In the world of business and commerce, effective procurement strategies are integral to the successful operation and growth of any organization. Among these strategies, a Request for Quote (RFQ) stands as a critical tool employed by businesses to solicit competitive bids from potential suppliers or vendors.
This article explores the RFQ process, its importance, and how it contributes to making informed purchasing decisions. As we delve into the intricacies of the RFQ process, we’ll discuss its advantages, potential pitfalls, and best practices to help businesses maximize their procurement efficiency and, consequently, their profitability.
Table of Contents
What is a request for quotation document?

A Request for Quotation (RFQ) is a standard business document typically used in procurement processes where an organization invites suppliers into a bidding process to bid on specific products or services. The RFQ represents a more formalized solicitation for vendors and suppliers, often indicating detailed specifications about the desired goods or services.
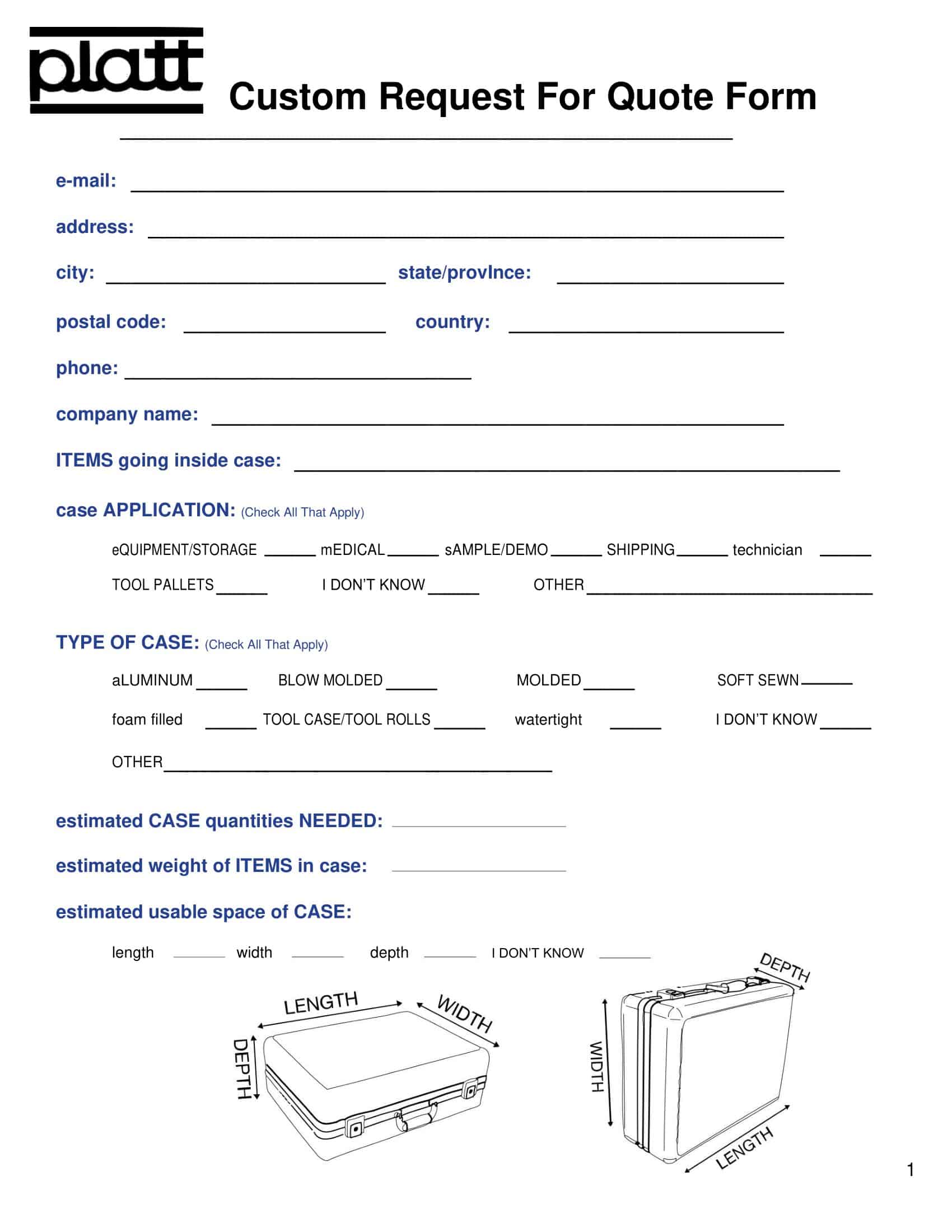
Request for Quote Templates
Streamline your procurement process and obtain accurate quotes with our comprehensive collection of Request for Quote Templates. Whether you’re a business seeking goods or services, our templates provide a structured framework for requesting competitive quotes from potential vendors. These customizable and printable templates include sections for specifying the required products or services, quantities, delivery timelines, and any additional specifications.
By using our Request for Quote Templates, you can efficiently gather multiple quotes, compare offerings, and make informed purchasing decisions. Save time, simplify your procurement process, and ensure a fair and transparent bidding process with our user-friendly templates. Download now and streamline your sourcing efforts to secure the best deals for your business.
When to use a request for quote?
A Request for Quote (RFQ) is typically used under the following circumstances:
Standardized Goods or Services: RFQs are ideal when you’re sourcing standardized or commoditized products or services, where quality and specifications are unlikely to vary significantly between suppliers.
Price is a Key Determinant: When price is the primary decision-making factor, RFQs are useful. They allow for easy comparison of bids from different suppliers based purely on cost.
Large Orders: If you’re placing a large order where economies of scale come into play, an RFQ can be beneficial. Vendors are likely to provide more competitive pricing for larger orders.
Repeat Purchases: If the products or services are bought frequently or on a recurring basis, RFQs help in standardizing the process and making it more efficient over time.
Clear Requirements: When the specifications of the goods or services are clear and detailed, an RFQ can help get precise quotes from vendors.
What is the RFQ process?
The Request for Quotation (RFQ) process is a key part of many businesses’ procurement strategies. It involves several well-defined steps:
Identify Needs: The first step in the RFQ process involves identifying the specific needs or requirements of the company. This could be for goods, services, or any combination thereof. The company must have a clear understanding of what it needs before it can ask suppliers for quotations.
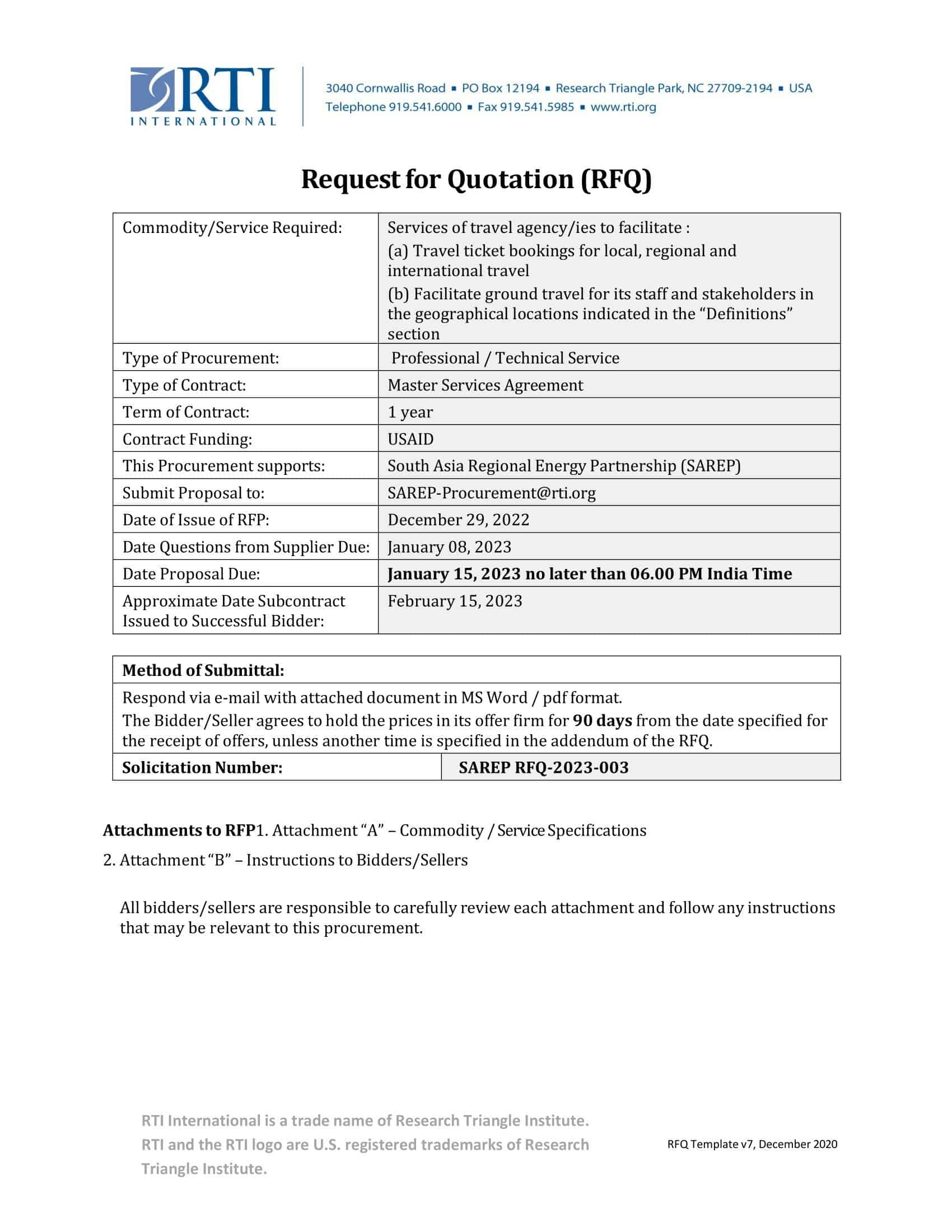
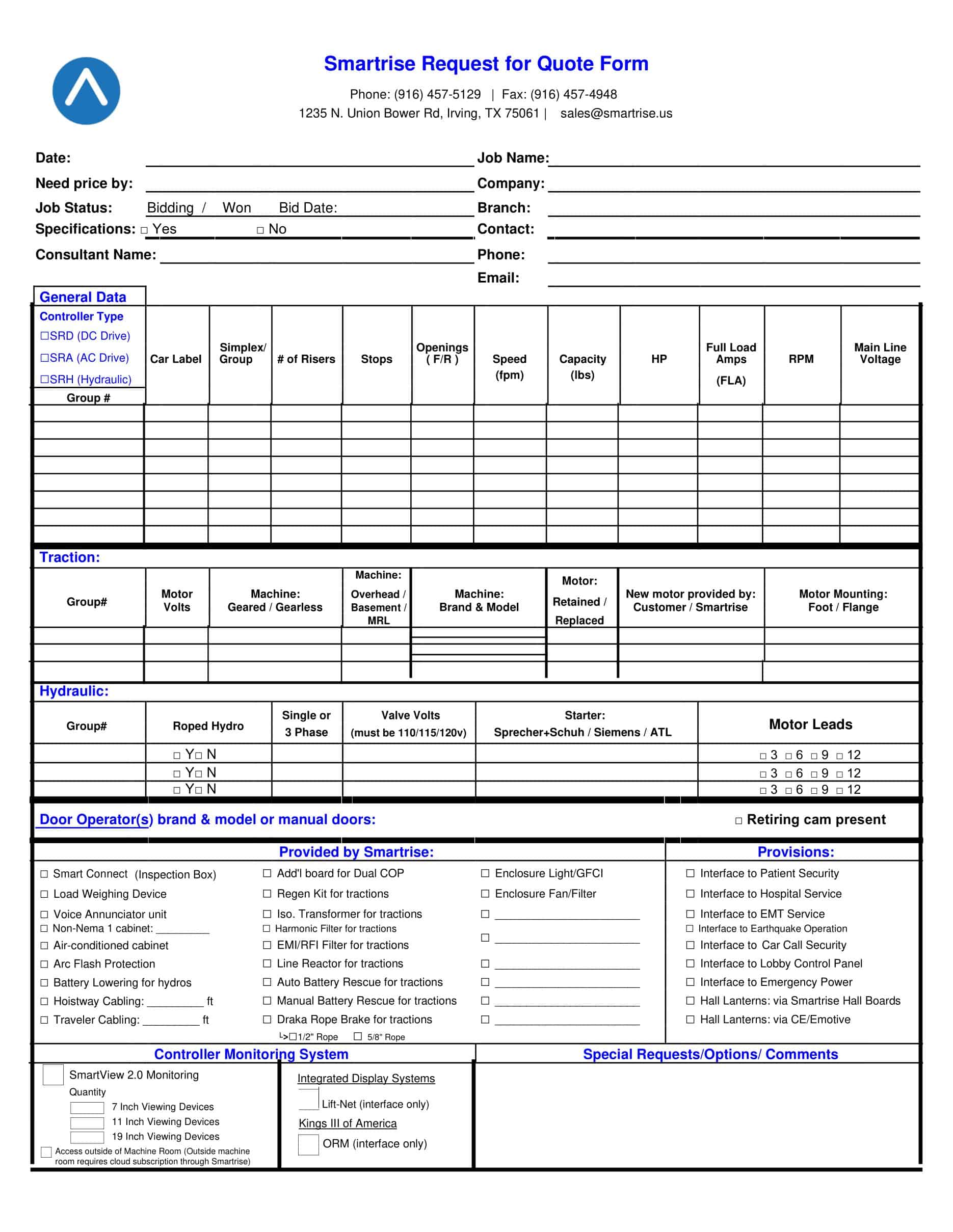
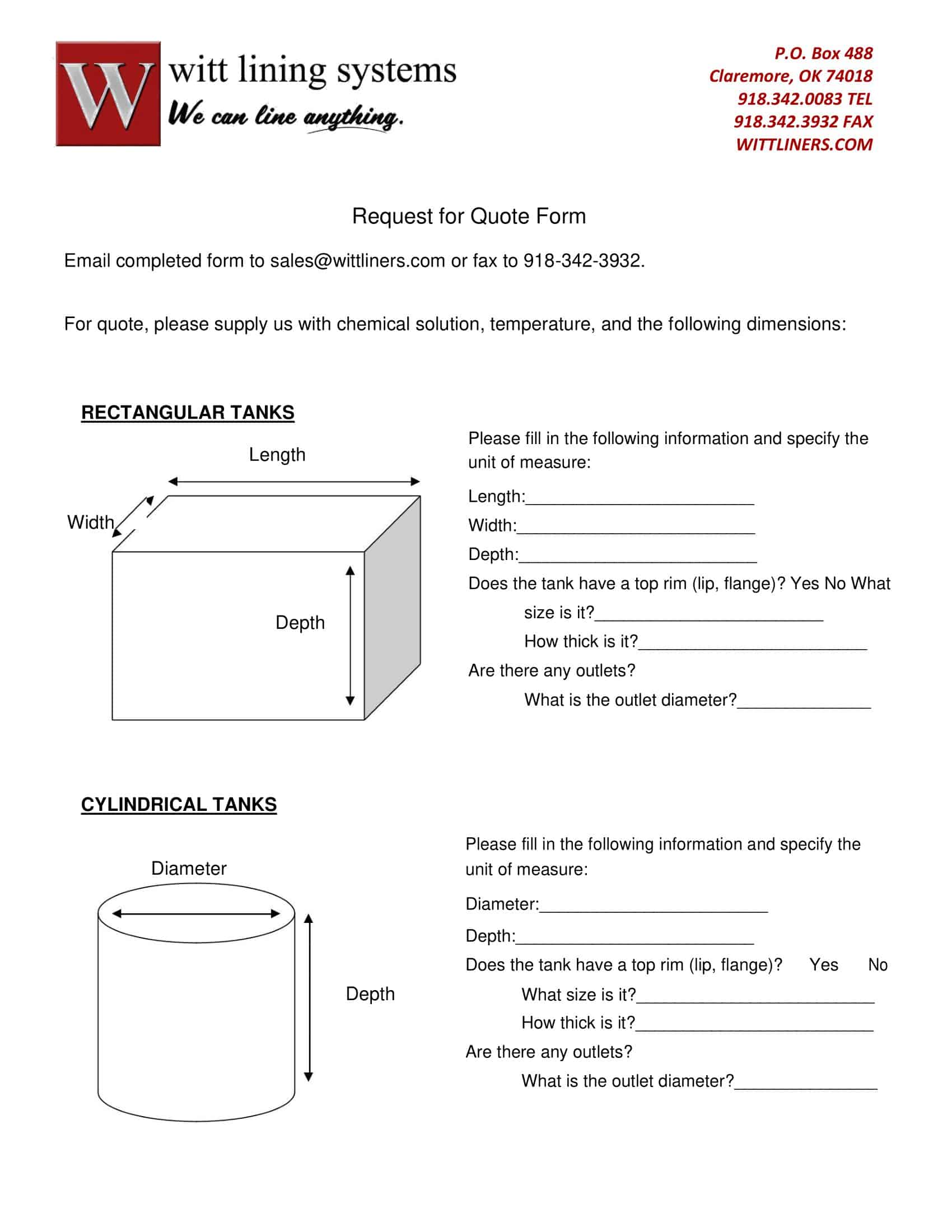
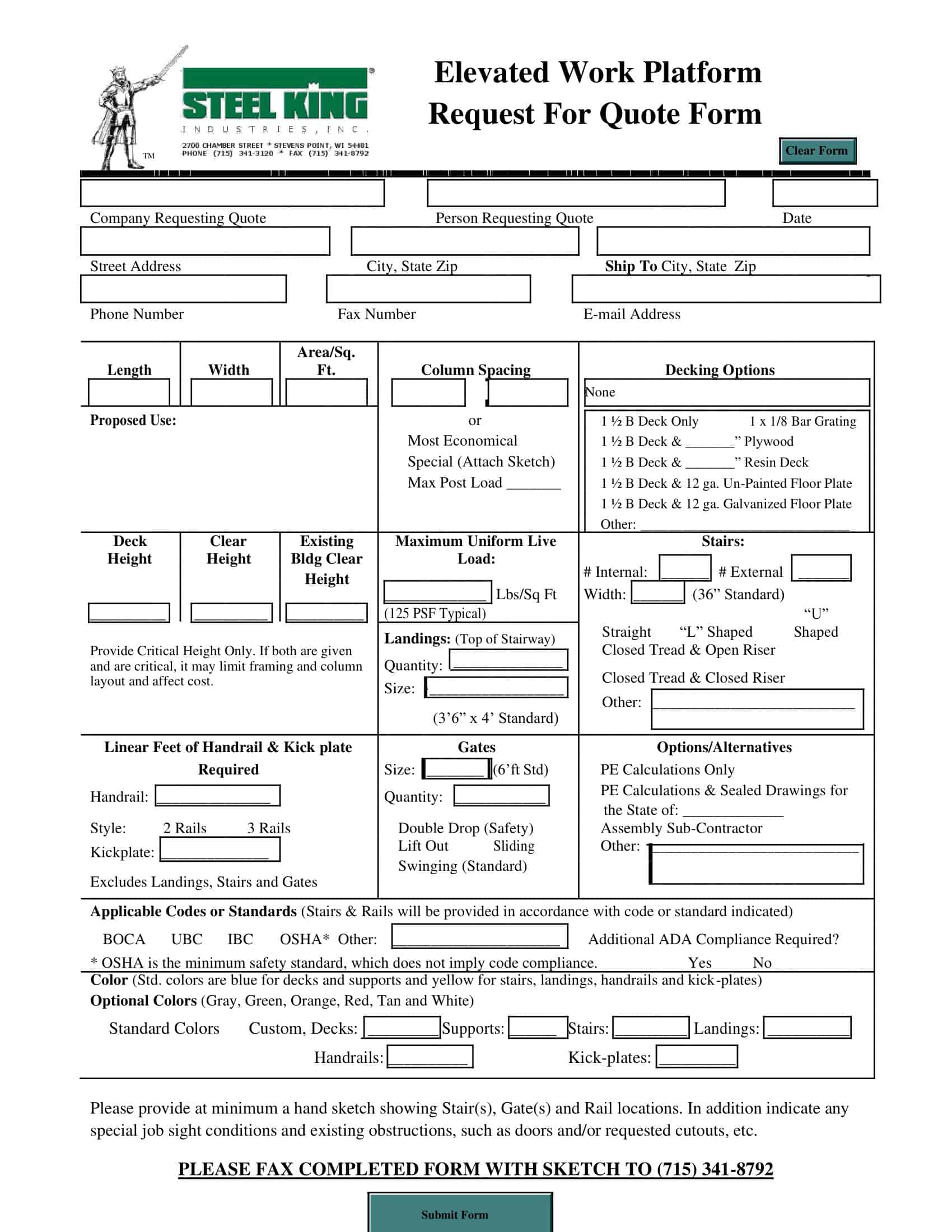
Prepare the RFQ Document: The next step is to prepare the RFQ document. This typically includes a detailed description of the product or service required, quantity, delivery schedule, terms and conditions, and the criteria that will be used to evaluate the quotes. It also outlines how suppliers should submit their quotes and the deadline for submission.
Identify Potential Suppliers: The company then identifies potential suppliers who could fulfill its needs. This could involve researching suppliers, checking past performance records, financial stability, market reputation, and capacity to deliver.
Distribute the RFQ: The RFQ is then sent to the potential suppliers. This could be done via email, a procurement portal, or even by post.
Receive Quotations: Suppliers review the RFQ and decide whether they can meet the specified requirements. If they can, they prepare and submit their quote by the specified deadline.
Evaluate Quotations: Once all the quotes are received, they are evaluated against the criteria specified in the RFQ. This usually involves comparing prices, but it could also include other factors like delivery schedule, supplier’s reputation, quality of goods, etc.
Negotiate: Depending on the results of the evaluation, the company may choose to negotiate with one or more suppliers to get better terms.
Select a Supplier: After the evaluation and negotiation, the company selects a supplier and informs them of their decision. The other suppliers are also notified that they were not selected.
Issue a Purchase Order: Finally, the company issues a purchase order to the selected supplier, which formalizes the agreement and sets the procurement process in motion.
Types of Requests for Quotes
There are several types of Requests for Quotes (RFQs), each tailored to specific business needs and situations. Understanding the different types can help a business choose the right one for its unique circumstances. Here are some common types:
Open RFQ
This type of RFQ is open to any supplier who wishes to participate. It is often used when a business is looking to attract new suppliers or wants to ensure it gets the most competitive price.
Invitational RFQ
In this case, an RFQ is sent only to selected suppliers. This type is typically used when a business has a preferred list of suppliers or wants to limit the process to suppliers with specific qualifications or credentials.
Standing RFQ
This type of RFQ is used for goods and services that are procured on a recurring basis. It sets up a long-term agreement with a supplier, where goods or services are supplied as and when required.
Single RFQ
This RFQ is for a one-off purchase of a product or service. It is often used for non-recurring or unique purchases.
Emergency RFQ
This type of RFQ is used when goods or services need to be procured urgently due to unforeseen circumstances. In such cases, the normal procurement process is expedited.
E-RFQ
Electronic Request for Quotation (E-RFQ) is the digital version of the traditional RFQ process, where all communications and submissions are done electronically, typically through a dedicated procurement software or platform.
How To Write A Request For Quote (RFQ) ?
here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to write a Request for Quote (RFQ):
Step 1: Understand Your Needs
Before beginning to write an RFQ, it’s essential to understand your needs clearly. Identify the product or service you need, the quantity, the delivery schedule, and any other specific requirements.
Step 2: Create the RFQ Document
The RFQ document serves as the formal communication between you and potential suppliers. Here’s how to structure it:
Introduction: Briefly introduce your company and explain the purpose of the RFQ.
Scope of Work: Describe in detail what you need. For products, specify the quantity, model, specifications, etc. For services, outline the tasks, objectives, deliverables, and timeline. Be as precise and clear as possible to avoid misunderstandings.
Submission Guidelines: Provide clear instructions on how suppliers should submit their quotes. This includes the format of the quote, the details to be included, the submission method (email, online portal, etc.), and the deadline.
Evaluation Criteria: State how you will evaluate the quotes. Common criteria include price, supplier’s experience and reputation, quality of goods/services, and delivery schedule.
Terms and Conditions: Include any contractual terms and conditions that will apply, such as payment terms, delivery terms, warranty, etc.
Contact Information: Provide a point of contact for suppliers to reach out if they have any questions.
Step 3: Identify Potential Suppliers
Research potential suppliers who could fulfill your needs. Consider their capabilities, reputation, financial stability, and previous experience in similar projects. You can find suppliers through online searches, business directories, trade shows, and industry referrals.
Step 4: Distribute the RFQ
Send the RFQ to the identified suppliers. This can be done via email, online procurement platforms, or even by post, depending on what’s most suitable for your business and the suppliers.
Step 5: Receive and Evaluate Quotes
Once you receive quotes from suppliers, evaluate them based on the criteria you specified in the RFQ. It’s a good practice to use a standardized evaluation matrix to ensure a fair and objective comparison.
Step 6: Negotiate
Based on the evaluations, you may choose to negotiate with one or more suppliers to get better terms. Ensure you maintain professionalism and fairness throughout the negotiation process.
Step 7: Select a Supplier and Issue a Purchase Order
After finalizing the negotiation, select a supplier and notify them of your decision. Also, inform the other suppliers that they were not selected this time but you appreciate their time and effort. Finally, issue a purchase order to the selected supplier to formalize the agreement.
Step 8: Review and Improve
After the RFQ process is complete, review it to identify any areas for improvement. This could be in the way you define your needs, how you evaluate quotes, or how you negotiate with suppliers. Continuous improvement is key to making the RFQ process more efficient and effective.
FAQs
How does an RFQ differ from a Request for Proposal (RFP)?
An RFQ is generally used when the needs and specifications are clearly defined and price is the main factor for selection. On the other hand, an RFP is used when the project is complex, the needs are not fully defined, and factors other than price, such as expertise and approach, are equally or more important.
How do I respond to an RFQ?
As a supplier, when you respond to an RFQ, you should provide a quote that includes pricing for the goods or services requested, along with any additional information specified in the RFQ document. This may include your company’s background, your ability to fulfill the order, delivery timelines, and terms and conditions.
Can an RFQ be negotiated?
Yes, often after quotes have been submitted and evaluated, the buyer may negotiate with one or more suppliers to get better terms. This could be in regards to price, delivery timeline, or other contractual conditions.
Who can issue an RFQ?
Any organization or individual that is looking to procure goods or services and wants to solicit competitive quotes can issue an RFQ. This includes businesses, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and even individuals for personal projects.
What happens after an RFQ is issued?
After an RFQ is issued, suppliers will submit their quotations by the specified deadline. The issuer will then evaluate these quotes based on the evaluation criteria outlined in the RFQ. They may choose to negotiate with one or more suppliers before selecting a supplier and issuing a purchase order.
How long should I give suppliers to respond to an RFQ?
The response time can vary depending on the complexity of the goods or services being procured. However, it’s important to give suppliers enough time to prepare a thorough and competitive quote. This is typically between one to four weeks.
How many suppliers should I send the RFQ to?
The number of suppliers can vary based on the size and nature of the project, as well as the number of potential qualified suppliers. However, to ensure a competitive process, it’s often recommended to send the RFQ to at least three to five suppliers.
What should I do if the quotes received are too high or do not meet my expectations?
If the quotes received are not satisfactory, you have several options. You can negotiate with the suppliers to see if better terms can be reached, or you can revisit and adjust your RFQ if you think your requirements or budget might have been unrealistic. Alternatively, you can issue a new RFQ to a different set of suppliers.
What is the difference between an RFQ and an Invitation to Bid (ITB)?
Both RFQ and ITB are used to solicit bids from suppliers. However, an RFQ is typically used for smaller, less complex purchases where the requirements are well-defined, while an ITB is often used for larger, more complex projects where there are strict rules about the bidding process.
Do I have to select the supplier with the lowest quote?
Not necessarily. While price is a significant factor, it’s not the only one. The aim is to achieve the best value for money, which might also involve considering the quality of the goods or services, the supplier’s reputation and reliability, their capacity to deliver on time, and their after-sales service.
What is a sealed bid in the context of an RFQ?
A sealed bid is a method of bidding where all bids are submitted in sealed envelopes, and they’re all opened at the same time. This method ensures fairness and transparency, as no bidder knows what others are bidding until all bids are revealed.
Can I issue an RFQ electronically?
Yes, e-RFQ or electronic RFQ is a common practice in many industries. This process is typically managed through a procurement software or platform, making it more efficient and easier to manage.
What if a supplier asks for clarification on the RFQ?
It’s common for suppliers to have questions or need clarifications. You should provide clear and consistent responses to all suppliers. If a question highlights an ambiguity or error in the RFQ, it’s good practice to share the clarification or correction with all suppliers to ensure a fair process.
How confidential is the RFQ process?
The RFQ process should be handled with a high degree of confidentiality. Quotes from suppliers should not be disclosed to other suppliers, and any proprietary information from suppliers should be protected. Confidentiality helps to maintain a fair and competitive process.

























































![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)
