Unlocking the secrets of a well-structured, compelling research paper is no less than embarking on a thrilling intellectual expedition. Scholars and students, novices and experts alike, often find themselves wrestling with the intricate web of thesis statements, arguments, evidence, and conclusions, all under the stern gaze of academic rigor.
Striking the delicate balance between engaging storytelling and robust scientific discourse is indeed a high-wire act. This article seeks to unravel the art and science of crafting an effective research paper, transforming daunting academic challenges into achievable milestones.
Table of Contents
What is a research paper?

A research paper is a comprehensive piece of academic writing that involves the thorough investigation and exploration of a particular topic. Rooted in a specific research question, a research paper aims to analyze, interpret, and argue a point based on an extensive review and synthesis of existing literature, original data, or a combination of both.
This critical exercise demands deep understanding, clear articulation, and rigorous analysis from the author. The end product is a detailed presentation that not only contributes to the existing knowledge base but also invites readers, often scholars or students, to engage in a thoughtful discussion on the topic.
Research Paper Templates
Research papers present in-depth analyses and findings on a given topic. Creating a cohesive research paper requires careful formatting and organization. Research paper templates provide helpful writing frameworks for papers.
The templates contain pre-formatted document layouts including title pages, abstracts, headings, reference lists, and appendices. They incorporate proper citations and styles like APA or MLA. Templates have space for the paper’s title, student name, course name, professor, and date. Outline sections prompt writers to include introductions, background information, methodologies, results, analyses, conclusions, and recommendations.
Research paper templates guide writers through the process. They help writers logically structure papers and position elements appropriately. Templates ensure proper formatting so writers can focus on content. They allow students at all levels to produce polished papers that adhere to academic standards. Research writing is simplified and streamlined with paper templates. Educators may provide templates to students as writing aids for assignments. Whether required by professors or used voluntarily, research paper templates are valuable tools for developing strong academic papers.
The Purpose of Research Writing
Research writing serves multiple essential purposes in academic, professional, and societal contexts. At its core, it is an avenue to investigate, explore, and contribute to the body of knowledge about a specific topic or field.
Knowledge Generation: One of the primary goals of research writing is to generate new knowledge. It may involve filling gaps in existing literature, offering new insights or perspectives, challenging established theories, or creating a novel theoretical framework. By doing this, research contributes to the evolution of academic disciplines and professional practices.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: Research writing fosters the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It requires the researcher to analyze complex problems, scrutinize evidence, evaluate differing perspectives, and synthesize information to form a coherent argument or conclusion. This process strengthens analytical abilities and cultivates an inquisitive mindset, both of which are invaluable in a broad range of contexts.
Communication Skills: Research writing is also a powerful tool for honing communication skills. A well-written research paper clearly and persuasively communicates complex ideas, making them accessible to a range of audiences. This skill is critical in academic settings, professional careers, and public discourse.
Career Development: For many professions, particularly in academia, research writing is a critical part of career progression. Publication of research papers in peer-reviewed journals is often a requirement for academic promotion, professional recognition, and grants. It can also establish the researcher’s reputation as a leading expert in their field.
Informed Decision-Making: In a broader societal context, research writing plays a pivotal role in informing policy decisions, business strategies, and social interventions. Policymakers, business leaders, and social workers rely on robust research to understand complex issues, predict outcomes, and make decisions that can have far-reaching impacts.
Record of Human Progress: Lastly, every piece of research writing contributes to the historical record of human knowledge and progress. The cumulative effect of these research outputs shapes our collective understanding of the world and helps drive future discoveries and innovations.
Types of Research Papers
Research papers can come in a variety of forms, each with its unique characteristics, purpose, and writing style. Understanding the different types of research papers can help you identify the most suitable format for your research and guide the structure of your paper.
Analytical Research Paper
This type of paper requires the author to gather relevant information on a topic from various sources. The goal here is not to persuade but to provide a well-rounded exploration of the topic. Analytical papers require the researcher to evaluate the information, draw conclusions, and present the findings in a systematic and unbiased manner.
Argumentative (or Persuasive) Research Paper
These papers aim to persuade the reader towards the author’s point of view by using evidence and logic. The researcher posits a thesis statement, then builds an argument to support it, leveraging scholarly evidence. These papers require a well-articulated stance on a contentious issue, followed by a rigorous defense of the chosen position.
Definition Research Paper
This paper focuses on defining a complex term or concept. A definition paper goes beyond dictionary meanings to present in-depth interpretations and possible controversies related to the term. It often explores historical evolution, differing perceptions, and practical implications of the defined term or concept.
Compare and Contrast Research Paper
This type requires the author to take two or more subjects and analyze their similarities and differences. Such papers demand a comprehensive understanding of the subjects at hand and can range from simple topics to complex theories.
Cause and Effect Research Paper
These papers explore the cause of a particular event or phenomenon and its effects. They require a thorough understanding of the subject, as well as strong analytical skills to identify and discuss causality and impact.
Experimental Research Paper
Often used in the natural and social sciences, this type involves conducting experiments or surveys and reporting the results. The researcher designs an experiment, collects and analyzes data, and then presents the findings, along with interpretations and conclusions.
Survey Research Paper
This paper uses data from surveys to provide insights into behaviors, opinions, or attitudes. The researcher designs and administers a survey, then uses statistical analysis to interpret the data and draw conclusions.
Interpretive Research Paper
This type of research paper is common in the humanities, where the researcher uses a theoretical framework to interpret a cultural or literary phenomenon. The author uses their subjective judgment and analytical skills to present a unique perspective or interpretation.
Report Paper
This type of paper involves reporting on an event, a circumstance, a book, or a movie, including details about the event and analysis. The author may also offer a personal interpretation or suggest a potential course of action.
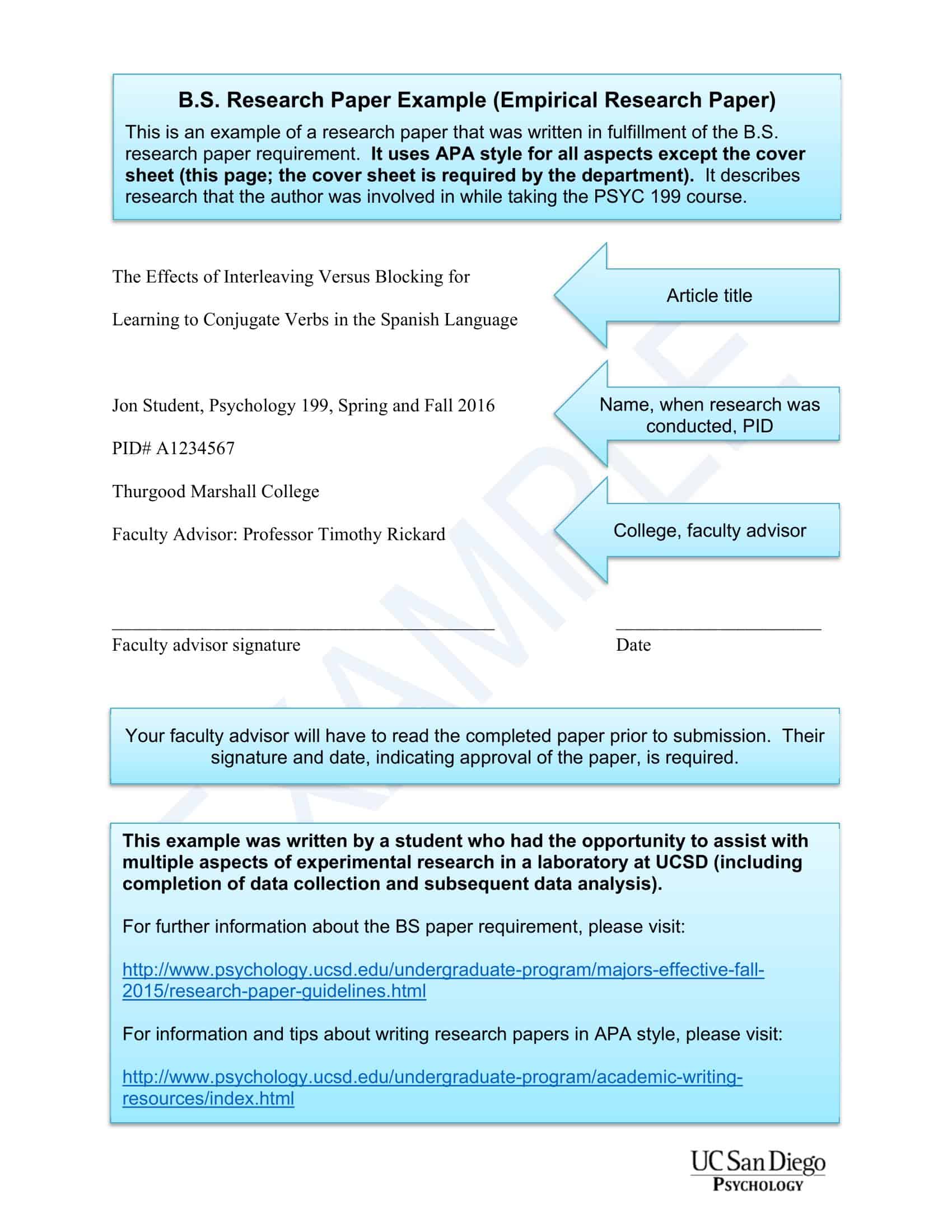
Parts of a Research Paper
A research paper typically comprises several critical sections, each with its unique purpose and requirements. The general format can slightly vary depending on the academic discipline, the nature of the research, or the specific guidelines of a journal or a conference. Here are the standard parts of a research paper:
Title
The title should be concise yet informative, indicating the main topic and the nature of the research. An effective title attracts the reader’s attention and gives them a clear idea of the paper’s content.
Abstract
The abstract is a brief summary of the research, typically about 150-250 words. It provides an overview of the research question, methods, key findings, and implications. The abstract should be self-contained, clear, and concise, as it’s often used by readers to decide whether to read the full paper.
Introduction
The introduction lays the foundation for the research. It outlines the research problem, provides background information, explains the relevance of the study, and introduces the research question or hypothesis. The introduction often ends with a thesis statement, which articulates the paper’s main argument or objective.
Literature Review
This section situates the research within the context of existing literature. It involves a critical review of relevant studies, theories, or models, demonstrating the gaps or contradictions that the current research aims to address. A good literature review not only summarizes previous works but also provides a synthesis that guides the direction of the new research.
Methodology
The methodology section explains how the research was conducted. It describes the research design, data collection methods, participants, materials, procedures, and any statistical techniques used for data analysis. This section should provide enough detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
Results or Findings
This section presents the findings of the research. Depending on the nature of the research, it may involve descriptive statistics, analytical narratives, tables, graphs, or other visual aids. The results should be presented in a logical, clear, and precise manner without interpreting their meaning or implications.
Discussion or Analysis
This part interprets the results in light of the research question or hypothesis. The researcher explains the implications of the findings, explores possible explanations, addresses any unexpected results, and relates the findings back to the literature review. This section might also acknowledge the study’s limitations and suggest avenues for future research.
Conclusion
The conclusion synthesizes the key findings, reaffirms the thesis statement, and highlights the study’s significance. It might also provide recommendations for practical applications, policy changes, or future research.
References or Bibliography
The references section lists the details of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style (like APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.). It allows readers to find the original sources and helps maintain academic integrity by giving credit to the authors whose works have been referred to in the research.
Appendices (if necessary)
An appendix includes any supplementary material that is not integral to the main text but still relevant, such as raw data, detailed methodologies, interview transcripts, or additional graphs and charts.
How long should a research paper be?
The length of a research paper can significantly vary depending on several factors such as the nature of the topic, depth of the research, academic level, and specific guidelines of the course, professor, or the publishing journal. Here are some general guidelines:
High School
A high school research paper typically ranges from 5 to 20 pages.
Undergraduate Level
In college, research papers often fall in the range of 10-30 pages. Certain extensive research projects like senior theses or capstone projects can be much longer, up to 40-60 pages or more.
Graduate Level
Master’s theses usually range from 40-80 pages (excluding bibliography), while doctoral dissertations can be several hundred pages long.
Journal Articles
The length of research papers intended for publication in academic journals can vary widely based on the field of study and the specific journal. However, they typically range from about 3,000 to 10,000 words.
How to write a research paper
Writing a research paper is a complex task involving numerous steps, from preliminary brainstorming to final proofreading. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process:
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before you start, it’s essential to fully understand what is required. If you’re writing a research paper for a class, make sure you understand the assignment prompt and grading criteria. You might need to consider the required length, deadline, format, number of sources, and any specific topics or questions you need to address.
Example: Let’s say your professor assigns a 10-page research paper on the topic of climate change due in a month, using at least 10 scholarly sources. You should clarify whether there are any specific aspects of climate change that you should focus on, what citation style to use, and whether there are any specific formatting requirements.
Step 2: Choose a Topic
Based on your understanding of the assignment, choose a topic that interests you and fits within the given guidelines. A good topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow and should be complex enough to warrant a full research paper.
Example: Given the broad topic of climate change, you might choose to focus on “The Impact of Climate Change on Coral Reefs.”
Step 3: Conduct Preliminary Research
Before you formulate your research question or thesis statement, do some preliminary research to familiarize yourself with the topic. This can help you identify important subtopics, questions, debates, or theories related to your topic.
Example: In your preliminary research on the impact of climate change on coral reefs, you might read scholarly articles, books, reports, or reputable websites to get a general idea of the main threats, the regions most affected, and the potential consequences for marine life and human societies.
Step 4: Develop Your Research Question or Thesis Statement
Based on your preliminary research, develop a research question that your paper will answer, or a thesis statement that your paper will argue. This should be specific, focused, and debatable.
Example: You might develop the research question: “How does climate change impact the biodiversity of coral reefs in the Great Barrier Reef?” Or the thesis statement: “Climate change, through warming ocean temperatures and ocean acidification, is causing significant biodiversity loss in the Great Barrier Reef.”
Step 5: Create a Research Plan
Next, develop a plan for your research. This should include what kind of sources you will use (books, journal articles, websites, etc.), where you will find these sources (online databases, library, etc.), and how you will keep track of these sources.
Example: You might plan to use academic databases like JSTOR or ScienceDirect to find scholarly articles on your topic, and a reference management tool like Zotero or Mendeley to organize your sources.
Step 6: Conduct In-depth Research
Now, carry out your research based on your plan. As you read, take notes, and record all necessary citation information. Be critical and look for any biases, limitations, or inconsistencies in the sources.
Example: As you research your topic, you might find articles on how rising ocean temperatures and acidification affect different species in the Great Barrier Reef. You would take detailed notes on these findings and record all source information for future citation.
Step 7: Create an Outline
An outline will help structure your paper and ensure you cover all necessary points. It should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should have a main point and supporting evidence.
Example: Your outline might look something like this:
- Introduction
- Brief background on coral reefs and climate change
- Thesis statement
- Body
- Paragraph 1: How climate change leads to warming ocean temperatures
- Paragraph 2: Impact of warming ocean temperatures on coral reefs
- Paragraph 3: How climate change leads to ocean acidification
- Paragraph 4: Impact of ocean acidification on coral reefs
- Paragraph 5: Case study of the Great Barrier Reef
- Conclusion
- Recap of main points
- Implications of findings
Step 8: Write the First Draft
Start writing your paper based on your outline. Begin with a draft and expect to revise it later. Be sure to integrate your sources and cite them properly.
Example: In your first body paragraph, you might explain the scientific processes that cause ocean temperatures to rise due to climate change, citing various sources. You would then go on to discuss how these rising temperatures impact coral reefs.
Step 9: Revise and Edit
After writing your first draft, take some time to revise and edit. Check for any errors, unclear sentences, or weak arguments. Ensure your paper is well-organized and your thesis statement is well-supported.
Example: You might find that some paragraphs don’t support your thesis as well as they could. You might need to find additional sources, add more analysis, or clarify your explanations.
Step 10: Proofread
Finally, proofread your paper for any spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors. Double-check your citations and references to ensure they are accurate and correctly formatted.
Example: You might use a tool like Grammarly to check for any grammatical errors and manually check that all in-text citations match the references in your bibliography.
Writing a research paper is a time-consuming process that requires careful planning, diligent research, and meticulous writing and editing. However, by breaking it down into manageable steps, you can tackle this task with confidence and create a high-quality research paper.
Research Paper Topics
Finding the right research paper topic can be quite a challenging yet exciting task. It’s akin to embarking on a quest for knowledge, where the topic serves as the compass guiding the research process. A well-chosen topic can inspire a profound investigation and lead to valuable discoveries, while an ill-chosen one can make the research process tedious and unproductive. It’s crucial to choose a topic that aligns with your interests, is relevant to your field of study, and is complex enough to warrant a detailed examination. Additionally, an ideal research paper topic is not only engaging but also novel, adding a fresh perspective to existing literature. Here are 50 diverse research paper topics spanning a variety of disciplines and areas of interest:
- The Impact of Climate Change on Global Public Health.
- Artificial Intelligence and its Influence on Job Markets.
- The Role of Social Media in Modern Political Movements.
- The Effects of Veganism on Human Health and the Environment.
- The Future of Cryptocurrencies in the Global Economy.
- The Psychological Impact of Long-term Remote Work.
- The Role of Microplastics in Marine Ecosystem Disruption.
- Mental Health Stigma in the Workplace.
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare.
- The Influence of Climate Change on Migration Patterns.
- Cybersecurity Threats in the Age of the Internet of Things (IoT).
- The Effects of Parenting Styles on Child Development.
- The Role of Gut Microbiome in Human Health.
- The Ethical Implications of Genetic Editing Technologies.
- The Impacts of Sustainable Farming on Food Security.
- Representation of Minorities in Popular Media.
- The Influence of Yoga on Stress Management.
- The Pros and Cons of Renewable Energy Sources.
- The Effects of Bilingualism on Cognitive Development.
- The Role of the Internet in Shaping Modern Society.
- The Ethical Considerations of Animal Testing.
- The Impact of Fast Fashion on the Environment.
- Understanding the Gender Wage Gap.
- The Impacts of School Bullying on Child Mental Health.
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Productivity.
- The Evolution of Feminism.
- The Role of Augmented Reality in Education.
- The Relationship between Gun Control Policies and Gun Violence Rates.
- The Impact of Artificial Sweeteners on Human Health.
- Privacy Concerns in the Age of Big Data.
- The Effects of Meditation on Mental Well-being.
- Exploring the Causes of Teenage Suicide.
- The Role of Video Games in Cognitive Development.
- The Impact of Organic Farming on Crop Yield.
- The Relationship between Poverty and Education.
- The Influence of Music on Mood and Performance.
- The Effects of Climate Change on Global Food Production.
- The Role of Vaccination in Preventing Disease Outbreaks.
- The Impact of Autonomous Vehicles on Traffic Safety.
- The Role of Drones in Modern Warfare.
- The Effects of Screen Time on Child Development.
- The Impact of Deforestation on Biodiversity.
- The Influence of Advertising on Consumer Behavior.
- The Role of Microfinance in Poverty Reduction.
- The Ethical Dilemmas of Euthanasia.
- The Impact of Single-Use Plastics on Ocean Life.
- The Influence of Celebrity Culture on Youth.
- The Role of Probiotics in Digestive Health.
- The Impact of Space Exploration on Technological Advancements.
- The Role of Social Media in Shaping Public Opinion.
FAQs
How do I choose a topic for my research paper?
When selecting a topic for your research paper, consider your interests, the requirements of your assignment, and the available resources. Look for a topic that is specific enough to be manageable but broad enough to have relevant literature and information available.
How do I conduct research for my paper?
To conduct research for your paper, start by defining your research question or objective. Then, gather relevant information from various sources such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and databases. Take notes, organize your findings, and critically evaluate the information to ensure its credibility and relevance to your study.
How do I revise and edit my research paper?
During the revision process, read your paper critically to identify and correct any errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Ensure the logical flow of ideas and coherence between sections. Review the clarity of your writing and make sure that your arguments are supported by evidence. Consider seeking feedback from peers or professors to gain different perspectives on your work.
How many references should I include in my research paper?
The number of references in a research paper can vary depending on the topic, depth of research, and specific requirements. As a general guideline, aim to include enough references to support your arguments and provide a comprehensive overview of the existing literature on the topic. However, the emphasis should be on quality rather than quantity. Ensure that the references you include are relevant, recent, and from reputable sources.
Can I include personal opinions or experiences in a research paper?
Research papers are primarily focused on presenting evidence-based findings and objective analysis rather than personal opinions or experiences. While some fields, such as social sciences or humanities, may allow for some degree of subjective interpretation, it’s important to maintain a balanced and evidence-based approach in your research paper. Personal opinions or experiences should be clearly identified as such and appropriately contextualized within the broader scholarly discussion.
What is the difference between a research paper and a review paper?
A research paper presents original research conducted by the author(s), including the methodology, findings, and analysis. It contributes new knowledge or insights to a specific field. On the other hand, a review paper summarizes and evaluates existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps or controversies, and may suggest avenues for future research.
Can I publish my research paper if it has already been presented at a conference?
In many cases, presenting your research at a conference does not preclude you from publishing it in a journal. However, it’s important to check the policies of the journal you intend to submit to, as some journals may have specific guidelines regarding previously presented or published work. Additionally, if you plan to publish your research, it’s good practice to expand and enhance the conference presentation into a full-length research paper.
How long does it take to publish a research paper?
The time it takes to publish a research paper can vary significantly. The process typically involves several stages, including submission, peer review, revisions, and final acceptance. The duration of each stage can depend on factors such as the journal’s review process, the responsiveness of reviewers, and the complexity of revisions required. On average, the publication process can take several months to over a year.
How can I increase the chances of getting my research paper accepted?
To increase the likelihood of your research paper being accepted for publication, it’s important to ensure that your study is rigorous, well-designed, and addresses a significant research question. Adhere to the guidelines and formatting requirements of the target journal. Revise your paper based on feedback from colleagues or reviewers. Finally, choose a journal that aligns well with the scope and focus of your research.
Can I include figures, tables, or graphs in my research paper?
Yes, including visual elements such as figures, tables, or graphs can enhance the presentation and understanding of your research findings. Ensure that they are properly labeled, referenced, and relevant to your discussion. Follow the formatting guidelines of the target journal for the placement and formatting of visual elements.
Should I include an abstract in my research paper?
Including an abstract is common practice in research papers. The abstract provides a concise summary of your research, including the research question, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. It helps readers quickly understand the main points of your paper and decide whether to read it in detail. Check the guidelines of the journal you’re submitting to for specific requirements regarding the length and format of the abstract.
Can I collaborate with others on a research paper?
Collaboration on research papers is common and often encouraged. Working with colleagues or experts in the field can provide diverse perspectives, enhance the quality of research, and increase the likelihood of publication. However, it’s important to appropriately acknowledge and credit all contributors, and ensure that the division of work and responsibilities is clear from the outset.















































![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Lined Paper Templates [Word, PDF] +Editable 2 Lined Paper](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Lined-Paper-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Lined-Paper-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 3 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
