Questionnaires and social surveys are crucial tools for gaining insights on your audience or customers. By collecting standardized data from large numbers of people, you can obtain valuable information about their demographics, lifestyles, and opinions.
This method of data collection is widely used by government entities to make informed decisions about programs and initiatives. The standardized nature of questionnaires ensures that all information is collected in the same way, making the data easy to analyze and interpret in a statistical form.
Table of Contents
What is a questionnaire?

A questionnaire is a research tool used to gather information from a group of people. It is typically composed of a series of questions that are answered by the participants. Questionnaires can be self-administered, meaning participants fill them out on their own, or they can be administered by an interviewer who asks the questions and records the answers. The format and structure of questionnaires can vary, but they are commonly used to collect data on topics such as opinions, attitudes, behaviors, and demographics.
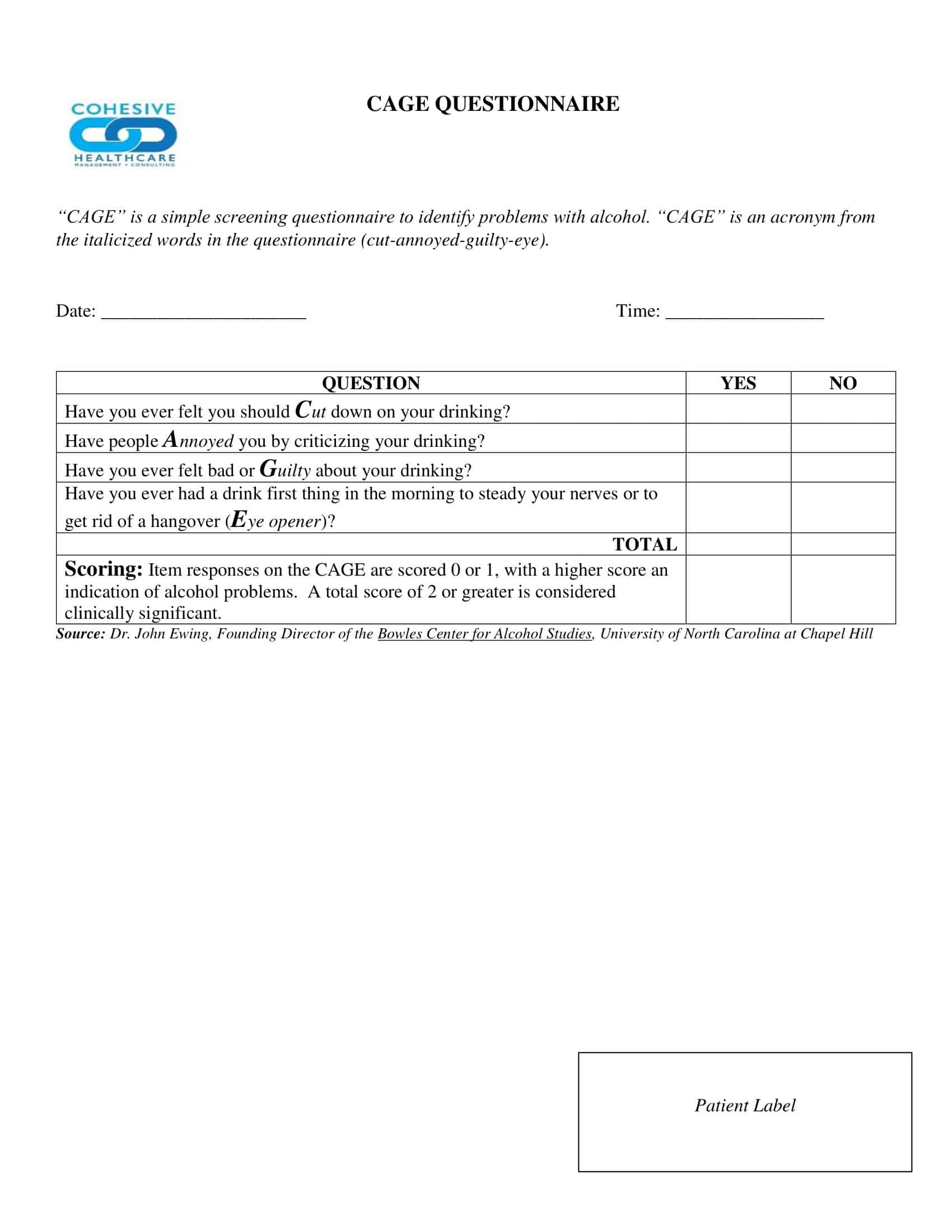
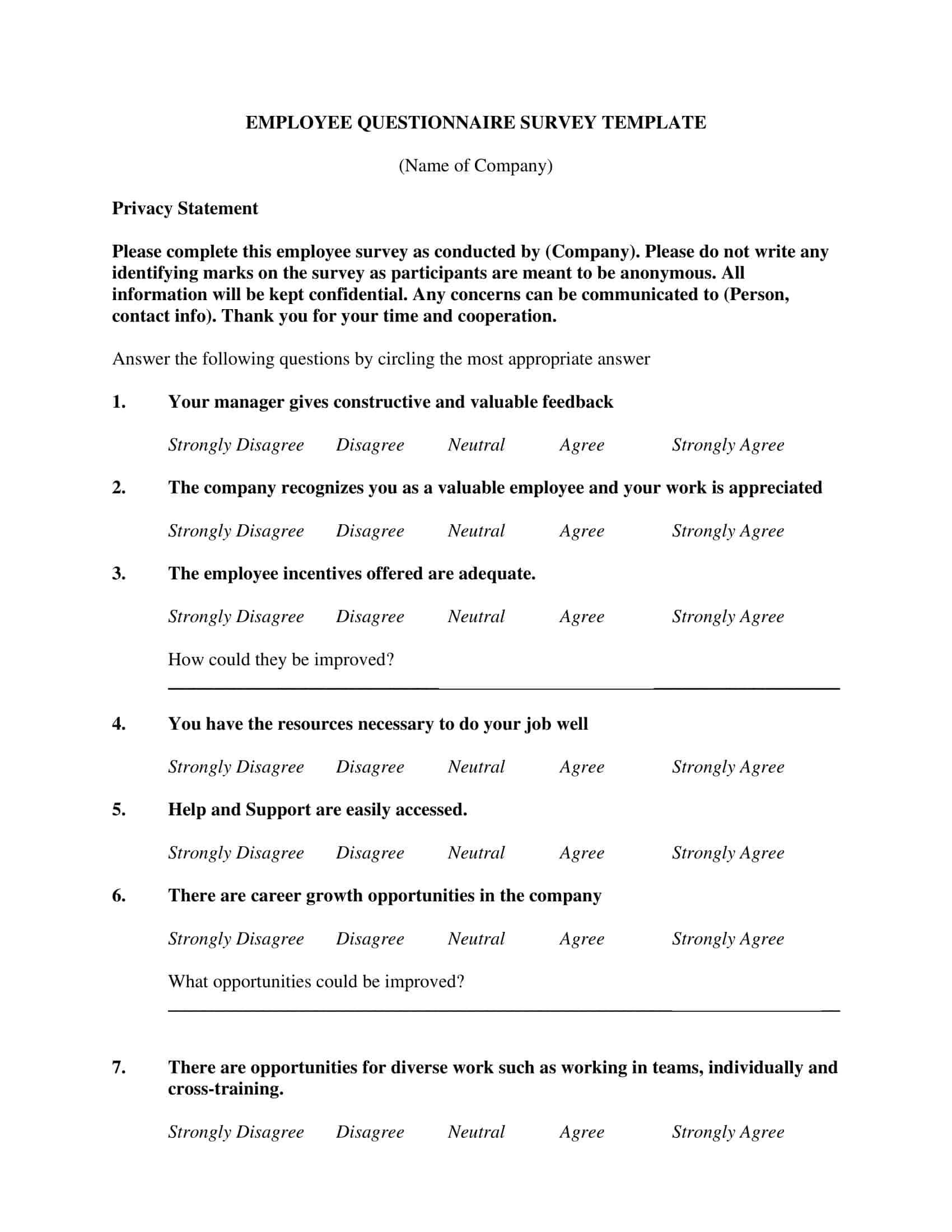
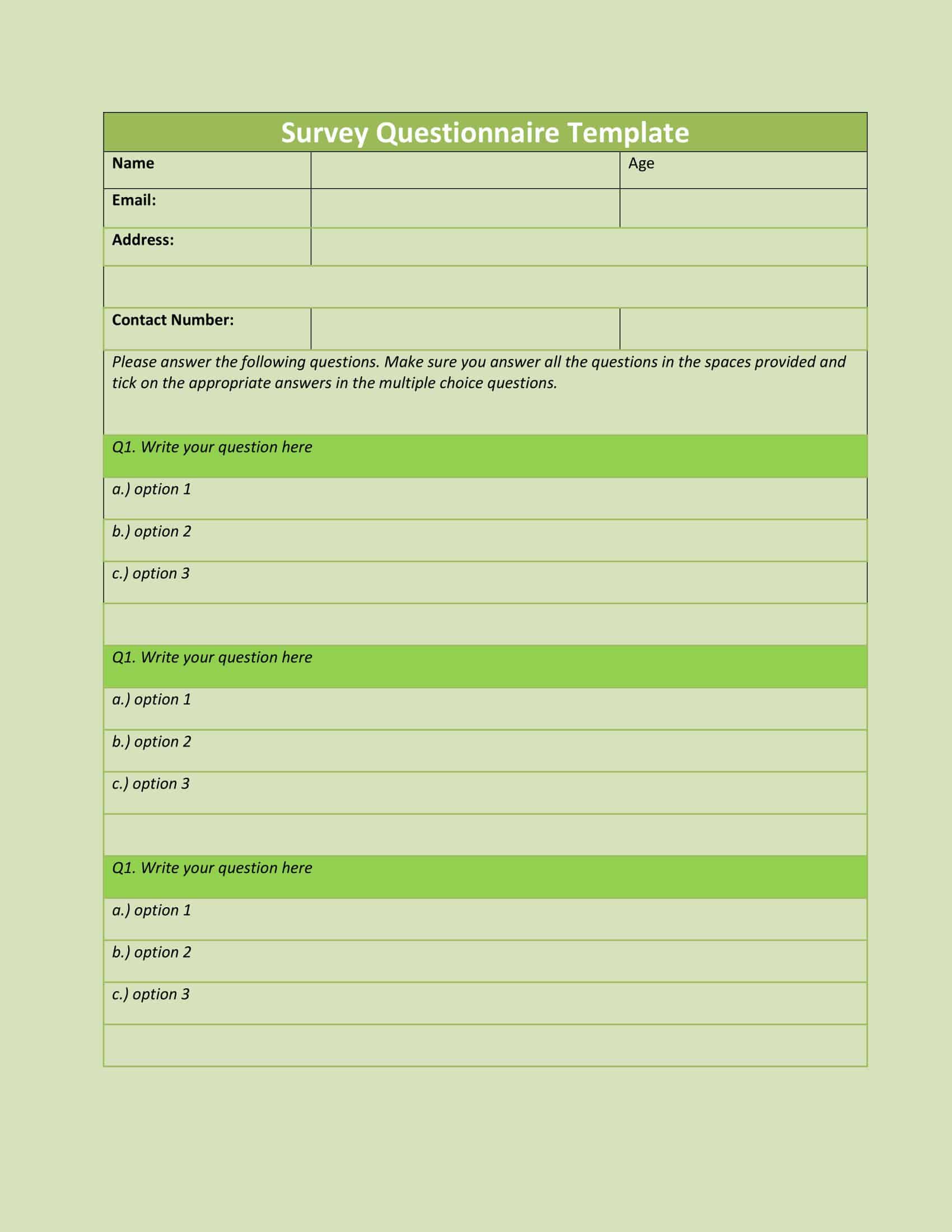
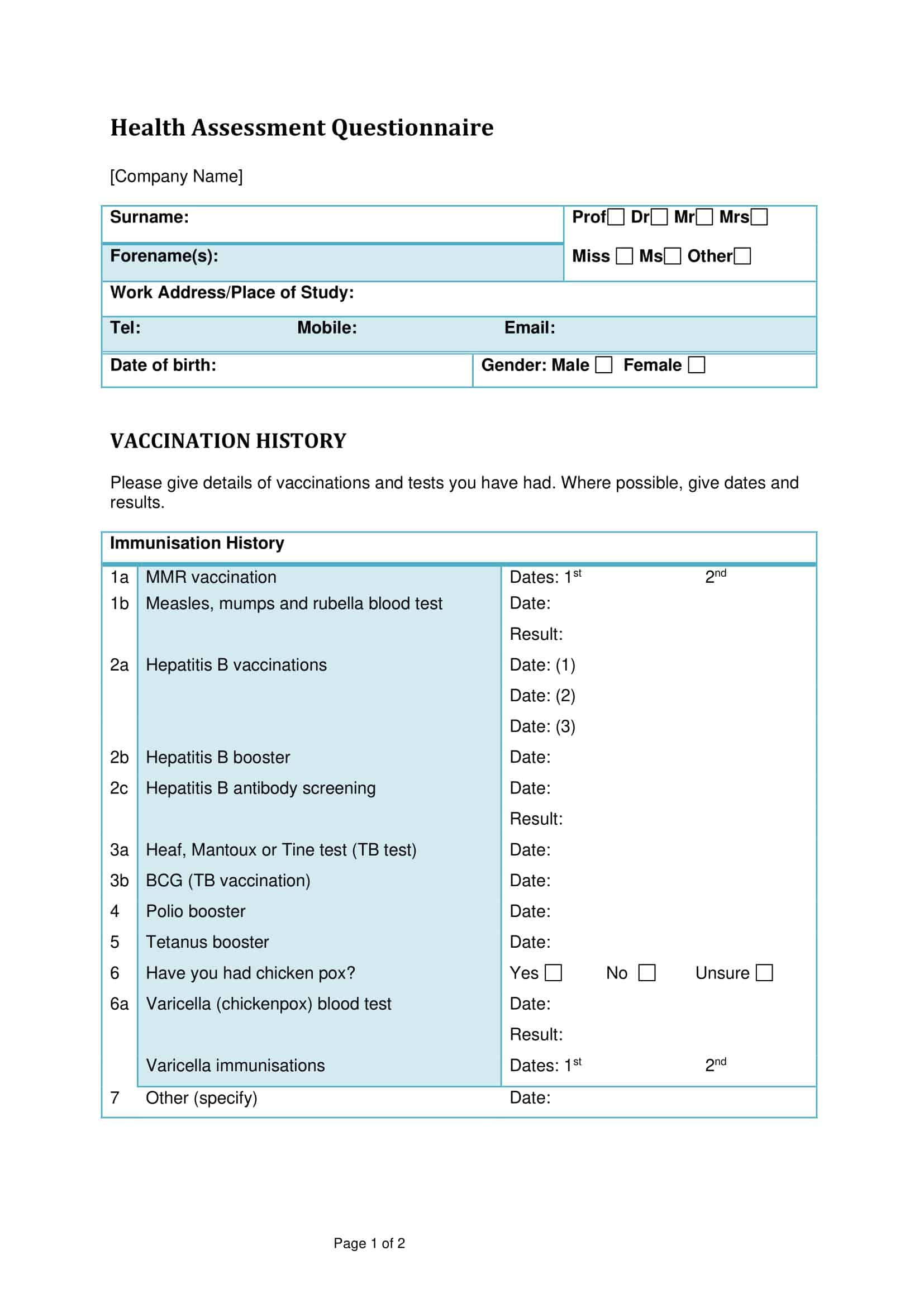
Questionnaire Templates
Gather valuable insights and data with ease using our versatile collection of Questionnaire Templates. Whether you’re conducting market research, gathering customer feedback, or collecting survey responses, our free, printable templates provide a user-friendly framework for designing and distributing questionnaires.
With customizable sections for various question types, such as multiple choice, rating scales, and open-ended responses, our templates allow you to tailor the questionnaire to your specific needs. Streamline the data collection process, save time, and ensure consistency in your surveys.
From professional researchers to small business owners, our Questionnaire Templates are a valuable resource for obtaining meaningful information. Download now and start gathering valuable insights to drive informed decisions and enhance your understanding of your target audience.
How do companies leverage the power of questionnaires and surveys to gather insights and drive success?
Businesses use questionnaires and surveys to gather valuable information about their customers, employees, and market trends. Some common ways businesses utilize this data include:
Customer satisfaction: Companies can survey their customers to gauge satisfaction with their products or services and identify areas for improvement.
Market research: Businesses can use questionnaires to gather data on market trends, consumer preferences, and buying habits.
Employee engagement: Employers can use surveys to gather feedback from employees on job satisfaction, work environment, and company culture.
Product development: Companies can survey their target audience to gather information on what features and benefits are most important to them when developing new products.
Sales and marketing: Questionnaires and surveys can help businesses gather information to support sales and marketing efforts by identifying target audience segments and determining the most effective marketing channels.
Overall, questionnaires and surveys provide businesses with a cost-effective way to gather information that can help inform decision-making, improve products and services, and drive business growth.
What makes a perfect questionnaire?
A perfect questionnaire is one that effectively collects the information you need while providing a positive experience for the respondent. Some key characteristics of a good questionnaire include:
Clarity and simplicity: The questions should be easy to understand and answer, using clear and straightforward language.
Relevance: The questions should be directly related to the topic being studied, and should not include irrelevant or unnecessary information.
Appropriate question types: Different types of questions (e.g., multiple choice, open-ended, ranking) should be used in appropriate ways to effectively gather the desired information.
Logical order: The questions should be presented in a logical order, with related questions grouped together.
Neutral tone: The questions should be neutral in tone, avoiding bias or leading questions.
Optimal length: The questionnaire should be long enough to gather the necessary information, but short enough to avoid participant fatigue.
Pilot testing: The questionnaire should be pilot tested to ensure that it works as intended, with any necessary revisions made before finalizing it.
By considering these factors, you can create a questionnaire that is effective in collecting the information you need while also being user-friendly and efficient.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research
Pros of using questionnaires in research:
Cost-effective: Questionnaires are a cost-effective way to gather data from large numbers of people, as they can be self-administered or distributed widely.
Efficient: Questionnaires can be completed quickly and easily, making data collection more efficient.
Standardized data: The standardized nature of questionnaires ensures that data is collected in the same way from all participants, making it easy to compare and analyze.
Access to a large sample: Questionnaires can reach large numbers of people, allowing researchers to gather data from a representative sample of the population.
Anonymity: Respondents can complete questionnaires anonymously, which may increase their willingness to answer truthfully and candidly.
Cons of using questionnaires in research:
Response bias: Respondents may not answer truthfully or may respond in a way that presents themselves in a favorable light, leading to response bias.
Limited depth of information: Questionnaires are limited in the amount and depth of information they can gather, as they rely on self-reported information.
Difficulty with sensitive topics: Questionnaires may not be appropriate for gathering information on sensitive topics, as respondents may be reluctant to answer truthfully.
Limited ability to probe: The standardized format of questionnaires does not allow for follow-up questions or clarification, which may limit the depth of information gathered.
Limited control over administration: If questionnaires are self-administered, researchers have limited control over the conditions under which they are completed, which may affect the validity of the data.
Types of Questionnaires
There are several types of questionnaires used in research and survey studies, including:
Structured questionnaires: These are questionnaires with a fixed set of pre-determined questions, where the answer options are limited to a specific set of choices. Examples include multiple choice and Likert scale questions.
Semi-structured questionnaires: These are questionnaires with a mix of pre-determined questions and open-ended questions, where the respondent has more freedom to provide a written response.
Unstructured questionnaires: These are questionnaires with open-ended questions only, allowing respondents to provide a written response without any limitations.
Web-based questionnaires: These are questionnaires that are completed online using a computer or mobile device.
Paper-based questionnaires: These are questionnaires that are completed on paper and then returned to the researcher for data entry.
Interview-administered questionnaires: These are questionnaires that are completed with the assistance of an interviewer, who reads the questions and records the answers.
The type of questionnaire used in a study will depend on the research question, the population being studied, and the resources available for data collection. The choice of questionnaire will also determine the level of structure and control that can be maintained over the data collection process.
Survey vs. Questionnaire
The terms “survey” and “questionnaire” are often used interchangeably, but there are some differences between the two.
A questionnaire is a set of questions that are used to gather information from a group of people. It can be self-administered or administered by an interviewer.
A survey, on the other hand, refers to the entire research study that is being conducted, which may include the questionnaire as one of its components. A survey also involves the planning, design, implementation, and analysis of data collected through the questionnaire or other methods.
In other words, a questionnaire is a tool used to gather data in a survey. A survey is the comprehensive study that uses the questionnaire or other methods to collect and analyze data.
So, in essence, all questionnaires are surveys, but not all surveys are questionnaires. Surveys can also involve other data collection methods, such as focus groups, interviews, and observations.
How to design a Questionnaire ?
Designing a questionnaire is a critical step in the survey research process, as the quality of the questionnaire can greatly impact the validity and reliability of the data collected. Here are the steps to designing a successful questionnaire:
Define the research objectives: The first step in designing a questionnaire is to clearly define the research objectives and determine the type of information needed to achieve these objectives.
Select the target population: The target population is the group of people from whom the data will be collected. It is important to select a representative sample of the population to ensure that the data is generalizable to the larger group.
Determine the questionnaire format: The format of the questionnaire will depend on the research objectives, the target population, and the data collection method. Structured questionnaires, semi-structured questionnaires, and unstructured questionnaires are the three main formats.
Write the questions: The questions should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. Questions should also be relevant to the research objectives and free from bias. The questions should be worded in such a way that they can be answered accurately and consistently by all respondents.
Choose the response format: The response format determines the type of answer options that will be provided to the respondent. The most common response formats include multiple choice, Likert scale, and open-ended questions.
Pre-test the questionnaire: Before distributing the questionnaire to the target population, it is important to pre-test it with a small sample to identify any problems or unclear questions. The pre-test can also help to refine the questionnaire and ensure that it is user-friendly.
Revise and finalize the questionnaire: After the pre-test, make any necessary revisions to the questionnaire to address any problems that were identified. The questionnaire should then be finalized and ready for data collection.
When designing a questionnaire, it is important to consider the following best practices:
Keep the questionnaire as short as possible: Respondents are more likely to complete a shorter questionnaire, and a shorter questionnaire is also less likely to result in fatigue or boredom.
Avoid double-barreled questions: Double-barreled questions ask two or more questions in one, which can lead to confusion and inaccurate responses.
Use easy-to-understand language: The questions should be worded in a clear and concise manner, using language that is easily understood by the target population.
Avoid leading questions: Leading questions are questions that suggest a particular answer or bias the respondent in a particular direction. Leading questions can result in inaccurate responses.
Minimize response burden: Response burden refers to the time, effort, and resources required by the respondent to complete the questionnaire. Minimizing response burden will increase the response rate and the quality of the data collected.
Consider the cultural and demographic characteristics of the target population: The questionnaire should be culturally sensitive and appropriate for the target population.
Pilot test the questionnaire: Piloting the questionnaire with a small sample of the target population can help to identify any problems or unclear questions before the questionnaire is distributed to the larger population.
Designing a questionnaire is a complex process, and it is important to consider all of the above steps and best practices to ensure that the questionnaire is effective, efficient, and reliable. By carefully considering the research objectives, target population, and questionnaire format, you can design a questionnaire that will provide high-quality data to support your research objectives.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a questionnaire?
The purpose of a questionnaire is to gather information from a large number of people in a standardized and efficient manner. Questionnaires are often used in market research, social sciences, and health research to gather information about people’s opinions, behaviors, and experiences.
What is response burden in a questionnaire?
Response burden refers to the time, effort, and resources required by the respondent to complete the questionnaire. Minimizing response burden is important to increase the response rate and the quality of the data collected.
What are leading questions in a questionnaire?
Leading questions are questions that suggest a particular answer or bias the respondent in a particular direction. Leading questions can result in inaccurate responses and should be avoided when designing a questionnaire.
How do I choose the right type of questionnaire for my research?
The choice of questionnaire depends on the research objectives, the target population, the type of data being collected, and the resources available. It is important to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each type of questionnaire and choose the one that is most appropriate for the research.
How do I ensure the quality of the data collected from a questionnaire?
To ensure the quality of the data collected from a questionnaire, it is important to design clear and concise questions, pilot test the questionnaire, use appropriate response formats, and minimize response burden. Additionally, it is important to monitor the response rate and consider non-response bias when interpreting the results.
How do I analyze the data collected from a questionnaire?
The data collected from a questionnaire can be analyzed using various statistical methods, including descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and multivariate analysis. The choice of analysis method depends on the research objectives and the type of data being collected.
How do I report the results of a questionnaire study?
The results of a questionnaire study can be reported using tables, graphs, and text. It is important to provide a clear and concise summary of the results, including a description of the sample, the response rate, and the main findings. Additionally, it is important to interpret the results in the context of the research objectives and to consider the limitations of the study.

























































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
