The Likert Scale is a commonly used measurement tool in the field of psychology and market research. Named after its inventor, Rensis Likert, it is a type of rating scale that allows individuals to express their level of agreement or disagreement with a particular statement.
The scale ranges from strongly agree to strongly disagree and provides a simple and effective way to gather data on attitudes, beliefs, and perceptions. The Likert Scale has been widely adopted in a variety of research areas due to its versatility and ease of use, making it a valuable tool for both researchers and practitioners.
Table of Contents
When to use Likert scale

The Likert scale is a type of rating scale that is commonly used in survey research to measure attitudes, opinions, and perceptions. It is named after Rensis Likert, who first developed the concept in the 1930s.
You should use a Likert scale when you want to gather information about the degree to which individuals hold a particular attitude or belief. It is a useful tool for measuring subjective information, such as how strongly someone agrees or disagrees with a statement, or how satisfied they are with a product or service.
Here are some examples of when you might use a Likert scale:
- To gauge customer satisfaction with a product or service
- To measure employee attitudes towards their job or workplace
- To assess the perceived effectiveness of a training program
- To evaluate the level of support for a particular policy or issue
Overall, the Likert scale is a flexible and widely used tool for collecting information about attitudes, opinions, and perceptions.
Likert Scale Templates
Measure opinions, attitudes, and perceptions effectively with our collection of Likert Scale templates. Whether you’re conducting surveys, research, or evaluations, Likert scales provide a reliable way to gather and analyze data. Our templates offer a range of pre-designed Likert scale formats, from 5-point to 7-point scales, making it easy to capture respondent feedback.
Customize the templates to fit your specific needs, add relevant questions, and adapt the scale to match your rating criteria. By using Likert scales, you can quantify subjective responses, compare data across different groups or time periods, and gain valuable insights for decision-making. Download, print, and use our Likert Scale templates to simplify the data collection process, ensure consistency in responses, and enhance the accuracy of your results. With our user-friendly templates, you can conduct surveys or research projects with confidence and obtain valuable data for analysis and reporting.
Benefits of using likert scale
There are several benefits to using a Likert scale in survey research:
Easy to understand: The Likert scale is a straightforward and simple way to measure attitudes, opinions, and perceptions. Respondents are asked to rate their agreement with a statement on a scale that is easy to understand.
Provides a range of responses: The Likert scale provides a range of responses, from strongly agree to strongly disagree, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of an individual’s attitudes and opinions.
Reliable: The Likert scale is a reliable method for measuring attitudes and opinions. It is used widely in research and has been found to produce consistent results over time.
Versatile: The Likert scale can be used to measure a wide range of attitudes, opinions, and perceptions, making it a versatile tool in survey research.
Easy to analyze: The data collected using the Likert scale is easy to analyze and interpret, making it a convenient tool for researchers.
Low response bias: The Likert scale helps reduce response bias by providing clear instructions and a standardized format for rating attitudes and opinions.
Saves time and resources: The Likert scale is a quick and cost-effective way to gather information about attitudes, opinions, and perceptions. It can be used in both online and paper-based surveys, making it accessible to a wide range of research settings.
Overall, the Likert scale is a useful tool in survey research due to its simplicity, reliability, versatility, ease of analysis, low response bias, and cost-effectiveness.
Types of Likert Scales
Likert scales are a type of rating scale used in surveys and questionnaires to measure the strength of people’s opinions, attitudes, or perceptions on a given topic. There are several different types of Likert scales, including:
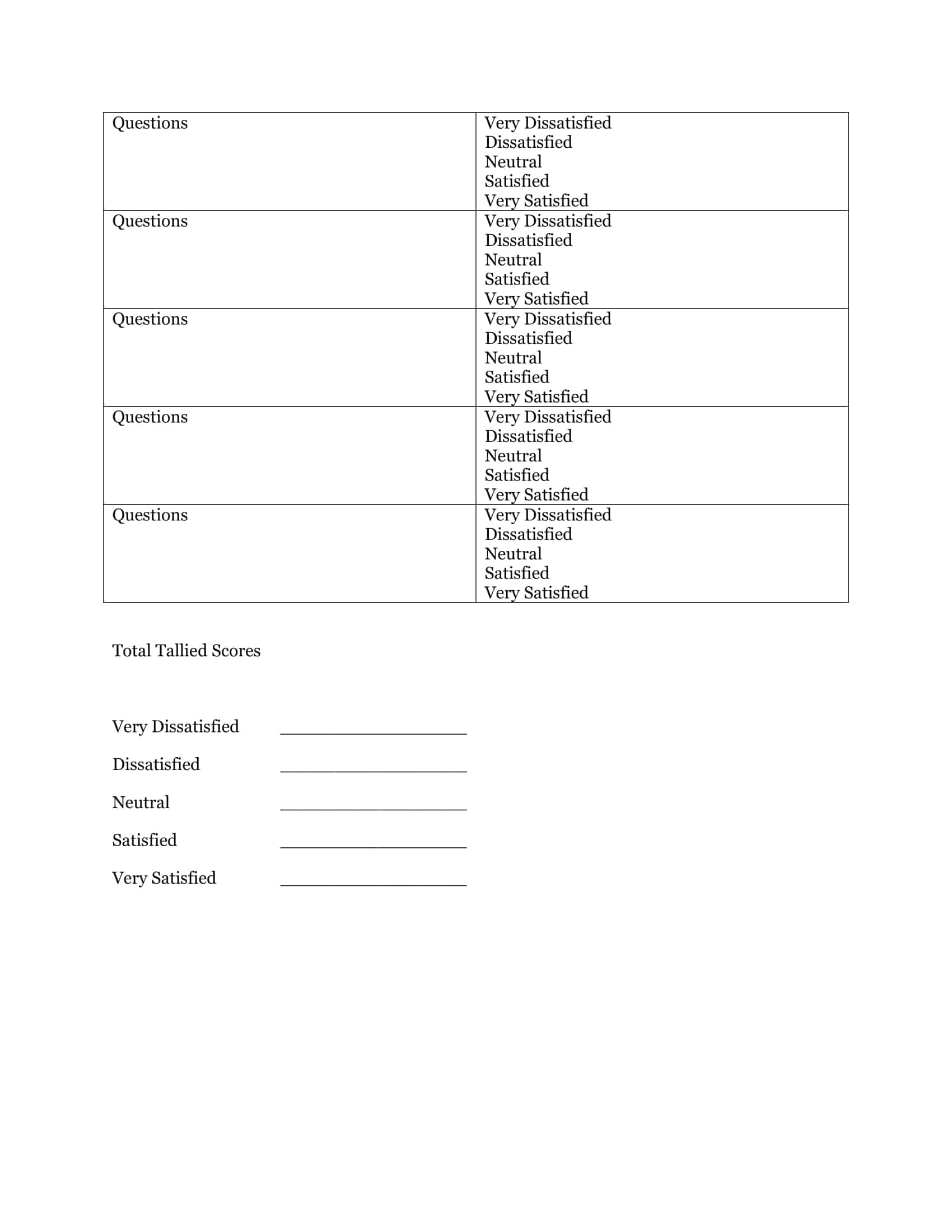
Binary Likert Scale: A binary Likert scale has only two response options, such as “agree” or “disagree”.
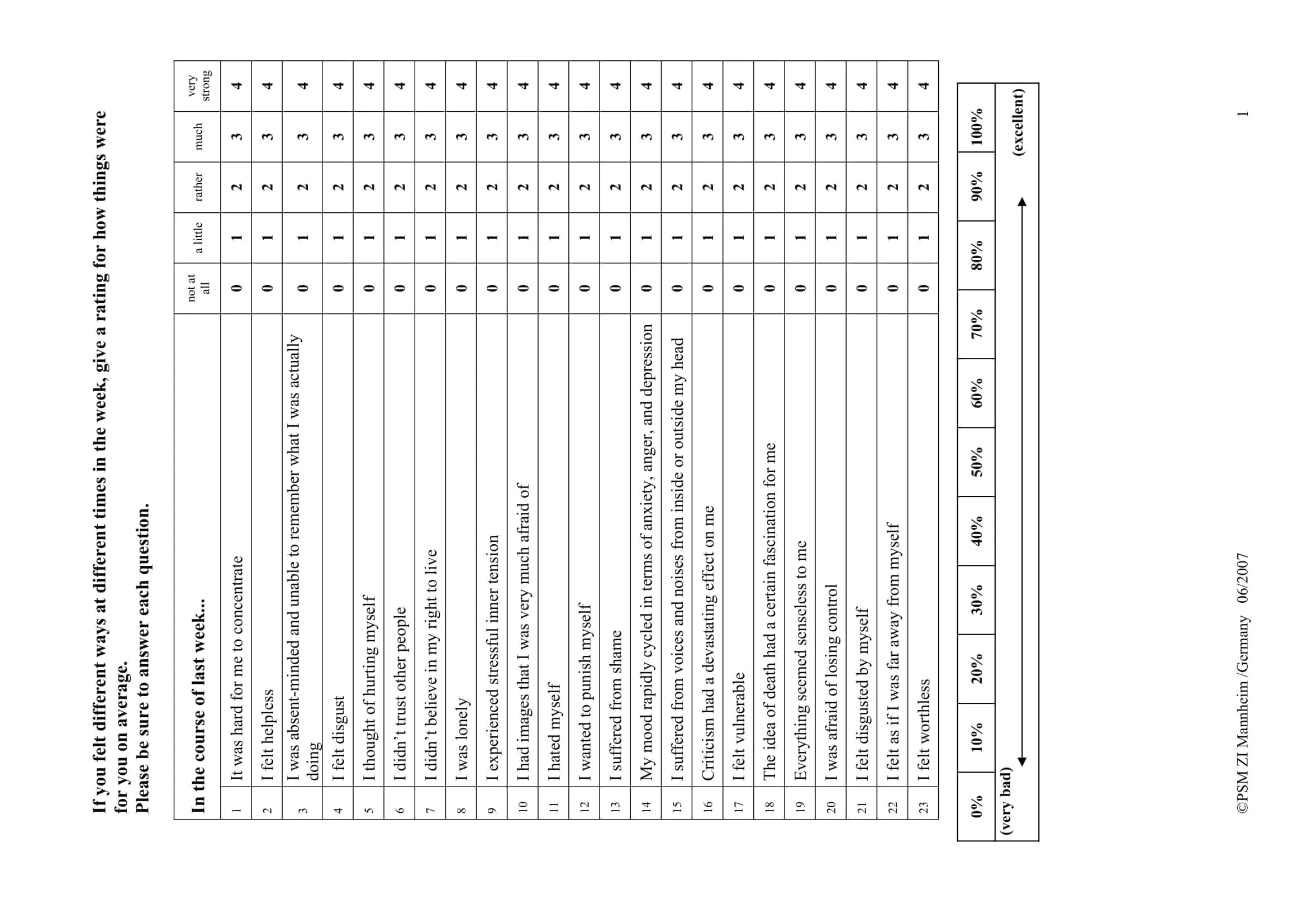
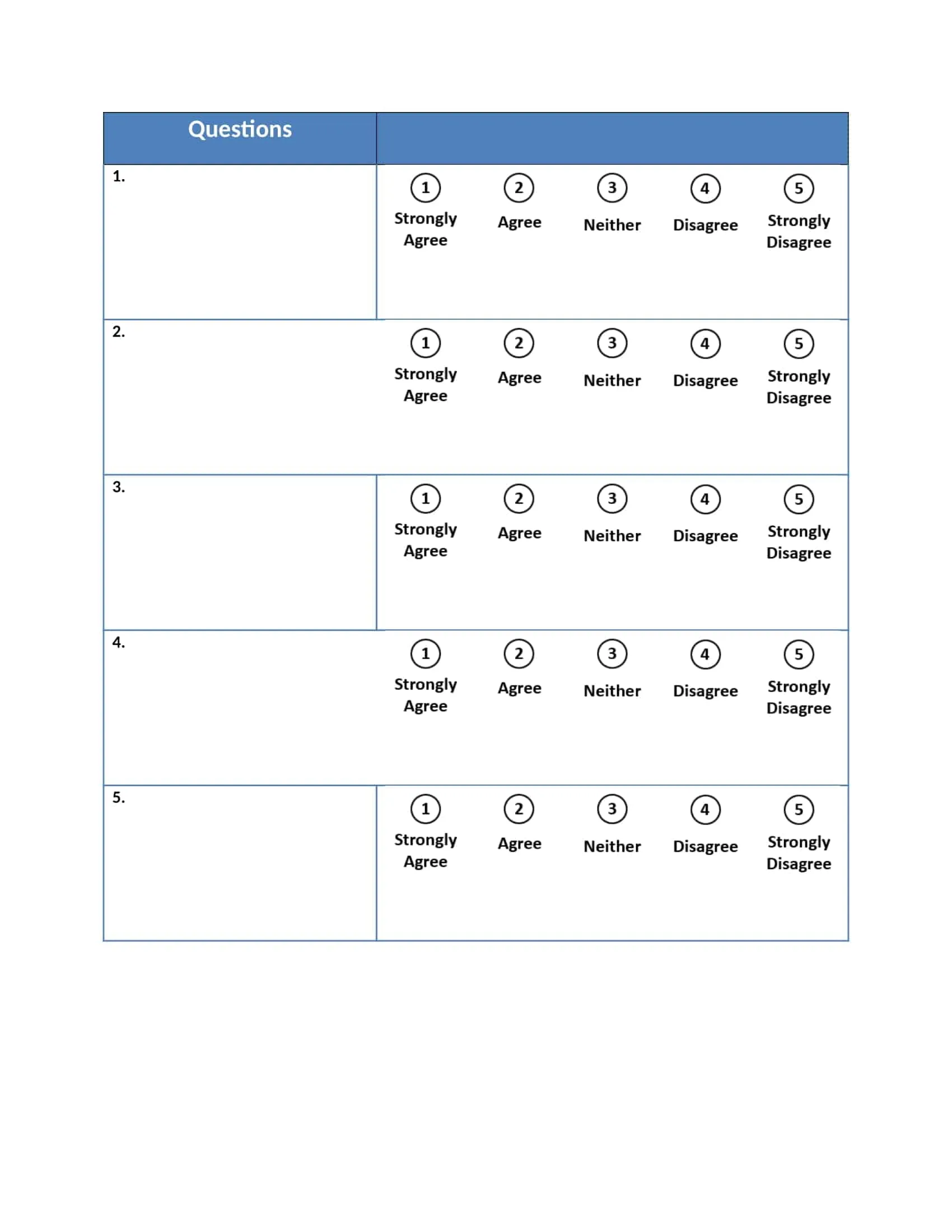
5-Point Likert Scale: A 5-point Likert scale is the most commonly used type of Likert scale and provides five response options, such as “strongly agree”, “agree”, “neutral”, “disagree”, “strongly disagree”.
7-Point Likert Scale: A 7-point Likert scale provides seven response options, such as “strongly agree”, “agree”, “somewhat agree”, “neutral”, “somewhat disagree”, “disagree”, “strongly disagree”.
9-Point Likert Scale: A 9-point Likert scale provides nine response options, such as “strongly agree”, “agree”, “moderately agree”, “somewhat agree”, “neutral”, “somewhat disagree”, “moderately disagree”, “disagree”, “strongly disagree”.
10-Point Likert Scale: A 10-point Likert scale provides ten response options, such as “strongly agree”, “completely agree”, “moderately agree”, “somewhat agree”, “neutral”, “somewhat disagree”, “moderately disagree”, “completely disagree”, “strongly disagree”.
It is important to choose the appropriate type of Likert scale based on the research question, the population being studied, and the goal of the study.
Characteristics of Likert scale
Likert scales are characterized by several key features:
Response Format: Likert scales are structured as a series of statements or questions to which respondents indicate their level of agreement or disagreement using a set of response options.
Response Options: The response options are usually arranged on a continuous scale that ranges from strongly agree to strongly disagree, or some variation of this format.
Interval-Level Measurement: Likert scales are considered to be interval-level measures, meaning that the response options are equally spaced and have a meaningful zero point.
Unidirectional: Likert scales are typically unidirectional, meaning that they measure a single construct or dimension, such as attitude or perception.
Additive: The responses on a Likert scale are additive, meaning that the scores can be summed to obtain a total score for each respondent.
Norm-Referenced: Likert scales are often used in a norm-referenced manner, meaning that the scores are compared to a reference group, such as the general population, to determine the relative standing of individual respondents.
Easy to Administer: Likert scales are easy to administer, either in written or electronic format, and can be used to collect data from a large number of respondents in a short amount of time.
Reusable: Likert scales can be reused in future studies, making it possible to compare data over time and across different groups of people.
Overall, Likert scales are a versatile and commonly used tool for collecting data in the social and behavioral sciences, and are well-suited for measuring attitudes, opinions, and perceptions.
How to write likert scale survey questions
A Likert scale is a type of survey question that is commonly used to measure attitudes, opinions, or perceptions. It is named after psychologist Rensis Likert, who first described the technique in 1932. Likert scales typically include a series of statements, and respondents are asked to indicate the extent to which they agree or disagree with each statement using a numerical rating or a series of response options, such as “strongly agree,” “somewhat agree,” “neither agree nor disagree,” “somewhat disagree,” or “strongly disagree.”
Here is a step-by-step guide for writing Likert scale survey questions:
Step 1: Define the purpose of your survey
Before you start writing your survey questions, it is important to have a clear understanding of the purpose of your survey. Are you trying to measure customer satisfaction with a particular product or service? Are you trying to assess employee attitudes toward a new company policy? Knowing the purpose of your survey will help you determine the type of information you need to gather and the types of questions you should ask.
Step 2: Develop a list of statements
Once you have a clear understanding of the purpose of your survey, you can start developing a list of statements that you want to ask your respondents about. These statements should be specific, relevant, and easily understood by your target audience.
Step 3: Decide on the type of response options you will use
Likert scales typically use a 5-point or 7-point scale, although you can use a different number of points if it is more appropriate for your survey. The most common response options are:
- Strongly agree
- Somewhat agree
- Neutral
- Somewhat disagree
- Strongly disagree
Step 4: Write your survey questions
Now that you have developed a list of statements and decided on the type of response options you will use, you can start writing your survey questions. When writing your questions, make sure they are clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoid using technical or specialized language that may not be familiar to your target audience.
Step 5: Pilot test your survey
Before you distribute your survey to your target audience, it is important to pilot test it to make sure it is effective and efficient. You can give your survey to a small group of people who are representative of your target audience and ask them for feedback on the questions and response options. Based on their feedback, you can make any necessary revisions to your survey.
Step 6: Distribute your survey
Once you have pilot tested your survey and made any necessary revisions, you are ready to distribute it to your target audience. There are a variety of ways to distribute a survey, including online, by email, by mail, or in person.
Step 7: Analyze your data
After you have collected your survey responses, you can start analyzing your data. There are a variety of statistical methods you can use to analyze Likert scale data, including frequency counts, means, standard deviations, and correlation coefficients.
A few tips to keep in mind when writing Likert scale survey questions:
- Make sure your statements are neutral and not leading or biased in any way.
- Avoid using overly complex or technical language.
- Use clear and concise statements that are easily understood by your target audience.
- Consider the length of your survey and make sure it is not too lengthy or time-consuming for your respondents.
- Avoid asking too many questions that are similar or redundant.
How to analyse likert scale survey data
Likert scale survey data is commonly used to measure attitudes, opinions, and perceptions and can be analyzed in a variety of ways to extract meaningful insights. The data collected from Likert scale surveys can be quantified using numerical ratings and can be used to compare the responses of different individuals or groups. Here is a step-by-step guide for analyzing Likert scale survey data:
Step 1: Prepare your data for analysis
Before you start analyzing your data, you need to prepare it for analysis by cleaning and organizing it. This includes checking for missing data, correcting any errors or inconsistencies, and converting the data into a format that is suitable for analysis.
Step 2: Descriptive statistics
The first type of analysis that you can perform on Likert scale data is descriptive statistics. This type of analysis involves calculating measures of central tendency, such as the mean, median, and mode, as well as measures of variability, such as the standard deviation and range. These measures provide a summary of the distribution of the data and give you an idea of the typical response patterns.
Step 3: Frequency distributions
Another type of analysis that you can perform on Likert scale data is a frequency distribution. A frequency distribution shows the number of responses for each response option on the Likert scale. This type of analysis can give you an idea of the distribution of the responses and help you identify any response patterns or trends.
Step 4: Cross-tabulations
Cross-tabulations are a type of analysis that involves comparing the responses of different subgroups of your data. For example, you could compare the responses of men and women, or the responses of different age groups. Cross-tabulations can help you identify any significant differences in the responses of different subgroups and can give you a more detailed understanding of the data.
Step 5: Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics is a type of analysis that involves making inferences about a population based on a sample of data. For example, you could use inferential statistics to determine whether the responses of your sample are representative of the responses of the entire population. Inferential statistics can also be used to test hypotheses about the relationships between different variables.
Step 6: Graphical representation
Another way to analyze Likert scale data is through graphical representation. This can include bar graphs, histograms, pie charts, or line graphs. Graphical representation of the data can provide a visual representation of the data and help you identify any patterns or trends that may not be immediately apparent from the numerical data.
Step 7: Interpretation of results
The final step in analyzing Likert scale data is the interpretation of the results. This involves using the insights gained from the analysis to draw meaningful conclusions and make recommendations based on the data. For example, you may use the results of the analysis to make recommendations for improving customer satisfaction or employee morale.
A few tips to keep in mind when analyzing Likert scale survey data:
- Make sure the data is clean and organized before you start the analysis.
- Choose the appropriate type of analysis based on the type of data you have and the questions you are trying to answer.
- Use clear and concise language to communicate the results of the analysis.
- Be mindful of potential biases or limitations in the data and consider their impact on the results of the analysis.
In conclusion, Likert scale survey data can provide valuable insights into attitudes, opinions, and perceptions. By following these steps, you can effectively analyze Likert scale survey data and draw meaningful conclusions based on the results.
FAQs
How is a Likert scale different from other types of surveys?
Likert scales differ from other types of surveys in a number of ways. For one, Likert scales are used to measure attitudes and opinions, whereas other types of surveys may be used to gather information about demographics, behaviors, or other types of data. Additionally, Likert scales typically use a standardized response format, whereas other types of surveys may allow for open-ended or qualitative responses.
What are the advantages of using a Likert scale?
The advantages of using a Likert scale include the ability to quantify attitudes and opinions, the ability to compare the responses of different individuals or groups, and the ability to draw meaningful conclusions based on the results of the survey. Likert scales are also easy to administer and can provide a quick and accurate assessment of attitudes and opinions.
What are the limitations of using a Likert scale?
The limitations of using a Likert scale include the potential for response bias, the potential for limited range of responses, and the potential for difficulty in accurately measuring complex attitudes and opinions. Additionally, Likert scales may not be suitable for all types of data, and other types of surveys may be more appropriate for certain types of data collection.
How can I ensure the validity of my Likert scale survey?
To ensure the validity of your Likert scale survey, it is important to carefully design and pilot test your questions and response options. Additionally, it is important to ensure that your survey is administered in a manner that is free from bias and that your participants understand the instructions and response options. Finally, it is important to carefully analyze the results of your survey to identify any patterns or trends in the data.
Can Likert scale questions be used to measure continuous data?
No, Likert scale questions are designed to measure categorical or ordinal data, not continuous data. Continuous data, such as height or weight, can take on any value within a range, while Likert scale questions only have a limited number of response options.
What are some common statistical techniques for analyzing Likert scale data?
Here are some common statistical techniques for analyzing Likert scale data:
Mean: The mean is the average of all the responses and is a good measure of central tendency.
Median: The median is the middle value in a set of responses and is another measure of central tendency.
Mode: The mode is the most common value in a set of responses and can be used to identify trends or patterns in the data.
Frequency distribution: A frequency distribution is a table that shows the number of times each response option was chosen. This can be used to identify the most common response and to determine the distribution of responses.
Cross-tabulation: Cross-tabulation is a technique that allows you to compare the responses of different groups. For example, you could compare the responses of men and women or of different age groups.
Regression analysis: Regression analysis is a technique that allows you to test for relationships between variables. For example, you could test for a relationship between age and level of agreement with a particular statement.
How do I know if my Likert scale questions are reliable and valid?
Reliability refers to the consistency of your results, while validity refers to the accuracy of your results. There are several ways to assess the reliability and validity of your Likert scale questions, including:
Test-retest reliability: This involves administering the same survey to the same group of people on two different occasions and comparing the results. If the results are consistent, the survey is considered to be reliable.
Internal consistency reliability: This involves calculating the reliability of the Likert scale as a whole by examining the consistency of the responses to each question. This can be done using techniques such as Cronbach’s alpha.
Validity: Validity can be assessed by comparing the results of your survey to other measures of the same construct. For example, if you are measuring attitudes towards a particular product, you could compare your survey results to sales data for that product.
What are some examples of Likert scale questions?
Here are some examples of Likert scale questions:
- On a scale from 1 to 5, how strongly do you agree with the following statement: “I am satisfied with the quality of customer service I received.”
- On a scale from 1 to 5, how strongly do you agree with the following statement: “I would recommend this product to a friend.”
- On a scale from 1 to 5, how strongly do you agree with the following statement: “I feel safe in my neighborhood.”
- On a scale from 1 to 5, how strongly do you agree with the following statement: “I am satisfied with my job.”
- On a scale from 1 to 5, how strongly do you agree with the following statement: “I believe that the government is doing a good job.”
























![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
