The Blood Type Diet, also known as the Blood Group Diet, is a nutritional approach that advocates eating specific foods based on an individual’s blood type. Proponents of the Blood Type Diet claim that different blood types metabolize food differently, and that following a diet tailored to one’s blood type can lead to improved health and weight loss.
The Blood Type Diet was popularized by Dr. Peter J. D’Adamo in his book “Eat Right 4 Your Type,” which outlines different food lists and charts for each of the four main blood types: A, B, AB, and O. However, the scientific evidence for the effectiveness of the Blood Type Diet is limited and controversial, with many experts and organizations dismissing it as a fad diet. Nevertheless, the Blood Type Diet continues to have a following, and its charts and guidelines continue to be widely available and discussed.
Table of Contents
Blood Type Diet Chart Templates
Blood type diet chart templates are pre-designed documents that provide a structured format for individuals to track and plan their dietary choices based on their blood type. These templates are designed to support the concept of the blood type diet, which suggests that an individual’s blood type influences their body’s response to certain foods.
Blood type diet chart templates typically include sections or columns that correspond to different blood types (A, B, AB, and O) and offer food recommendations, restrictions, and guidelines specific to each blood type. They may categorize foods as highly beneficial, neutral, or to be avoided, based on how they may interact with an individual’s blood type.
Using a blood type diet chart template allows individuals to monitor their food choices and align them with the recommendations associated with their blood type. It provides a structured framework for planning meals, making grocery lists, and promoting healthier eating habits based on the blood type diet theory.
What You Can Eat

The Blood Type Diet is based on the idea that different blood types metabolize food differently and that eating foods that are compatible with one’s blood type can lead to better health and weight loss. There are four main blood types: A, B, O, and AB. The following is a detailed guide to the food recommendations for each blood type:
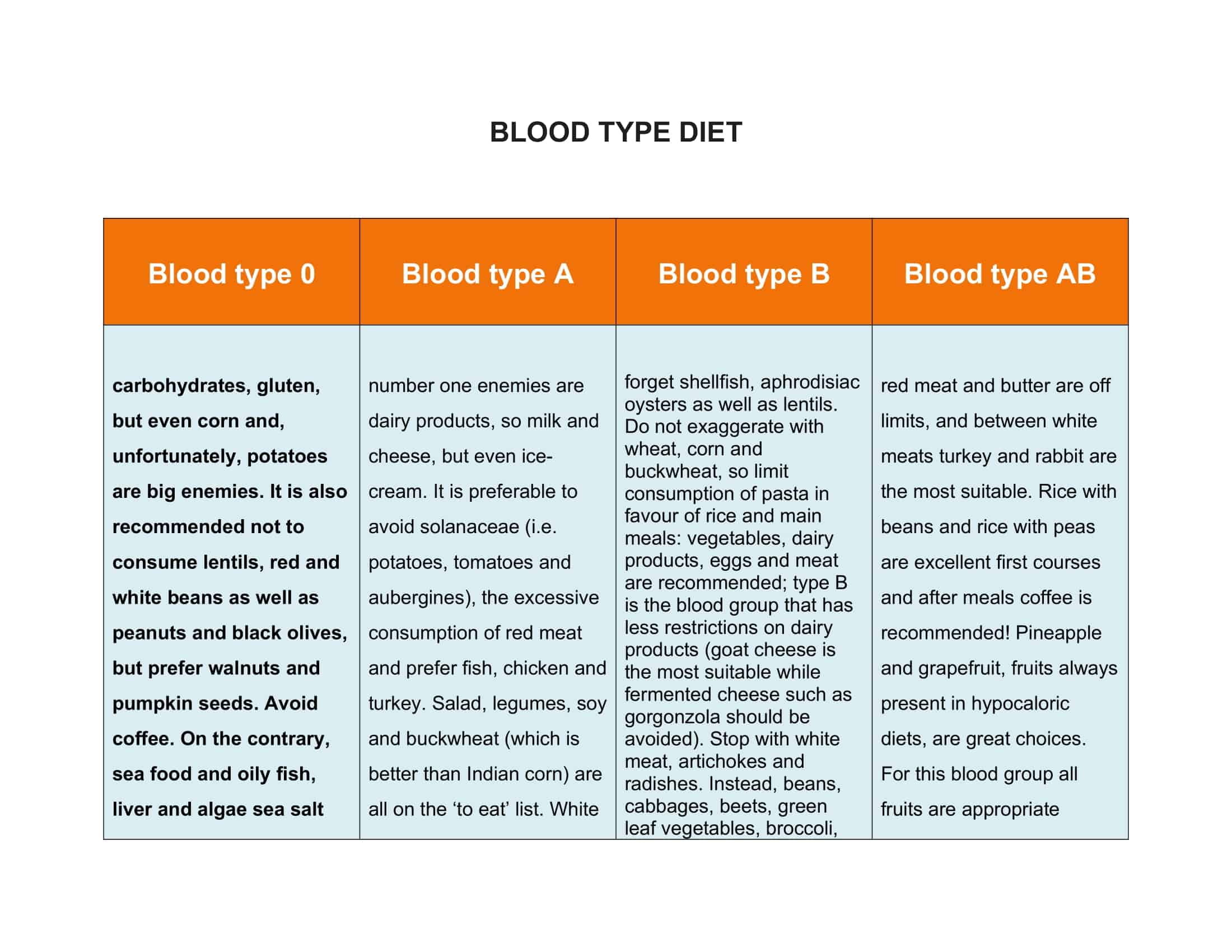
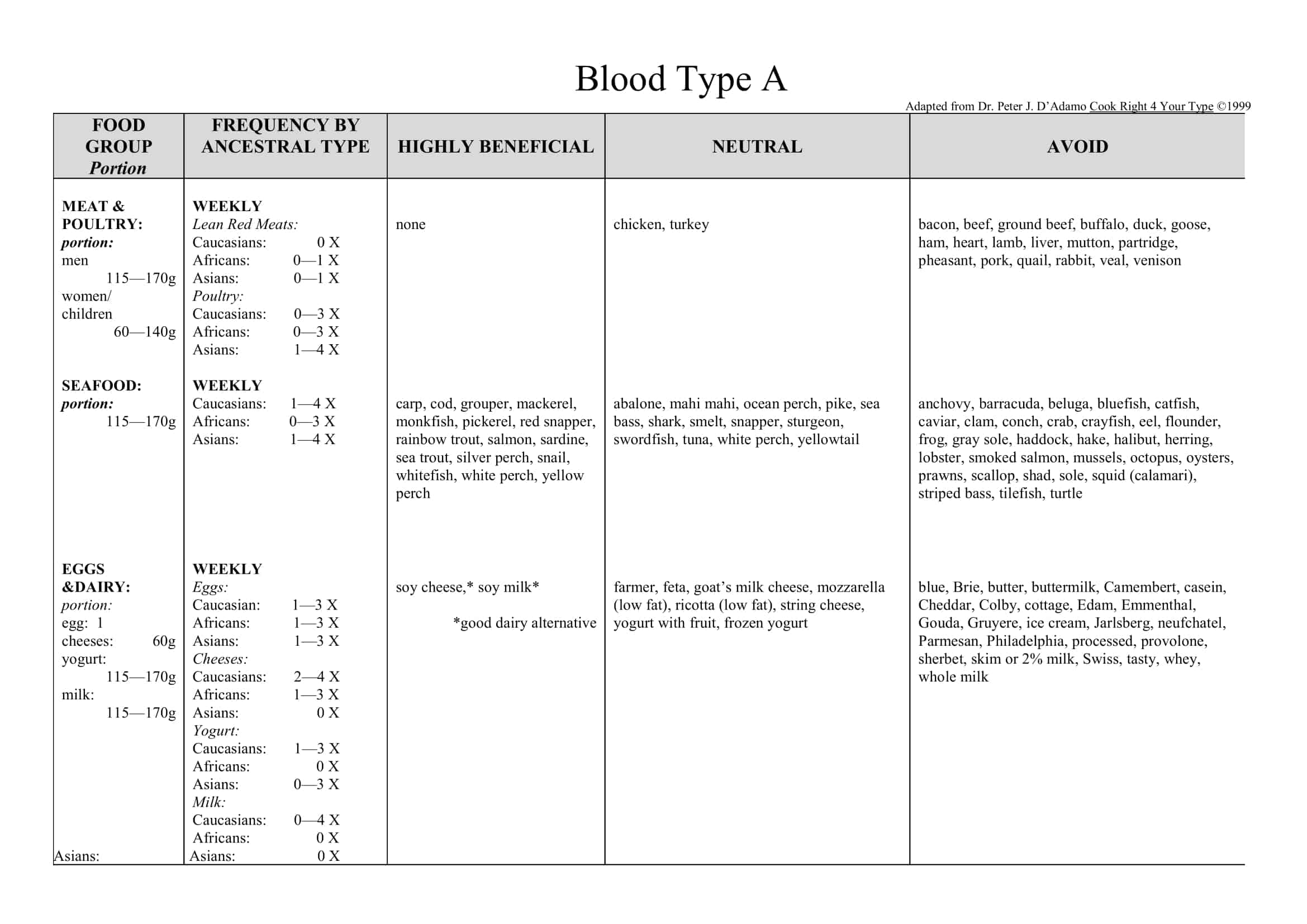
- Type A Diet:
Type A individuals are believed to be of agricultural descent and to have evolved to a vegetarian diet. The Blood Type Diet recommends that type A individuals focus on a plant-based diet, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and tofu. They are advised to avoid meat, dairy products, and wheat.
Foods to eat:
- Fruits: Apples, berries, melons, pears, grapes, plums, cherries, etc.
- Vegetables: Artichokes, asparagus, broccoli, carrots, cauliflower, spinach, etc.
- Grains: Rice, corn, quinoa, millet, amaranth, etc.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, etc.
- Other: Tofu, tempeh, miso, seaweed, green tea, etc.
Foods to avoid:
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, poultry, etc.
- Dairy: Milk, cheese, yogurt, butter, etc.
- Wheat: Bread, pasta, baked goods, etc.
- Processed foods: Processed meats, canned foods, artificial sweeteners, etc.
- Other: Alcohol, caffeine, corn, peanuts, and most beans.
- Type B Diet:
Type B individuals are believed to have evolved to a balanced diet of meat and plants. The Blood Type Diet recommends that type B individuals follow a balanced diet that includes meat, dairy products, and fruits and vegetables. They are advised to limit their intake of chicken, corn, wheat, and some legumes.
Foods to eat:
- Fruits: Pineapple, figs, plums, grapes, etc.
- Vegetables: Green beans, Brussels sprouts, kale, etc.
- Meat: Lamb, rabbit, mutton, etc.
- Dairy: Yogurt, kefir, etc.
- Grains: Quinoa, rice, millet, etc.
- Other: Eggs, low-fat cheese, green tea, etc.
Foods to avoid:
- Meat: Chicken, beef, pork, etc.
- Dairy: Milk, ice cream, cheese, etc.
- Wheat: Bread, pasta, baked goods, etc.
- Legumes: Lentils, kidney beans, etc.
- Other: Alcohol, caffeine, peanuts, corn, and sesame seeds.
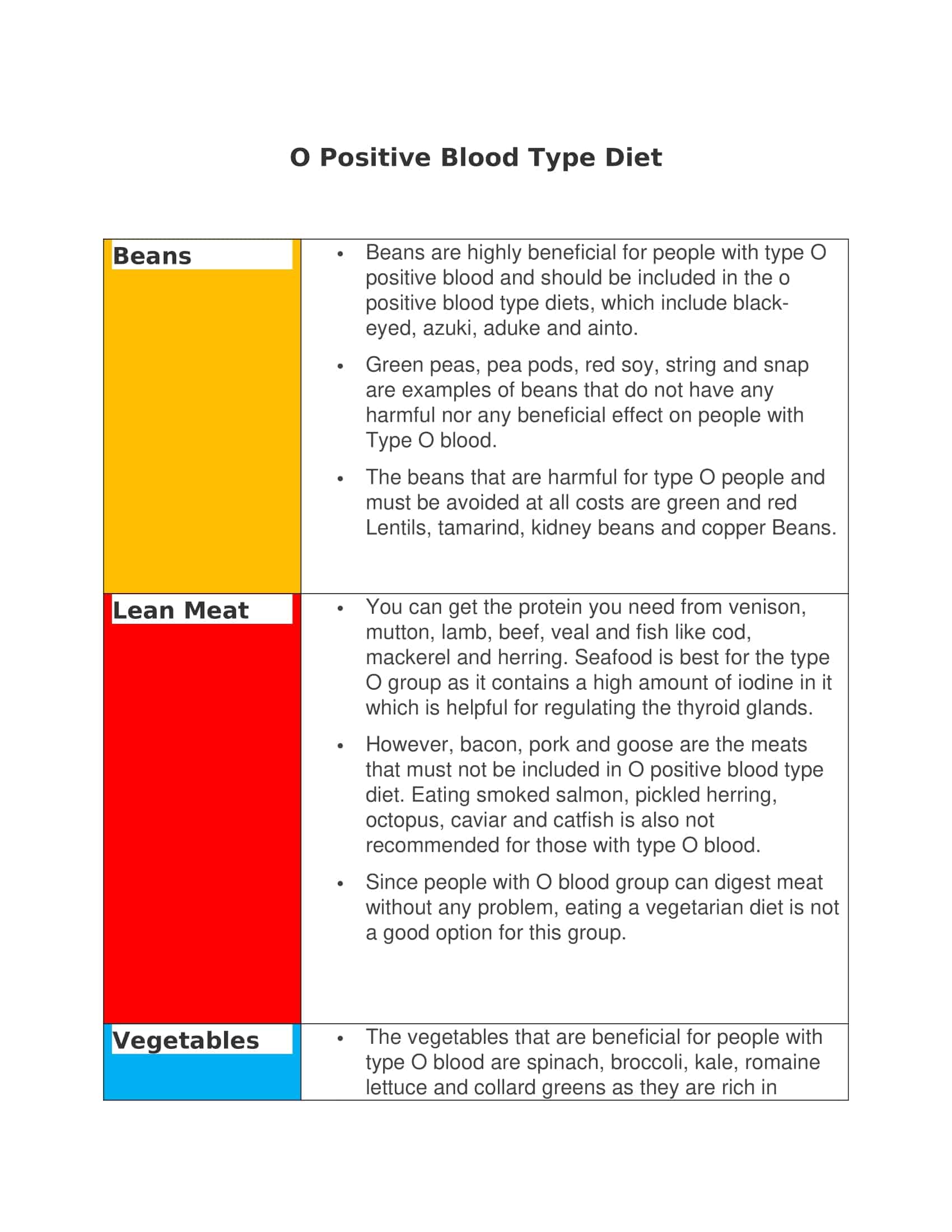
- Type O Diet:
Type O individuals are believed to have evolved as hunters and to have a high-protein diet. The Blood Type Diet recommends that type O individuals focus on a high-protein diet that includes meat, poultry, fish, and vegetables. They are advised to limit their intake of dairy products, grains, and legumes.
Foods to eat:
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, etc.
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey, etc.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, etc.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, kale, etc.
- Other: Eggs, olive oil, garlic, ginger, etc.
Foods to avoid:
- Dairy: Milk, cheese, yogurt, etc.
- Grains: Bread, pasta, baked goods, etc.
- Legumes: Lentils, beans, etc
- Other: Alcohol, caffeine, corn, peanuts, and most beans.
- Type AB Diet:
Type AB individuals are considered to have a mix of the characteristics of both type A and type B. The Blood Type Diet recommends that type AB individuals follow a diet that is a mixture of the recommendations for types A and B. They should focus on eating a balanced diet that includes meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, fruits, and vegetables, and limit their intake of wheat, corn, and legumes.
Foods to eat:
- Fruits: Pineapple, figs, grapes, etc.
- Vegetables: Artichokes, broccoli, spinach, etc.
- Meat: Lamb, rabbit, etc.
- Poultry: Turkey, chicken, etc.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, etc.
- Dairy: Yogurt, kefir, low-fat cheese, etc.
- Grains: Rice, quinoa, millet, etc.
- Other: Eggs, green tea, tofu, etc.
Foods to avoid:
- Meat: Beef, pork, etc.
- Dairy: Milk, ice cream, cheese, etc.
- Wheat: Bread, pasta, baked goods, etc.
- Legumes: Lentils, kidney beans, etc.
- Other: Alcohol, caffeine, corn, peanuts, and most beans.
It is important to note that while the Blood Type Diet has a following, it is not widely accepted by the scientific community. Many experts and organizations consider it to be a fad diet, and there is limited scientific evidence to support its effectiveness. Additionally, following the Blood Type Diet too strictly can lead to an unbalanced and potentially unhealthy diet. Before making any drastic changes to your diet, it is always best to consult a doctor or a registered dietitian.
Advantages of Eating Right for Your Type
According to proponents of the Blood Type Diet, eating foods that are recommended for your specific blood type can have a number of benefits, including:
Improved digestion: By following a diet that is tailored to your blood type, you may experience better digestion and reduced symptoms of indigestion and bloating.
Increased energy: By eating the right foods for your blood type, you may feel more energetic and experience a reduction in fatigue.
Better weight management: By avoiding foods that are not recommended for your blood type, you may be able to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Better immune system function: The Blood Type Diet emphasizes the importance of eating foods that support optimal immune system function, which can help prevent illness and disease.
Reduced risk of chronic conditions: By eating a diet that is tailored to your blood type, you may be able to reduce your risk of developing chronic conditions, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
It is important to note that while these benefits are claimed by proponents of the Blood Type Diet, there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims. As with any diet, the best approach is to eat a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains, regardless of your blood type.
Disadvantages of Eating Right for Your Type
While proponents of the Blood Type Diet tout the many benefits of eating for your blood type, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
Lack of scientific evidence: The Blood Type Diet is not supported by a large body of scientific research, and many of its claims remain unproven. This makes it difficult to determine its effectiveness and whether it is a safe and healthy way of eating.
Restrictive nature: The Blood Type Diet can be restrictive in nature, as it eliminates certain food groups and emphasizes others based on your blood type. This can make it challenging to follow, especially for individuals who have a varied and diverse palate.
Risk of nutrient deficiencies: Eliminating entire food groups, such as dairy or grains, can put you at risk of nutrient deficiencies if not balanced with other sources of nutrition. It’s important to ensure that you are eating a balanced diet that includes all the essential nutrients.
Difficult to stick to: The Blood Type Diet requires a significant amount of commitment and discipline, as it requires you to make changes to your diet that may be difficult to stick to long-term.
Potential for conflict with other dietary needs: The Blood Type Diet may not be compatible with other dietary needs, such as vegetarianism, gluten-free diets, or diets for diabetes management. This can make it difficult for some individuals to follow the diet and achieve their health goals.
Potential for social isolation: The Blood Type Diet may also lead to social isolation, as it may be difficult to find restaurants or social events that cater to your specific dietary needs.
How to Prepare the Blood Type Diet & Tips
If you’re interested in trying the Blood Type Diet, here are some steps and tips to help you get started:
Determine your blood type
The first step in preparing for the Blood Type Diet is to determine your blood type. This can be done through a simple blood test performed by a medical professional.
Familiarize yourself with the recommended foods for your blood type
Each blood type has a different list of recommended foods, as well as foods that are discouraged. You can find lists of these foods in books or online resources dedicated to the Blood Type Diet.
Plan your meals and snacks
Once you have a list of recommended foods, you can start planning your meals and snacks. Aim to include plenty of fruits and vegetables, along with lean protein sources, healthy fats, and whole grains. Make sure you avoid foods that are discouraged for your blood type.
Stock up on pantry essentials
Make sure you have all the staples you need to prepare meals and snacks that are in line with the Blood Type Diet. This may include ingredients like rice, quinoa, millet, tofu, and spices.
Get creative in the kitchen
Don’t be afraid to get creative and experiment with different recipes and meal combinations. You can also try using spices and herbs to add flavor to your dishes, and make healthy eating more enjoyable.
Stay hydrated
It’s important to stay hydrated throughout the day, especially if you’re making changes to your diet. Make sure you drink plenty of water, and consider adding herbal teas and other beverages to your diet as well.
Keep track of your progress
Keep a food diary or log to help you stay on track and track your progress. This can also help you identify any areas where you may need to make adjustments or improvements.
Consult a doctor or dietitian
Before starting any new diet, it’s always a good idea to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian. They can help you determine if the Blood Type Diet is right for you and provide guidance on how to make healthy dietary choices that are in line with your specific needs and goals.
Tips for success:
Gradually transition to the Blood Type Diet: Don’t try to make all the changes at once. Gradually transition to the new way of eating so your body has time to adjust.
Focus on variety: Try to eat a variety of different foods within the recommended food groups for your blood type. This will help ensure that you get all the nutrients you need and prevent boredom.
Avoid processed foods: The Blood Type Diet emphasizes the importance of eating whole, unprocessed foods. Avoid processed foods as much as possible, and aim to eat mostly fresh, whole foods.
Plan ahead: Planning ahead can help you stay on track and avoid reaching for unhealthy snacks when you’re on the go. Pack healthy snacks like fruit, nuts, or vegetable sticks to keep with you throughout the day.
Be patient: Changing your diet can take time, and it’s important to be patient and persistent. Stick with the diet and make adjustments as needed, and you’ll eventually see the results you’re looking for.
Overall, the Blood Type Diet can be a useful tool for those looking to make healthy dietary choices. However, it’s important to remember that there is limited scientific evidence to support its effectiveness, and it’s always best to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian before making any drastic changes to your diet.
FAQs
Is the Blood Type Diet scientifically proven?
There is limited scientific evidence to support the claims made by proponents of the Blood Type Diet. While some studies have shown a correlation between blood type and the ability to metabolize certain nutrients, there is not enough evidence to support the idea that blood type should dictate a person’s entire diet.
Are there any risks associated with the Blood Type Diet?
While the Blood Type Diet is generally considered safe, it is important to ensure that you are eating a balanced diet that includes all the essential nutrients. Some proponents of the diet recommend avoiding certain food groups altogether, which can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not balanced with other sources of nutrition.
Can the Blood Type Diet help with weight loss?
The Blood Type Diet may help with weight loss for some individuals, but this is not the primary focus of the diet. The primary focus is on eating in line with your blood type to improve overall health and prevent disease.
Is it necessary to eat based on your blood type?
There is no scientific evidence to support the idea that it is necessary to eat based on your blood type. A balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains, is recommended for optimal health regardless of blood type.
Is it possible to eat foods from all blood types on the Blood Type Diet?
It is possible to eat foods from all blood types on the Blood Type Diet, but proponents of the diet recommend sticking to the recommended foods for your specific blood type for maximum benefits.
Can the Blood Type Diet help with chronic health conditions?
While some proponents of the Blood Type Diet claim that it can help with various chronic health conditions, such as allergies, autoimmune disorders, and digestive issues, there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims. It’s important to note that a balanced diet and lifestyle modifications are generally recommended for the management of chronic health conditions.
Can the Blood Type Diet be modified for individuals with food allergies or intolerances?
Yes, the Blood Type Diet can be modified for individuals with food allergies or intolerances. Proponents of the diet recommend eliminating any foods that are known to cause an allergic reaction or intolerance and replacing them with similar foods that are recommended for the individual’s blood type.
Does the Blood Type Diet have any religious or cultural restrictions?
The Blood Type Diet does not have any specific religious or cultural restrictions, but some proponents of the diet may have personal beliefs that influence their recommendations. It’s important to consider your own personal beliefs and cultural practices when following the Blood Type Diet or any other dietary plan.
How long does it take to see results from the Blood Type Diet?
The amount of time it takes to see results from the Blood Type Diet will vary depending on the individual and their specific health goals. Some people may see improvements in their overall health and wellness within a few weeks of starting the diet, while others may take several months to see significant changes.




































![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Morse Code Charts [Numbers, Alphabet] 2 Morse Code Chart](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Morse-Code-Chart-150x150.jpg)

