Harnessing the raw energy of ambition, let’s plunge into the riveting world of sales planning. This article serves as your comprehensive guide to craft a robust and strategic sales plan, empowered by a practical, easy-to-follow template.
We journey together into the trenches of market research, client profiling, goal setting, and action planning – pillars that elevate your business’ sales strategy. Strap in, this path ensures your company’s sales efforts align seamlessly with your overarching business objectives, paving the way for sustainable growth and increased revenue. Let’s start scripting your success story in the world of sales.
Table of Contents
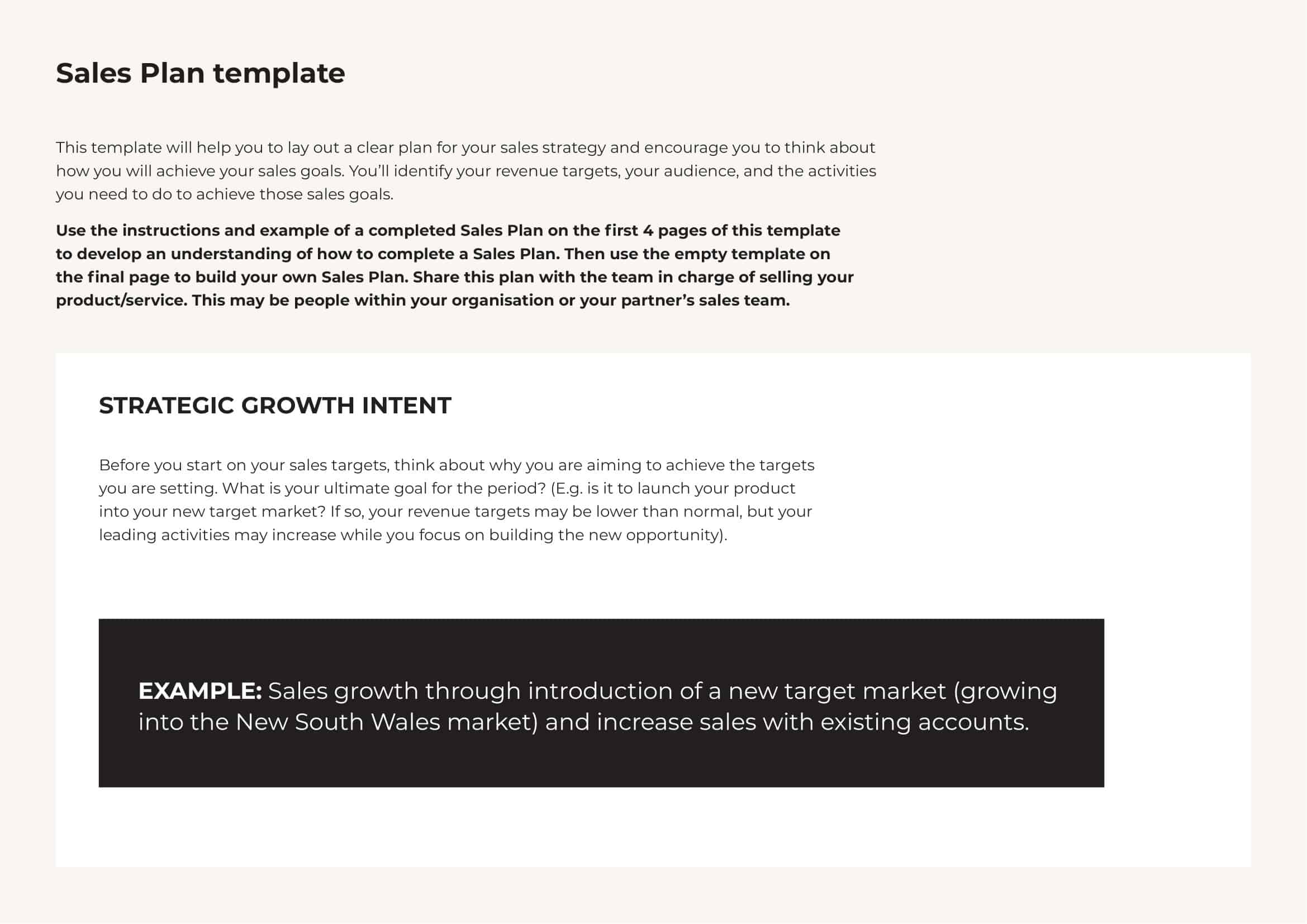
What Is a Sales Plan?

A sales plan is a strategic document that outlines a company’s sales strategy, detailing clear goals, target audience, the tactics to reach those objectives, and the resources required. This comprehensive roadmap enables businesses to focus their efforts effectively, mapping out the path from the current market position to a desired future state.
Key elements within a sales plan typically include specific sales objectives, a detailed customer profile, a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape, a defined sales process, and a clear plan of action for the sales team. Through these elements, a sales plan provides the direction and framework to drive sales, promote growth, and outpace competitors in the marketplace.
Sales Plan Templates
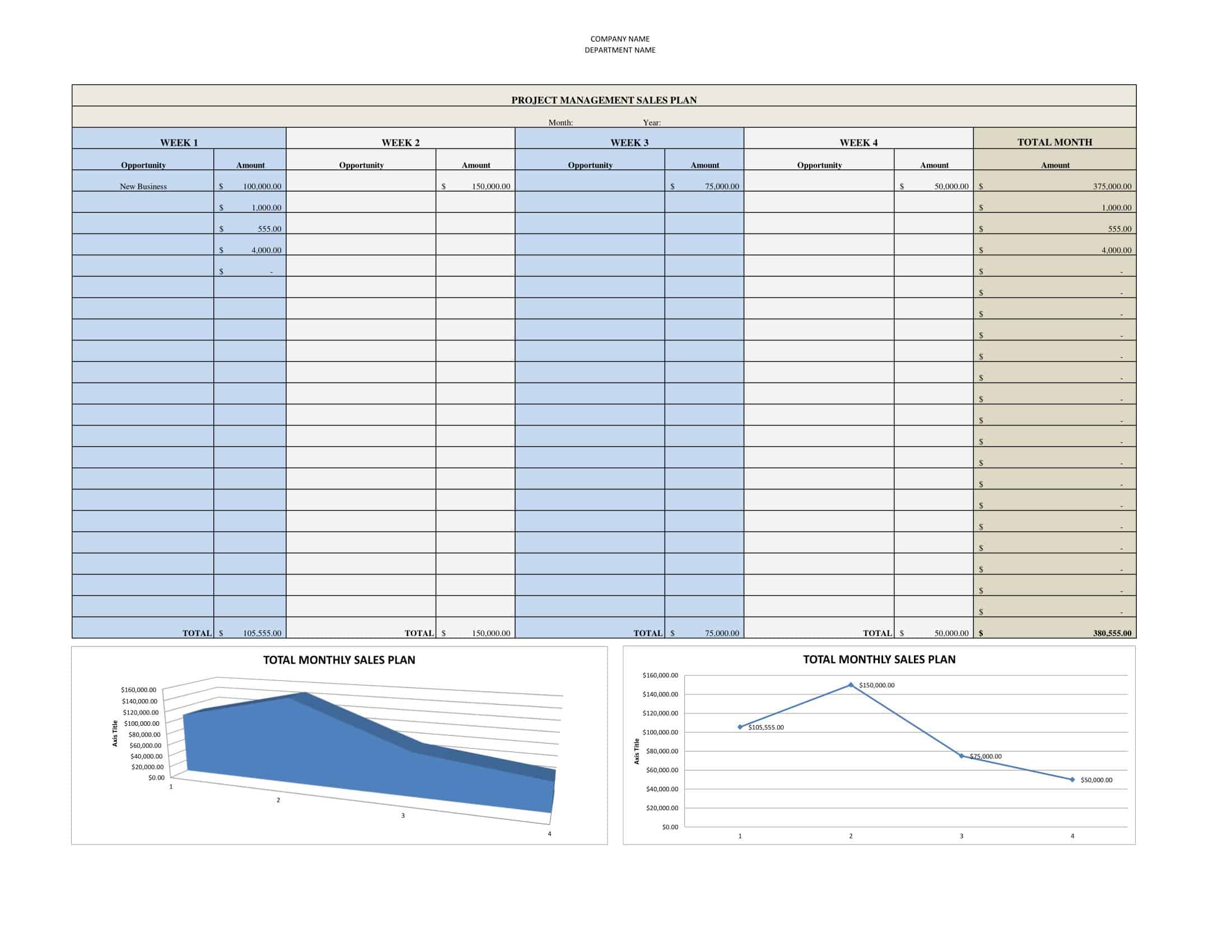
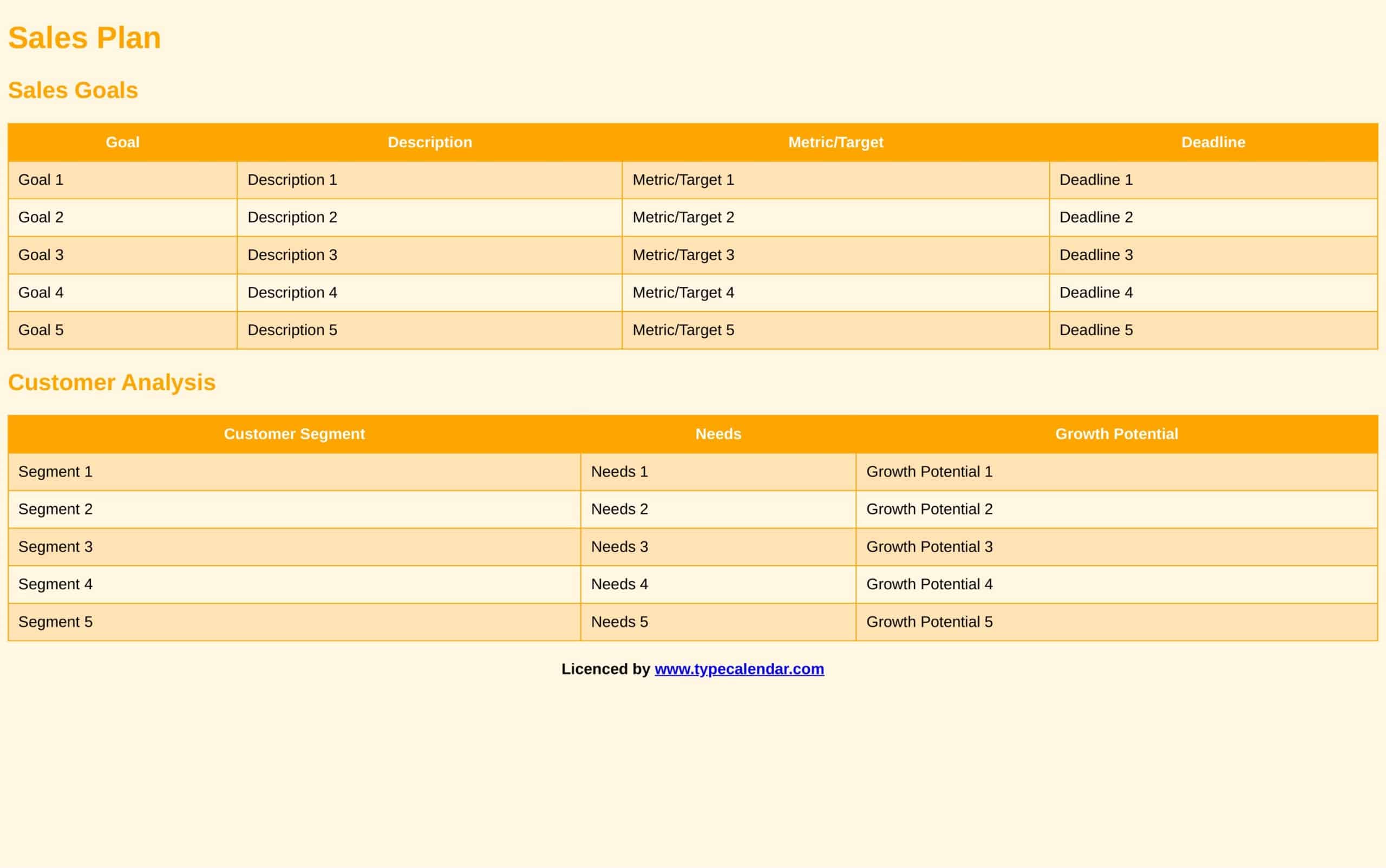
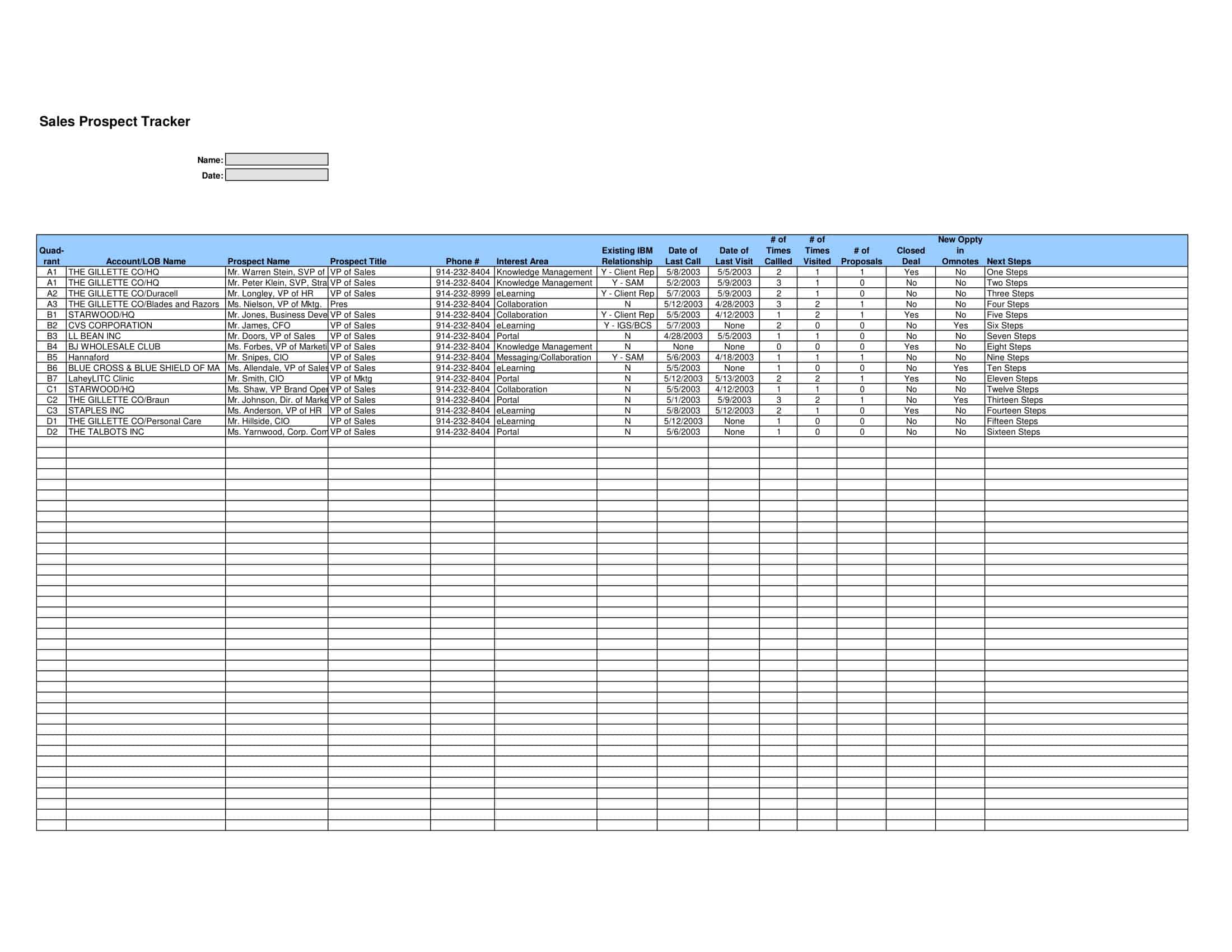
An effective sales plan is critical for business success. Sales plan templates provide a valuable structure for strategically developing sales plans. The templates make creating plans simple.
The templates contain sections for each element of a sales plan. This includes market analysis, growth strategies, sales processes, lead generation tactics, and more. Templates prompt users to include sales projections, expense budgets, and key metrics to track. Some are customized for product or service sales. The standardized formats enable thorough, cohesive planning.
Sales plan templates save time spent starting from a blank page. They guide users through key considerations and details so nothing is overlooked. Users just input their specific offerings, customers, challenges and goals. Templates can be easily updated as the business environment evolves. They provide a convenient starting point for creating polished plans tailored to the unique needs of any sales organization. Whether used by large sales teams or solo entrepreneurs, sales plan templates lead to actionable and effective sales plans that drive revenue growth.
The Benefits of a Sales Plan
The benefits of a sales plan are manifold and impact a variety of dimensions within a business. Let’s delve into this labyrinth of advantages, painting a comprehensive picture of how such a strategic document can elevate an organization’s sales efforts.
- Clear Direction: A sales plan provides the team with a detailed roadmap, outlining how to reach the organization’s sales goals. It offers direction, ensuring everyone is on the same page and working towards common objectives. This enhances team alignment and ensures collective effort.
- Enhanced Focus: It streamlines sales efforts by identifying the ideal target customers, effectively helping the sales team to prioritize their energy and resources. This increased focus can lead to higher conversion rates and more efficient use of resources.
- Informed Decision Making: Sales plans are based on careful analysis of market conditions, competitor activity, and customer needs. This research provides valuable insights that can be used to make informed decisions and develop strategies that are more likely to succeed.
- Increased Accountability: By clearly defining sales targets and the steps needed to reach them, a sales plan holds the sales team accountable. It tracks the progress towards goals and identifies any areas where performance is falling short, enabling corrective action to be taken quickly.
- Better Forecasting: Sales plans allow businesses to predict future sales trends based on historical data and market analysis. This ability to forecast can inform inventory management, budget planning, and other business decisions.
- Resource Allocation: A well-designed sales plan helps in optimal resource allocation. By understanding where to focus the sales efforts, businesses can allocate their time, manpower, and budget efficiently, leading to increased return on investment.
- Mitigating Risks: A sales plan identifies potential obstacles and market challenges. By anticipating these hurdles, the plan allows businesses to develop contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies, protecting the business from unexpected market fluctuations.
- Customer Understanding: A thorough sales plan includes a deep understanding of the target customer. This understanding can help to shape the sales messaging, tailor the product offering, and ultimately serve the customer more effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: By meticulously outlining the sales process, a sales plan gives a business the upper hand over competitors who may be operating without such strategic intent. It equips businesses with the foresight to recognize opportunities and the agility to seize them.
- Driving Growth: Ultimately, a good sales plan contributes to business growth. With clear goals, a focused strategy, and a dedicated team, businesses can scale their operations, increase their market share, and drive revenue growth.
What Is Included in a Sales Plan?
A comprehensive sales plan includes a wide range of elements that encompass a detailed sales strategy. Here, we’ll dissect a sales plan, diving deep into each of these components to understand how they contribute to an effective sales plan:
Executive Summary
This section provides a high-level overview of the entire sales plan. It should quickly communicate the main objectives and strategies, serving as a succinct yet comprehensive summary for stakeholders who might not delve into the full document.
Sales Objectives
Clear, measurable sales objectives are crucial. They should align with the broader business objectives, and they may be broken down into annual, quarterly, and monthly goals. These objectives could be based on revenue, unit sales, market share, or other relevant metrics.
Target Market and Customer Profile
This section describes the ideal customer for your product or service. It includes demographic information, psychographics, behaviors, and needs. In addition, the target market analysis will outline the size and characteristics of the market segments that the company aims to reach.
Competitive Analysis
Understanding your competition is critical. This involves identifying your direct and indirect competitors, understanding their products or services, sales strategies, market share, strengths, and weaknesses. This knowledge informs your unique value proposition and differentiating factors.
Sales Methodology and Process
This component outlines the sales tactics and methodologies your team will use to close deals. It defines each step of the sales process from lead generation to closing and after-sales service. This can also include any sales scripts, product positioning statements, or tools to be used.
Sales Team Structure and Roles
Detailing the structure of the sales team, including roles and responsibilities, is key. This can also include an assessment of current team skills and any areas that require development or new hires.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
These are the metrics by which the success of the sales plan will be measured. KPIs might include new customer acquisition, revenue growth, conversion rates, customer lifetime value, customer retention rates, and average deal size.
Sales Resources and Budget
This section outlines the resources available to the sales team, including budget, tools, and technology. This can include sales software, training budgets, marketing support, and any other resources that will help the team achieve their goals.
Sales Action Plan
This is the tactical section of the sales plan, outlining the specific steps the sales team will take to achieve the objectives. This could include lead generation tactics, customer relationship management strategies, sales promotion activities, and any other planned sales initiatives.
Contingency Planning
It’s essential to plan for potential challenges or changes in the market. This section outlines possible risks or obstacles and describes how the team will respond to keep the sales strategy on track.
Types of Strategic Sales Plans
In the world of sales, strategic planning takes many forms. Each approach caters to different needs, goals, and market scenarios. Let’s explore some of the key types of strategic sales plans, illustrating their unique features and their application through tangible examples.
Territory Sales Plan:
A territory sales plan is designed to manage and grow sales within a specific geographical area. It’s particularly useful for businesses with a broad market reach, where sales efforts need to be localized to suit specific regional needs. The plan includes territory segmentation, customer profiling within the region, setting territory-specific sales targets, and assigning sales teams based on the region. It also involves an understanding of the competitive landscape in each territory.
For example, a multinational beverage company might develop a territory sales plan for its operations in Asia. This plan would include the sales goals for the region, an understanding of local customer preferences, competition, and the tactics to promote their products within these markets.
Account Sales Plan:
This type of sales plan is used primarily in B2B sales scenarios, focusing on managing and growing relationships with specific key accounts. The emphasis is on understanding the client’s business, their needs, and challenges, and tailoring the offerings accordingly. The plan includes setting account-specific goals, mapping out decision-makers and influencers within the client organization, and developing tailored strategies to upsell or cross-sell.
For instance, a software company offering enterprise solutions might create an account sales plan for a major client. The plan would focus on understanding the client’s business needs, the decision-making hierarchy, and developing a sales strategy to expand the range of services sold to this client.
Channel Sales Plan:
A channel sales plan focuses on selling through third-party partners, such as distributors, resellers, or affiliate marketers. The plan outlines the goals for each channel, strategies to support partner sales, and measures to monitor and manage channel performance. It requires building strong relationships with channel partners, providing them with the necessary sales tools and incentives.
For instance, a smartphone manufacturer may have a channel sales plan in place for its network of global distributors. This plan would detail the sales targets for each distributor, strategies to support their sales efforts (like joint marketing campaigns or exclusive promotions), and mechanisms to monitor their performance.
Product Sales Plan:
This sales plan centers on selling a specific product or product line. It’s especially relevant for businesses with diverse product portfolios, where each product might cater to different customer segments or markets. The plan includes setting product-specific sales targets, understanding the product’s unique selling propositions, and identifying the ideal customer profiles for the product.
For example, a cosmetic brand with a wide range of products might create a product sales plan for a new skincare line. The plan would focus on the sales targets for this new product line, the unique selling points of the skincare range, and the ideal customers for these products.
Strategic Partnership Sales Plan:
This plan focuses on aligning sales efforts with another organization to leverage the partnership’s collective strength. The partners might offer complementary products or services, or they may share a similar target market. The plan outlines the partnership goals, terms of collaboration, sales responsibilities of each partner, and the strategies to support joint sales efforts.
For example, a health insurance company might develop a strategic partnership sales plan with a network of hospitals. They would work out collaborative packages and exclusive benefits for their mutual customers, thereby enhancing the overall value proposition and driving sales for both parties.
Direct Sales Plan:
A direct sales plan is centered on selling products or services directly to consumers, bypassing any intermediaries. It’s prevalent in businesses that prioritize direct customer relationships. This plan outlines the direct sales goals, strategies for customer acquisition and retention, and measures to enhance the customer buying experience.
For instance, a boutique fashion brand that sells exclusively through their website would have a direct sales plan. It would detail their online sales targets, strategies to drive website traffic and convert visitors into customers, and initiatives to deliver an outstanding online shopping experience.
Inside Sales Plan:
This sales plan involves selling remotely, often through phone calls, emails, or online meetings, without any in-person interactions. The plan sets out the targets for the inside sales team, the strategies for lead generation and conversion, and the tools to facilitate remote selling.
An example could be a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company that uses an inside sales plan. They would focus on generating and qualifying leads through online marketing, engaging potential customers through virtual demos and meetings, and closing deals remotely.
Event Sales Plan:
This plan involves selling at trade shows, conventions, fairs, or other events. The plan outlines the sales targets for each event, strategies to attract visitors to the booth or presentation, and tactics to engage potential customers and close sales during the event.
For instance, a publisher attending a book fair would have an event sales plan. They would strategize on how to attract attendees to their booth, how to effectively showcase their new releases, and tactics to drive on-the-spot sales.
What are examples of sales strategies?
Sales strategies are methods your business employs to sell more products or services in the marketplace. They provide the roadmap for businesses to achieve their sales objectives. Here are examples of different sales strategies and how they are applied:
1. Solution Selling: This strategy is all about identifying a customer’s pain point and then demonstrating how your product or service provides the solution. It is particularly effective for complex products or services where the value proposition is closely linked to the unique challenges of each customer. For example, a cybersecurity software company might use solution selling to demonstrate how their product addresses specific security vulnerabilities of a potential client.
2. Relationship Selling: This strategy is focused on building deep relationships with customers, prioritizing long-term customer engagement over immediate sales. This strategy might involve a comprehensive customer service program, regular check-ins with customers, or loyalty programs. An example of this might be a high-end car dealership that focuses on nurturing long-term relationships with its customers to encourage repeat business and referrals.
3. Up-selling and Cross-selling: These strategies aim to increase the value of a sale by encouraging customers to purchase a higher-priced item (up-selling) or by selling them an additional product (cross-selling). For example, a cable TV company might up-sell by promoting a premium package to a customer initially interested in a basic package, or cross-sell by offering a bundled internet service.
4. Value Selling: This strategy focuses on selling the value or benefit that a product or service can deliver rather than selling based on price. This involves clearly articulating the benefits and value proposition of your product and differentiating it from competitors. A designer furniture brand, for instance, might emphasize the craftsmanship, superior materials, and aesthetic appeal of its products to justify a higher price point.
5. Social Selling: This strategy involves leveraging social media platforms to find and engage with new prospects. It can involve sharing relevant content, engaging with potential customers through comments, and direct messaging. For example, a clothing brand may use Instagram to showcase its products and engage with its followers by responding to comments and DMs, or by sharing user-generated content.
6. Direct Selling: This strategy involves selling directly to the consumer, bypassing any middlemen. This could be through a physical store, online store, or direct salesforce. For example, a cosmetic company might sell its products directly to consumers through a network of sales representatives who host home-based parties.
7. Consultative Selling: This strategy involves acting as a consultant and advising customers to find the best solution to their problem or need. The salesperson asks probing questions to understand the customer’s situation and then recommends the best product or service for their specific needs. For example, a business consultant would use this strategy to understand a client’s business challenges and then recommend tailored solutions.
8. Channel Sales Strategy: This involves using a third party, whether it’s a retailer, distributor, affiliate, or a partner, to sell products. Businesses that don’t want to or can’t sell directly to their customers use a channel sales strategy. For example, a manufacturer might sell its products to a retailer, who then sells the products to the end customer.
Ideal Sales Strategy Handler: Who’s the Right Person?
The person best suited to handle a sales strategy will typically hold a leadership position within an organization’s sales or marketing division. Their title and responsibilities may vary based on the size and structure of the company. Here are some typical roles that often handle sales strategy:
- Sales Manager: In smaller organizations, the Sales Manager often takes the lead in developing and implementing the sales strategy. They have a deep understanding of their team, their product or service, and their customers, which makes them well equipped to devise effective sales strategies.
- Director of Sales: In larger organizations, a Director of Sales often oversees sales strategy. They usually manage multiple sales managers and have a broader, more strategic role. They’re responsible for setting sales goals, defining sales processes, and ensuring the sales teams are aligned with the company’s overall objectives.
- VP of Sales: In even larger corporations, the Vice President (VP) of Sales may be the one to handle sales strategy. This executive-level role oversees all sales activities across the organization. They are responsible for developing a high-level sales strategy that aligns with the company’s strategic vision and objectives.
- Chief Sales Officer (CSO) or Chief Revenue Officer (CRO): In some companies, a CSO or CRO is the highest-ranking individual in charge of sales strategy. They oversee all customer-related activities, from marketing to sales to customer service. Their role involves ensuring that all these departments work together effectively to drive revenue.
- Sales Operations Manager: In some cases, a Sales Operations Manager can also be involved in sales strategy. They handle the behind-the-scenes work that allows the sales team to run efficiently, including sales analytics, CRM management, and process optimization, which directly influence the strategic direction.
- Sales Strategist/Sales Strategy Manager: Some companies have a dedicated role specifically for sales strategy. This person’s entire role revolves around creating, implementing, and tracking sales strategies and their effectiveness.
How do you write a sales plan?
Sales plan templates function as pivotal roadmaps, charting the course for your sales team to achieve their targets. This indispensable resource, meticulously designed with your sales force in mind, outlines the path to success.
Depending on the nature of your business and its strategic objectives, the sales plan you construct may have an expansive scope spanning multiple years, or it might focus on the shorter term, such as an annual blueprint. In any eventuality, your sales plan serves as the compass guiding your team towards their sales aspirations. Let’s delve into the steps to craft this influential document:
Step 1: Executive Summary
Start your sales plan with an executive summary that provides an overview of the main points of your plan. This section should be concise and serve as a quick reference guide to the content of the plan. It should include the main objectives, key strategies, and expected outcomes. Write this section last, even though it comes first in your plan, as it summarizes the contents of your entire sales plan.
Step 2: Objectives
Outline the key objectives of your sales plan. These goals should align with your overall business objectives and should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Objectives could include increasing sales by a certain percentage, entering new markets, or improving customer retention rates.
Step 3: Current Situation Analysis
This section involves a detailed analysis of your current sales situation. Review your past performance, including what worked and what didn’t. Look at your current market position, the size of your potential market, your competitors, and any regulatory or external factors that could impact your sales. This step often involves conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats).
Step 4: Customer Segmentation
Identify your target customers. Break your customers into segments or groups based on characteristics such as industry, geography, buying habits, or company size (for B2B sales). For each segment, develop a buyer persona that includes their pain points, purchasing decision drivers, and where they seek information.
Step 5: Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Articulate your Unique Selling Proposition (USP) – the features, benefits, or attributes of your product or service that differentiates you from your competitors. Your USP should address the specific needs and pain points of your customer segments.
Step 6: Sales and Marketing Strategies
This is the core of your sales plan, where you outline your strategies for reaching your sales objectives. This could include strategies for lead generation, customer retention, upselling, cross-selling, and more. Consider your marketing strategies as well, such as content marketing, SEO, social media, or advertising, which will drive leads for your sales team.
Step 7: Sales Channels
Detail the channels you will use to sell your product or service, such as direct sales, e-commerce, distributors, resellers, or strategic partners. Outline the strategies and tactics you will use for each channel.
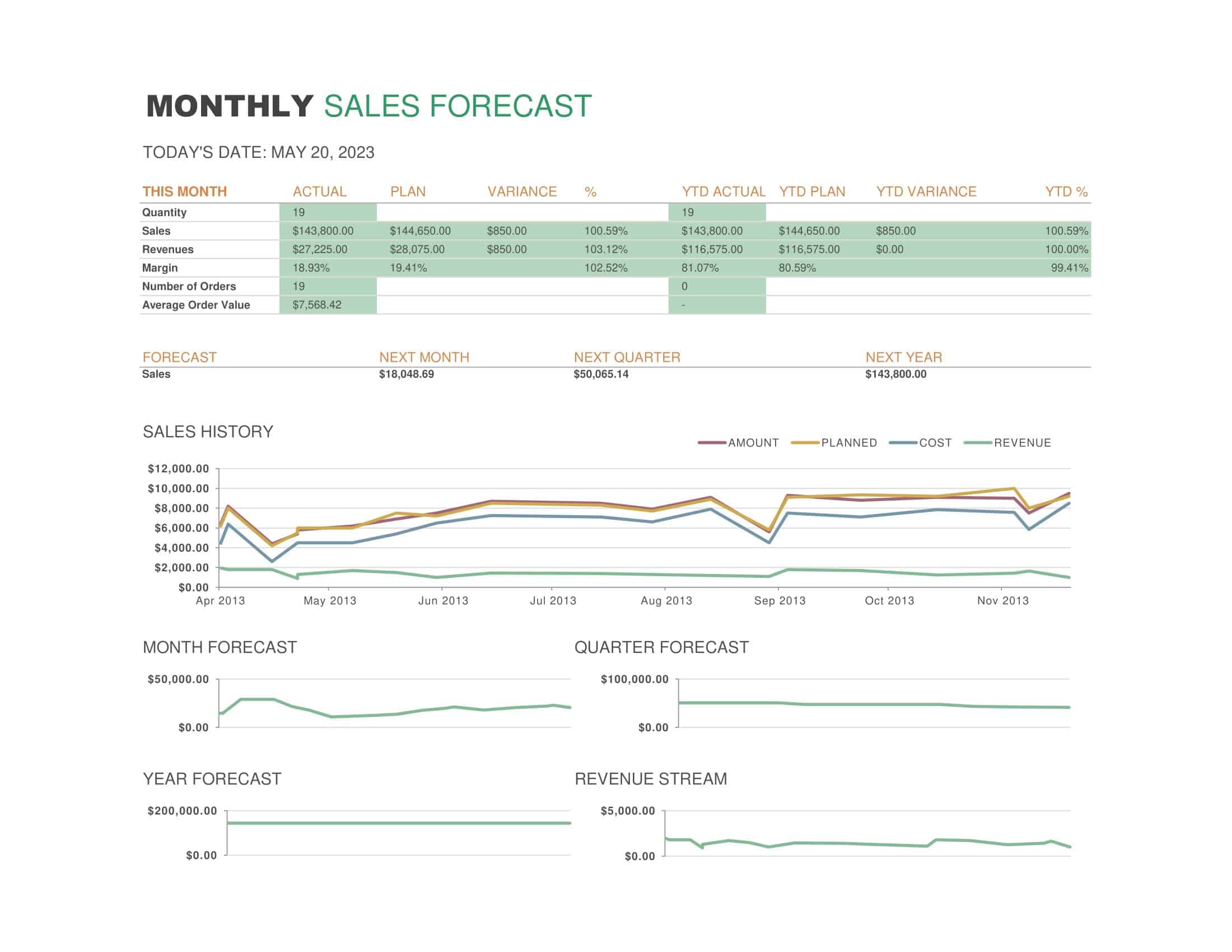
Step 8: Sales Forecast
Based on your strategies and market analysis, develop a sales forecast. This is a prediction of the sales revenue your strategies will generate. Your forecast should be as realistic as possible, using past sales data, market trends, and realistic assessments of what your team can achieve.
Step 9: Budget and Resources
Determine the budget and resources needed to implement your sales plan. This includes the cost of your sales team, marketing expenses, training costs, technology investments, and more.
Step 10: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define the key performance indicators you will use to measure the success of your sales plan. This could include the number of new customers, sales revenue, average deal size, sales cycle length, or customer retention rate.
Step 11: Action Plan
Outline the specific steps you will take to implement your sales plan. Assign responsibilities to specific team members and set timelines for each task. This action plan will guide your team in the execution of the sales plan.
Step 12: Review and Refine
Finally, set up a process to regularly review and refine your sales plan. This review process should assess whether you are on track to meet your objectives, what’s working well, and what needs adjustment. Sales plans are dynamic documents that should evolve based on your business performance and market changes.
FAQs
What is a sales strategy?
A sales strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines the approach and tactics used to achieve sales objectives. It encompasses the overall direction and methods for reaching and influencing customers, closing deals, and maximizing revenue. A sales strategy takes into account factors such as market analysis, competitive landscape, customer needs, and the company’s unique value proposition.
How often should a sales plan be reviewed and updated?
Sales plans should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure their relevance and effectiveness. It is recommended to review the sales plan at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in the market, business goals, or sales team structure. However, it’s also important to monitor sales performance on an ongoing basis and make adjustments to the plan as needed.
What role does market research play in sales planning?
Market research plays a critical role in sales planning. It provides valuable insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and market trends. By understanding the target market’s needs, pain points, and purchasing habits, businesses can tailor their sales strategies to effectively reach and engage customers. Market research helps identify opportunities, assess competition, and develop a competitive advantage, ultimately improving the chances of sales success.
How can a sales plan help in setting realistic sales targets?
A sales plan helps set realistic sales targets by considering various factors such as historical sales data, market analysis, and the organization’s capacity and resources. It enables businesses to evaluate their growth potential and align targets with market conditions and the overall business strategy. By setting achievable sales targets, businesses can motivate their sales team and create a sense of accomplishment while maintaining a focus on sustainable growth.
What is the difference between a sales plan and a sales forecast?
A sales plan and a sales forecast serve different purposes but are interconnected. A sales plan outlines the strategies, tactics, and actions to achieve sales goals, while a sales forecast estimates the expected sales revenue over a specific period. The sales plan guides the activities and initiatives that contribute to achieving the sales forecast. The sales forecast is typically based on historical sales data, market trends, and the sales team’s projections, whereas the sales plan focuses on the specific strategies and tasks to drive sales growth.
How can sales strategies be adjusted to accommodate changing customer needs?
To accommodate changing customer needs, sales strategies can be adjusted in the following ways:
- Stay informed: Continuously monitor customer feedback, market research, and industry trends to understand evolving customer needs.
- Adapt messaging: Modify sales messaging and value proposition to align with changing customer priorities and pain points.
- Offer flexibility: Provide flexible solutions and options that cater to different customer preferences and requirements.
- Leverage technology: Embrace technology tools and platforms that enhance customer engagement and provide personalized experiences.
- Customer segmentation: Refine customer segmentation to better target specific customer groups and tailor sales strategies accordingly.
- Collaboration with other departments: Work closely with marketing, product development, and customer service teams to gather insights and align strategies to meet changing customer needs.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of sales strategies and make necessary adjustments based on feedback and data.
How can a sales plan help in improving sales team performance?
A sales plan can improve sales team performance in several ways:
- Clear direction: A sales plan provides a clear roadmap and specific goals for the sales team, ensuring that everyone is aligned and focused on achieving common objectives.
- Accountability: By defining roles, responsibilities, and performance expectations, a sales plan establishes accountability within the sales team, driving motivation and productivity.
- Training and development: A sales plan identifies training needs and areas for skill development, enabling targeted training programs to enhance the sales team’s capabilities.
- Resource allocation: With a well-defined sales plan, resources such as budget, technology, and support can be allocated strategically, empowering the sales team to perform at their best.
- Performance measurement: The sales plan establishes key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure and evaluate sales team performance. Regular monitoring allows for timely feedback and coaching to address areas of improvement.
- Collaboration and communication: The sales plan fosters collaboration among team members by providing clarity on roles and encouraging open communication. This teamwork enhances overall sales team performance.
- Continuous improvement: Through regular reviews and adjustments, a sales plan facilitates continuous improvement, ensuring that the sales team remains adaptable and responsive to changing market dynamics.



































![Free Printable Sales Letter Templates [Word, PDF] Example Long Form 1 Sales Letter](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Sales-Letter-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Sales-Letter-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Sales Plan and Strategy Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Sales Plan and Strategy](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Sales-Plan-and-Strategy-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Sales Forecast Templates [Word, Excel] 3 Sales Forecast](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Sales-Forecast-150x150.jpg)
