Crafting a compelling bid proposal is a critical skill that can make or break your chances of securing a contract. This article will guide you through the intricate process of creating a persuasive proposal that effectively communicates the value of your services or products.
We’ll explore the essential elements of a successful bid, from understanding your client’s needs to presenting a clear, concise, and compelling case for why your company is the best fit. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a novice in the field, this article will provide you with the tools and insights needed to elevate your bid proposal game.
Table of Contents
What is a bid proposal?

A bid proposal is a formal document that businesses submit to potential clients in order to secure a contract. It outlines the goods or services the business is offering, the cost for these services, and how they plan to meet the client’s needs or solve their problems.
The proposal is typically in response to a request for proposal (RFP) issued by the client, which details the specific requirements for the project or job. The goal of a bid proposal is to demonstrate that the business is the best choice for the project, based on their expertise, experience, and the value they can provide.
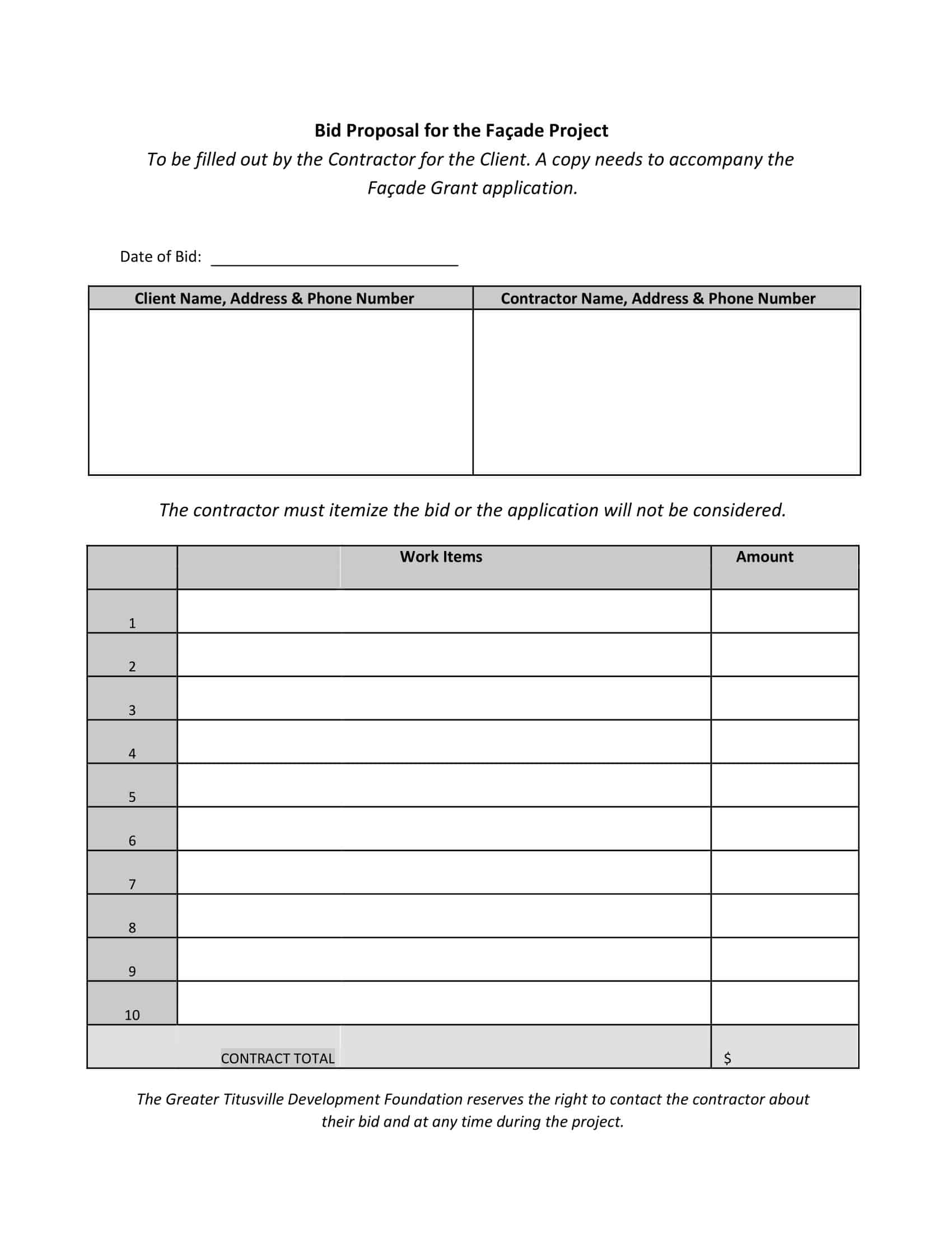
Bid Proposal Templates
Bid Proposal Templates are crucial tools in business and project management used when businesses need to secure new contracts or projects. They offer a standardized framework to present a company’s capabilities, proposed project solution, timeline, and costs to potential clients.
At the top of most templates is a cover page that typically includes a place for the project title, company name, company logo, proposal submission date, and the name of the potential client. This page serves as an introduction and gives a professional appearance to the bid proposal.
Following the cover page, there is usually a table of contents to outline the proposal sections, offering a navigable roadmap to the contents of the proposal. It aids in making the document user-friendly.
When to use a bid proposal
A bid proposal is used when a company or individual wants to secure a contract or project from another organization. This typically happens in a few scenarios:
- In response to a Request for Proposal (RFP): An RFP is a document that an organization posts to invite bids for a project. It outlines the specifics of the project and what the organization is looking for in a service provider.
- For government contracts: Government agencies often use a bidding process to award contracts for public projects. A bid proposal is necessary to compete for these contracts.
- In competitive industries: In industries where multiple businesses offer similar services, a company might use a bid proposal to stand out from the competition and convince a potential client of their unique value.
- For large projects: For complex or high-value projects, organizations often seek formal bids to ensure they are getting the best value and the most qualified provider.
- In all these cases, the bid proposal serves as a formal statement of the scope of work, the timeline for completion, and the cost of the services, along with any other details that might persuade the potential client to choose the bidder.
What to include in a bid proposal
Creating a bid proposal requires careful thought and planning. Here’s a detailed guide on what to include:
- Cover Letter: This is your first opportunity to make a good impression. The cover letter should be brief, professional, and personalized to the client. It should summarize your understanding of the project, your qualifications, and why you’re the best choice for the job.
- Executive Summary: This section provides an overview of your proposal. It should clearly state what you’re offering, how you plan to meet the client’s needs, and the benefits the client will receive from choosing your company.
- Company Profile: Here, you provide information about your company, including its history, mission, values, and team. Highlight your company’s strengths, achievements, and any unique qualities that set you apart from the competition.
- Detailed Response to the Request for Proposal (RFP): This section should address all the points raised in the RFP. Show that you understand the project’s requirements and objectives, and explain how you plan to meet them. Be specific and detailed in your response.
- Methodology and Approach: Explain your proposed approach to the project. This could include your project management methods, your process for delivering the services, and any innovative strategies or technologies you plan to use.
- Timeline: Provide a realistic timeline for the project, including key milestones and completion dates. This shows that you have a clear plan for delivering the project on time.
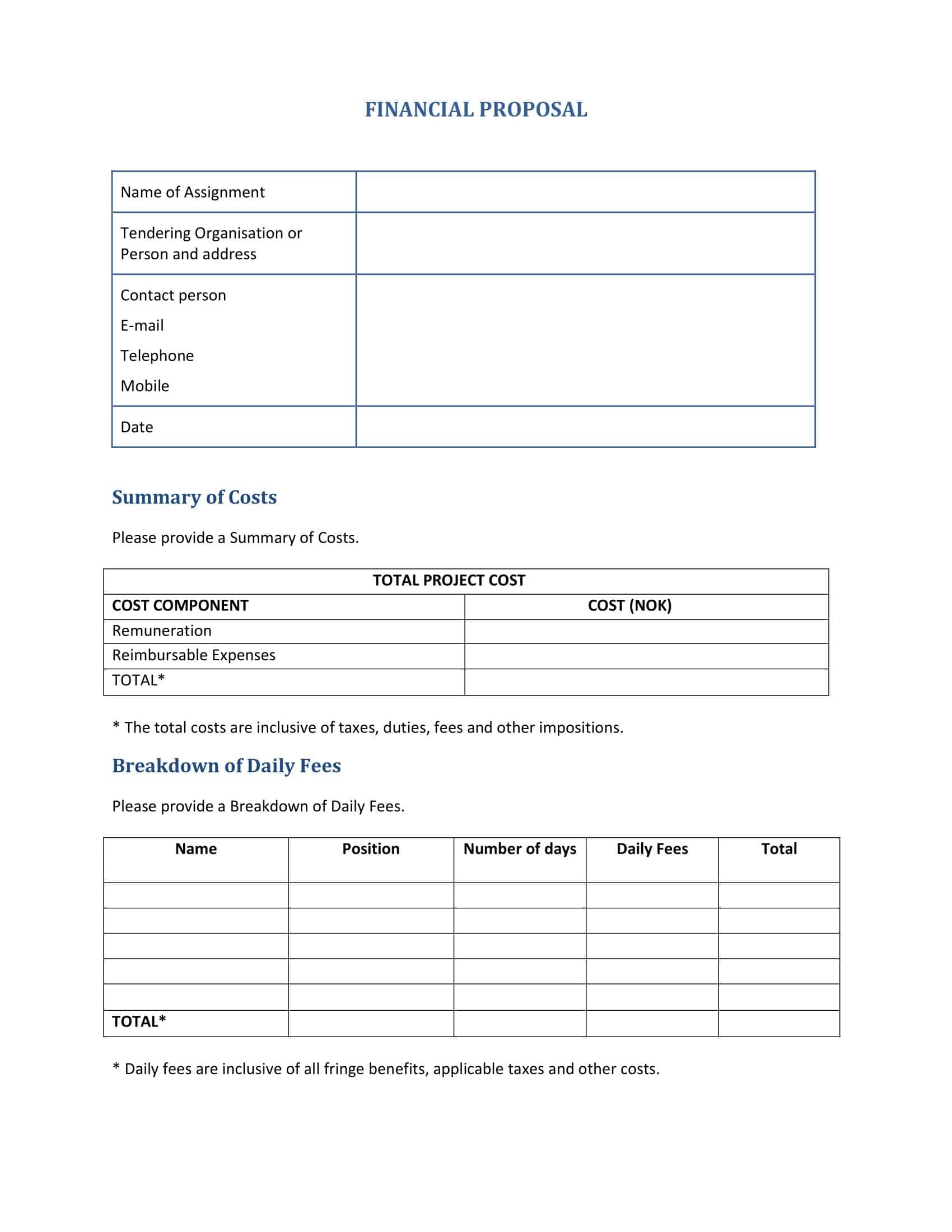
- Pricing and Cost Breakdown: Clearly outline the costs associated with your proposal. This could include labor costs, materials, overheads, and any other expenses. Be transparent and provide a detailed breakdown so the client understands what they’re paying for.
- References and Case Studies: Provide examples of past projects that are similar to the one you’re bidding on. Include testimonials or references from past clients. This helps to build trust and show that you have a proven track record.
- Terms and Conditions: Include any terms and conditions related to your proposal, such as payment terms, contract duration, and any warranties or guarantees.
- Conclusion and Call to Action: Summarize your proposal and encourage the client to take the next step, such as contacting you for a meeting or signing the contract.
Types of Bid Requests
There are several types of bid requests that businesses may encounter, each with its own specific requirements and processes. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Request for Proposal (RFP): An RFP is a document that outlines the project’s requirements and asks potential suppliers to submit a proposal detailing how they would meet these requirements and at what cost. The RFP process is often used for complex projects where the approach to solving the problem may not be clear-cut, and the client is interested in comparing different strategies. For example, a city government might issue an RFP for a new public transportation system, inviting companies to propose different solutions, such as buses, trams, or subway systems.
- Request for Quotation (RFQ): An RFQ is used when the client knows exactly what they need and is primarily interested in comparing prices from different suppliers. The client provides detailed specifications, and suppliers respond with a quote for the cost of providing the goods or services. For instance, a construction company might issue an RFQ for 1,000 tons of steel, specifying the grade, size, and delivery date, and suppliers would respond with their prices.
- Invitation to Bid (ITB): Also known as an Invitation for Bid (IFB), this type of bid request is used for straightforward projects where the client is looking for the lowest price. The client provides detailed specifications, and suppliers respond with a firm bid. This is often used in construction and other industries where the work is well-defined and the primary consideration is cost. For example, a school district might issue an ITB for a new school building, with detailed plans and specifications, and construction companies would bid on the project.
- Request for Information (RFI): An RFI is used when a client needs more information before they can define their project or start the bidding process. They might be looking for information on what solutions are available, what the current market prices are, or what the potential challenges might be. For example, a company considering a switch to solar power might issue an RFI to learn more about the types of solar panels available, the costs, and the potential benefits and drawbacks.
- Request for Expression of Interest (REOI): An REOI is used when a client wants to gauge interest in a potential project before starting the formal bidding process. They provide a brief overview of the project, and suppliers respond to express their interest and provide some initial information about their qualifications. For example, a government agency considering a new highway project might issue an REOI to see which construction companies might be interested in bidding on the project.
How To Write a Bid Proposal
Writing a bid proposal is a detailed process that requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Understand the Request for Proposal (RFP)
Before you start writing, thoroughly review the RFP or other bid request document. Understand the project’s scope, the client’s needs, and the specific requirements for the proposal. Make a list of any questions or clarifications you need, and reach out to the client if necessary. For example, if the RFP is for a website redesign, make sure you understand the client’s goals for the redesign, the target audience, the desired features, and any technical requirements.
Next, research the client and their industry. Understand their business model, their competitors, their challenges, and their customers. This will help you tailor your proposal to their specific needs and show that you understand their business. For instance, if the client is a nonprofit organization, you might research the issues they address, their funding sources, and the communities they serve.
Step 2: Plan Your Proposal
Start by outlining your proposal. This should include all the sections required by the RFP, as well as any additional sections you think would be beneficial. For example, your outline might include an executive summary, a detailed response to the RFP, a description of your proposed approach, a timeline, a pricing section, and a conclusion.
Next, decide on the key messages you want to convey in your proposal. What are the main reasons the client should choose your company? What unique value can you provide? These key messages should be woven throughout your proposal. For example, if your company is known for its innovative solutions, you might emphasize your creative approach to problem-solving and provide examples of innovative projects you’ve completed.
Step 3: Write Your Proposal
Start writing your proposal, following the outline you’ve created. Be clear, concise, and persuasive. Use professional language, but avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Remember to focus on the client’s needs and how you can meet them, rather than just talking about your company.
For example, in the executive summary, you might start by summarizing the client’s needs as you understand them, then briefly explain your proposed solution and why it’s the best choice. In the detailed response to the RFP, you would go through each point in the RFP and explain how you plan to meet that requirement. In the approach section, you might describe your project management process, your team, and any innovative strategies or technologies you plan to use.
Step 4: Review and Revise Your Proposal
Once you’ve written your proposal, take the time to review and revise it. Check for clarity, persuasiveness, and professionalism. Make sure you’ve addressed all the points in the RFP and that your key messages come through clearly.
For example, you might read through your proposal and realize that you’ve focused too much on the technical details of your solution, and not enough on the benefits for the client. In this case, you might revise your proposal to better highlight the benefits, such as cost savings, improved efficiency, or increased customer satisfaction.
Step 5: Proofread and Finalize Your Proposal
Finally, proofread your proposal carefully. Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Make sure the formatting is consistent and professional. If possible, have someone else proofread it as well, as they might catch errors you’ve missed.
For example, you might check that all headings are the same font and size, that all bullet points are aligned, and that there are no extra spaces or missing punctuation marks. You might also check that all numbers and calculations are correct, especially in the pricing section.
- Once you’re satisfied with your proposal, finalize it and prepare it for submission. This might involve printing and binding it, saving it as a PDF, or uploading it to an online portal, depending on the client’s requirements.
Sample Bid Proposal Template
[Your Company Logo]
[Your Company Name]
[Your Company Address]
[Your Company Contact Information]
[Date]
[Client’s Company Name]
[Client’s Company Address]
Subject: Bid Proposal for [Project Name]
1. Cover Letter
Dear [Client’s Name],
We appreciate the opportunity to submit our proposal for your project, [Project Name]. We understand that you require [briefly describe the project requirements]. Our team is well-equipped to meet these requirements and deliver a high-quality, timely solution.
2. Executive Summary
This proposal outlines our approach to [Project Name], including our proposed solution, timeline, and cost. We believe our [unique selling proposition, e.g., innovative approach, experienced team, competitive pricing] makes us the ideal choice for this project.
3. Company Profile
[Your Company Name] is a [brief description of your company, including history, mission, and main services]. We have successfully completed similar projects for clients such as [names of past clients or brief case studies].
4. Detailed Response to the RFP
[Briefly summarize the RFP requirements, then go through each one and explain how you plan to meet it. Be specific and detailed.]
5. Methodology and Approach
Our approach to [Project Name] will involve [describe your proposed approach, including project management methods, processes, and any innovative strategies or technologies].
6. Project Timeline
We propose the following timeline for [Project Name]:
- [Date]: [Milestone 1]
- [Date]: [Milestone 2]
- [Date]: [Milestone 3]
- [Date]: Project Completion
7. Pricing and Cost Breakdown
The total cost for [Project Name] will be [Total Cost]. This includes:
8. References and Case Studies
We have successfully completed similar projects for clients such as [names of past clients or brief case studies]. References are available upon request.
9. Terms and Conditions
[Include any terms and conditions related to your proposal, such as payment terms, contract duration, and any warranties or guarantees.]
10. Conclusion and Call to Action
We are confident that our proposed solution for [Project Name] will meet your needs and deliver significant value to [Client’s Company Name]. We look forward to the opportunity to discuss this proposal further and answer any questions you may have.
[Your Name]
[Your Title]
[Your Contact Information]
FAQs
How do I write an effective bid proposal?
To write an effective bid proposal, start by thoroughly understanding the requirements of the RFP/ITB. Tailor your proposal to address the client’s needs, showcase your expertise, highlight your unique selling points, and provide a clear and detailed pricing structure.
How long should a bid proposal be?
The length of a bid proposal can vary depending on the complexity of the project. However, it is generally recommended to keep it concise and focused, ranging from a few pages for smaller projects to more extensive proposals for larger contracts.
How do I determine the appropriate pricing for my bid proposal?
Determining pricing for a bid proposal involves considering factors like project scope, labor costs, materials, overhead expenses, and desired profit margin. Conduct a thorough cost analysis and competitive research to arrive at a fair and competitive price.
Is it necessary to visit the project site before submitting a bid proposal?
While it’s not always mandatory, visiting the project site before submitting a bid proposal can provide valuable insights. It allows you to better understand the project requirements, assess any potential challenges, and fine-tune your proposal accordingly.
Can I make changes to my bid proposal after submission?
Generally, bid proposals are considered binding once submitted. However, some clients may allow minor revisions or clarifications within a specified timeframe. Always review the RFP/ITB instructions regarding amendments to ensure compliance.
What happens after I submit my bid proposal?
After you submit your bid proposal, the client will typically evaluate all submitted proposals based on the specified criteria. This evaluation may involve reviewing qualifications, pricing, approach/methodology, and past performance. The client will then select the most suitable bidder.
What if my bid proposal is not selected?
If your bid proposal is not selected, you can request feedback from the client to understand the reasons behind their decision. Use this feedback to improve your future bid proposals and continue pursuing other opportunities.








































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
