Choosing the perfect diamond can be overwhelming if you don’t know where to start. That’s why I always recommend using a free printable diamond size chart for easy reference. These convenient charts show actual diamond sizes on a hand for round, princess, emerald and other cuts so you can visualize the proportions. Whether for an engagement ring or other special jewelry, a printable size chart helps you shop smart.
Diamond size charts provide all the details you need in one simple document – carat weights, millimeter dimensions, cut types, and of course photographs showing real life diamond sizes. Many also have mm ruler graphics so you can measure your own or your partner’s finger and find the right fit. The best part is that high quality printable diamond charts are available free online – no cost to access this vital information!
I encourage all my customers to use printable diamond size charts to kickstart the selection process. Narrow down the exact carat weight and cut that looks stunning on your hand within your budget.Being able to see actual diamond sizes takes the guesswork out of choosing a diamond you’ll treasure forever. Read on for links to download the most useful and accurate size charts that I recommend to shoppers every day.
Table of Contents
What is a Diamond Carat?

Although a carat is generally known to many as the size of a diamond, the main thing is the weight of the stone. The term carat, which is used to determine the weight of the diamond or stone, is a word specific to the diamond industry. People often assume that the size of a diamond is synonymous with its carat weight, but this is not true. The fact that its weight is more does not mean that its size will be that large because other factors affect the value of the diamond.
A carat is one-fifth of a gram. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams. One carat represents 100 points, and 0.25 carats represents 25 points. Size is an important factor in diamond valuation, but two equally sized diamonds can cost very differently depending on their quality.
Diamond Size Chart Templates
Diamond size chart templates are useful tools for determining the size of a diamond by comparing its weight with its dimensions. These templates can be printed out and used by jewelers, appraisers, or anyone looking to buy or sell a diamond. With a range of sizes and shapes available, diamond size chart templates can help ensure accuracy and transparency in diamond transactions.
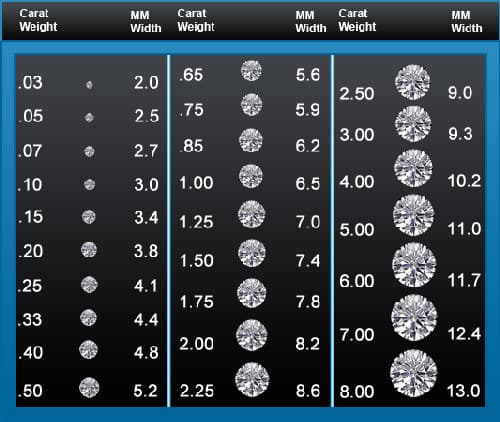
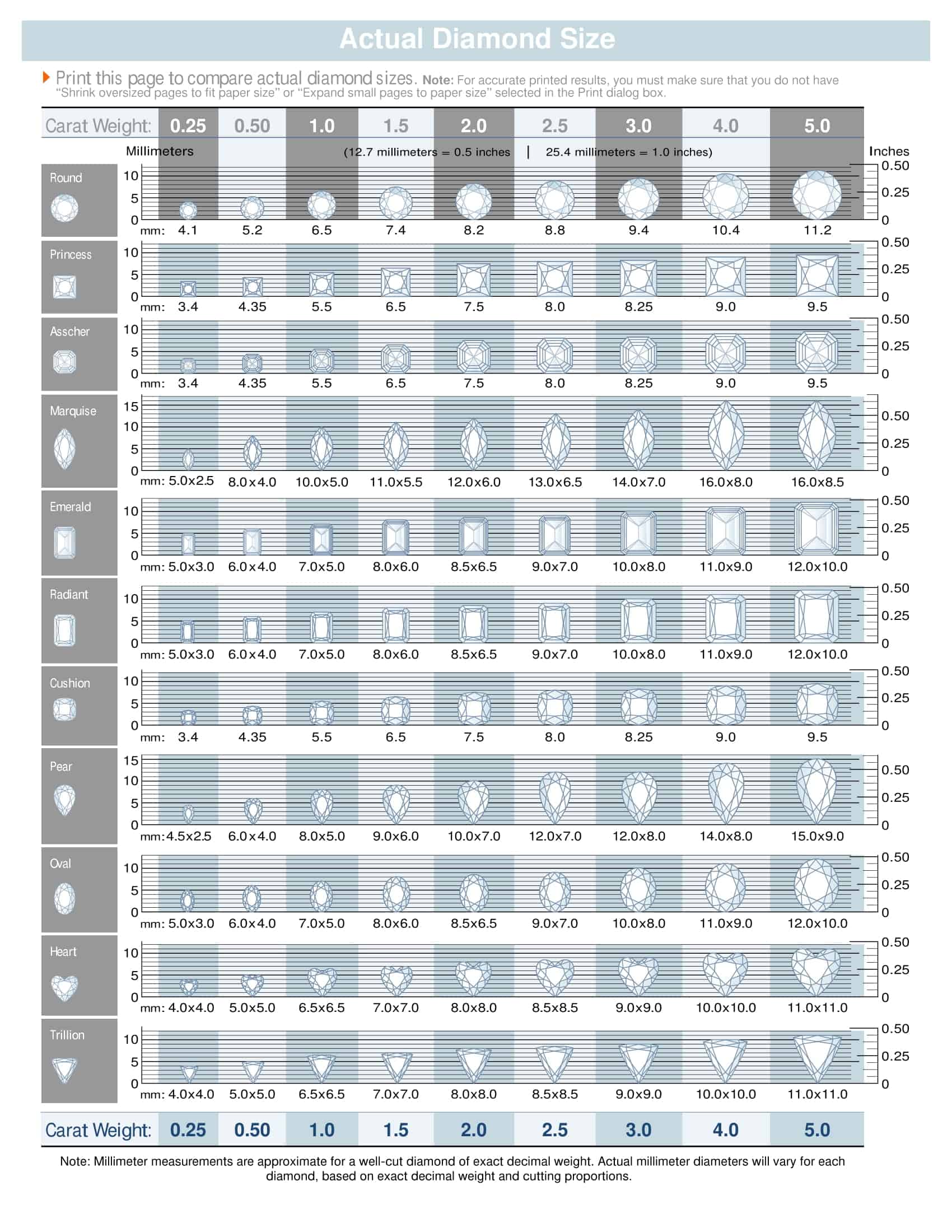
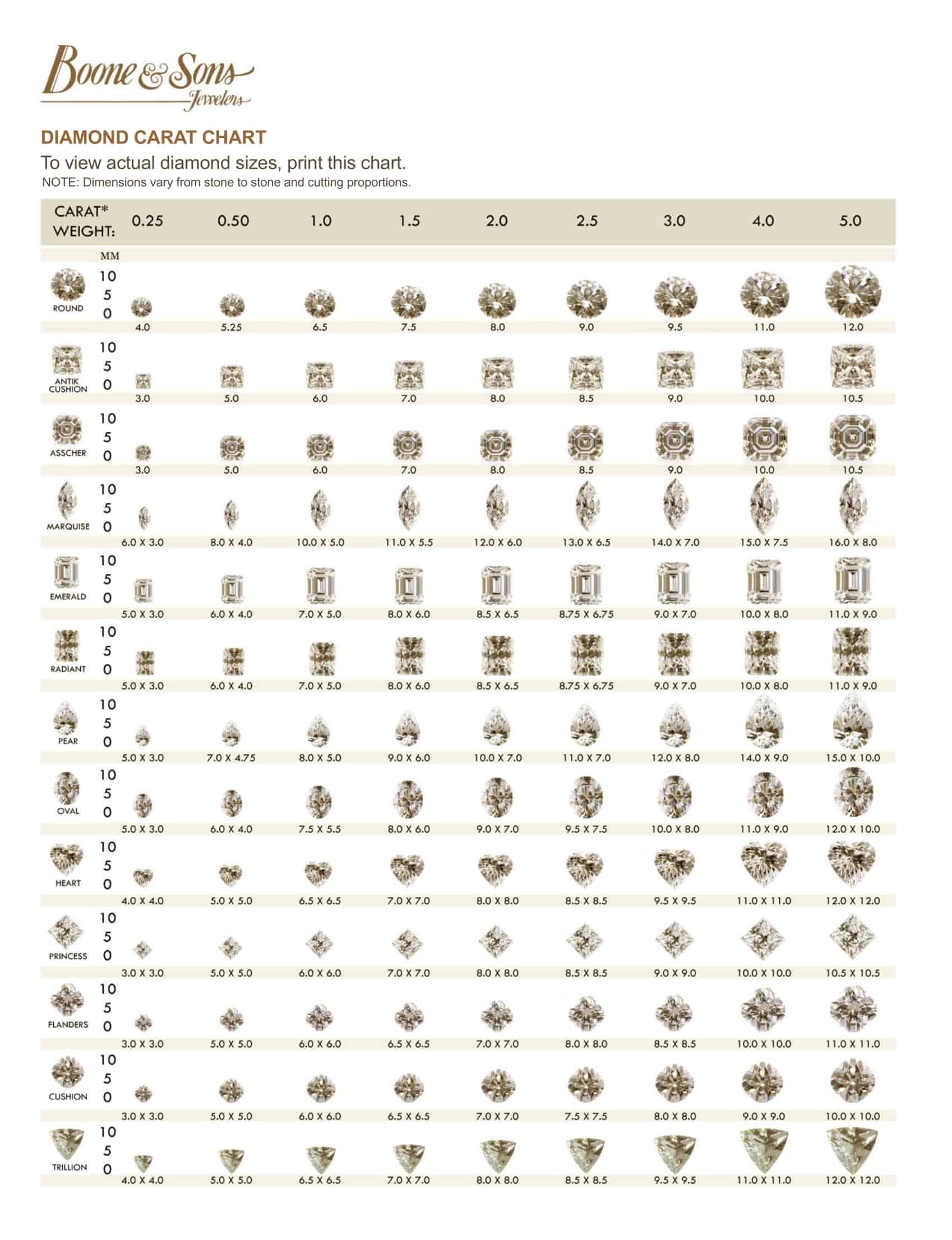
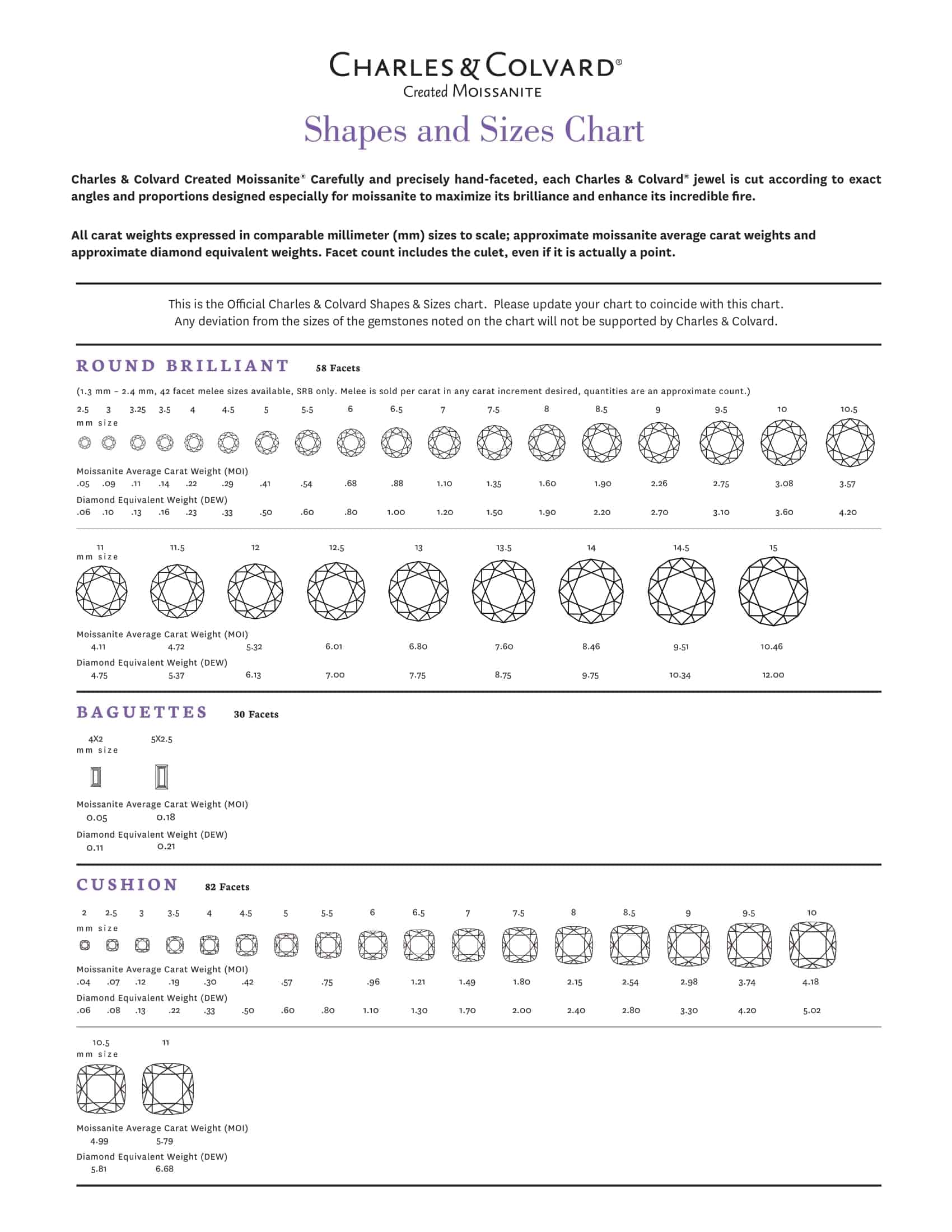
The first key element of diamond size charts is listing the carat weights. Carat refers to the diamond’s mass – one carat equals 0.2 grams. The charts break down the common carat sizes ranging from 0.25 to over 2 carats. They also include the exact measurements in millimeters of diamonds in each carat weight for shapes like round, princess, and emerald. This allows direct size comparisons.
Diamond size templates also indicate diamond quality characteristics like color, clarity, and cut grade. Quality has a significant impact on diamond prices. Top color ratings are D-F, excellent clarity ratings are IF-VS2, and ideal cut grades exhibit maximum brilliance. The charts list price ranges for different carat weights taking these factors into account. Photographs demonstrate each size and shape. In summary, diamond size charts present all the variables in selecting a diamond in a comprehensive, visually appealing template.
| Carat | Weight | Dimensions (mm) | Cut | Color | Clarity | Cut Quality | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.05 g | 4.8 x 2.9 x 1.6 | Round | G-J | SI2-I3 | Good | $100-$250 |
| 0.50 | 0.10 g | 5.9 x 3.9 x 2.1 | Princess | G-J | SI2-I1 | Very Good | $400-$600 |
| 1.00 | 0.20 g | 6.5 x 6.5 x 3.9 | Oval | G-H | VS2-SI1 | Excellent | $2,000-$4,000 |
| 1.50 | 0.30 g | 7.4 x 7.3 x 4.3 | Emerald | D-F | VS2-VS1 | Ideal | $7,000-$10,000 |
| 2.00 | 0.40 g | 8.2 x 8.1 x 4.8 | Pear | D-E | IF-VVS2 | Excellent | $15,000-$25,000 |
Understanding the 4Cs: The Ultimate Diamond Guide
There are four main features to consider when choosing a quality diamond. These dimensions called 4C;
- Carat
- Clarity
- Color
- Cut
Cut
Diamond cut is a feature related to the symmetry and dimensions of the stone. The cut determines the ability of the diamond to sparkle and refract light. Although the stone has perfect color and clarity, this is a feature that should be given importance as it will display a dull appearance with a poor cut. Because the better the cut, the better the diamond will shine. The light entering from one surface of the diamond cut in the right proportions is reflected from the other surface and dispersed and radiated from the upper part called the “crown.” If the cut is too deep, some of the light escapes from the lower part of the diamond, called the “cone.” If the cut is not deep enough, it causes the light to escape from the cone and causes the diamond not to shine enough.
The famous diamond expert, Saul Spero, explains that as a result of his research with people who bought diamonds for 25 years, which type of woman prefers a diamond as follows:
- Round: loyal to his family, reliable, calm
- Marquise: Extroverted, aggressive, creative businesswoman.
- Drop: Gentle, respectful, harmonious.
- Emerald: Disciplined, conservative, honest.
- Oval: Creative, organized, seizing opportunities.
- Heart: Emotional, feminine, sensitive.
Carat
Carat is the unit of measurement that expresses the weight of the diamond. In India, where the diamond was first found, the carob kernel is taken primarily, and 1 carat weighs 200 milligrams (i.e., one-fifth of a gram).
In the jewelry industry, stones weighing less than 1 carat are generally sold. One carat is determined as 100 points. A half carat is 50 points and is written as 0.50 ct.
Size is an essential factor in diamond valuation, but two equally sized diamonds can cost very differently depending on their quality. The fact that two different diamonds have the same carat weight does not necessarily mean that they are of the same price.
Color
Diamonds are formed under extreme heat and pressure, and during this formation, particles of other elements can also be included in the atomic structure of diamonds, thus creating a variety of colors. These granules are so small that they are expressed as “one in a million.” The diamond progresses from dark yellow to a vibrant, bright white. Diamonds are classified based on how close they are to colorless.
The rarest and whitest ones are D, E, F, and G. But mostly diamonds are between H and L.
Diamonds between M and Z have a visible yellow tone. Diamonds in K-Z values will show their yellow color more strikingly and shine less when used with white gold or platinum.
To understand the color of the diamond, you will buy and ask the colorimeter for a printout. Compare with other diamonds and make sure its certification is correct.
D: Completely Colorless. The best quality diamond color is very rare.
E – F: Colorless. However, they contain very light hues that gemologists can determine. rare
G-H: Almost colorless. Classes that are perceived as white, the hue of which cannot be understood unless they are compared with whiter diamonds. The highest quality/price ratio.
I-J: Almost colorless. The latest colorless grades with a warm tone that can be noticed when viewed carefully with the naked eye are very affordable compared to top grades.
K-Z: Colorful.
Clarity
Almost all diamonds contain “tiny particles of pure carbon” as building blocks. These particles turn each diamond into a rare, unique stone and are called “inclusions.” The clarity feature distinguishes each diamond completely from the others. No two diamonds can have the same inclusion in the same place. Large laboratories such as the GIA and HRD also have five factors used to determine the clarity grade of a diamond.
FL, IF Flawless, flawless. A class of diamonds with no flaws inside or out. It is very rare.
VVS1, VVS2 Few flaws are very hard to see with a magnifying glass. It represents an excellent quality.
VS1, VS2 Class with a certain number of defects that can only be seen with a magnifying glass. The most preferred clarity class.
SI1 and SI2 Defects can be easily seen with a magnifying glass; sometimes, they may contain some imperfections that can be seen with the naked eye. An economical choice
Stones with many defects are seen in I1, I2, and I3.
Main Diamond Carat Weights
The carat weight measures a diamond’s mass. The most common carat sizes are:
- 0.5 carat
- 1 carat
- 2 carats
- 3 carats
A 1 carat diamond is exceptionally popular for fine jewelry like engagement rings. As the carat weight increases, so does the diamond’s physical size and rarity, leading to higher prices.
Diamond Dimensions
A diamond’s dimensions, listed as length x width x depth in mm, also affect its price.
- Round brilliant cuts tend to be the smallest per carat.
- Emerald cuts are among the largest.
- Princess and oval cuts fall in between.
It’s important to balance size with cut quality when choosing a diamond shape. An ideal cut will maximize brilliance.
Average Diamond Prices
Setting a budget first allows customers to immediately narrow down options in their price range. The chart’s prices per carat provide realistic cost expectations.
For example, a 1 carat diamond averages around $5,000 while a 3 carat averages over $20,000.
Higher quality colors, clarities, and cuts raise prices for a given carat weight. An IF clarity 1 carat can cost well over $10,000.
Conclusion
With knowledge from a diamond size chart, you can walk into a jewelry store informed and confident. Focus first on the 4Cs – carat, cut, clarity, and color – and use the chart to narrow down diamonds in your preferred size and price range. This will make the shopping experience much smoother!
FAQs
What is a respectable diamond size?
There is no definitive “respectable” diamond size. However, 1 carat is considered an iconic size for solitaire engagement rings and other fine jewelry. Anything above 0.75 carats makes a beautiful statement. Ultimately the best size is what looks great and fits your budget.
What size diamond is best value?
Generally diamonds between 0.7-1.5 carats offer excellent value. Prices jump more steeply above 1.5 carats. You get significant size increase from 0.5 to 1 carat, without a huge price jump. Ideal cut diamonds in this range maximize sparkle.
How much is 2 carats worth?
On average, a 2 carat diamond costs around $15,000-$25,000. However prices vary based on the 4Cs – cut, clarity, color and carat. High quality 2 carat diamonds can cost over $50,000. The price per carat increases significantly at each carat milestone.
How much is 1.5 carats of diamonds worth?
A 1.5 carat diamond averages around $7,000 to $12,000 depending on the 4Cs. Well-cut 1.5 carat diamonds with high clarity ratings offer great value compared to the 2 carat price jump.
What diamond cut gives the most sparkle?
Round brilliant cuts give the most sparkle with optimal light reflection and dispersion. An ideal cut grade maximizes the fire and brilliance.
How close can you go below 1 carat without noticing?
You typically won’t notice much visual difference between a 1 carat and 0.95 carat diamond. Anything above 0.9 carats will still look like 1 carat. Best to save money on just below milestone sizes.

























![Free Printable Morse Code Charts [Numbers, Alphabet] 1 Morse Code Chart](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Morse-Code-Chart-150x150.jpg)

![43+ Free Printable 134A PT Charts [Download PDF] 3 134A PT Chart](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/134A-PT-Chart-150x150.jpg)