Blood sugar levels are an important aspect of overall health and well-being, as they can impact energy levels, mood, and the ability to concentrate. Keeping track of blood sugar levels can be helpful for individuals with conditions such as diabetes, who need to manage their blood sugar levels on a daily basis. A blood sugar chart is a tool that helps track and monitor blood sugar levels over time.
By tracking changes in blood sugar levels, individuals can identify patterns and make adjustments to their diet, exercise, and medication as needed to keep their blood sugar levels within a healthy range. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to using a blood sugar chart, including information on what levels are considered normal, and tips for using the chart to improve blood sugar management.
Table of Contents
Blood Sugar Chart Templates
Blood sugar chart templates are pre-designed documents that help individuals monitor and track their blood sugar levels over a specific period of time. These templates provide a structured format for recording blood sugar readings, facilitating effective diabetes management and promoting overall health.
Blood sugar chart templates typically include columns or sections for dates, times of the day, blood sugar readings, and any notes or observations related to factors that may affect blood sugar levels, such as meals, medication, exercise, or stress.
Using a blood sugar chart template allows individuals with diabetes or those monitoring their blood sugar levels to establish a consistent monitoring routine. It provides a visual representation of blood sugar trends and helps identify patterns, highs, lows, and potential triggers that may require adjustments in diet, medication, or lifestyle.
Why are good blood sugar levels important?

Good blood sugar levels are important for several reasons:
Preventing diabetes: High blood sugar levels over a long period of time can lead to type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition that can lead to serious health problems if not managed properly. Maintaining good blood sugar levels can help reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Avoiding complications from diabetes: If an individual already has diabetes, good blood sugar control can help prevent or delay the onset of complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and kidney disease.
Better physical health: Good blood sugar levels can lead to better overall physical health, including increased energy levels and a lower risk of fatigue.
Improved mental health: High or low blood sugar levels can cause mood swings, irritability, and other emotional problems. Maintaining good blood sugar levels can help improve mental health and emotional stability.
Better weight management: Good blood sugar control can help prevent weight gain, as well as promote weight loss and weight management.
Reduced risk of heart disease: High blood sugar levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes. Maintaining good blood sugar levels can help reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
In short, good blood sugar levels are important for overall health and well-being, and can help prevent or manage chronic health conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. It is important to monitor blood sugar levels and work with a healthcare provider to develop an effective plan for managing blood sugar levels.
Understanding the test and chart of blood sugar
Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, is a vital component of overall health and well-being. It provides the body with energy and fuels the brain and other vital organs. In order to ensure that blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, individuals can track and monitor their levels using a blood sugar chart.
Understanding Blood Sugar Test
Blood sugar testing involves measuring the amount of glucose in a person’s bloodstream. There are several different methods for testing blood sugar levels, including:
Fingertip blood glucose test: This is the most common type of blood sugar test and involves pricking the tip of the finger to obtain a small drop of blood. The blood is then placed on a strip and inserted into a glucose meter, which measures the glucose levels in the blood.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): A continuous glucose monitoring system is a device that is worn on the body and measures glucose levels in the fluid under the skin. It provides real-time data and alerts the wearer if their blood sugar levels are too high or too low.
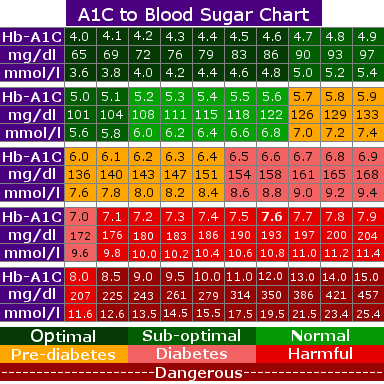
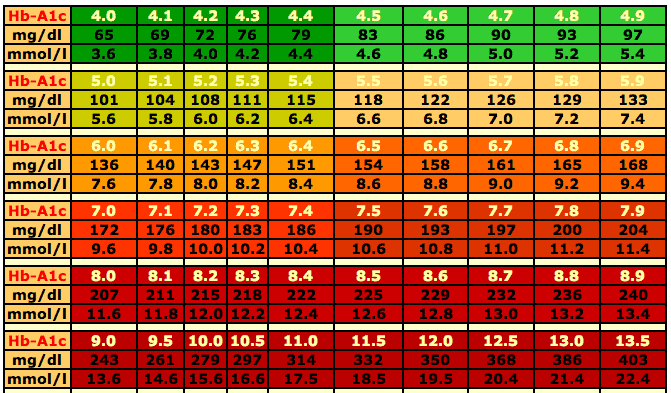
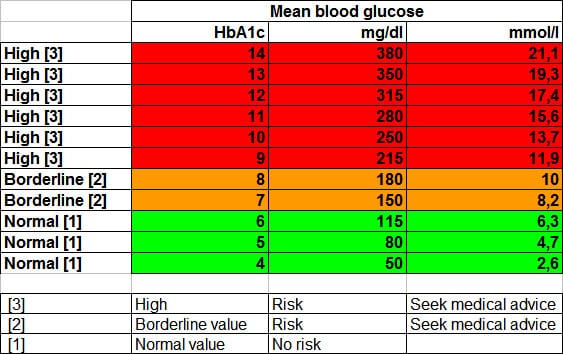
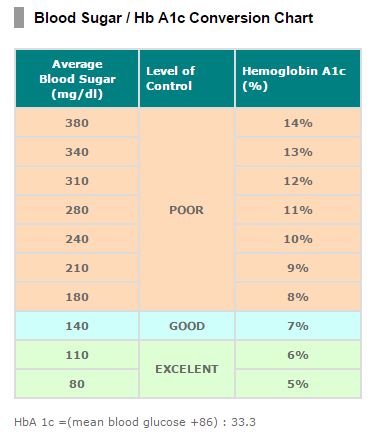
A1C test: The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months. It is a useful tool for individuals with diabetes, as it provides a long-term view of their blood sugar levels.
Using a Blood Sugar Chart
A blood sugar chart is a tool that allows individuals to track their blood sugar levels over time. By tracking changes in blood sugar levels, individuals can identify patterns and make adjustments to their diet, exercise, and medication as needed to keep their blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
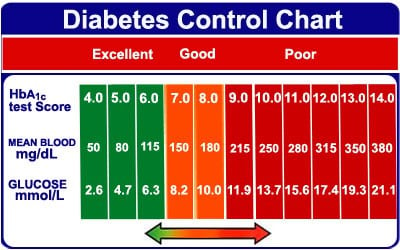
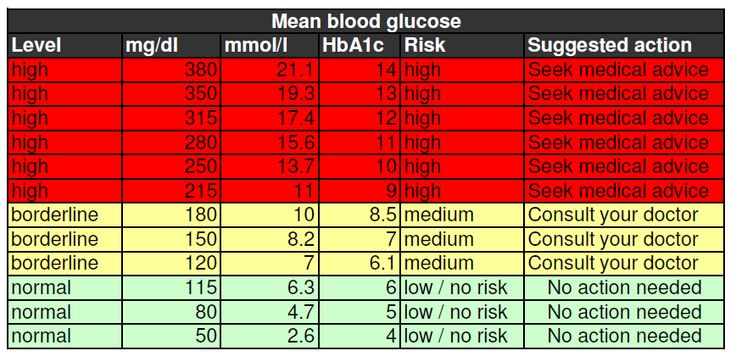
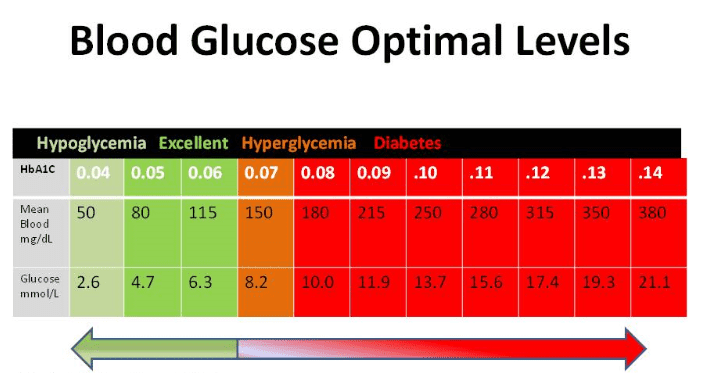
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels vary depending on the individual and their specific health status. However, in general, blood sugar levels should fall within the following ranges:
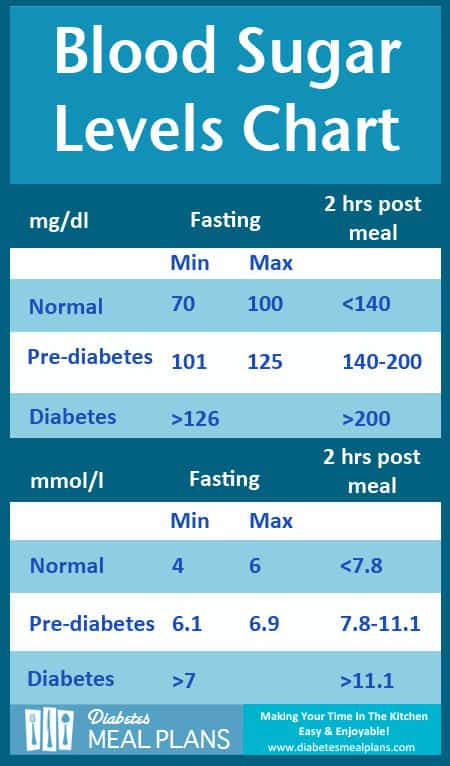
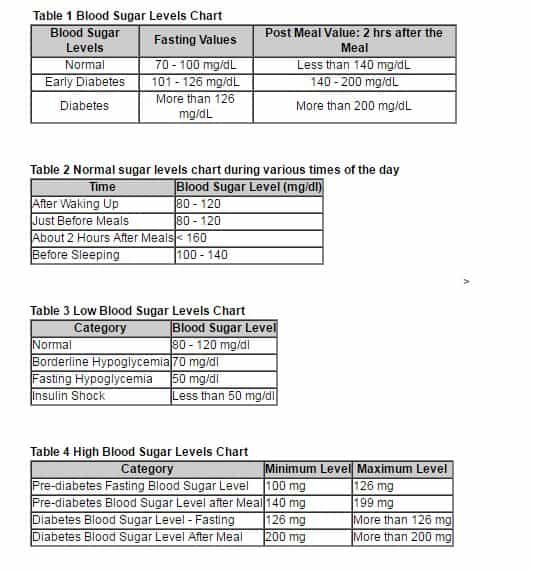
- Fasting blood sugar (first thing in the morning before eating): 70-100 mg/dL
- One to two hours after eating: Less than 140 mg/dL
- A1C test: Less than 5.7%
It’s important to note that these ranges may be different for individuals with diabetes, and they should work with their healthcare provider to determine what blood sugar levels are considered normal for them.
Tracking Blood Sugar Levels
To effectively track blood sugar levels using a blood sugar chart, it’s important to:
Test regularly: Test blood sugar levels at the same times each day, such as first thing in the morning, before and after meals, and before bedtime.
Record results: Write down the results of each blood sugar test in the blood sugar chart. It’s important to also record the time of the test and any food or drink consumed beforehand.
Identify patterns: Look for patterns in the blood sugar levels over time. For example, are blood sugar levels consistently high after eating certain foods? Are they low at certain times of the day?
Make adjustments: Based on the patterns identified, make adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication as needed to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Tips for Improving Blood Sugar Management
Eat a balanced diet: A balanced diet that is low in sugar and high in fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Exercise regularly: Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Monitor carbohydrate intake: Pay attention to the amount of carbohydrates consumed at each meal, as they can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels.
Take medications as prescribed: If prescribed, take diabetes medications as directed by a healthcare provider.
Reduce stress: Stress can have a negative impact on blood sugar levels, so it’s important to find ways to manage stress levels, such as through exercise, meditation, or talking with a mental health professional.
Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can have a negative impact on blood sugar levels, so it’s important to get enough sleep each night.
Avoid alcohol: Alcohol can raise blood sugar levels and should be consumed in moderation, if at all.
Manage portion sizes: Consuming large portions can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, so it’s important to manage portion sizes and eat smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
Work with a healthcare provider: Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider can help ensure that blood sugar levels are within a healthy range and provide support and guidance on how to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Blood Sugar Levels Chart
Blood sugar levels chart is an important tool to help individuals understand and manage their blood sugar levels effectively. Blood sugar levels can be measured through various tests, including fasting blood sugar, two-hour post-prandial blood sugar, random blood sugar, and glucose tolerance test.
Fasting Blood Sugar: Fasting blood sugar is a measure of blood sugar levels after an 8 to 12 hour period of not eating or drinking anything except water. This test helps to determine the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels and can be used to diagnose prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. A healthy fasting blood sugar level is between 70-99 mg/dL.
Two-Hour Post-Prandial Blood Sugar: This test measures blood sugar levels 2 hours after eating a meal. This test can help to determine how well the body is able to regulate blood sugar levels after a meal and can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes. A healthy two-hour post-prandial blood sugar level is less than 140 mg/dL.
Random Blood Sugar: Random blood sugar is a measure of blood sugar levels taken at any time during the day, regardless of when the last meal was consumed. This test can be used to screen for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. A healthy random blood sugar level is between 70-99 mg/dL.
Glucose Tolerance Test: The glucose tolerance test measures how well the body is able to regulate blood sugar levels over a period of time. During this test, an individual will drink a sweet solution and have their blood sugar levels tested at regular intervals over the next 2 hours. This test can be used to diagnose gestational diabetes or type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to understand that these blood sugar levels charts are just general guidelines and the normal range may vary depending on the individual’s age, weight, and overall health status. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on what blood sugar levels are considered normal for you.
In addition to understanding blood sugar levels, there are several ways to help manage and maintain healthy blood sugar levels:
Eat a balanced diet: A diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Regular exercise: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity each day.
Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, so it’s important to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Limit processed and high-sugar foods: Processed foods and foods high in added sugars can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, so it’s important to limit these foods and choose more nutrient-dense options.
Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help identify patterns and determine the effectiveness of lifestyle changes and treatments. A healthcare provider can provide guidance on how often to test blood sugar levels and what results are considered normal for you.
Medications: If needed, medications such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents can be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. These medications should be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGMs are wearable devices that measure blood sugar levels in real-time. These devices can provide a more complete picture of blood sugar levels and can alert individuals to changes that may need to be addressed.
Work with a healthcare provider: Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider can help monitor blood sugar levels and provide guidance and support on how to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
FAQs
How often should blood sugar levels be tested?
The frequency of blood sugar testing can vary depending on an individual’s health status, type of diabetes (if applicable), and treatment plan. A healthcare provider can provide guidance on how often to test blood sugar levels.
What is considered a normal blood sugar level?
Normal blood sugar levels vary based on the type of test and the individual’s health status. Generally, fasting blood sugar levels should be less than 100 mg/dL, while two-hour post-prandial (after eating) blood sugar levels should be less than 140 mg/dL. Random blood sugar levels should be less than 200 mg/dL. However, normal ranges can vary based on the individual and the testing method.
What can cause high or low blood sugar levels?
High blood sugar levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including overeating, lack of physical activity, stress, certain medications, and health conditions such as diabetes. Low blood sugar levels can be caused by skipping meals, taking too much insulin, excessive exercise, and certain medications.
What should I do if my blood sugar levels are consistently high or low?
If an individual’s blood sugar levels are consistently high or low, they should discuss this with their healthcare provider. The healthcare provider can provide guidance on lifestyle changes, medications, and other treatments to help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Are there any side effects of managing blood sugar levels?
Managing blood sugar levels can sometimes have side effects, depending on the treatment approach. For example, taking insulin or oral medications for managing blood sugar levels can sometimes cause low blood sugar levels, and may lead to weight gain. It is important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider and weigh the benefits and risks of any treatment plan.
Can blood sugar levels be affected by diet?
Yes, diet plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. Consuming a balanced diet with the right amount of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Certain foods and drinks, such as sugary or high-carb foods, can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, consuming low-carb or high-protein foods can help keep blood sugar levels stable.
Is it necessary to follow a specific diet for managing blood sugar levels?
Not necessarily. While certain diets, such as the low-carb or Mediterranean diet, can help manage blood sugar levels, it is not necessary to follow a specific diet. Rather, it is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine an individualized approach to managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medications (if necessary).
What are the long-term complications of uncontrolled blood sugar levels?
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to a variety of long-term complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, blindness, and amputations. Maintaining good blood sugar control is important for reducing the risk of these and other complications.
Are there any alternative methods for managing blood sugar levels?
In addition to diet and medications, physical activity and stress management can also help regulate blood sugar levels. Some individuals may also benefit from alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or herbal remedies, but it is important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and effectiveness.














![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 2 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 3 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
