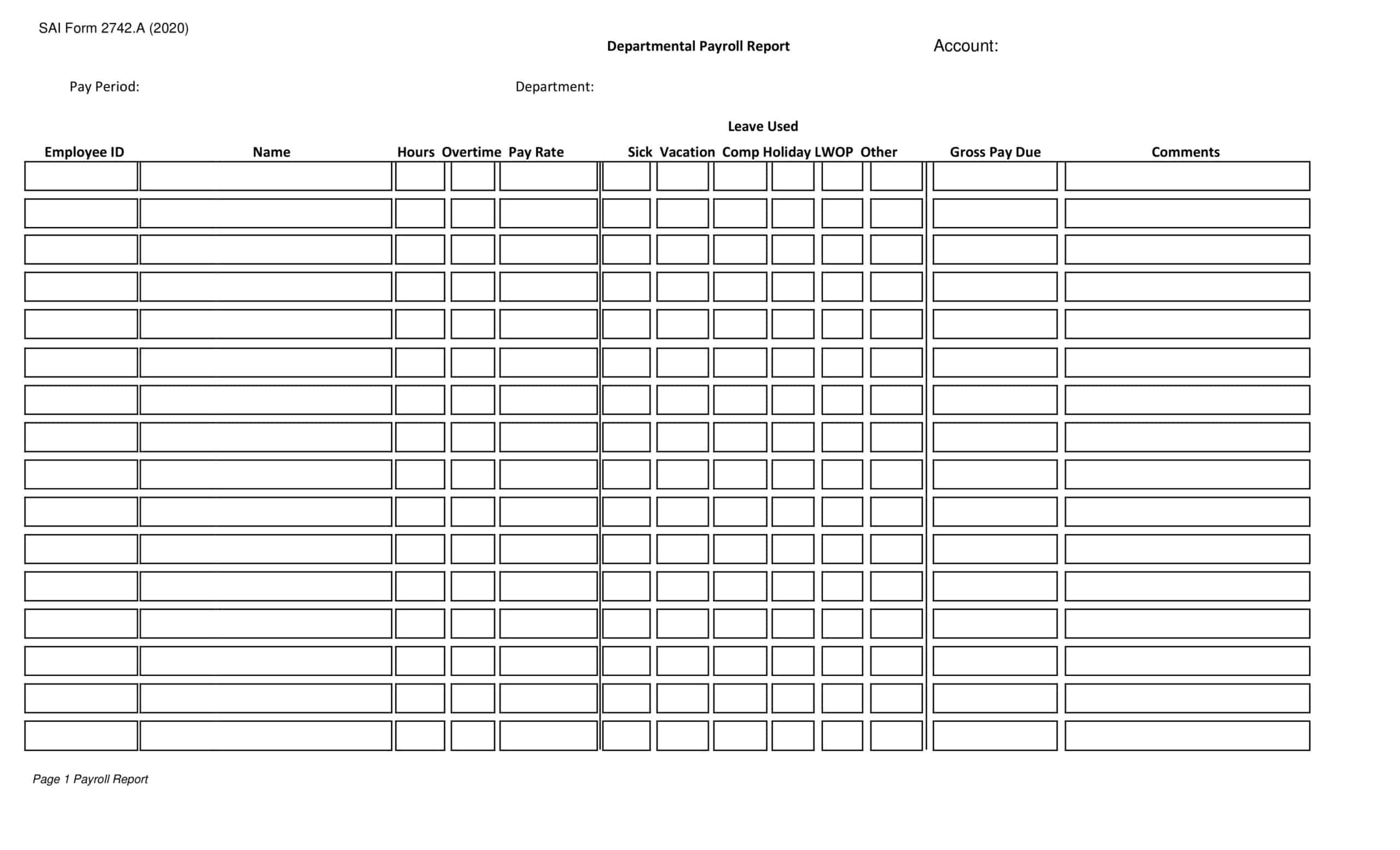
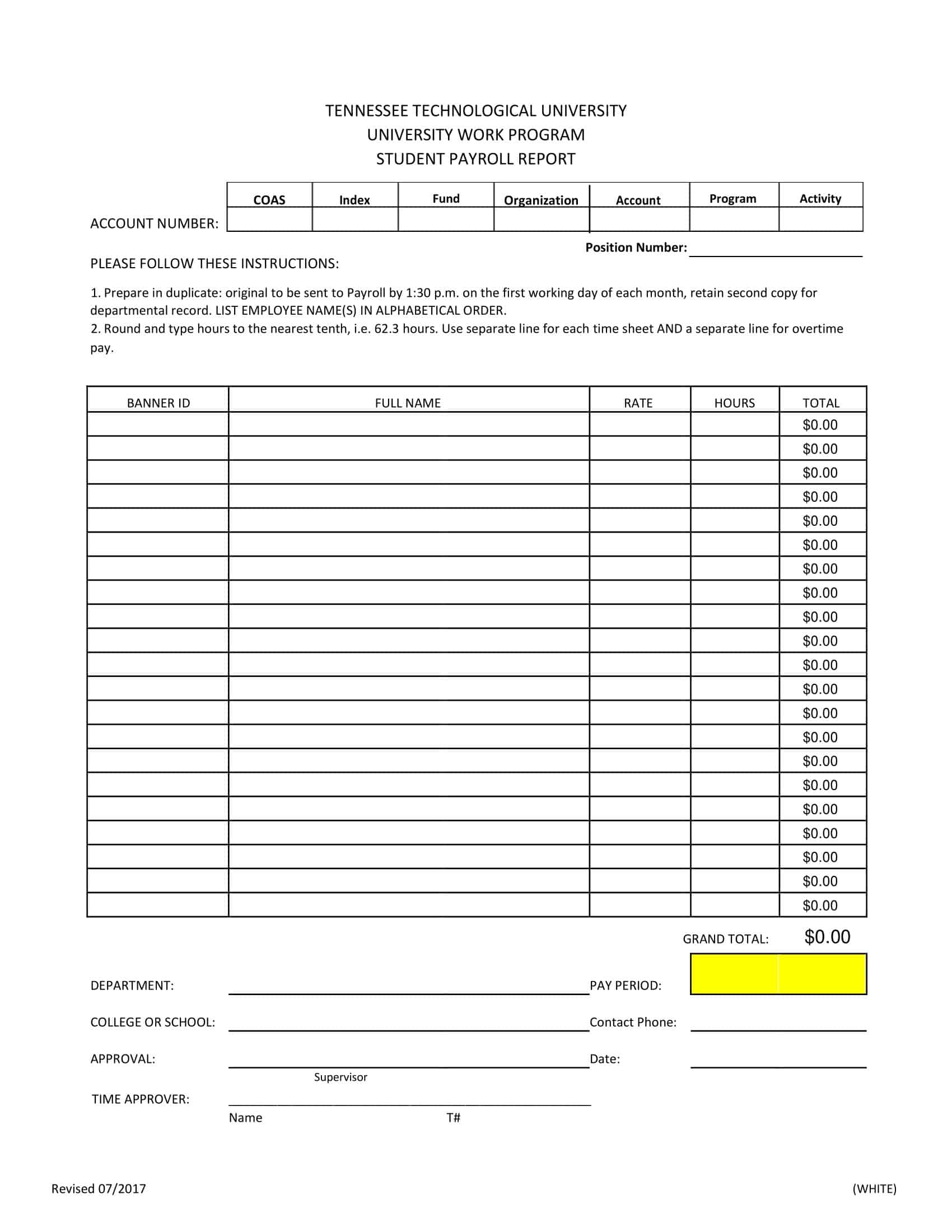
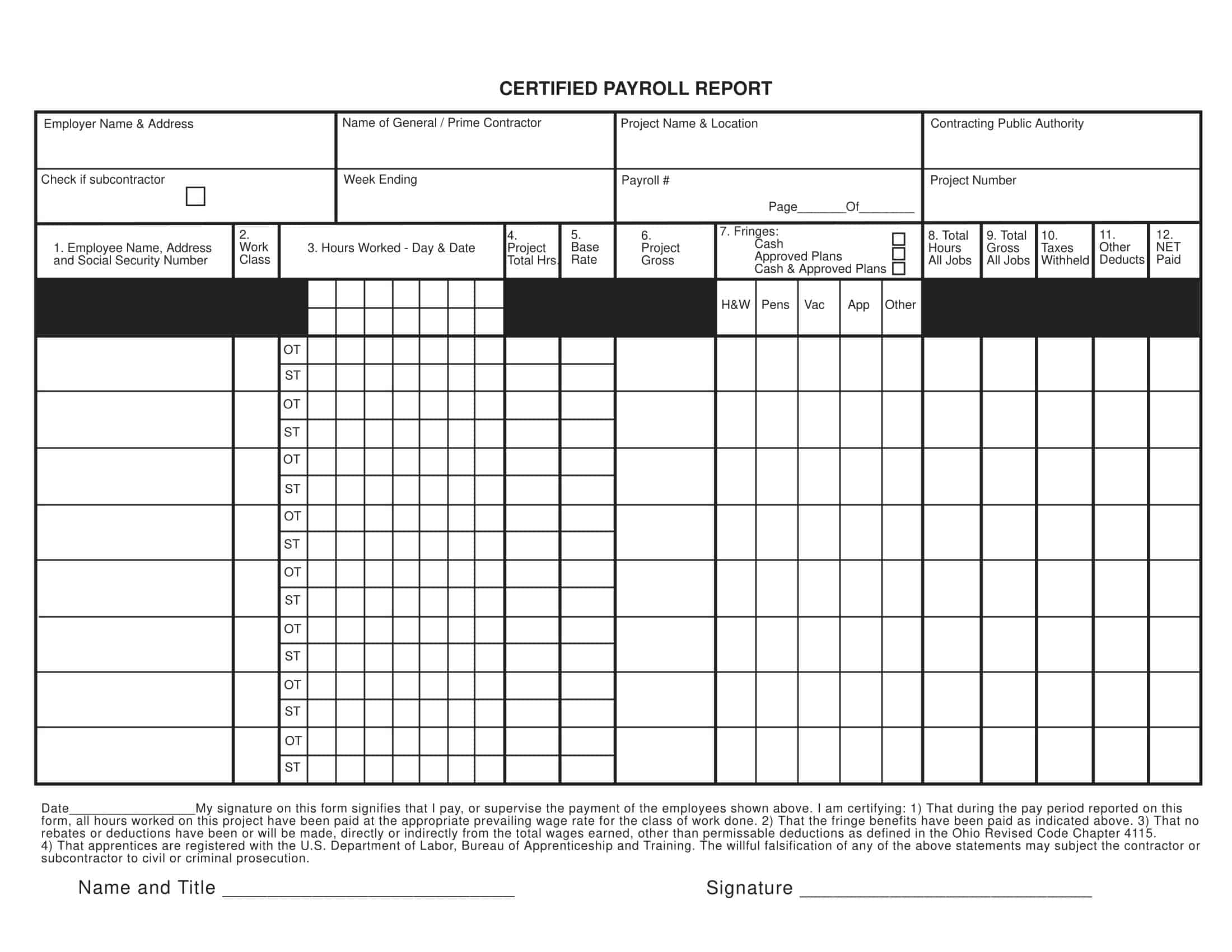
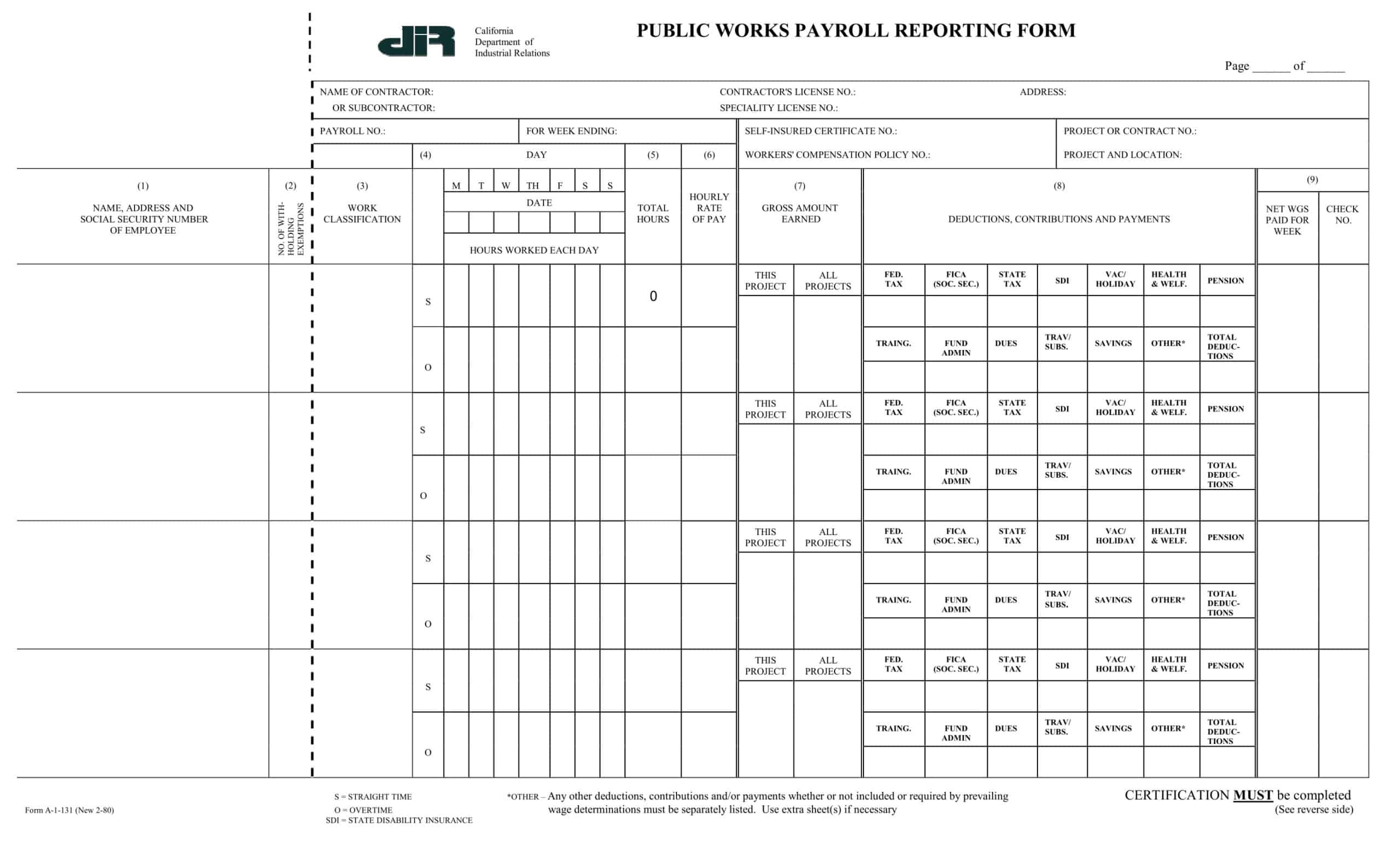
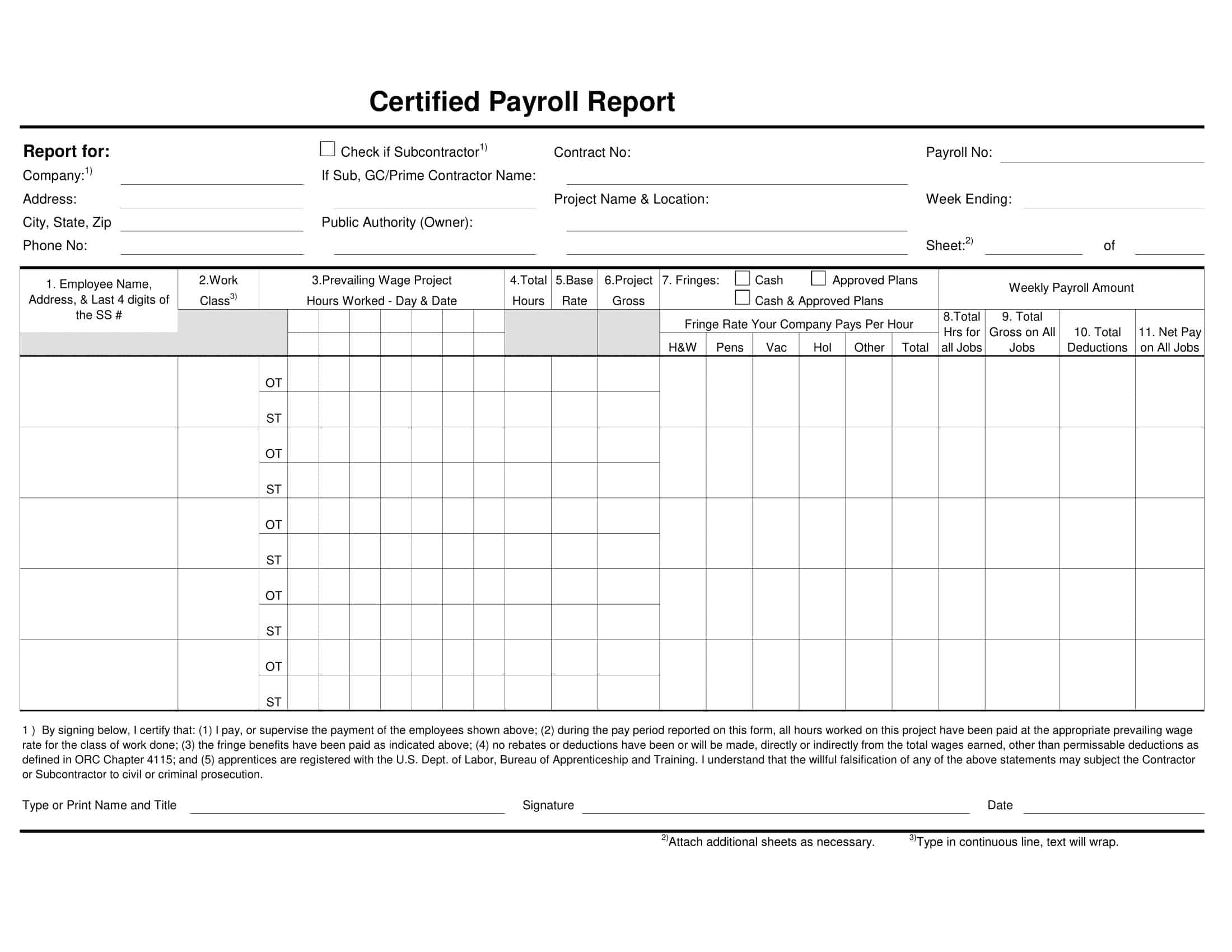
Payroll Report Templates
Payroll Report Templates are comprehensive documents used to summarize and analyze payroll-related information within an organization. These templates provide a structured format for presenting data related to employee compensation, tax withholdings, deductions, and other payroll-related details. Payroll Report Templates ensure consistency, accuracy, and efficiency in managing and analyzing payroll information.
Payroll Report Templates are essential tools for organizations to effectively manage and analyze payroll data. They provide a clear overview of employee compensation, deductions, taxes, and other payroll-related information, allowing organizations to ensure accuracy, transparency, and compliance. By using these templates, organizations can streamline their payroll processes, maintain accurate records, and make informed decisions related to employee compensation and financial management.
What Is a Payroll Report?

A payroll report is a document that outlines various details about the salaries, wages, and bonuses paid to employees within a specific period. These reports provide an overview of all payroll-related expenses incurred by a business, including federal and state taxes, Social Security and Medicare contributions, and other deductions. Payroll reports are typically created by HR or payroll departments within a business, and they are used to track employee compensation and ensure that payments are accurate and timely.
The information contained in a payroll report can be used for a variety of purposes, such as budgeting, financial analysis, and compliance with regulatory requirements. By examining payroll reports, business owners can gain valuable insights into their labor costs, identify trends, and make informed decisions to optimize their payroll and improve their bottom line.
Benefits of Payroll Reports
Payroll reports offer a range of benefits for businesses, including:
Accurate financial reporting: Payroll reports provide a comprehensive overview of labor costs, making it easier for businesses to keep track of their expenses accurately. This can help ensure that financial reports and tax filings are accurate and compliant.
Identifying trends: By analyzing payroll reports over time, business owners can identify trends in labor costs, such as seasonal fluctuations or changes in employee compensation. This information can help businesses plan for future labor costs more effectively.
Budgeting: Payroll reports can be used to create and manage budgets more effectively, allowing businesses to allocate resources more efficiently and make informed decisions about staffing levels and compensation.
Compliance: Payroll reports can help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, such as tax laws and labor laws. By maintaining accurate and detailed payroll records, businesses can avoid penalties and legal disputes.
Performance analysis: Payroll reports can be used to evaluate employee performance and productivity, as well as to identify areas where labor costs could be reduced or optimized.
When Should You Produce Payroll Reports?
Payroll reports should be produced on a regular basis, typically at the end of each pay period. This ensures that businesses have accurate and up-to-date information on labor costs and employee compensation, which can be used for a range of purposes, including financial reporting, budgeting, and compliance.
In addition to producing payroll reports at the end of each pay period, businesses may also generate reports on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis. These reports can be used to track trends in labor costs, identify areas where cost savings can be achieved, and evaluate employee performance over a more extended period.
Types of payroll reports
There are various types of payroll reports that organizations use to keep track of their payroll-related activities. Here are some common types of payroll reports:
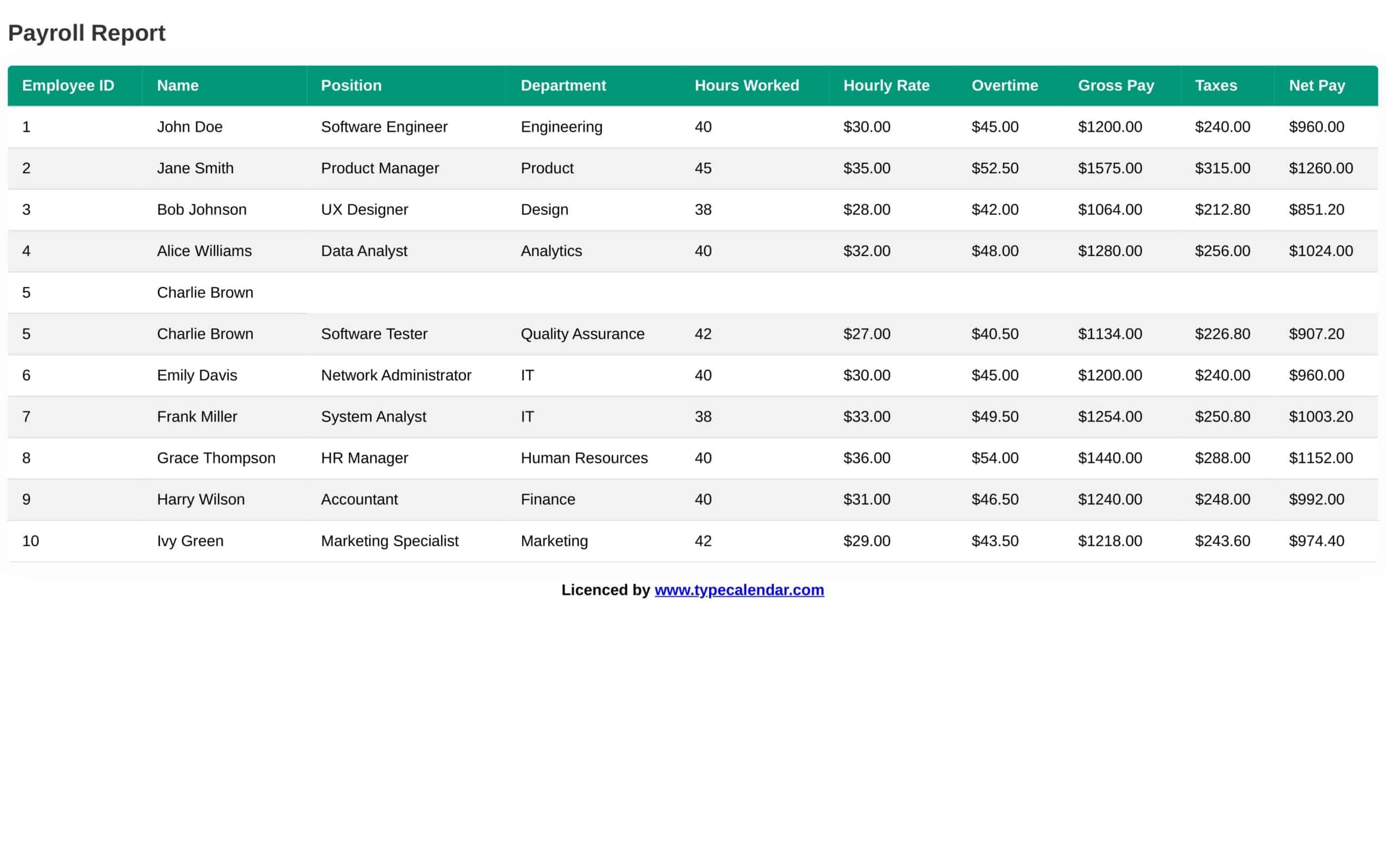
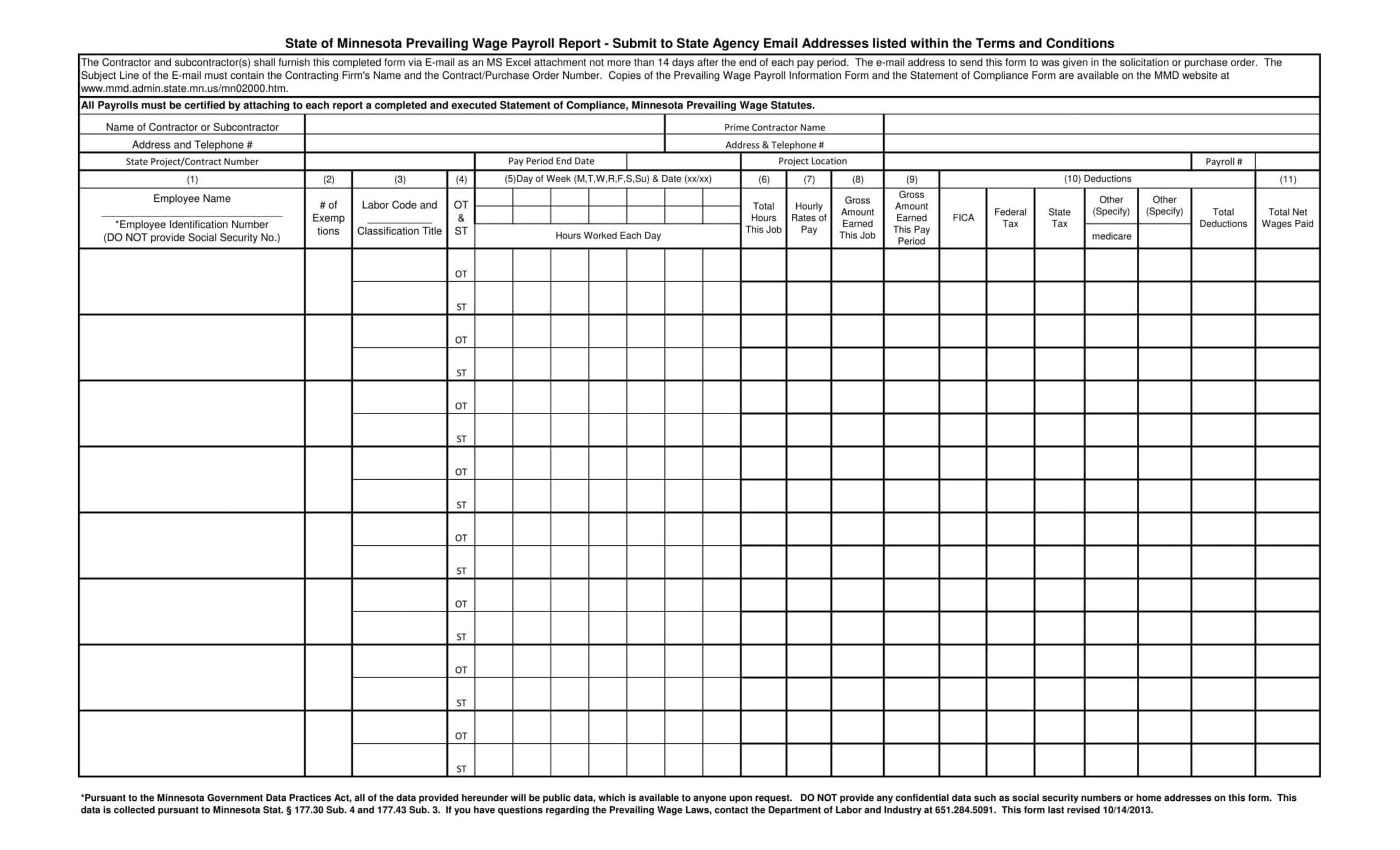
Payroll Register
A payroll register is a specific type of payroll report that provides a detailed record of employee compensation for a specific pay period. This report typically includes information on each employee’s earnings, deductions, and taxes, as well as the employer’s contributions to employee benefits and retirement plans.
The payroll register is an essential tool for businesses that need to track and manage payroll expenses accurately. By providing a detailed breakdown of labor costs, the payroll register enables businesses to identify trends in labor costs, monitor employee compensation and benefits, and ensure compliance with tax and labor laws.
Paycheck Details
A Paycheck Details report provides a detailed breakdown of an employee’s earnings and deductions for a given pay period. The report typically includes the following information:
Employee Information: The report usually starts with the employee’s name, social security number, and pay period covered by the paycheck.
Earnings: The earnings section of the report shows the employee’s gross pay, which is the total amount earned before any taxes or deductions are taken out. This section may also include details of any overtime pay, commissions, bonuses, or other forms of compensation earned during the pay period.
Taxes: The taxes section of the report shows the amount of federal, state, and local income taxes withheld from the employee’s gross pay. This section may also include information about Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as any other taxes or contributions that are required by law.
Deductions: The deductions section of the report shows the amount of money deducted from the employee’s gross pay for items such as insurance premiums, retirement contributions, and other benefits.
Net Pay: The net pay section of the report shows the employee’s take-home pay after all taxes and deductions have been taken out.
Employee Earnings Statement
An employee earnings statement, also known as a pay stub or pay advice, is a document that provides employees with a detailed breakdown of their earnings and deductions for a specific pay period. The statement typically accompanies an employee’s paycheck and provides a record of their compensation for the pay period.
The employee earnings statement is an essential tool for employees, as it allows them to verify that they have been paid accurately and on time. It provides a breakdown of the employee’s gross earnings, taxes withheld, and other deductions, as well as their net pay or take-home pay.
Tax Liability Report
This report summarizes the amount of taxes owed by the employer for a given pay period, including federal and state income tax, Social Security and Medicare taxes, and any other applicable taxes.
The report typically includes the following information:
Employer Information: The report typically begins with the employer’s name, identification number, and the pay period covered by the report.
Federal Income Tax: The report shows the amount of federal income tax withheld from employee paychecks during the pay period.
State and Local Taxes: The report also shows the amount of state and local income taxes withheld from employee paychecks during the pay period.
Social Security and Medicare Taxes: The report includes the employer’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as the amount of taxes withheld from employee paychecks for these programs.
Other Taxes: The report may also include information about other taxes or contributions required by law, such as unemployment insurance or workers’ compensation.
Total Tax Liability: The report summarizes the total tax liability for the pay period, which is the sum of all taxes and contributions owed by the employer.
Tax Liability Reports are important documents for employers to track their payroll tax obligations, ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, and avoid penalties and fines for late or incorrect tax payments. Employers may be required to file these reports with government agencies, such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or state tax departments, depending on their specific tax requirements.
Payroll Summary Report
A payroll summary report is a document that provides an overview of payroll expenses for a specific pay period. It typically includes information on employee compensation, taxes, and deductions, as well as the employer’s contributions to employee benefits and retirement plans.
The payroll summary report is an essential tool for businesses that need to manage payroll expenses effectively. It provides a detailed breakdown of labor costs, which can be used to identify trends in labor expenses and to monitor employee compensation and benefits. This information can be used to make informed decisions about staffing and compensation, as well as to ensure compliance with tax and labor laws.
Year-to-Date (YTD) Report
A year-to-date (YTD) report is a document that provides a summary of payroll information for an employee from the beginning of the calendar year to the current date. The report typically includes information on employee earnings, taxes, and deductions, as well as the employer’s contributions to employee benefits and retirement plans.
The YTD report is an essential tool for businesses that need to track and manage payroll expenses effectively. By providing a detailed record of an employee’s compensation for the year-to-date, the report can be used to identify trends in labor costs, monitor employee compensation and benefits, and ensure compliance with tax and labor laws.
Benefits Report
This report provides an overview of employee benefits, including retirement plans, healthcare benefits, and other forms of compensation.
The report typically includes the following information:
Employee Information: The report usually starts with the employee’s name, social security number, and other identifying information.
Benefits Overview: The report provides a summary of the benefits offered by the organization, including healthcare, retirement plans, paid time off, and other forms of compensation.
Healthcare Benefits: The report includes details of the organization’s healthcare benefits program, including information about the types of plans offered, the cost to employees and the organization, and any restrictions or limitations.
Retirement Benefits: The report provides information about the organization’s retirement plans, including 401(k) plans, pension plans, and other forms of retirement benefits. This section may include details of the organization’s contributions to these plans and any matching contributions offered to employees.
Paid Time Off: The report includes information about the organization’s policies regarding paid time off, including vacation days, sick leave, and holidays. This section may include details of the organization’s accrual policies and any restrictions or limitations on the use of paid time off.
Other Forms of Compensation: The report may also include information about other forms of compensation offered by the organization, such as stock options, profit sharing, or other incentives.
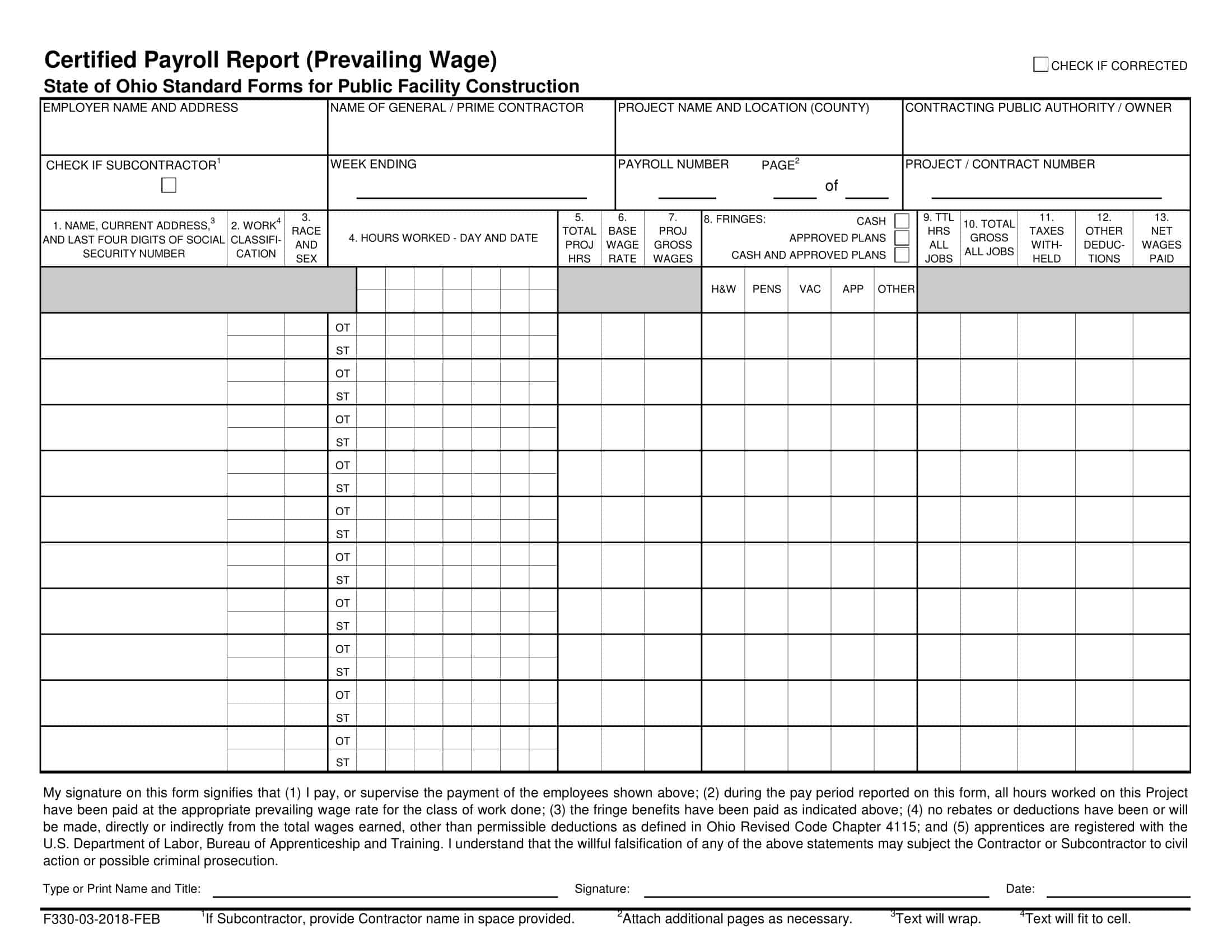
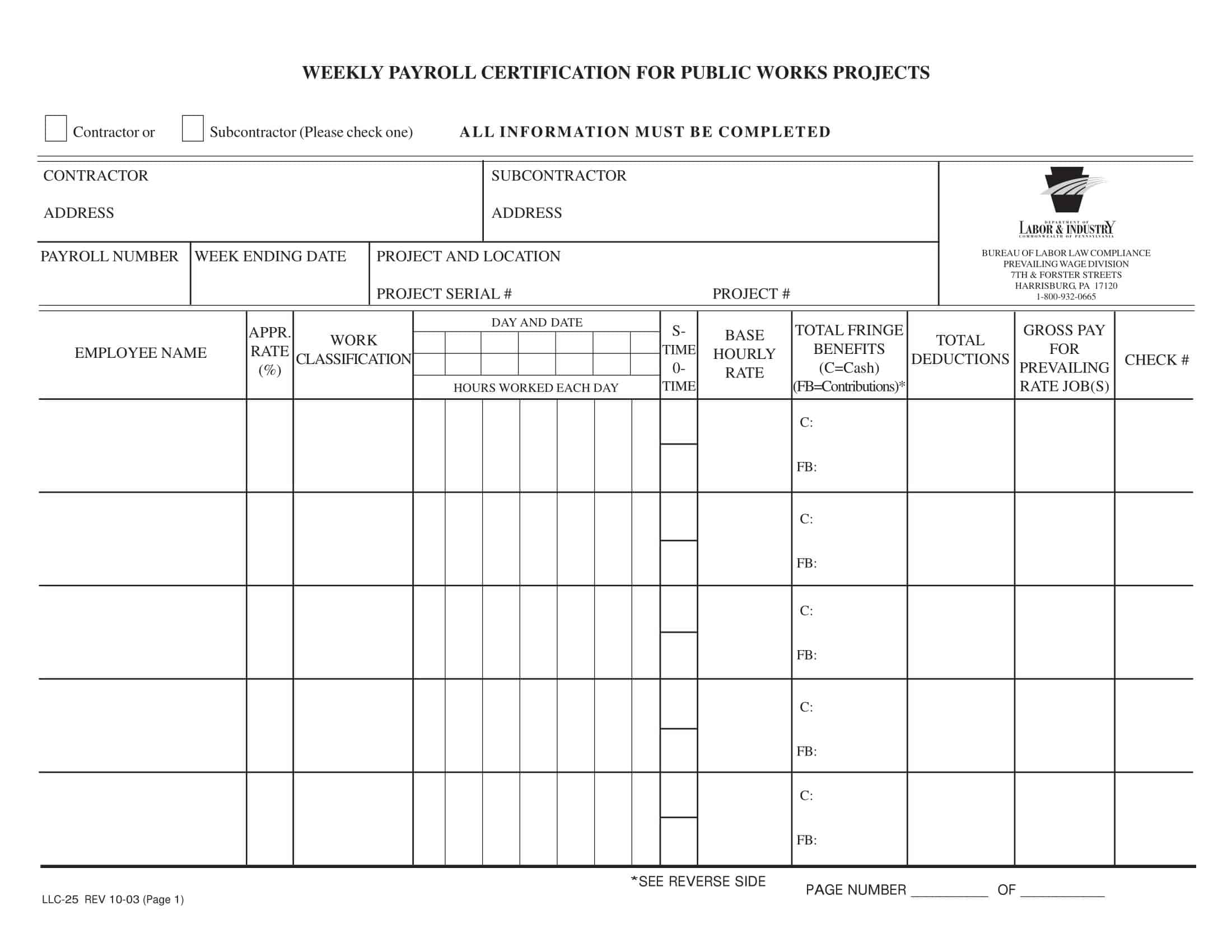
Wage and Hour Compliance Report
A wage and hour compliance report is a document that provides an overview of a company’s compliance with federal and state labor laws related to employee compensation, including minimum wage and overtime requirements. The report typically includes information on employee hours worked, compensation, and overtime pay, as well as compliance with record-keeping requirements.
The wage and hour compliance report is an essential tool for businesses that need to ensure compliance with labor laws and avoid potential penalties and lawsuits related to wage and hour violations. It can be used to identify areas of non-compliance, monitor employee compensation and benefits, and ensure that accurate records are being kept.
Typically, the wage and hour compliance report includes the following information:
- Total hours worked by each employee, broken down by week or pay period
- Employee compensation, including regular pay and any bonuses or other compensation
- Overtime hours worked by each employee, if applicable
- Overtime pay, including the calculation of overtime pay based on federal and state requirements
- Compliance with record-keeping requirements, including the retention of accurate and complete payroll records
- Any potential violations of wage and hour laws, such as failure to pay minimum wage or overtime, or improper record-keeping practices
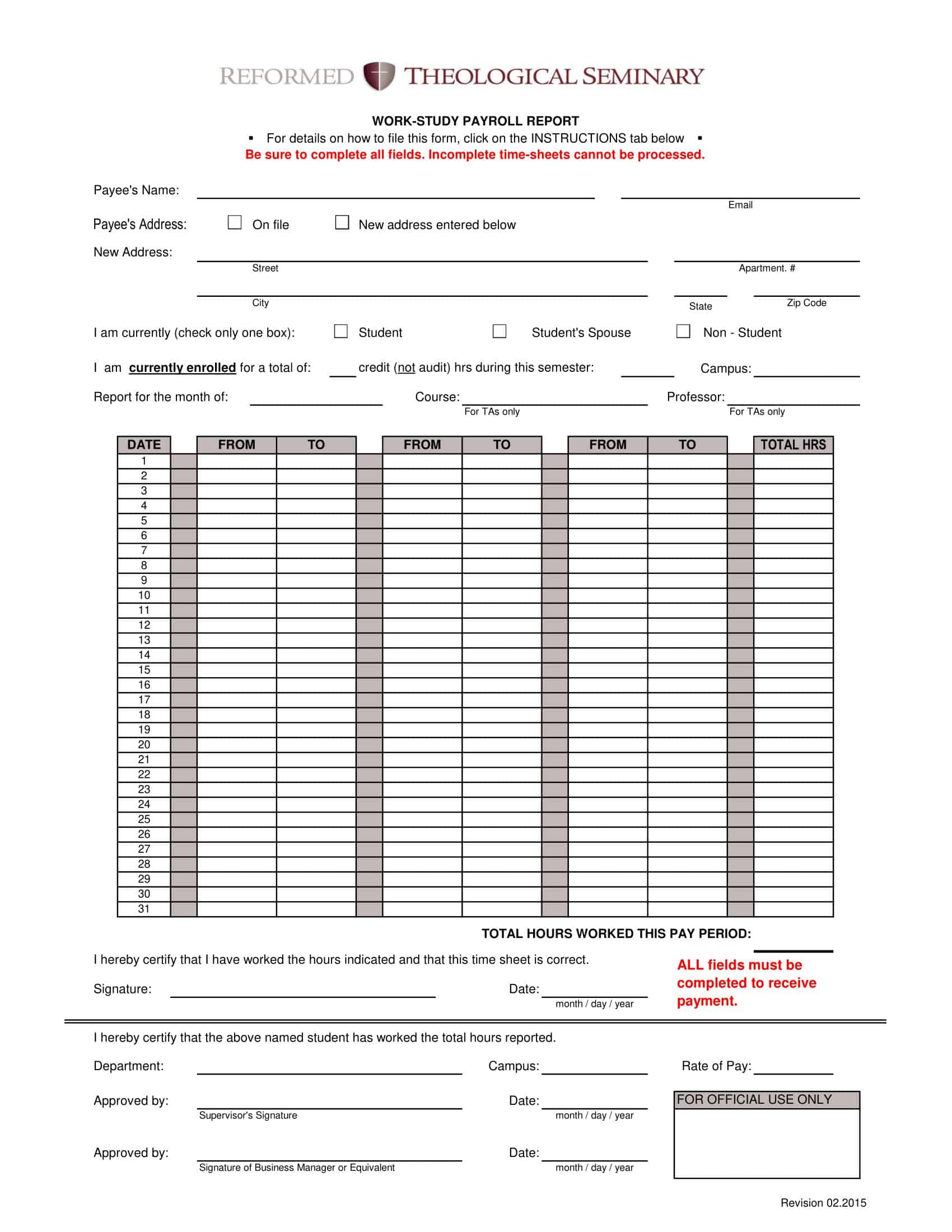
What is included in a payroll report?
A payroll report is a document that provides information about payroll expenses for a specific period, such as a pay period or a fiscal year. The specific information included in a payroll report can vary depending on the type of report being generated and the needs of the business. However, some common information that may be included in a payroll report includes:
Employee information: This includes details about each employee, such as their name, address, social security number, job title, and pay rate.
Compensation: This includes the total amount paid to each employee for the pay period, including regular wages, overtime pay, and any bonuses or commissions.
Tax withholdings: This includes the amounts withheld from employee paychecks for federal, state, and local taxes, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Deductions: This includes any deductions from employee paychecks, such as for health insurance, retirement plans, or garnishments.
Employer contributions: This includes any contributions made by the employer to employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, or other benefits.
Payroll expenses: This includes the total amount of money paid by the employer for payroll expenses, including employee compensation, taxes, and benefits.
Year-to-date totals: This includes the total amounts paid to each employee for the current fiscal year-to-date, as well as the total payroll expenses for the fiscal year-to-date.
The specific information included in a payroll report can vary depending on the needs of the business and the type of report being generated. However, the main goal of a payroll report is to provide a comprehensive overview of payroll expenses, which can be used to monitor employee compensation and benefits, ensure compliance with tax and labor laws, and make informed decisions about staffing and compensation.
What payroll reports do employers need to file?
The payroll reports that employers need to file may vary depending on their specific requirements and the applicable laws and regulations in their location. However, here are some common payroll reports that employers may need to file:
Form 941
Employers in the United States are required to file Form 941, which is a quarterly tax return that reports the employer’s share of Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as federal income tax withholding from employee paychecks.
Form W-2
Employers are required to provide employees with a Form W-2, which reports the employee’s earnings and tax withholdings for the year. Employers must also file a copy of the Form W-2 with the Social Security Administration.
State and Local Tax Returns
Employers may also be required to file state and local tax returns, which report the employer’s share of state and local income taxes, as well as any other taxes or contributions required by law.
Unemployment Insurance Reports
Employers are required to report their payroll information to their state’s unemployment insurance program, which is used to calculate the employer’s unemployment insurance tax liability.
Form 1099
Employers who hire independent contractors may need to file a Form 1099, which reports the payments made to the contractor during the year.
Form 940
Employers in the United States who are subject to federal unemployment tax (FUTA) must file Form 940, which reports their FUTA tax liability for the year.
Form 945
Employers who withhold federal income tax from nonpayroll payments, such as pensions, annuities, and gambling winnings, must file Form 945.
Form 5500
Employers who offer a retirement plan, such as a 401(k), must file Form 5500, which reports information about the plan’s operation, funding, and investments.
Electronic Filing Requirements
In some locations (Alaska), employers may be required to file payroll reports electronically, rather than on paper.
How to Create a Payroll Report
Creating a payroll report can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it’s essential for any business that wants to monitor employee compensation and benefits, ensure compliance with tax and labor laws, and make informed decisions about staffing and compensation. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps of creating a payroll report, from collecting the necessary data to generating and analyzing the report.
Step 1: Gather Employee Data
The first step in creating a payroll report is to gather employee data, including information on each employee’s compensation, tax withholdings, and benefits. This information can typically be found in your payroll software or system, but you may also need to collect data from other sources, such as employee records or benefit providers.
Some of the key employee data that you’ll need to collect for your payroll report includes:
- Employee name and identification number
- Pay rate and compensation information, including regular pay, overtime pay, and any bonuses or commissions
- Tax withholding information, including federal, state, and local taxes, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes
- Deductions, such as for health insurance, retirement plans, or garnishments
- Employer contributions to employee benefits, such as health insurance or retirement plans
Once you’ve collected this employee data, you’ll need to organize it in a way that makes it easy to generate a payroll report.
Step 2: Choose Your Reporting Period
The next step in creating a payroll report is to choose your reporting period. This will typically be a specific pay period, such as a week, bi-weekly, or monthly, but it can also be a fiscal year or other time period.
The reporting period that you choose will depend on the needs of your business and the type of report that you’re generating. For example, if you’re generating a payroll register report, you’ll need to choose a specific pay period to report on.
Step 3: Select Your Reporting Format
Once you’ve chosen your reporting period, you’ll need to select your reporting format. This will depend on the type of report that you’re generating and the needs of your business.
Each reporting format will require different data and have different reporting requirements, so it’s important to choose the format that best meets the needs of your business.
Step 4: Generate Your Report
Once you’ve collected your employee data, chosen your reporting period, and selected your reporting format, it’s time to generate your payroll report.
This will typically involve using your payroll software or system to generate the report, but you may also need to use spreadsheets or other tools to organize and analyze the data.
Some key steps in generating your payroll report may include:
- Importing employee data into your payroll software or system
- Choosing your reporting period and reporting format
- Running the report and reviewing the data for accuracy
- Exporting the report to a format that can be easily shared or analyzed
- Saving a copy of the report for future reference
It’s important to review the data in your payroll report carefully to ensure that it’s accurate and complete. This may involve reviewing employee data for errors or discrepancies, double-checking calculations, and verifying compliance with tax and labor laws.
Step 5: Analyze Your Report
The final step in creating a payroll report is to analyze the data to gain insights into your business and make informed decisions about compensation, benefits, and staffing.
Some key steps in analyzing your payroll report may include:
- Reviewing payroll expenses and identifying areas for cost savings or optimization
- Comparing employee compensation and benefits to industry benchmarks or market rates to ensure that your business remains competitive
- Analyzing overtime pay and hours worked to identify opportunities for staffing adjustments or process improvements
- Verifying compliance with tax and labor laws and making any necessary adjustments to ensure that your business remains in compliance
Analyzing your payroll report can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it’s essential for any business that wants to make informed decisions about compensation and benefits, optimize payroll expenses, and ensure compliance with tax and labor laws.
Tips for Creating a Payroll Report
Creating a payroll report can be a complex and time-consuming process, but there are some tips and best practices that can help you streamline the process and ensure that your report is accurate and complete.
Here are some tips for creating a payroll report:
- Use a reliable payroll system or software that can handle complex calculations and ensure compliance with tax and labor laws.
- Double-check your data for accuracy and completeness to ensure that your report is reliable and accurate.
- Choose your reporting format carefully to ensure that your report meets the needs of your business and provides the insights and information that you need.
- Review your report carefully to identify areas for optimization, cost savings, or compliance improvements.
Document your payroll report process and procedures to ensure that you can easily replicate the process in the future and make adjustments as needed.
FAQs
How often should employers run payroll reports?
The frequency of payroll reports may vary depending on an organization’s specific requirements and the applicable laws and regulations in their location. However, many organizations run payroll reports on a regular basis, such as weekly, biweekly, or monthly.
Who uses payroll reports?
Payroll reports may be used by a variety of individuals and organizations, including employers, human resources professionals, accountants, tax professionals, and government agencies.
What are the consequences of failing to file payroll reports?
Failing to file payroll reports accurately and on time can result in penalties, fines, and other legal consequences. Additionally, it can create financial and operational risks for an organization.
How are payroll reports typically generated?
Payroll reports can be generated using various methods, depending on an organization’s specific needs and resources. Many organizations use payroll software that generates reports automatically based on data entered into the system. Other organizations may use spreadsheets or other manual methods to compile and analyze payroll data.
Can payroll reports be customized to an organization’s needs?
Yes, payroll reports can typically be customized to an organization’s specific needs. Most payroll software allows for the customization of reports based on the type of information needed, the frequency of reporting, and other factors.
How long should payroll reports be kept on file?
The length of time that payroll reports should be kept on file may vary depending on the applicable laws and regulations in an organization’s location. However, it is generally recommended that employers keep payroll records for a minimum of three years.
What should an organization do if it identifies errors on a payroll report?
If errors are identified on a payroll report, the organization should take steps to correct the errors as soon as possible. This may involve reviewing and adjusting the payroll data, issuing corrected paychecks, or filing amended payroll reports. It is important for organizations to communicate any errors or discrepancies to employees and ensure that they are resolved in a timely and compliant manner.
How can an organization ensure the accuracy of its payroll reports?
To ensure the accuracy of payroll reports, organizations should establish sound payroll processes and controls, use reliable payroll software or systems, and regularly review and reconcile payroll data. Additionally, it is important to stay up-to-date with changes to applicable laws and regulations and to consult with qualified experts as needed.
Can payroll reports be used for other purposes besides payroll management?
Yes, payroll reports may be used for other purposes besides payroll management. For example, they may be used for financial reporting, budgeting and forecasting, or compliance purposes. Additionally, the data included in payroll reports may be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, or other insights that can be used to improve an organization’s performance or operations.


































![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Annual Report Design Templates [PDF, Excel] 2 Annual Report](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Annual-Report-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Annual-Report-120x120.jpg 120w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Annual-Report-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 3 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
