Harnessing the power of a personal budget spreadsheet can truly transform your financial future. This simple, yet incredibly powerful tool, enables you to track your income and expenditures, fostering control and clarity about your personal finances.
In this enlightening article, we’re going to explore various aspects of designing and utilizing an effective personal budget spreadsheet, from crafting your own unique template to making savvy financial decisions based on the insights you gain. Prepare to unlock the secret to financial discipline, ushering in a new era of financial stability and freedom.
Table of Contents
What is a personal budget spreadsheet?

A personal budget spreadsheet is a comprehensive financial management tool that aids individuals in monitoring their income, expenses, and savings. Using rows and columns, this digital ledger provides a detailed breakdown of your financial activities, typically on a monthly basis.
It allows you to identify trends, patterns, and potential issues by categorizing and documenting all forms of income and expenditure. By offering a clear, real-time overview of your financial health, a personal budget spreadsheet empowers you to plan ahead, save more effectively, reduce unnecessary spending, and work towards your financial goals.
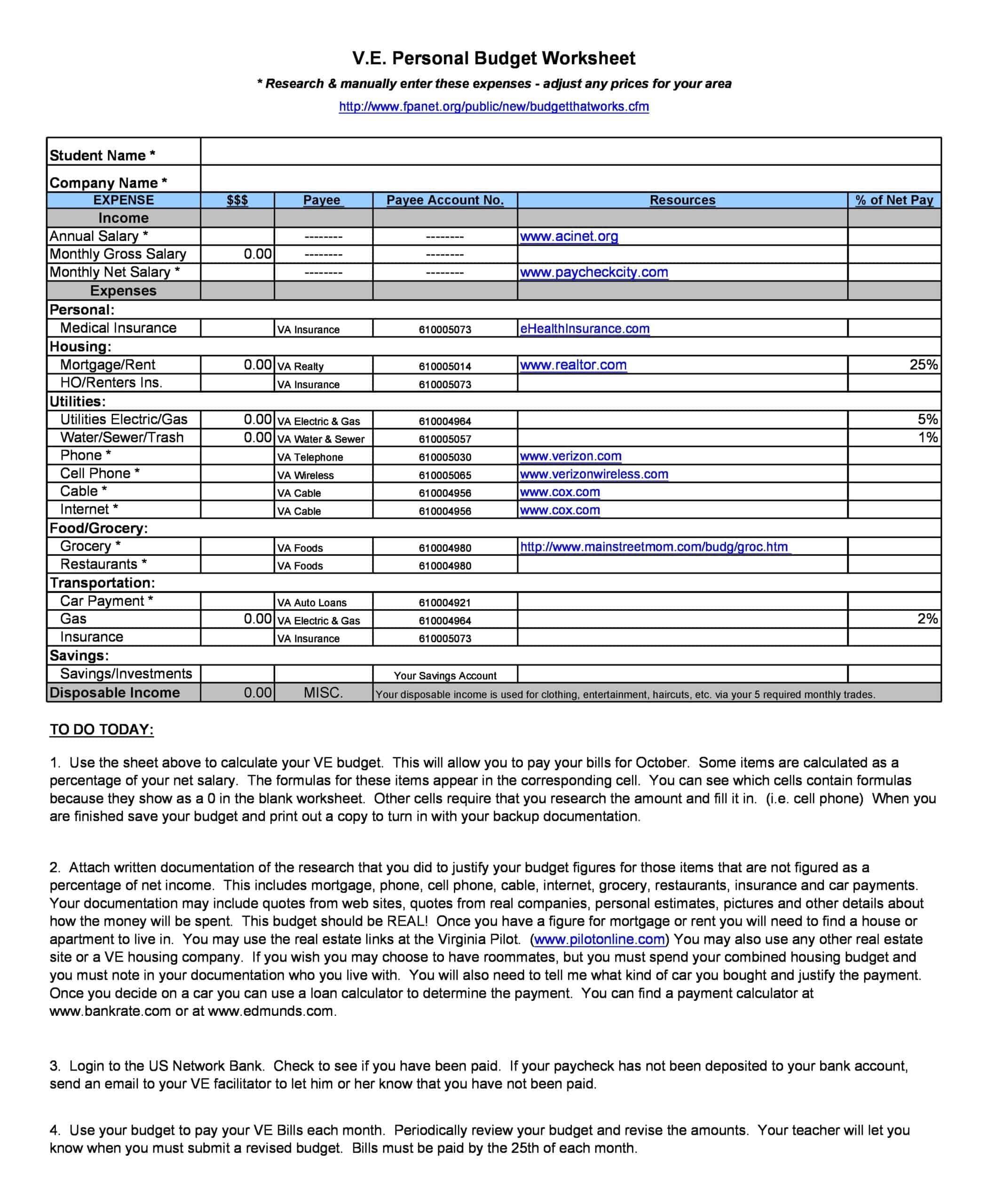
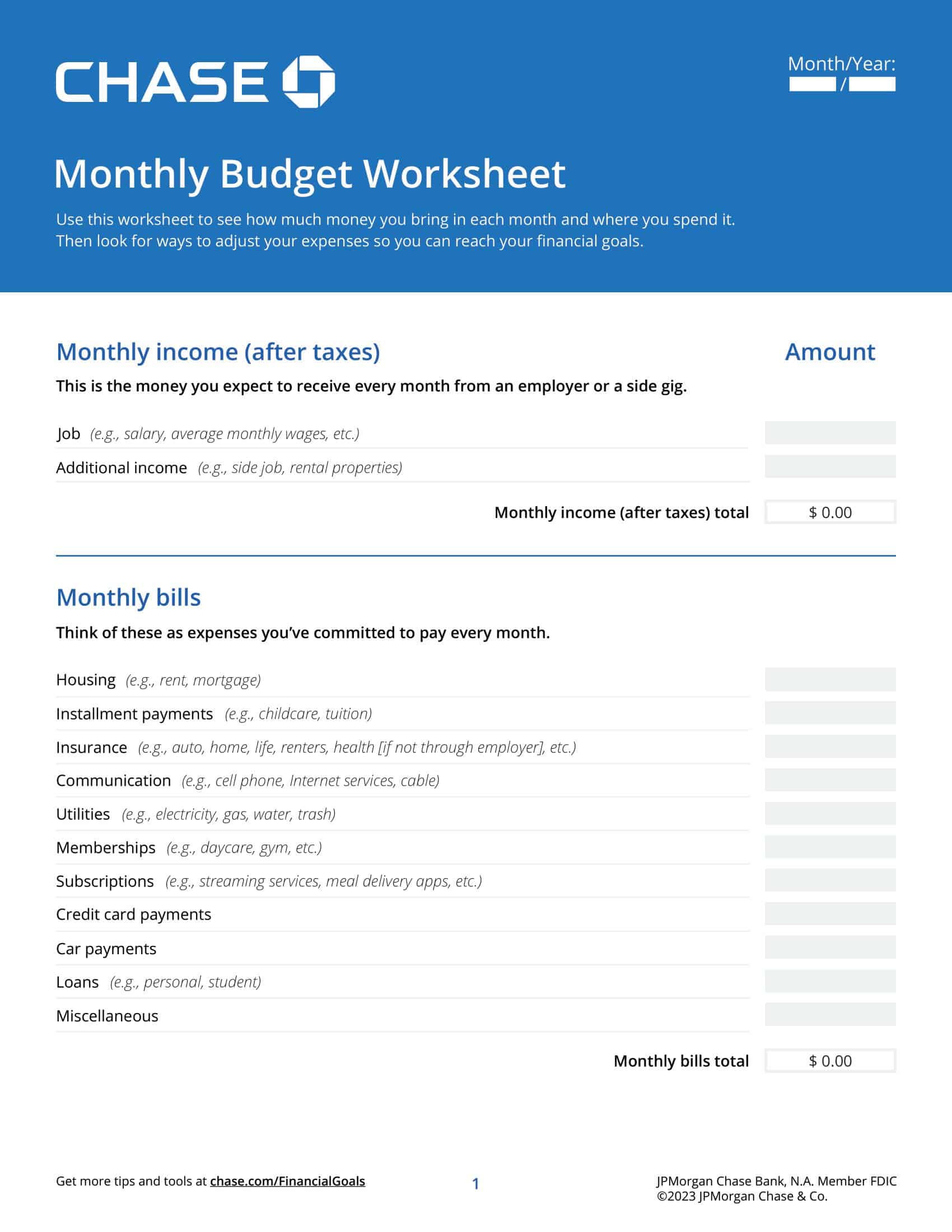
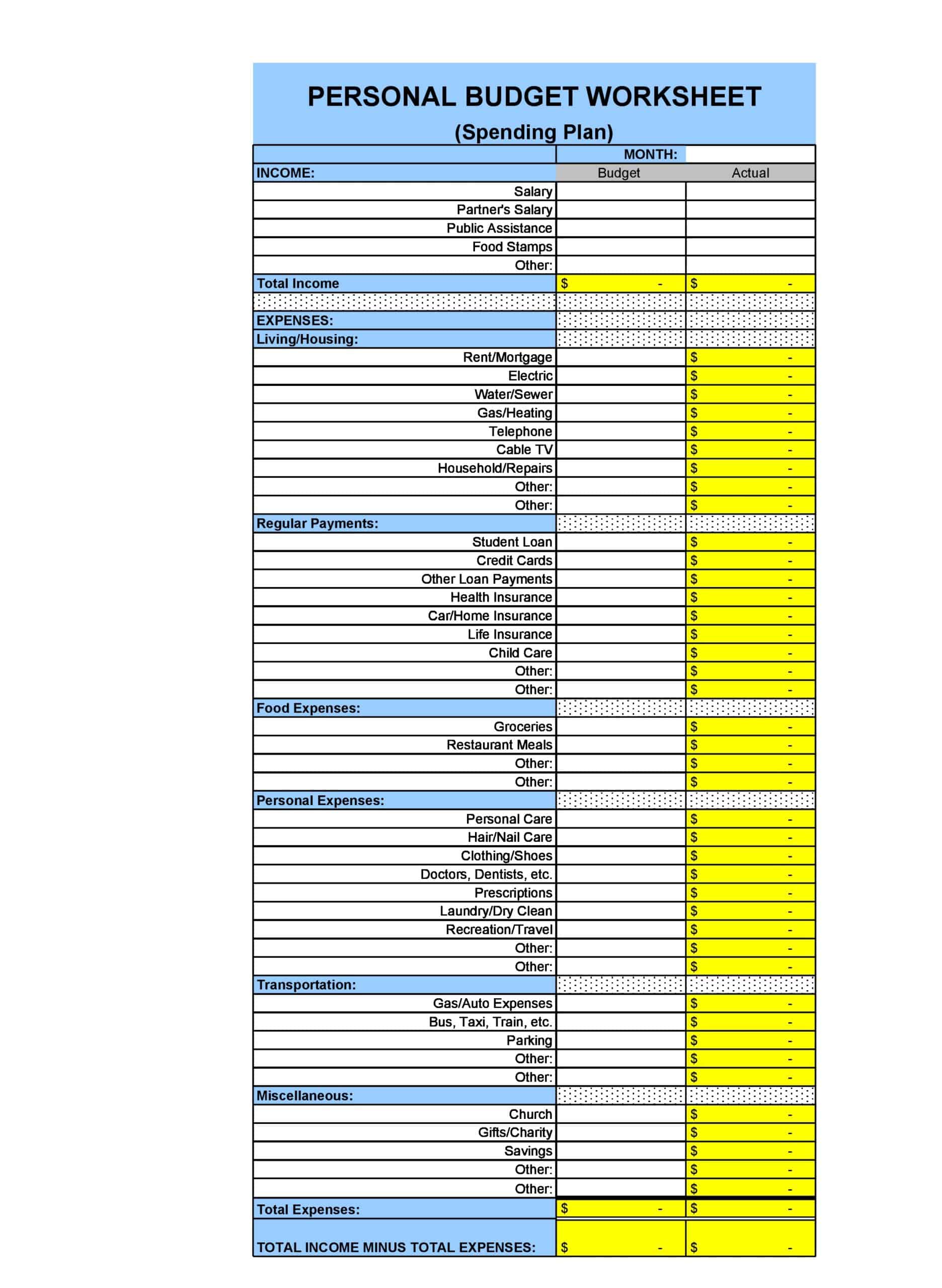
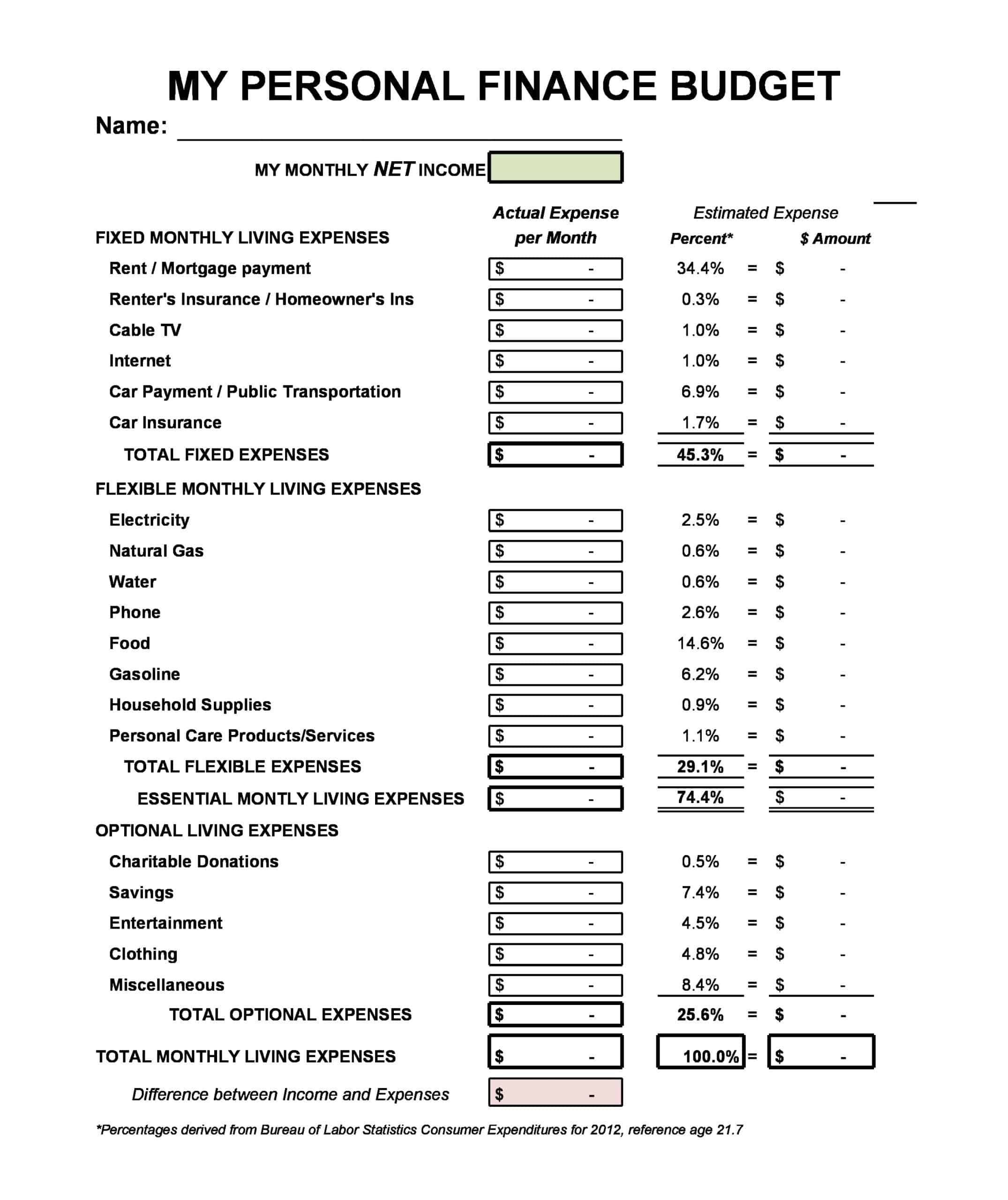
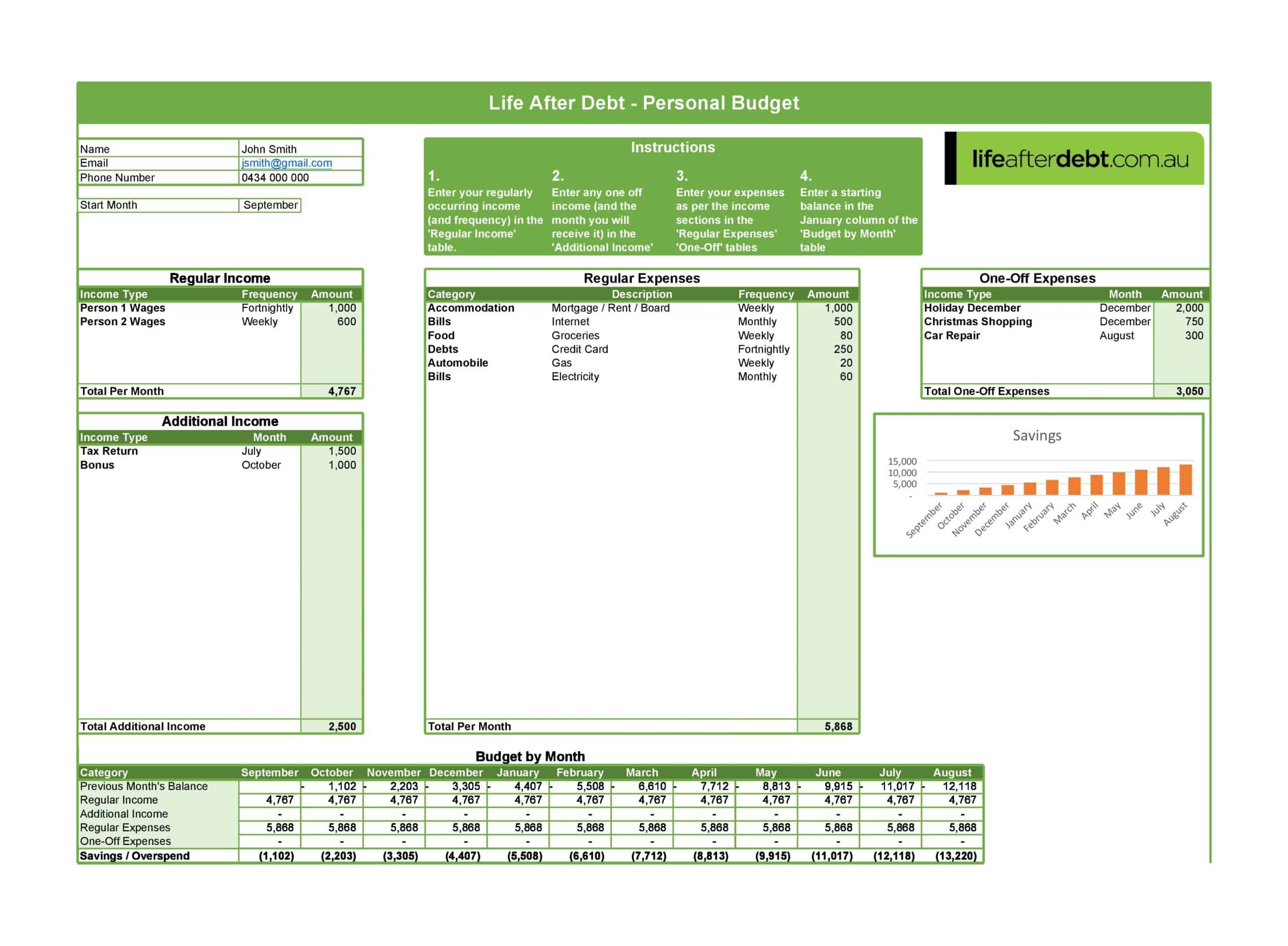
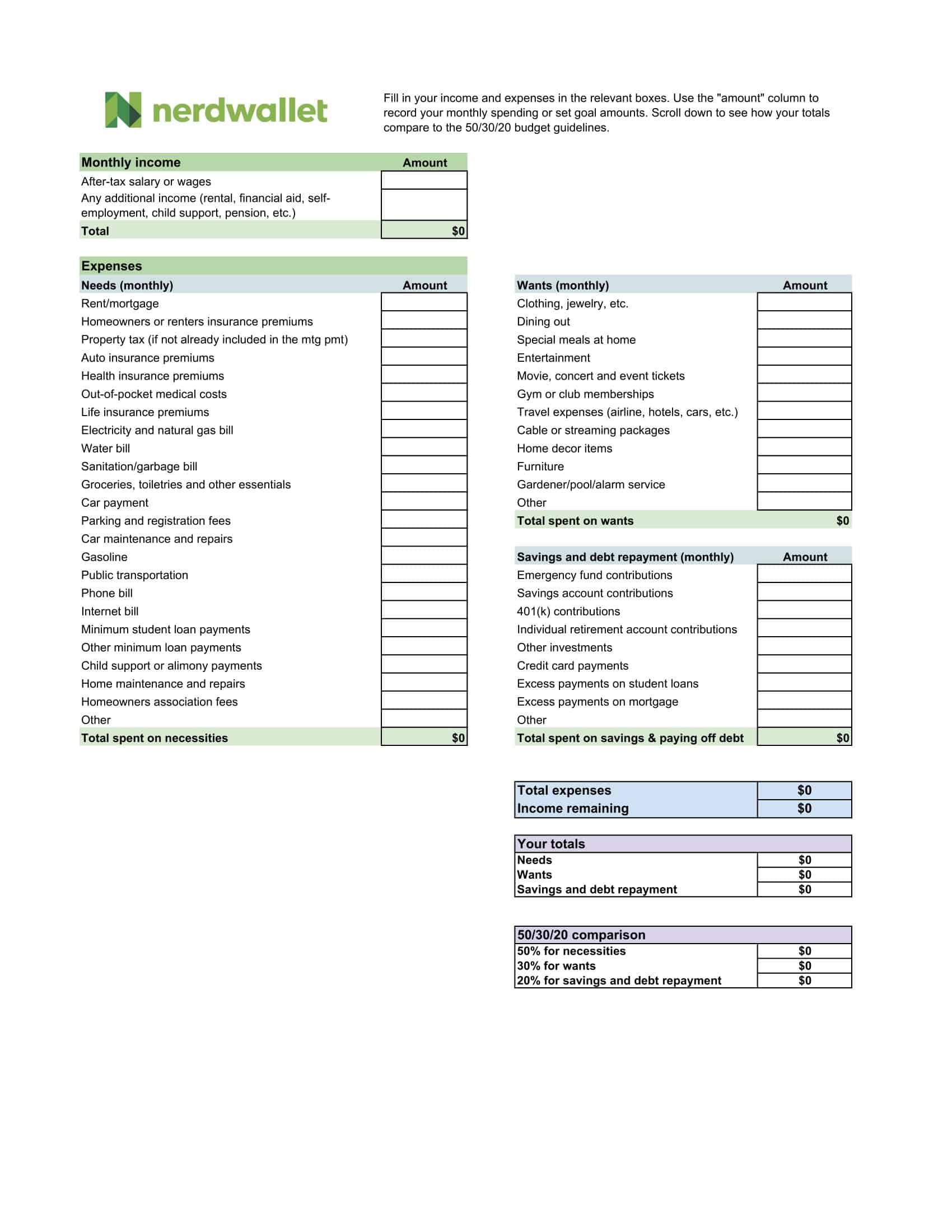
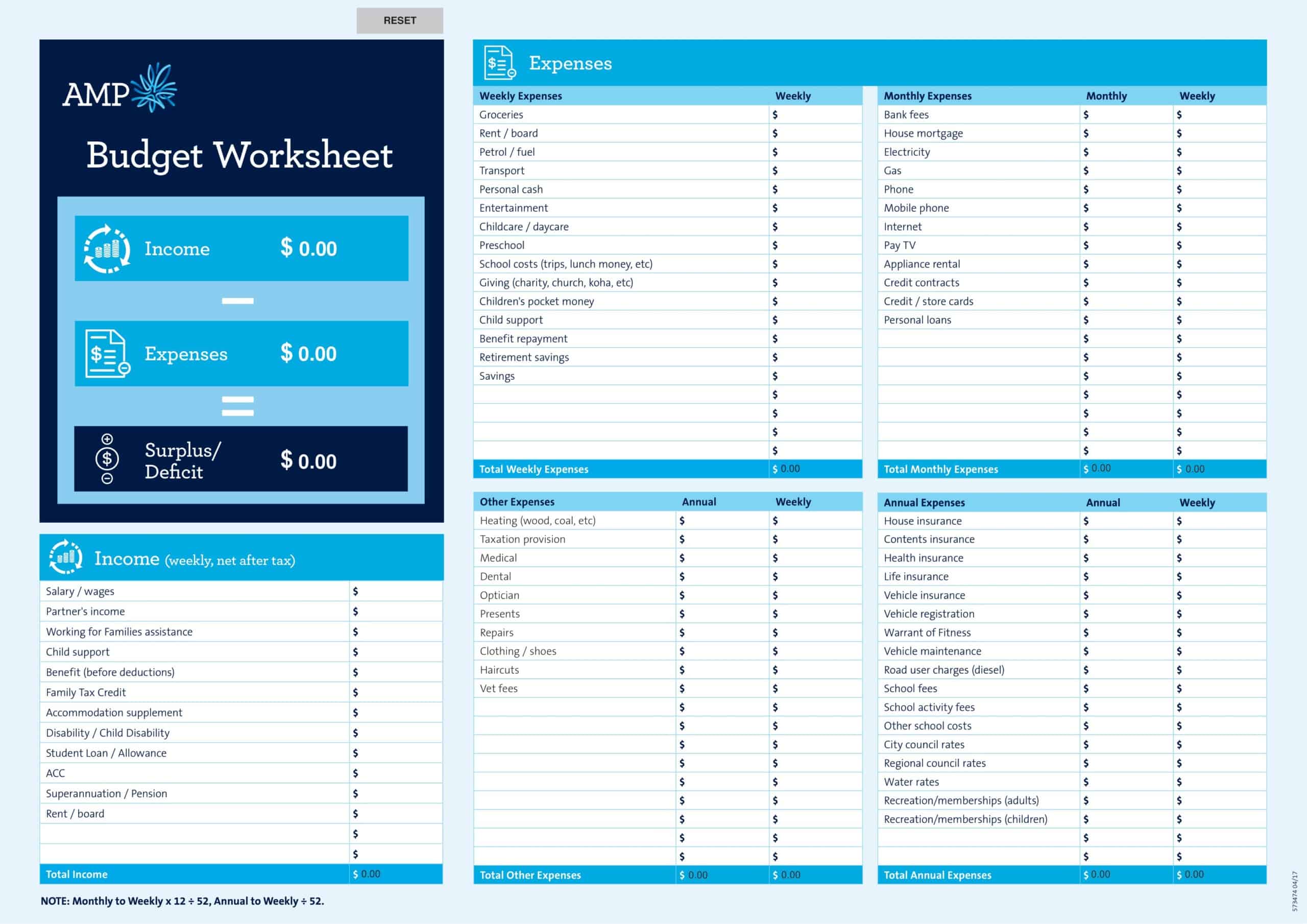
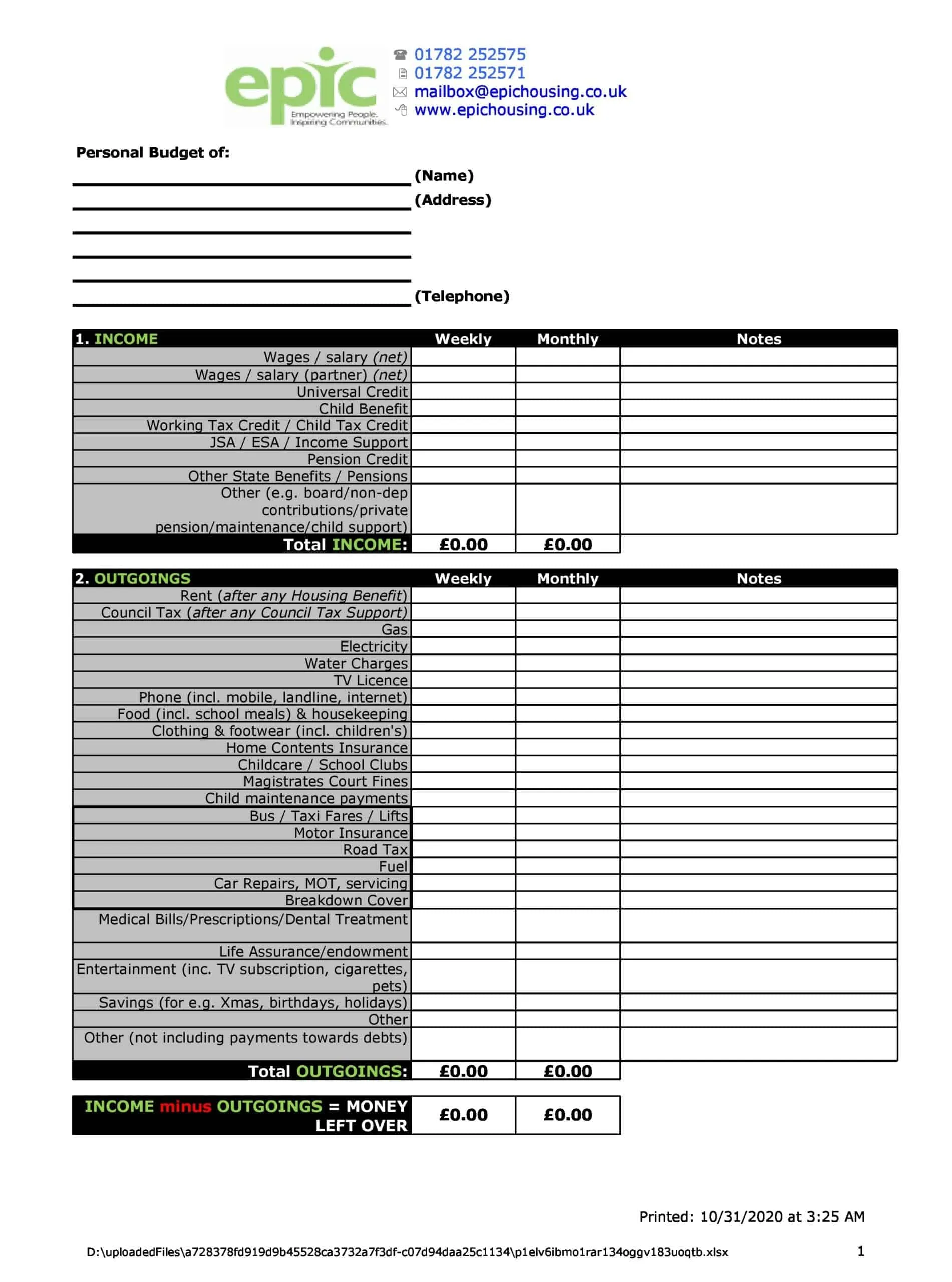
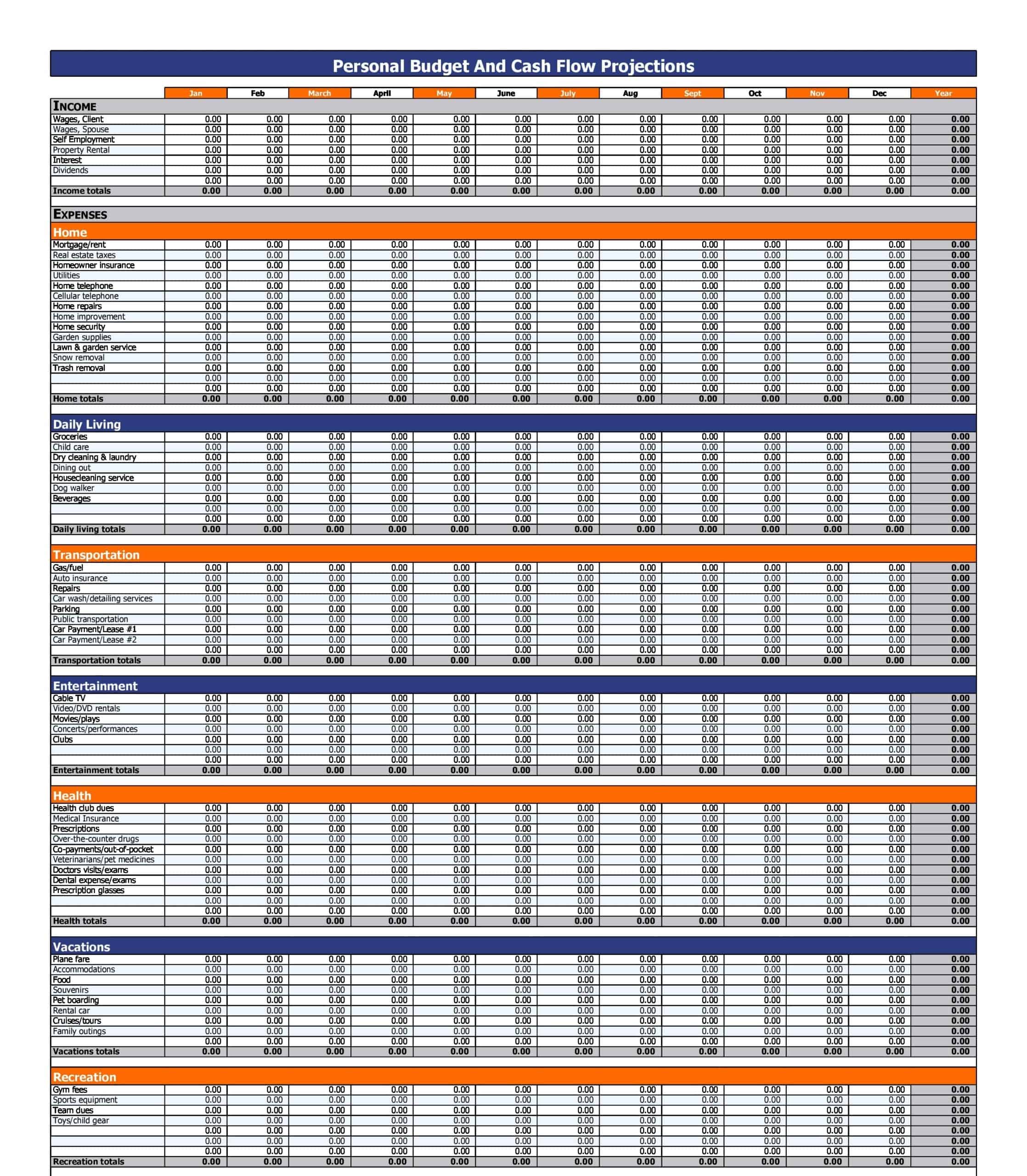
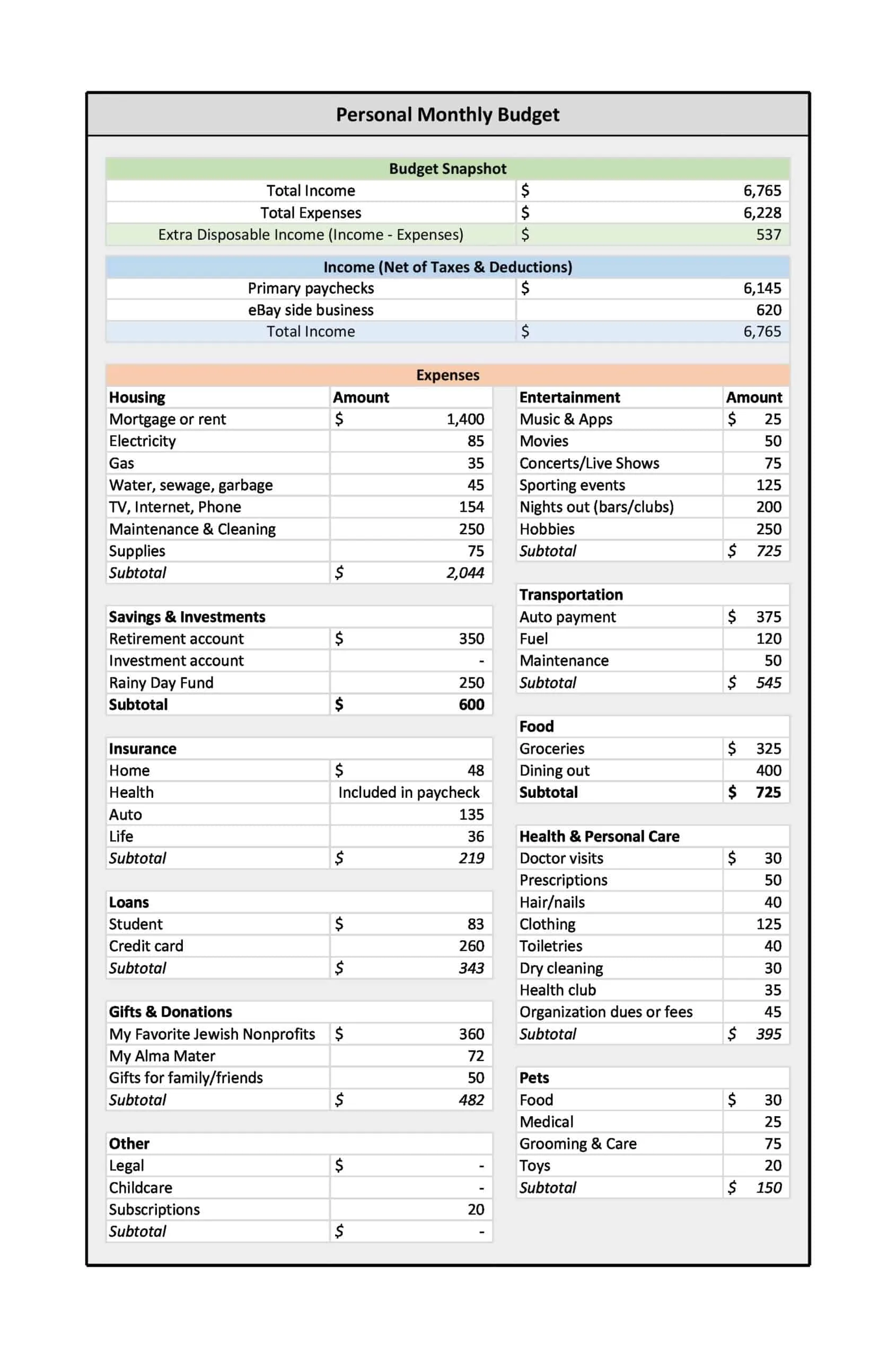
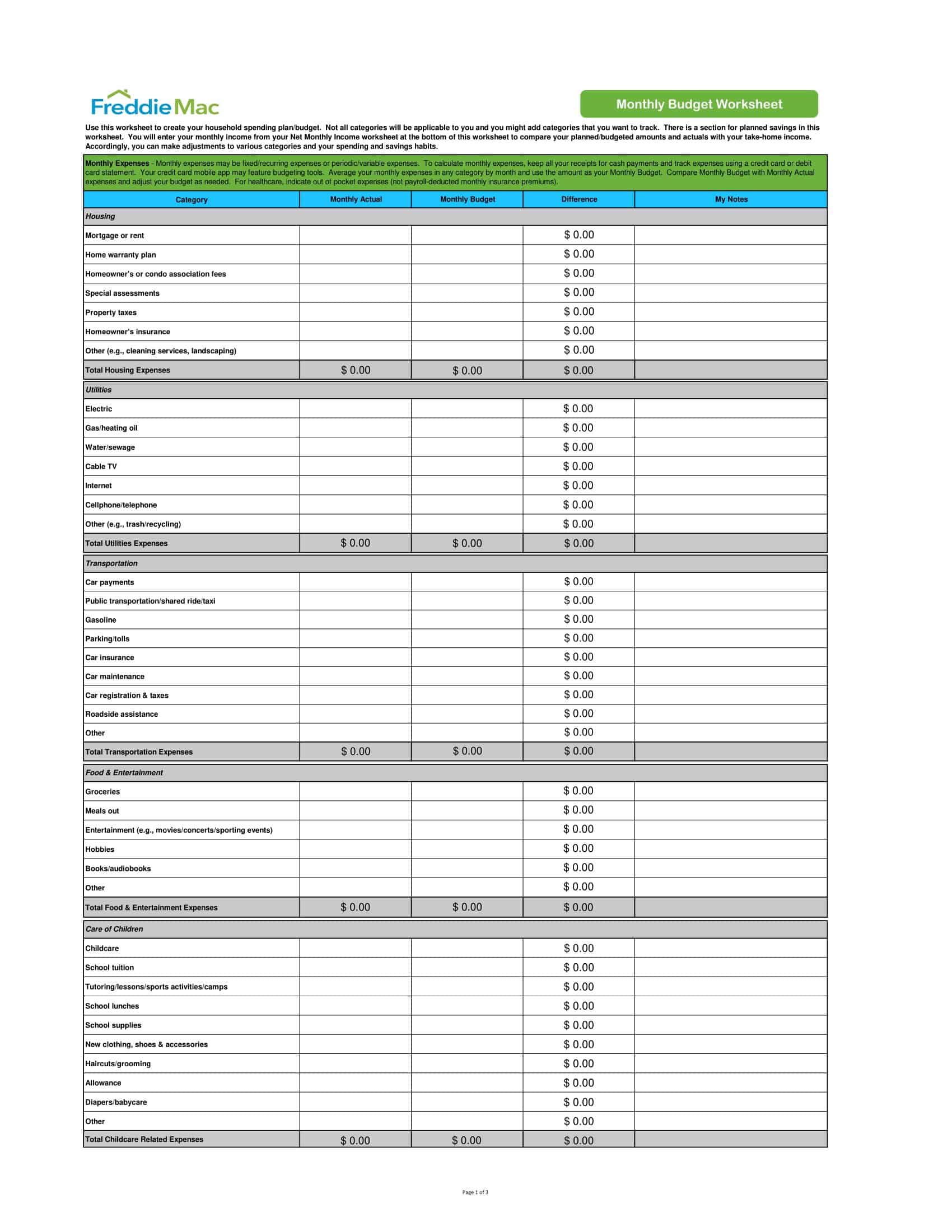
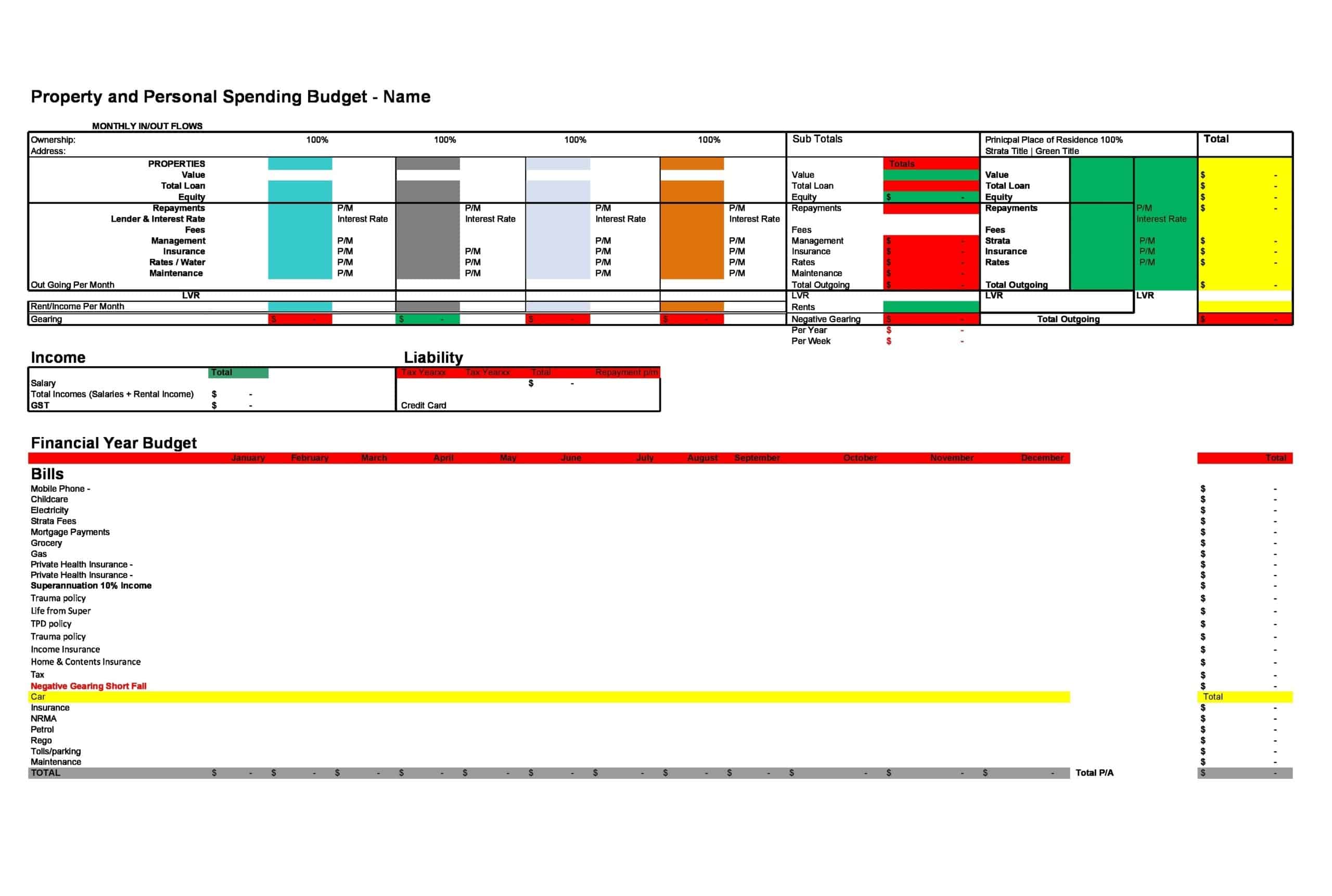
Personal Budget Spreadsheet Templates
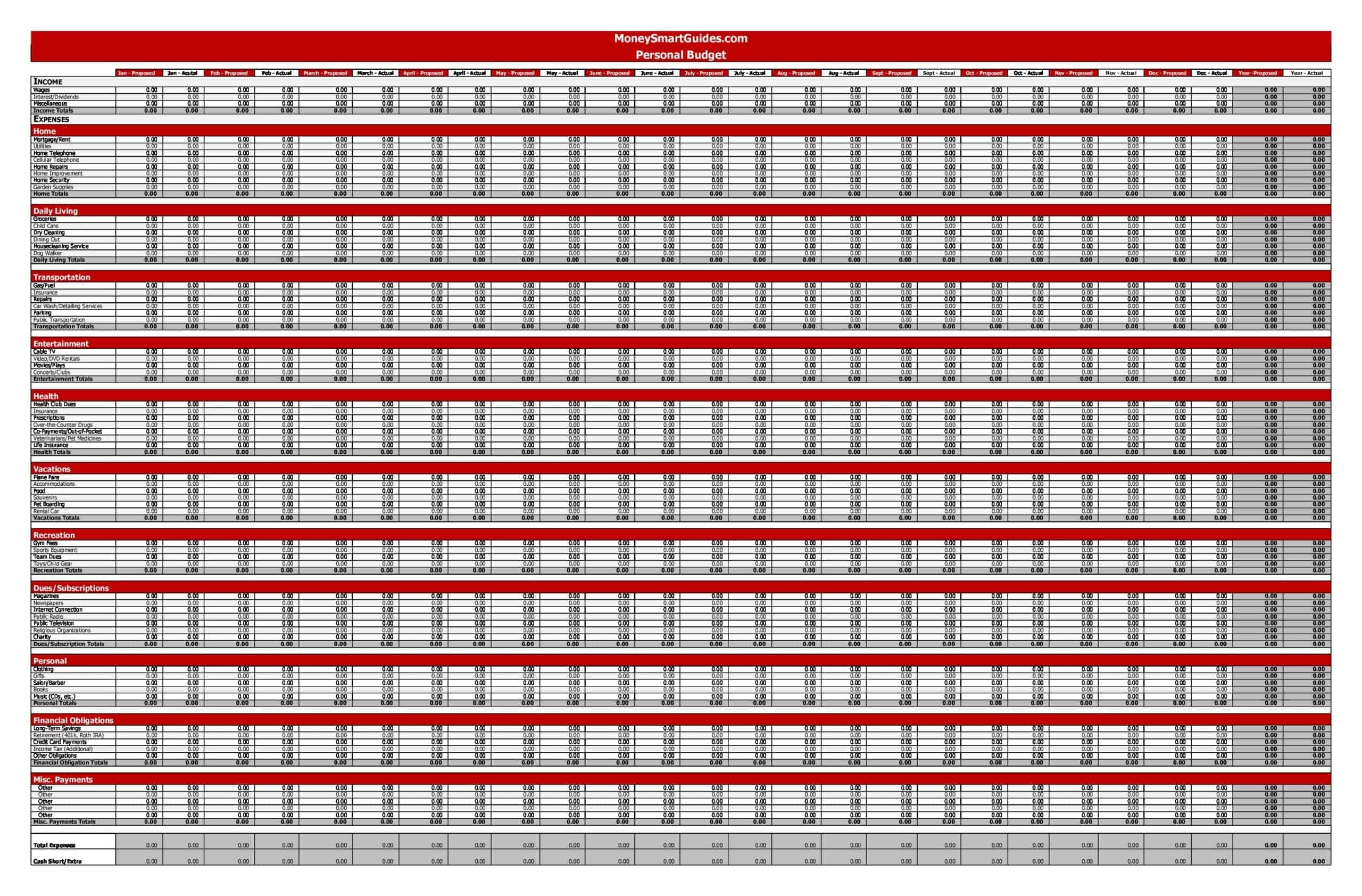
Carefully planning personal finances is important for financial health. Personal budgets allocate incomes and track spending. Personal budget spreadsheet templates provide formats to easily build budgets.
The templates contain columns to itemize income sources and expense categories. Formulas calculate totals, balances, and percent of income by category. Charts visually depict spending. Templates allow custom expense types and saving goals. Some link to bank accounts for automated data feeds.
Personal budget spreadsheet templates enable individuals to produce detailed budgets without complex setup. Users simply enter their own incomes, fixed costs, and variable spending. The templates reveal spending behaviors to guide changes. They make managing budgets efficient on any device. Whether getting started budgeting or optimizing existing finances, personal budget spreadsheet templates empower individuals with insights to meet goals and secure financial wellbeing.
Importance of Using a Personal Budget Spreadsheet
Utilizing a personal budget spreadsheet offers multiple benefits essential for financial health and long-term planning. It promotes financial transparency, showing exactly where your money is going, which is crucial for identifying habits and making necessary changes. Furthermore, it enables effective budgeting, allowing you to allocate resources towards your needs and wants strategically, thereby preventing overspending.
It also encourages savings and investment, as tracking your income and expenses often reveals opportunities to save more or invest wisely. Moreover, it offers foresight, enabling you to plan for large expenses, avoid debt, or work towards financial goals such as buying a house or retirement. Ultimately, a personal budget spreadsheet fosters financial independence and provides the necessary tools to navigate your economic future proactively.
What is included in a personal budget?
Creating a comprehensive personal budget involves several critical components, each serving a unique function in portraying a holistic picture of your financial situation. Here’s a detailed guide:
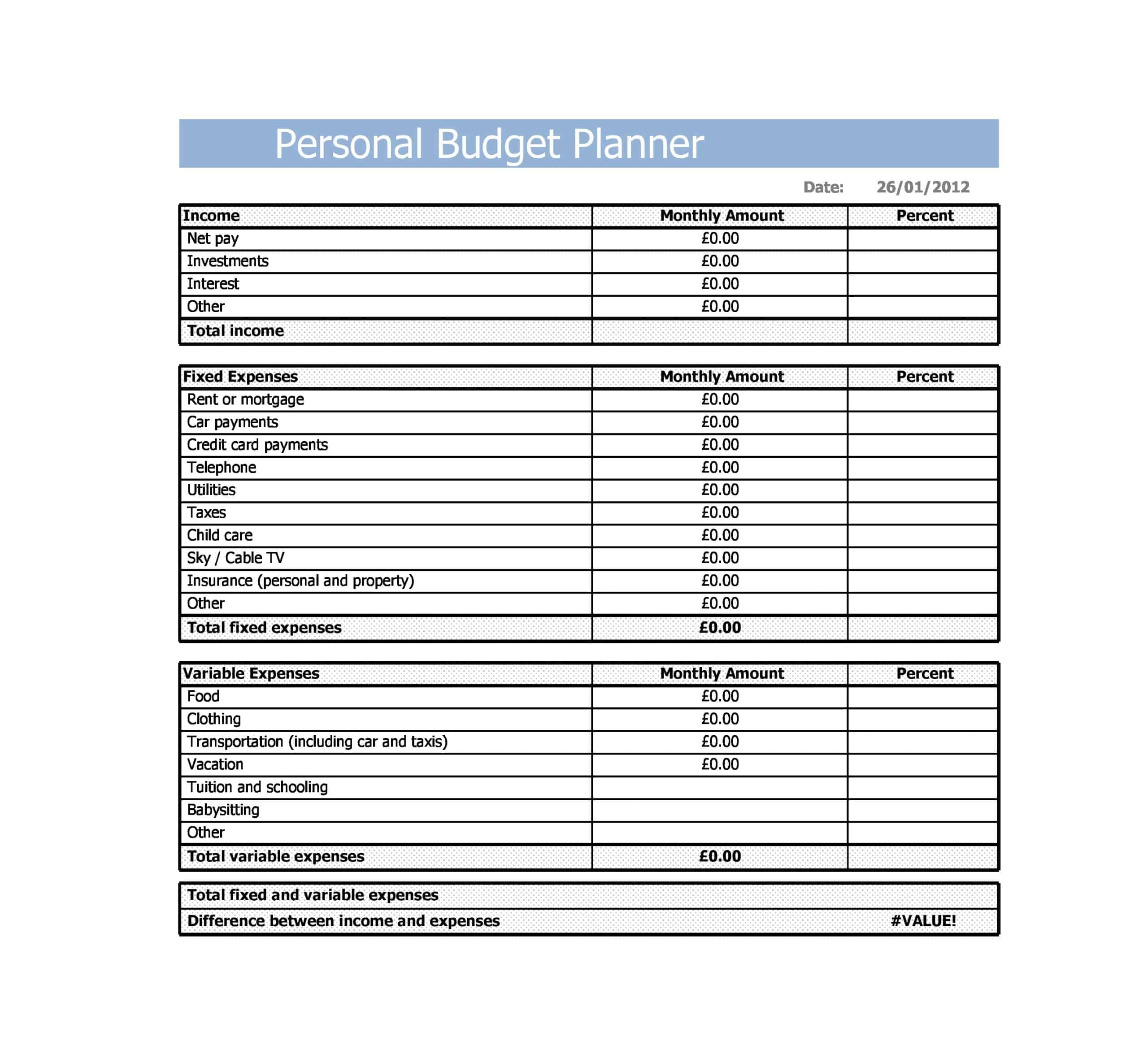
- Income: This is the first section of your personal budget, encompassing all sources of income. This might include salaries, bonuses, dividend income, rental income, or any other streams you have.
- Fixed Expenses: These are the regular, unchanging expenses you need to pay each month. This category may include rent or mortgage payments, car payments, insurance premiums, and subscription services.
- Variable Expenses: These are the costs that fluctuate from month to month, such as groceries, utilities, gas, dining out, entertainment, and personal care items.
- Periodic Expenses: These are expenses that do not occur monthly but at different times throughout the year, such as property taxes, annual insurance premiums, car maintenance, or holiday gifts.
- Savings and Investments: This category is vital for your financial health and future. It could include savings for emergencies, retirement accounts like a 401k or IRA, other investments, and specific savings goals like a house down payment or vacation fund.
- Debt Repayment: If you have any debts such as student loans, credit card debt, car loans, or personal loans, you’ll want to include a section in your budget for debt repayment.
- Net Income: This is your income minus all the above-mentioned expenses, savings, and debt repayments. It gives you a clear idea of whether you’re living within your means or overspending. Ideally, you should aim for a positive net income, meaning you’re spending less than you’re earning.
- Goals: Your budget should also consider your short-term and long-term financial goals. These could range from paying off debt to saving for a vacation, buying a home, or investing in your future.
Tips for Effective Budgeting
Creating a successful and functional budget can be a game changer for your financial life. Here are some practical tips to make your budgeting journey more effective:
- Start with a Realistic Approach: Begin by assessing your income and expenses honestly. Overestimating your income or underestimating your expenses will only lead to budgeting pitfalls down the line.
- Track Expenses Consistently: This is a crucial habit for successful budgeting. Regularly record every expense, no matter how small. This helps you see exactly where your money is going and identify areas where you might be overspending.
- Categorize Your Expenses: Divide your expenses into fixed, variable, and periodic costs. This way, you can see what is necessary, what fluctuates, and what can potentially be trimmed.
- Prioritize Saving and Investing: Pay yourself first by allocating a portion of your income towards savings and investments. Even a small amount can grow significantly over time due to the power of compound interest.
- Set Clear Financial Goals: Having both short-term and long-term financial goals can motivate you to stick to your budget. Whether it’s saving for a vacation or planning for retirement, knowing what you’re working towards can help maintain your financial discipline.
- Review and Adjust Your Budget Regularly: Your budget isn’t set in stone. Review it at least once a month and adjust it as necessary. Your income, expenses, and financial goals are likely to change over time, and your budget should adapt accordingly.
- Automate Where Possible: Automating payments for recurring expenses or savings can help avoid late fees and make sure you’re consistently contributing to your savings or investment goals.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Financial uncertainties can occur at any time. An emergency fund provides a financial buffer that can keep you afloat during difficult times without disrupting your regular budget.
- Avoid Unnecessary Debt: While certain debts like mortgages or student loans can be considered as investments in your future, avoid unnecessary debt like high-interest credit card debt that can quickly spiral out of control.
- Seek Professional Advice, if Needed: If you’re feeling overwhelmed by the process of budgeting, consider seeking advice from a financial advisor. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific financial situation and goals.
How to create a personal budget spreadsheet?
Creating a personal budget spreadsheet might seem complex at first, but with these step-by-step instructions, you’ll have a robust tool to manage your finances effectively:
Step 1: Open a new spreadsheet: You can use any spreadsheet program that you’re comfortable with, such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or Numbers for Mac users.
Step 2: Identify Income Streams: Label the first row ‘Income‘ and list all your income sources in the following rows, with the amounts in the next column. Be sure to include regular salaries, bonuses, and any other consistent income like rental or investment returns.
Step 3: Calculate Total Income: At the end of the income section, sum up all your income sources to get your total income for the month.
Step 4: List Fixed Expenses: Label a new section ‘Fixed Expenses’ and list all your regular, unchanged monthly expenses like rent or mortgage, utilities, insurance, car payments, and any subscriptions.
Step 5: List Variable Expenses: Next, create a ‘Variable Expenses’ section for costs that fluctuate each month, such as groceries, dining out, fuel, personal care, and entertainment.
Step 6: Detail Periodic Expenses: Under ‘Periodic Expenses,’ list expenses that occur periodically but not every month, like annual insurance premiums or car maintenance costs. You can calculate a monthly amount by dividing the yearly cost by 12.
Step 7: Outline Savings and Investments: Include a section for ‘Savings and Investments,’ setting specific financial goals like emergency funds, retirement savings, or other investment contributions.
Step 8: Allocate for Debt Repayment: If you have debts, include a ‘Debt Repayment‘ section listing each debt and the monthly payment towards it.
Step 9: Calculate Total Expenses: At the end of these sections, add up all expenses to get your total monthly expenditure.
Step 10: Determine Net Income: Subtract your total expenses from your total income to find your net income. If it’s negative, review your budget for areas to cut back on; if it’s positive, consider boosting your savings or investments.
Step 11: Review and Adjust Regularly: Lastly, make a commitment to review and adjust your budget regularly, ideally every month. This allows your budget to evolve as your income, expenses, and financial goals change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a personal budget spreadsheet is a vital tool for successful financial management. It allows for the careful monitoring of income, fixed and variable expenses, periodic costs, savings, investments, and debt repayments. This comprehensive view of one’s financial situation serves as the foundation for strategic decision-making, promoting saving, investment, and effective management of debts.
The steps to create a budget spreadsheet are straightforward: defining income sources, categorizing expenses, setting aside amounts for savings and investments, planning for debt repayment, and calculating net income. This tool becomes even more powerful when paired with good budgeting practices such as consistent expense tracking, regular reviews and adjustments, and seeking professional advice when needed.
The importance of maintaining an ongoing budget management process cannot be overstated. Regularly updating your budget allows it to evolve with your changing financial circumstances and goals. It is this dynamic aspect of budgeting that makes it truly effective, as it not only reflects the reality of your financial life but also directs it.
FAQs
Can a personal budget spreadsheet help me get out of debt?
Yes, a personal budget spreadsheet can be a helpful tool for debt management. By outlining your income and expenses, it can help you determine how much money you can allocate towards paying off your debt each month, and track your progress over time.
How often should I update my personal budget spreadsheet?
It’s best to update your spreadsheet regularly. Some people choose to update their budget after each financial transaction, while others do so weekly or monthly. Choose a schedule that works best for you and stick to it.
Can I use a personal budget spreadsheet to save for future goals?
Absolutely! A personal budget spreadsheet can help you allocate funds to specific savings goals, like buying a home, funding an education, or planning a trip. It’s a tangible way to see your progress and stay motivated.
Do I need special software to create a personal budget spreadsheet?
Not necessarily. While there are specialized budgeting software and apps available, you can also create a simple personal budget spreadsheet using programs like Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or even just pen and paper. It all depends on your preference and familiarity with these tools.
What if my actual expenses are more than I budgeted for in my spreadsheet?
That’s a sign you may need to adjust your budget. Review your spreadsheet to see where you’re overspending and consider ways to cut back. Alternatively, you may need to adjust your budget to reflect a more realistic view of your expenses.
What’s the difference between a personal budget spreadsheet and a budgeting app?
A personal budget spreadsheet is a self-created tool where you input and track your income and expenses. It requires manual updates and oversight. A budgeting app, on the other hand, can often link to your bank accounts and automatically update and categorize your transactions. Both tools have their pros and cons, and it comes down to personal preference and needs.


























![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 1 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 2 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Financial Projections Templates [Excel, PDF] 3 Financial Projection](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Financial-Projection-1-150x150.jpg)
