A bill of lading is a critical document in international shipping that serves as evidence of receipt of goods and outlines important information such as the shipping method, origin, and destination of the parcel. Business owners who frequently engage in international shipping should be familiar with this document, as it is a key component of the shipping process.
Table of Contents
What is a Bill of Lading?

A bill of lading (B/L) is a legal document that serves as a receipt for goods that are being shipped by a carrier, such as a trucking company, shipping line, or airline. It serves as proof of the contract of carriage and is issued by the carrier to the shipper.
The B/L is a document of title, meaning it can be used to transfer ownership of the goods. It also serves as a document of transport, as it shows that the goods have been loaded onto the carrier’s transportation and are en route to their final destination. The B/L includes key information such as the names of the shipper and consignee, the type and quantity of goods being shipped, the point of origin and destination, and any special instructions or handling requirements.
Bill of Lading Templates
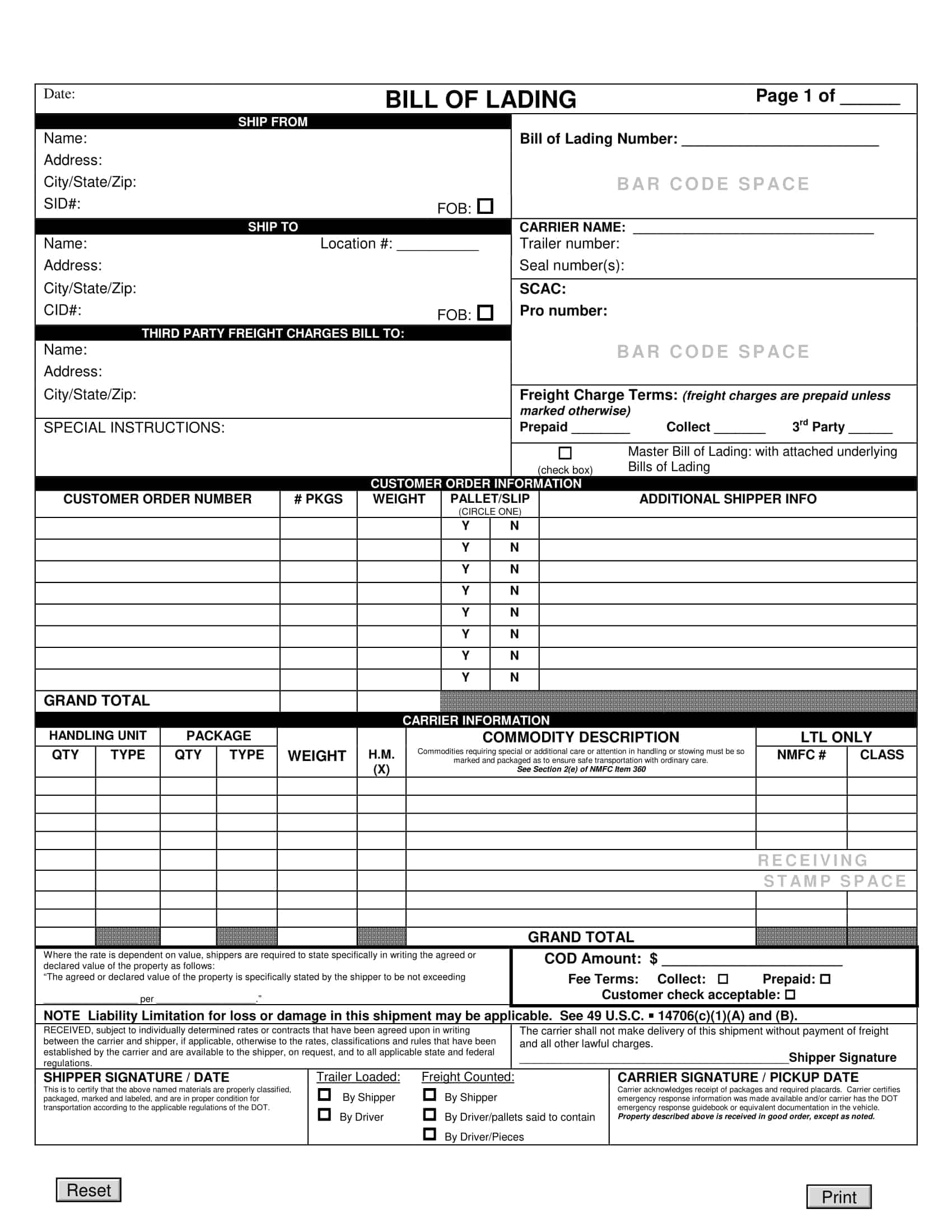
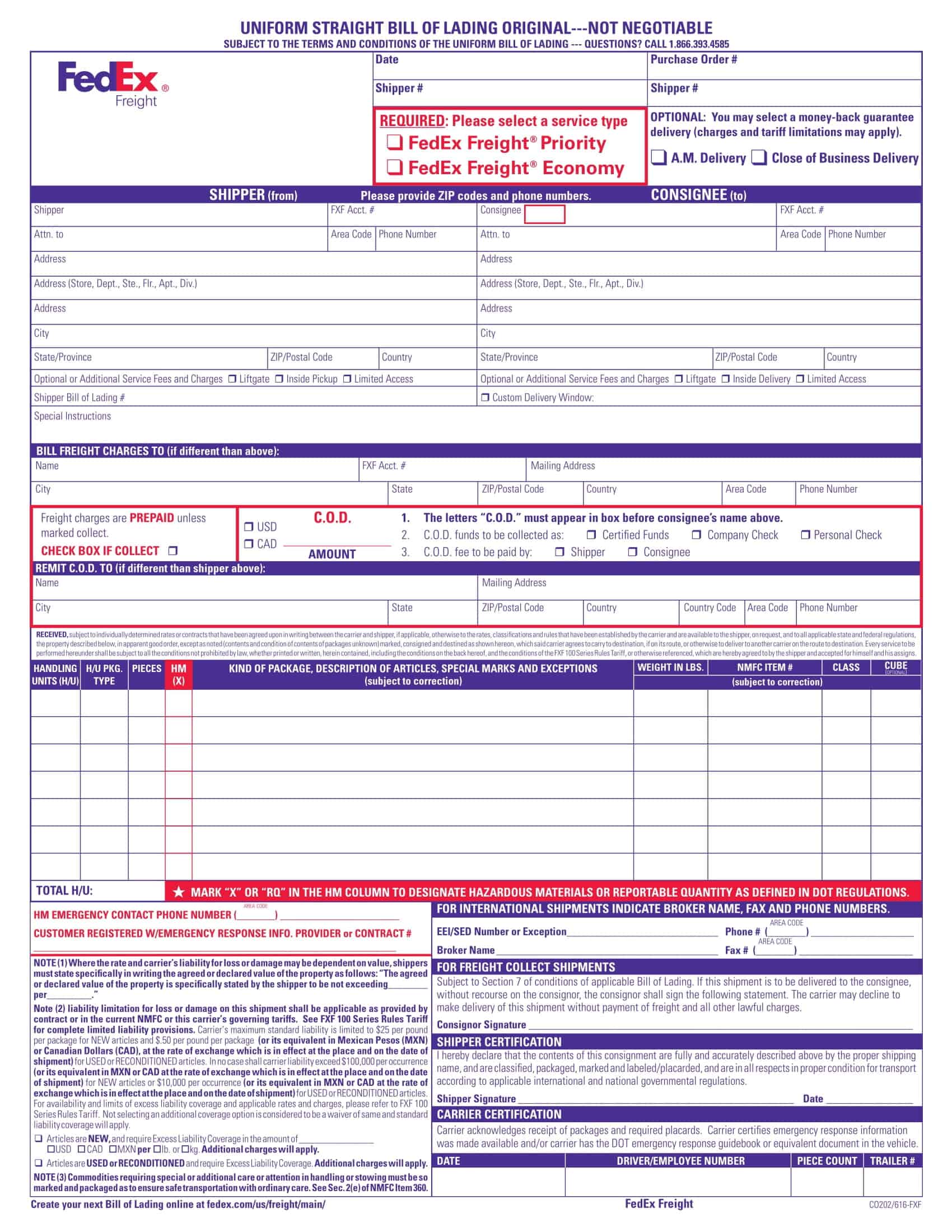
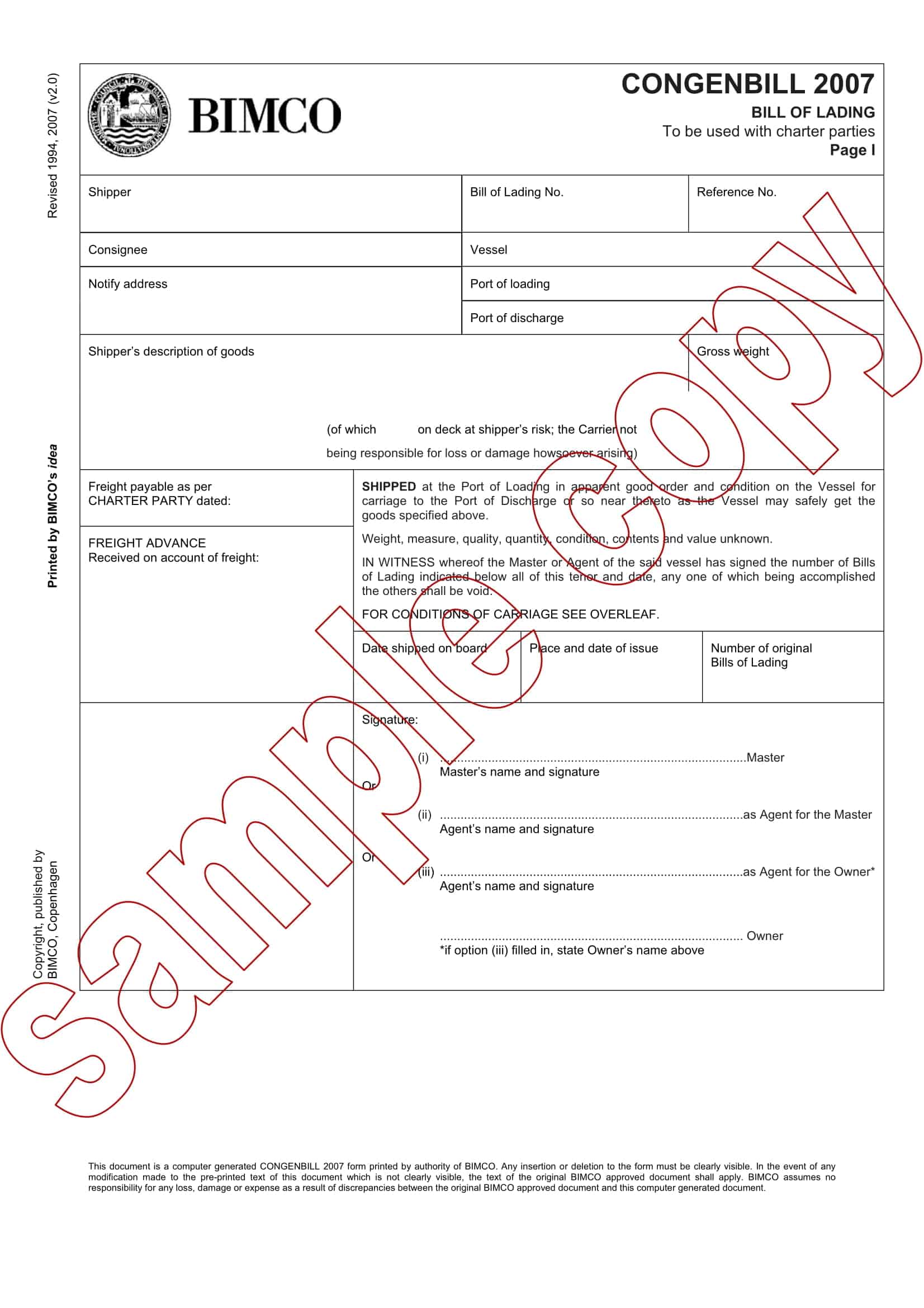
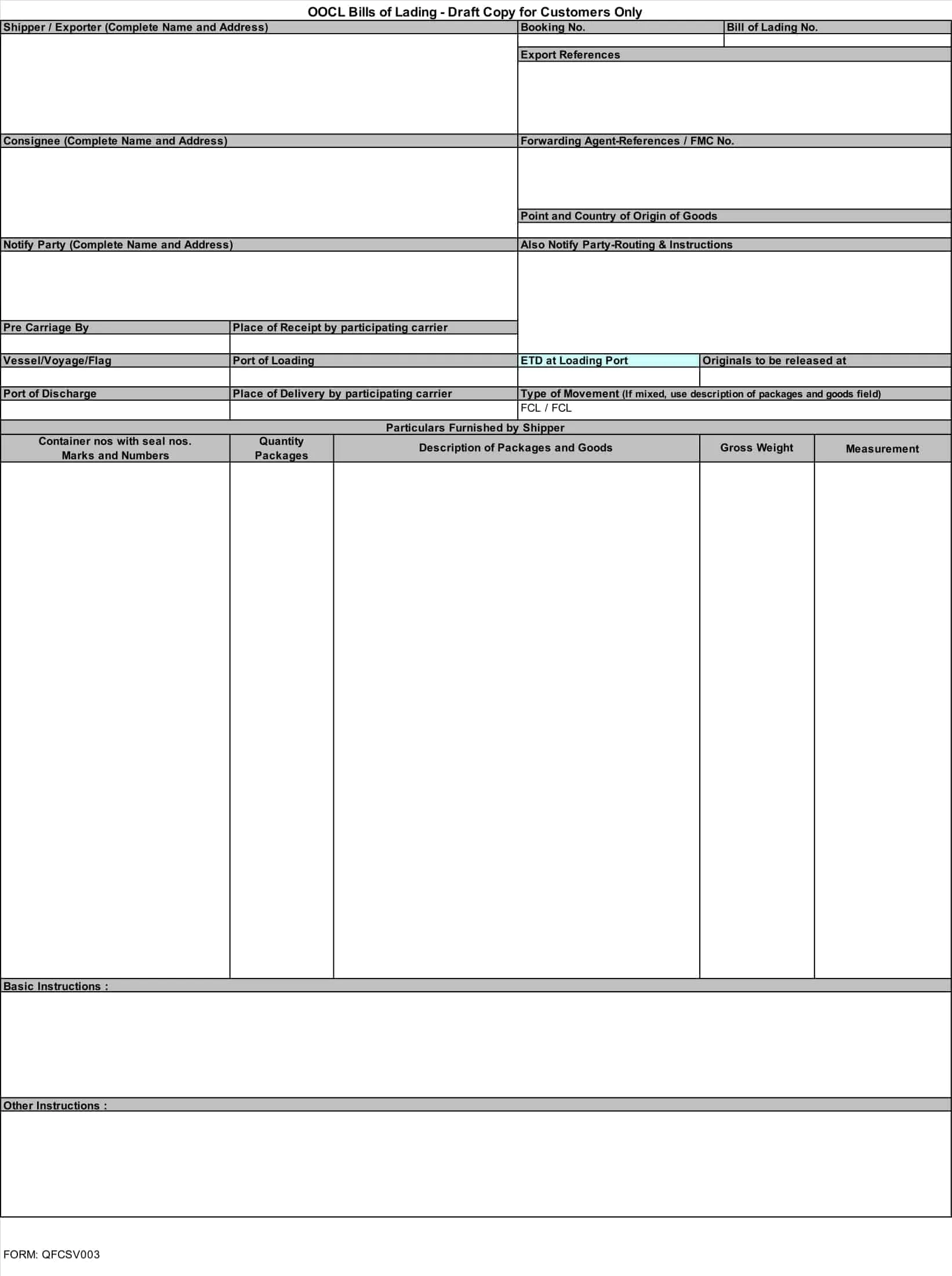
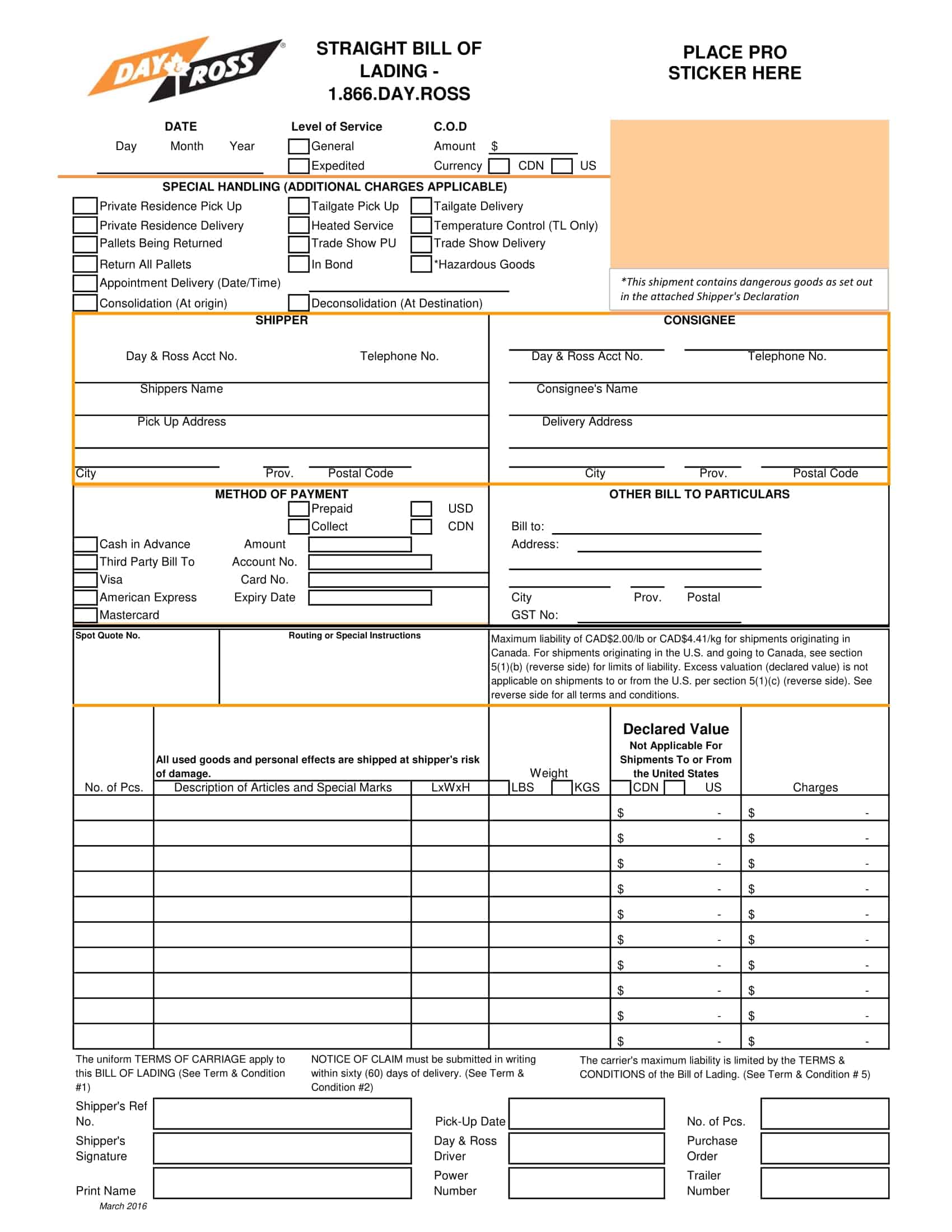
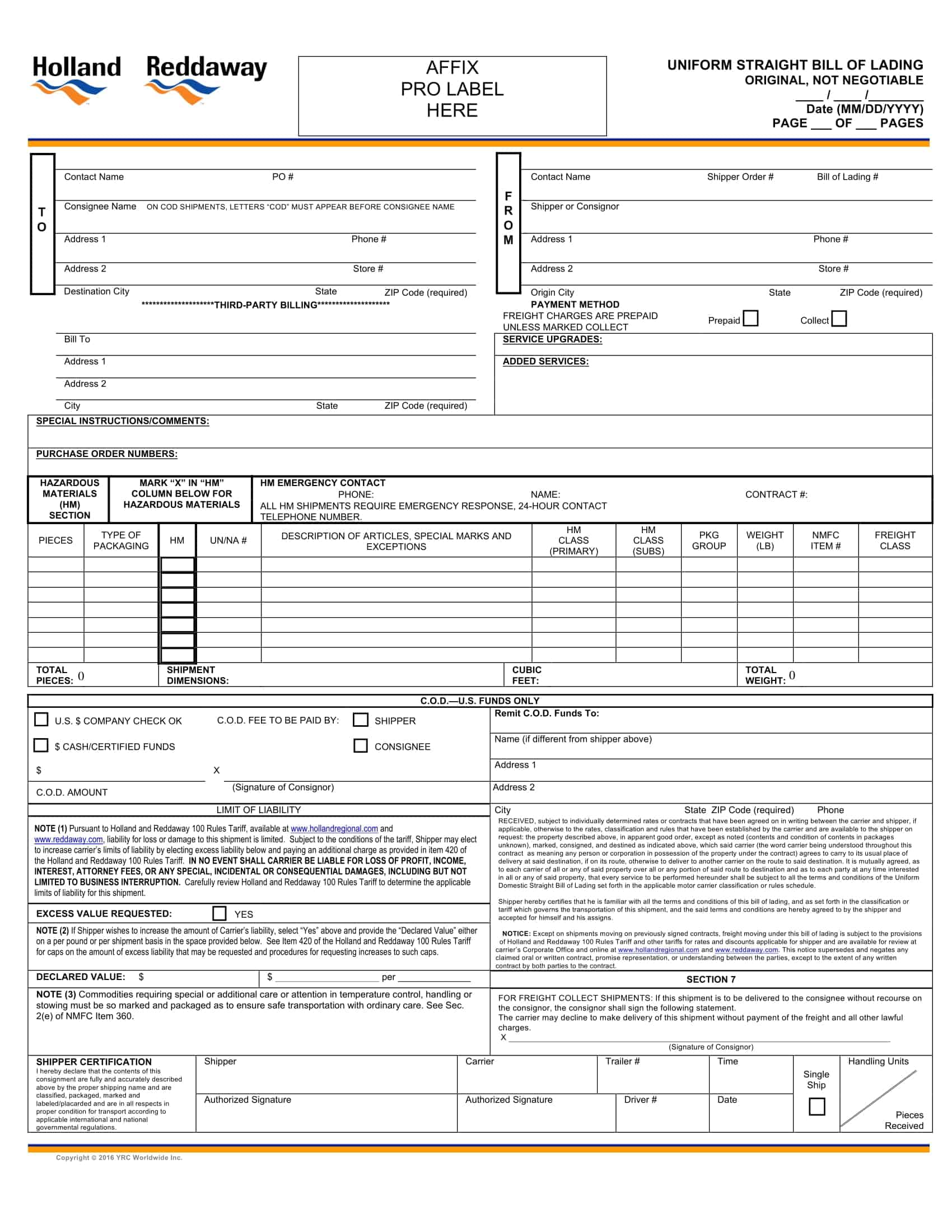
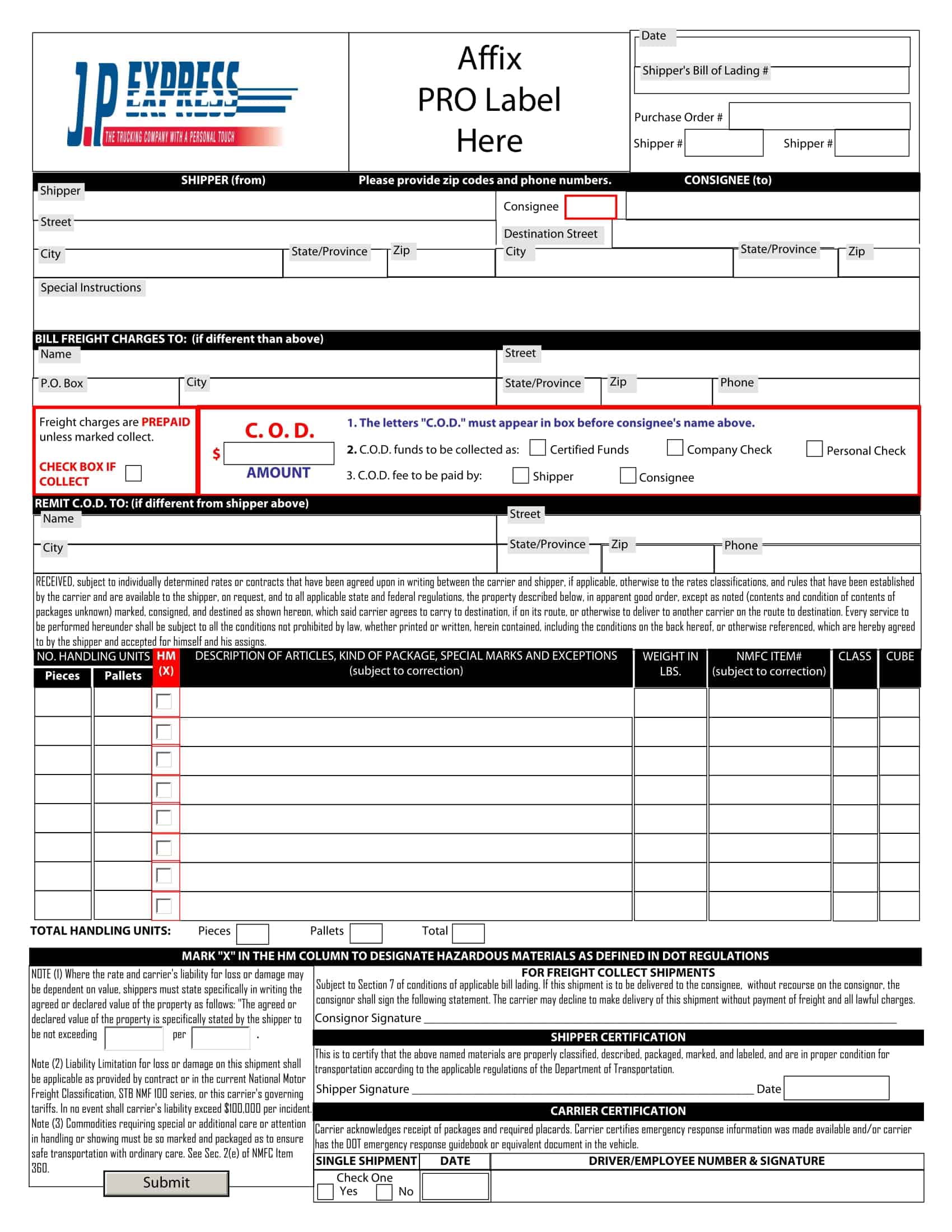
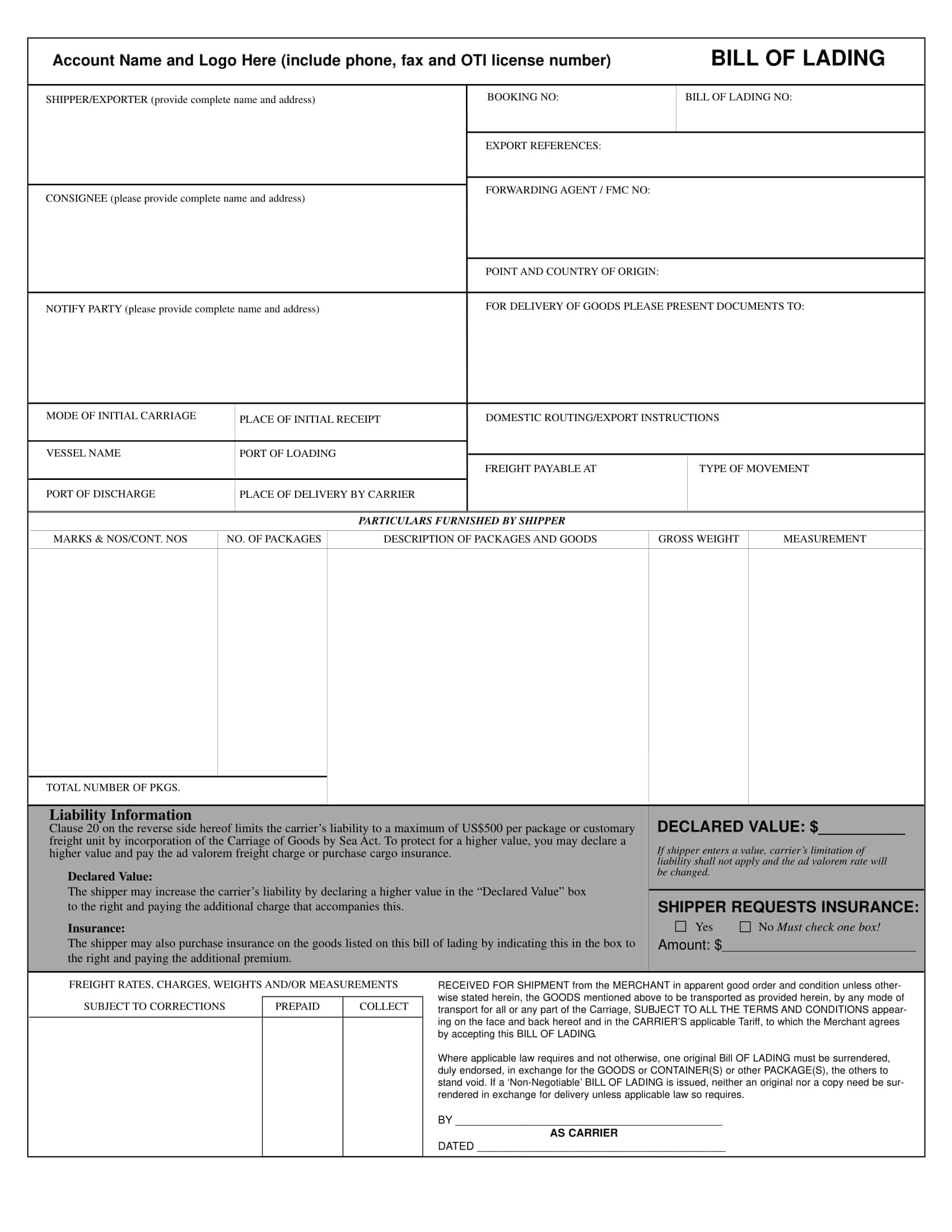
Bill of lading templates are pre-designed documents that provide a standardized format for creating bills of lading. These templates serve as a starting point for generating accurate and consistent bills of lading for the transportation of goods by sea, air, or land.
Bill of lading templates typically include sections that capture important information related to the shipment, such as the names and addresses of the shipper, carrier, and recipient, a detailed description of the goods being transported, the quantity or weight of the goods, and the terms and conditions of the transportation agreement. They may also include sections for additional details like special handling instructions or insurance requirements.
Using a bill of lading template streamlines the process of creating this essential shipping document. It ensures that all necessary information is included and properly formatted, saving time and minimizing errors or discrepancies that can occur in manual documentation.
Types of Bill of Lading
There are several types of bill of lading, including:
Shipped Bill of Lading: This type of bill of lading is issued by the carrier to the shipper, acknowledging that the goods have been received on board the ship for transportation. It serves as a receipt for the goods and also serves as a contract of carriage between the carrier and the shipper. It is often considered the most basic type of bill of lading, and it serves as evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods.
Through Bill of Lading: Another type of bill of lading is used for the transportation of goods through multiple modes of transportation, such as by sea and then by rail or truck. It serves as a single document covering the entire journey and is issued by the carrier at the point of origin. It is useful for shippers who are transporting goods over long distances and through several different modes of transportation.
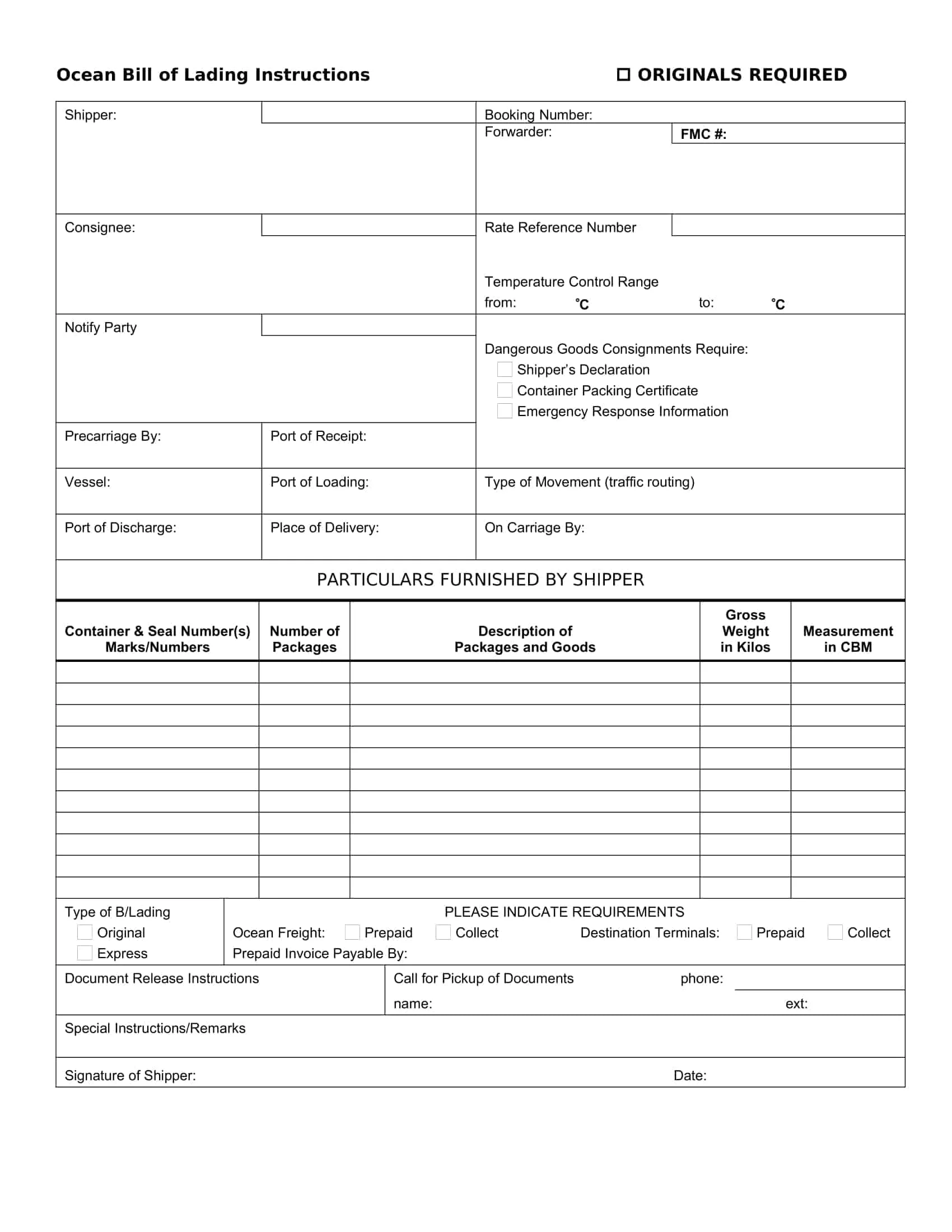
Ocean Bill of Lading: Most common type of bill of lading is used for the transportation of goods by sea. It is issued by the carrier and serves as a receipt for the goods, a contract of carriage, and evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods. It is also used to document the terms of the freight and other charges for the voyage.
Inland Bill of Lading: This type of bill of lading is used for the transportation of goods by inland waterway, such as by river or canal. It serves as a receipt for the goods, a contract of carriage, and evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods. It is also used to document the terms of the freight and other charges for the voyage.
Received Bill of Lading: Other type of bill of lading is issued by the carrier to the shipper, acknowledging that the goods have been received for transportation, but it does not confirm that the goods have been loaded on board the ship. It serves as a receipt for the goods, but it does not serve as a contract of carriage or evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods.
Claused Bill of Lading: Other type of bill of lading is issued by the carrier to the shipper, acknowledging that the goods have been received on board the ship for transportation, but with the notation that the goods were received in damaged condition. It serves as a receipt for the goods, a contract of carriage, and evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods, but it also documents any damage to the goods at the time of receipt.
Uniform Bill of Lading: Another type of bill of lading is issued by the carrier and conforms to a standard format that has been adopted by the National Motor Freight Traffic Association or other industry groups. It serves as a receipt for the goods, a contract of carriage, and evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods. It also includes standard information such as the names of the shipper and consignee, the description of the goods, and the terms of the freight and other charges for the voyage.
Clean Bill of Lading: This type of bill of lading is issued by the carrier to the shipper, acknowledging that the goods have been received on board the ship for transportation, and that the goods were received in good order and condition. It serves as a receipt for the goods, a contract of carriage, and evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods, but it also confirms that the goods were received in good condition.
What are the key purposes of the bill of lading?
The purpose of a bill of lading (BL) is to serve as a document of title, a receipt for goods, and a contract of carriage between the carrier and the shipper.
Document of title: A BL serves as evidence of ownership for the goods being shipped. It allows the holder of the BL, typically the shipper or consignee, to take possession of the goods upon arrival at the destination port. This is important for goods that are being shipped to a third party, as it allows the shipper to transfer ownership of the goods to the consignee without physically transferring the goods.
Receipt for goods: A BL serves as a record of the goods that have been received by the carrier for shipment. It contains detailed information about the goods being shipped, including the quantity, description, weight, and any special handling instructions. This information is used by the carrier to ensure that the correct goods are loaded onto the ship and transported to the correct destination.
Contract of carriage: A BL serves as a legally binding agreement between the carrier and the shipper. It sets out the terms and conditions of the shipment, including the carrier’s obligations and liabilities for the goods being shipped. This includes the carrier’s responsibility to transport the goods safely and efficiently, and to deliver them in the same condition as when received.
Evidence of carrier’s liability: A BL serves as evidence of the carrier’s liability for the goods being shipped. It documents the condition of the goods when received by the carrier, and any damage or loss that may occur during transport. This can be important in the event of a dispute between the carrier and the shipper over the condition of the goods upon delivery.
Facilitation of trade: A BL also serves as an important document for international trade. It is used to clear goods through customs, and to provide evidence of the origin, value, and description of the goods being shipped. This helps to ensure compliance with international trade regulations and tariffs.
Electronic bill of lading (e-BL): Many companies are now using electronic bill of lading to facilitate faster and more efficient trade. An e-BL is a digital document that can be issued and transmitted electronically, which eliminates the need for a physical paper document. The e-BL can also be used to track the location and condition of the goods being shipped in real-time.
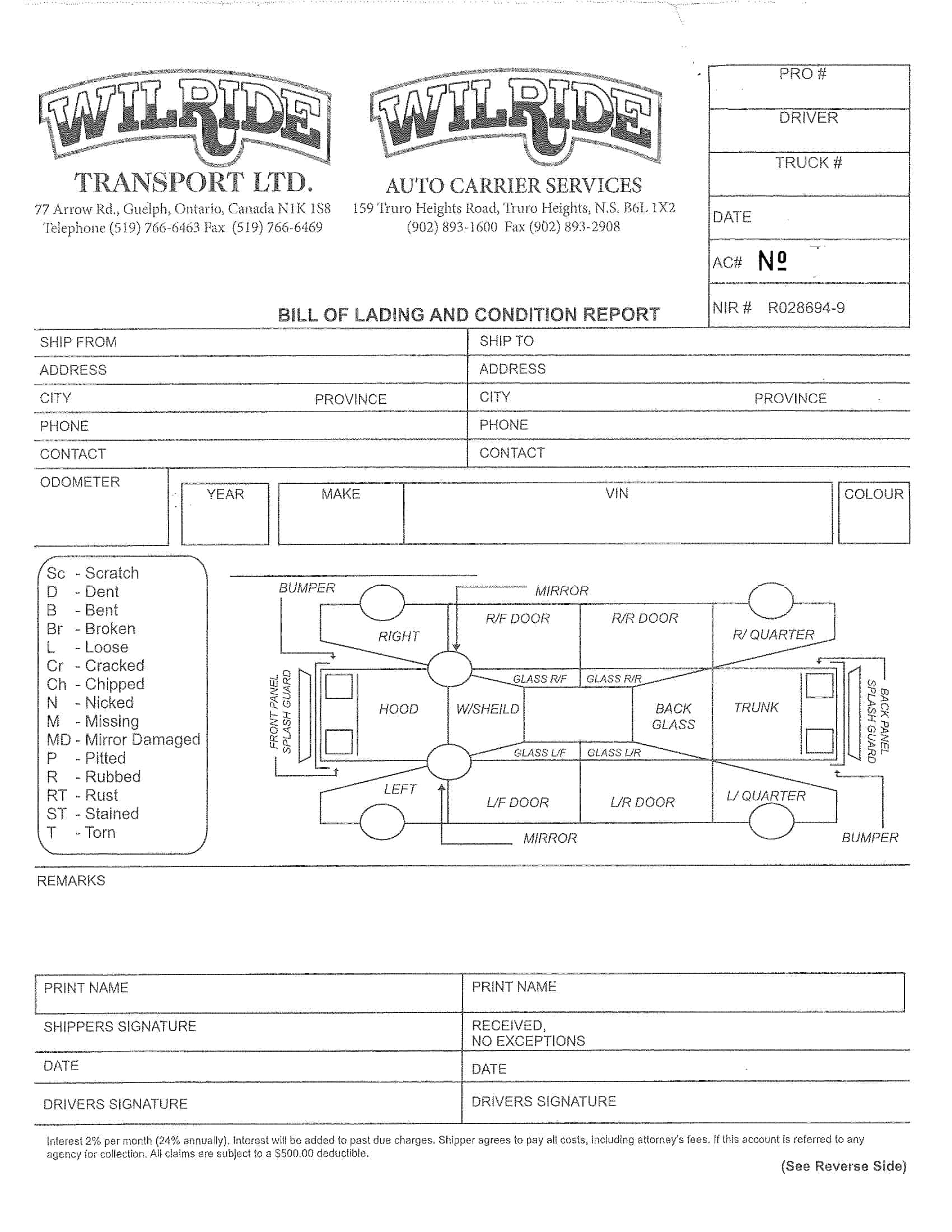
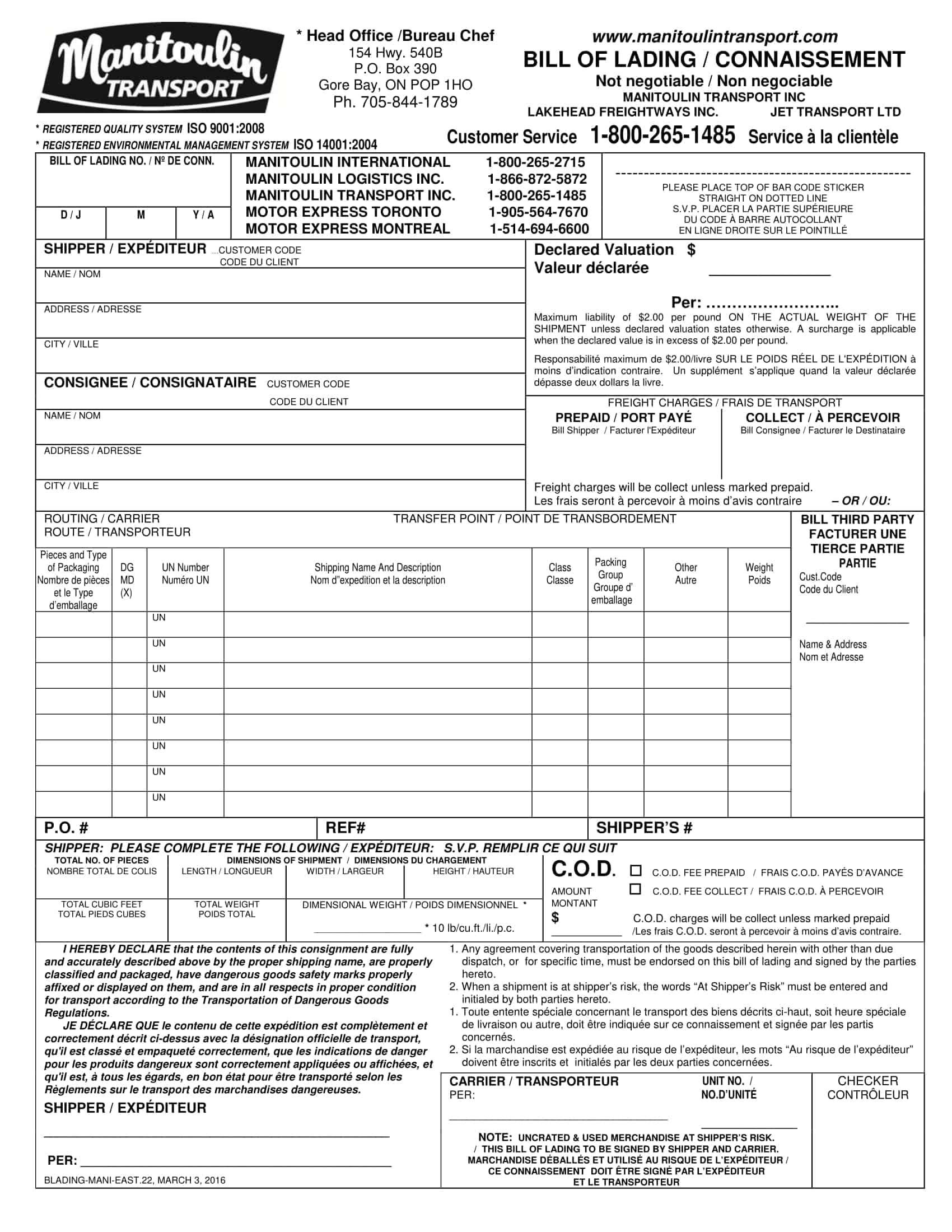
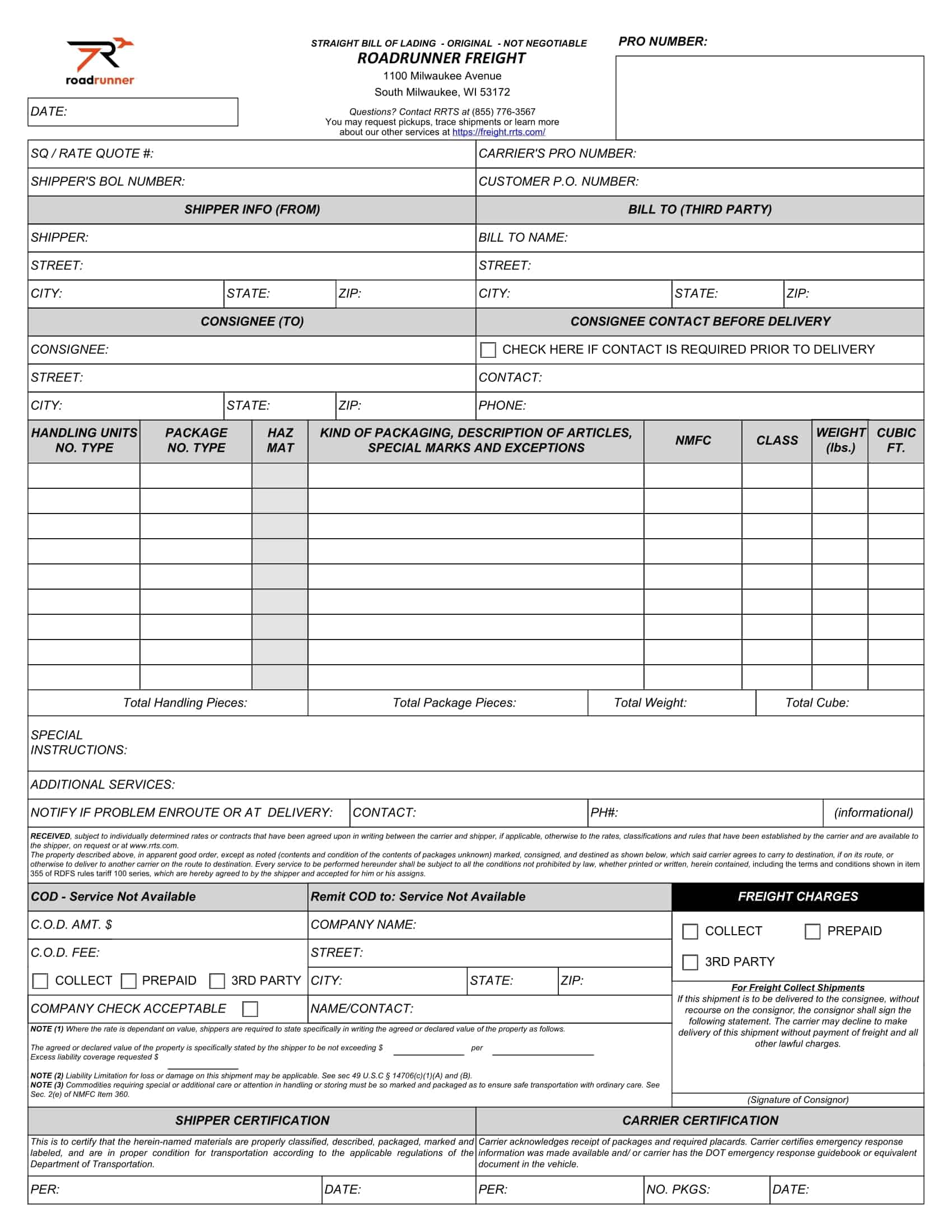
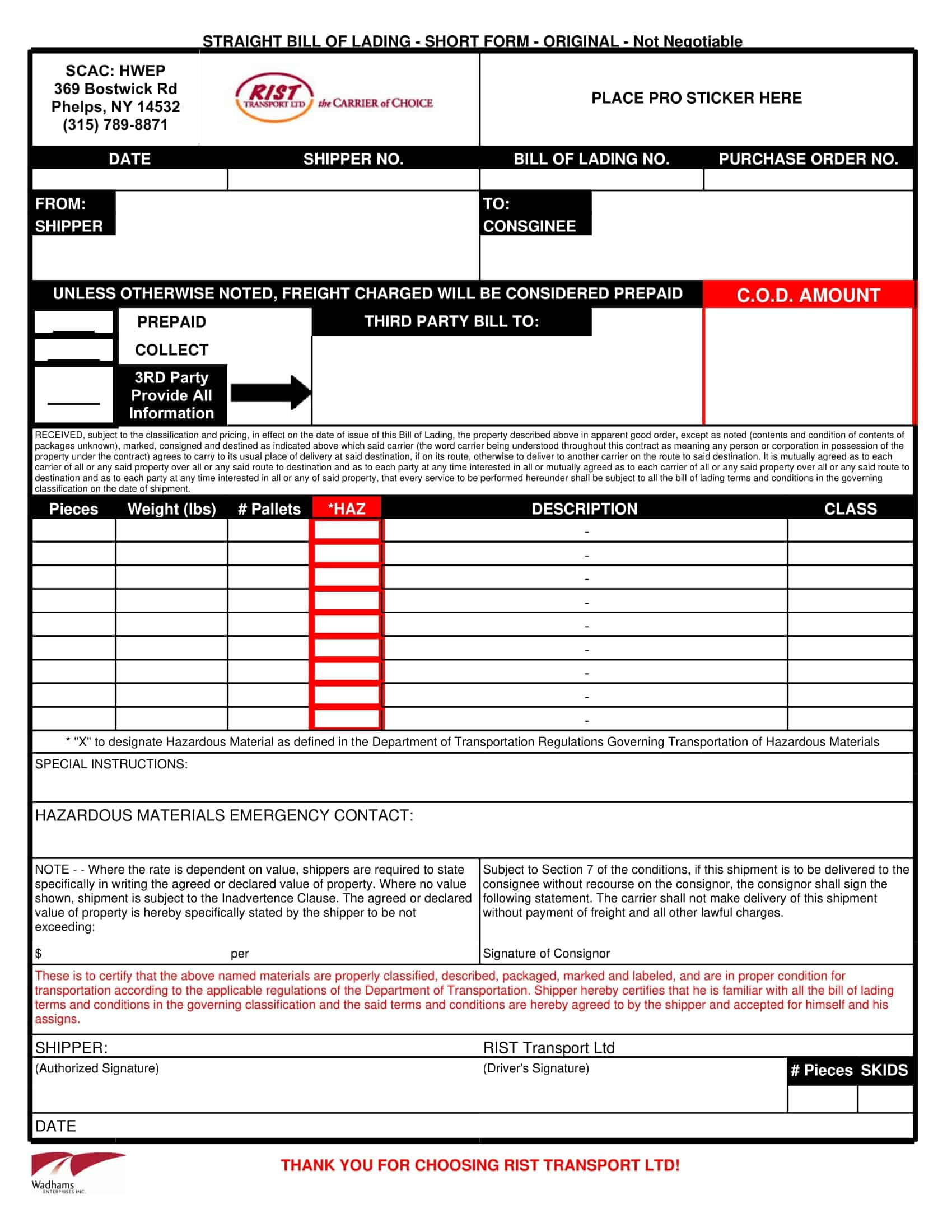
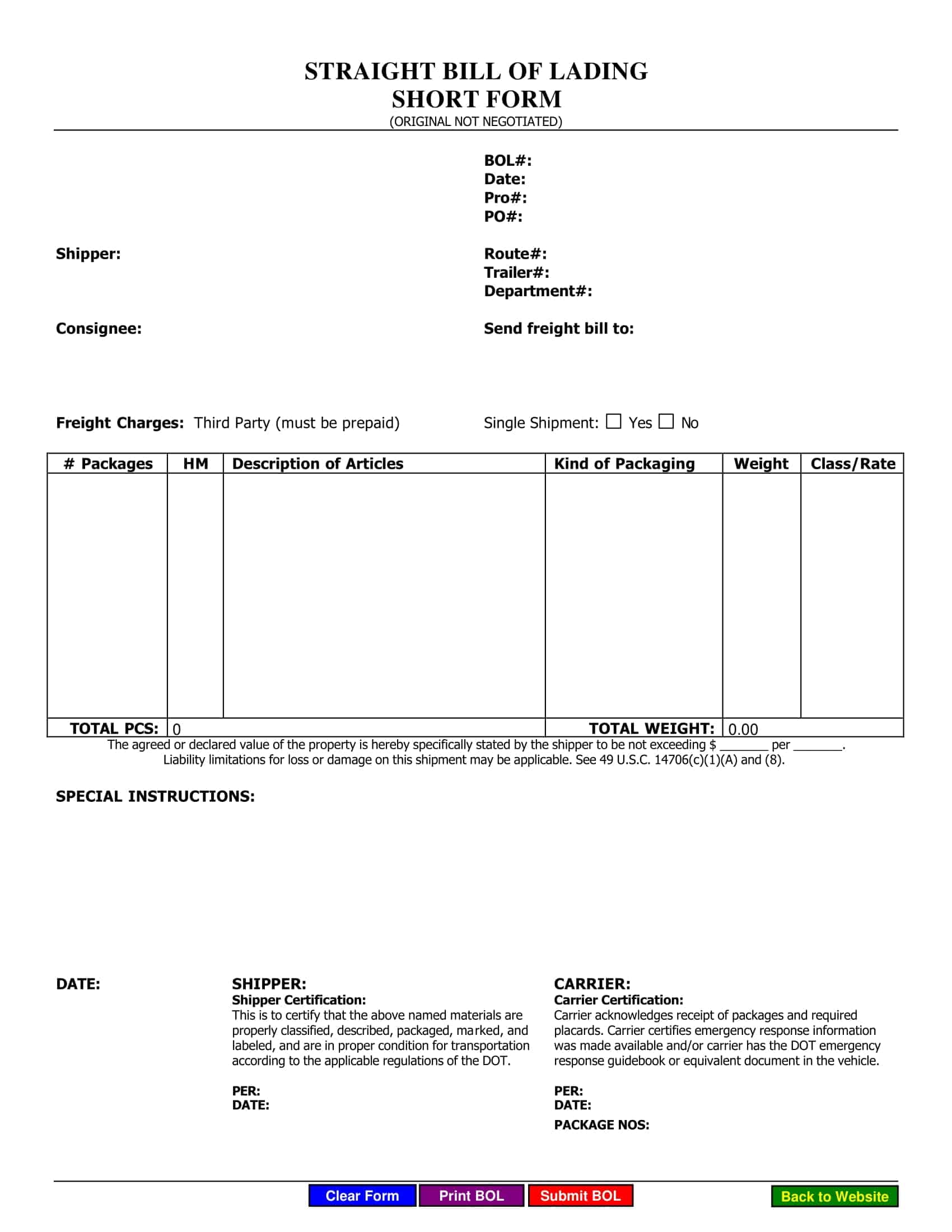
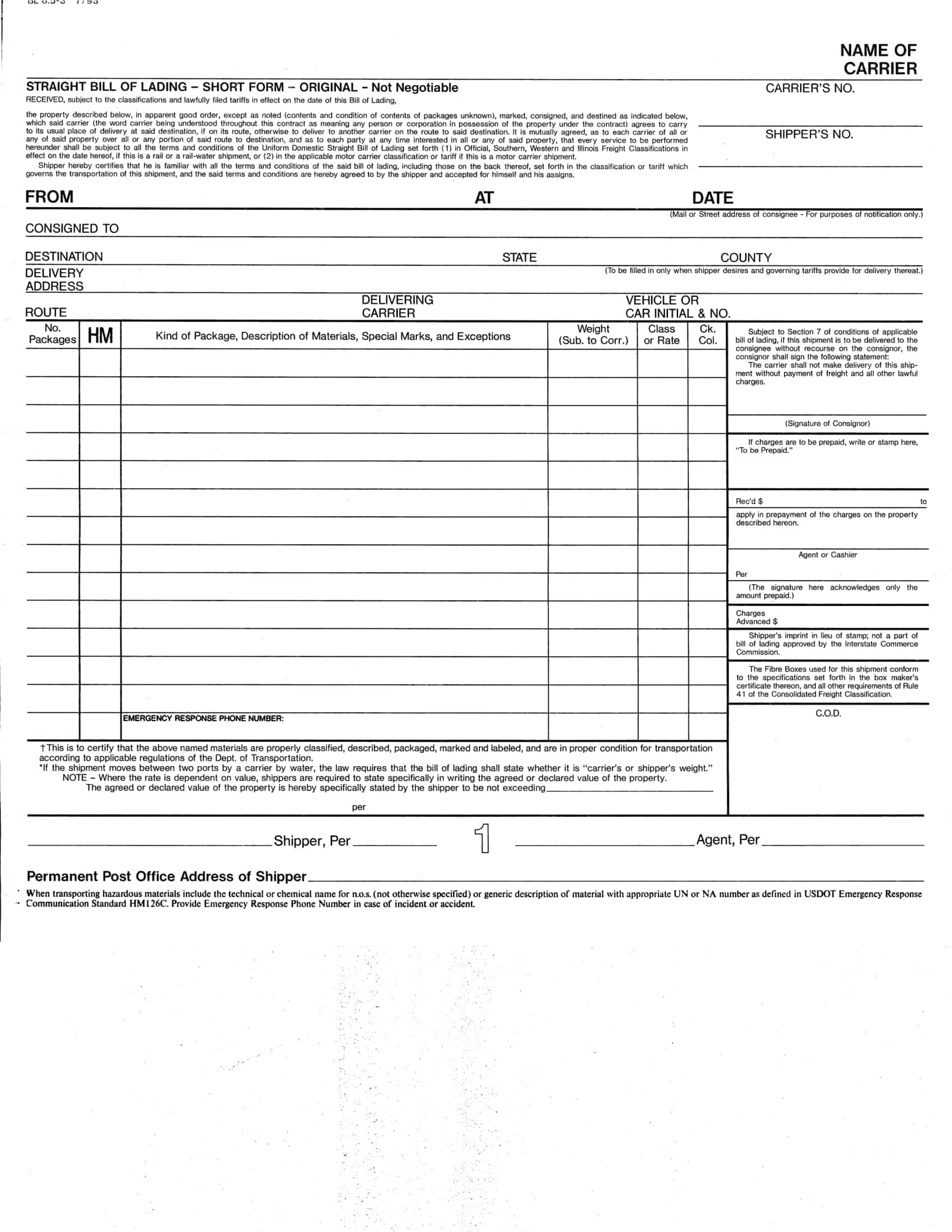
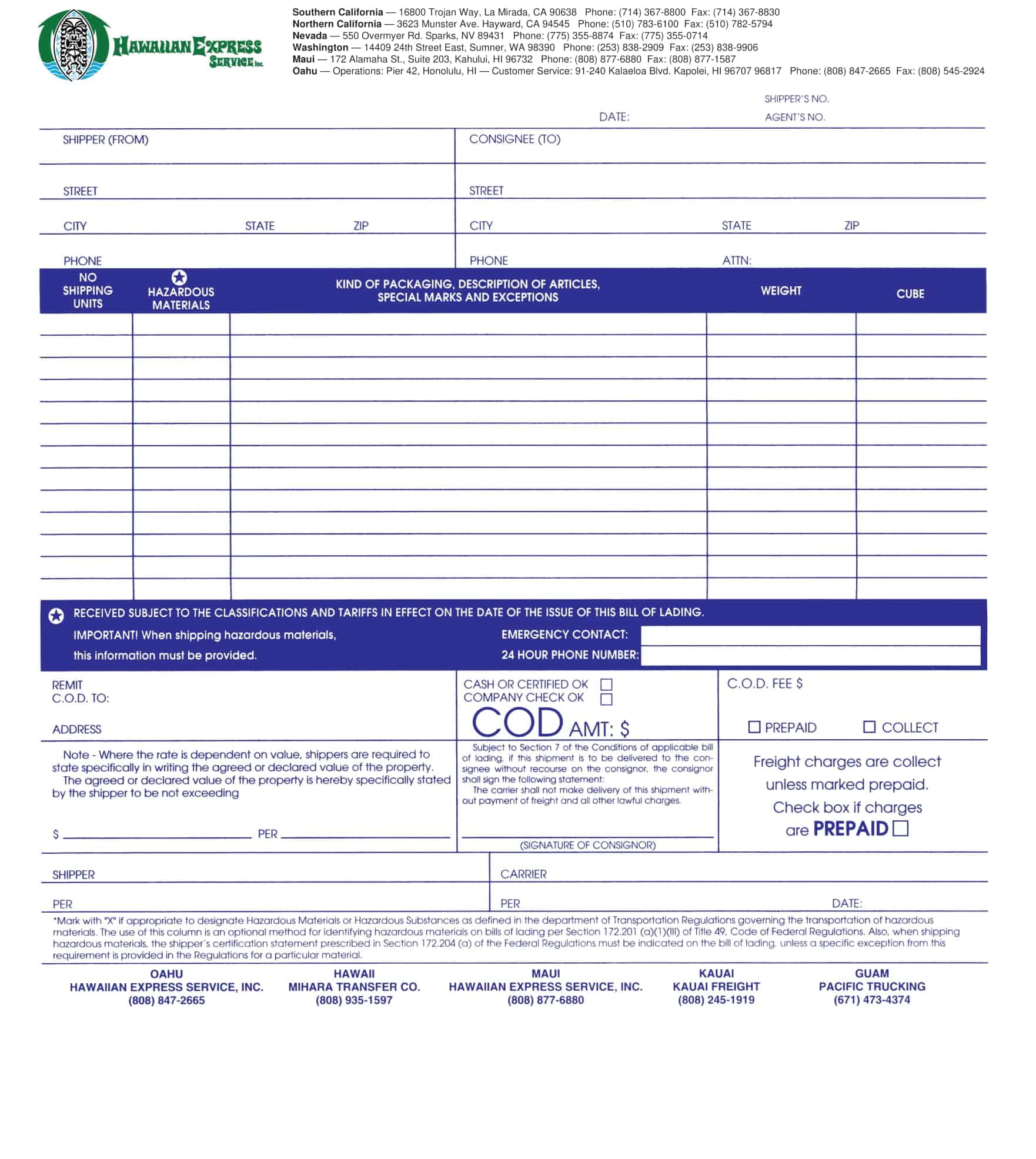
Essential Elements of a Bill of Lading
A bill of lading (BL) is a legal document that serves as a record of the goods being shipped, and the terms and conditions of the shipment. The following are the necessary information that should be included in a bill of lading:
Shipper’s information: The name and contact information of the shipper, including the company name, address, and telephone number.
Consignee’s information: The name and contact information of the consignee, including the company name, address, and telephone number.
Description of goods: A detailed description of the goods being shipped, including the quantity, weight, and any special handling instructions.
Route of shipment: The origin and destination of the shipment, including any intermediate ports of call.
Mode of transportation: The mode of transportation being used to ship the goods, such as by sea, air, or rail.
Bill of lading number: A unique number assigned to the BL by the carrier.
Date of shipment: The date on which the goods were shipped.
Terms of carriage: The terms and conditions of the shipment, including the carrier’s obligations and liabilities for the goods being shipped.
Freight and charges: The cost of the shipment, including any freight and other charges that will be incurred.
Signatures: The signature of the carrier, shipper, and any other parties involved in the shipment.
Notations: Any notations or clauses that are added to the BL such as claused bill of lading, which would indicate the goods were received in damaged condition.
FAQs
What happens if a bill of lading is lost or damaged?
If a bill of lading is lost or damaged, the carrier may issue a replacement document. However, if the original bill of lading is required for customs clearance or other legal reasons, the carrier may be liable for any delays or additional expenses incurred as a result.
How is a bill of lading used in international trade?
A bill of lading is an essential document for international trade. It is used to clear goods through customs and provide evidence of the origin, value, and description of the goods being shipped. It is also used to document the terms of the freight and other charges for the voyage.
What is the difference between a bill of lading and a freight bill?
A bill of lading is a legal document that serves as a record of the goods being shipped and the terms and conditions of the shipment. It serves as a document of title, a receipt for goods, and a contract of carriage between the carrier and the shipper. A freight bill, on the other hand, is a document that shows the charges for the transportation of goods. It is often used to bill the shipper for the cost of the shipment.
















































![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 2 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 3 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)

Attestation Services Dubai play a crucial role in authenticating documents for legal and official purposes. These services ensure that documents such as birth certificates, marriage certificates, educational certificates, and commercial documents are genuine and can be accepted internationally. With Dubai being a hub for business and expatriates, attestation services are in high demand to facilitate various transactions and processes.
Notary services in Dubai play a crucial role in ensuring the legality and authenticity of various documents. From business contracts to personal agreements, having documents notarized provides peace of mind and legal certainty. It’s an essential service for anyone navigating the legal landscape in the UAE’s vibrant business hub.