Project management plays a crucial role in ensuring the successful execution of complex tasks. One of the key concepts in project management is the critical path, which helps identify the activities that must be completed on time to ensure the timely completion of the entire project. Today, we will explore the importance of the critical path method and provide a comprehensive guide on how to create and utilize a critical path template for efficient project management.
Table of Contents
What is a critical path?

The critical path is the longest sequence of project activities that determines the shortest possible duration for completing the project. It represents the sequence of activities that must be completed on time to prevent any delay in the project’s overall timeline. In simple terms, the critical path is the backbone of any project, as it identifies the tasks that cannot be delayed without impacting the project’s completion date.
So, what is the importance of the critical path in project management? By identifying the activities on the critical path, project managers can prioritize their efforts and allocate resources effectively. It allows them to focus on the tasks that have the greatest impact on the project’s completion date and ensure that these tasks are executed efficiently.
Critical Path Templates
The critical path provides project managers with valuable insights into the project’s timeline and helps them set realistic deadlines for each task. By understanding the critical path, project managers can mitigate risks, make informed decisions, and allocate resources strategically to ensure the project’s success.
Moreover, the critical path also aids in identifying potential bottlenecks and areas of concern. By analyzing the critical path, project managers can identify tasks that have little or no flexibility in their completion time. These tasks are known as “critical tasks” and require close monitoring and attention to ensure they are completed on time.
Furthermore, the critical path allows project managers to identify opportunities for optimization and efficiency. By focusing on the tasks that are on the critical path, project managers can identify areas where resources can be allocated more effectively, reducing unnecessary delays and improving overall project performance.
The Basic Elements of a Critical Path

To comprehend the critical path, it is important to understand its basic elements:
- Tasks: These are the individual activities required to complete the project. Each task has a unique identifier, such as a task name or number.
- Dependencies: Dependencies represent the relationships between tasks. Some tasks may be dependent on the completion of others, so their sequence is crucial.
- Duration: The duration of each task indicates the amount of time required to complete it. It is usually estimated based on historical data or expert judgment.
Understanding these elements is essential for accurately identifying and analyzing the critical path. By considering the tasks, dependencies, and duration, project managers can effectively plan and execute projects, ensuring timely completion and successful outcomes.
A well-designed critical path template is crucial for effective project management, acting as a beacon for project teams. It visually represents the project’s tasks, dependencies, and timeline, offering a comprehensive overview of the project’s scope and goals. This foundation enables all involved parties to fully grasp their roles and the project’s objectives.
Task List: The Foundation of the Critical Path Template
Overview of the Task List
The Task List section is the cornerstone of the critical path template. It enumerates all tasks necessary to complete the project, with each task assigned a unique identifier and described briefly. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that every task is accounted for and accurately assessed, preventing any oversight or underestimation.
Importance of Detailed Task Listing
By providing a detailed list of tasks, project teams gain a thorough understanding of the project’s requirements. This clarity is essential for the seamless execution of each task, ensuring that the project progresses without any hitches.
Dependencies: The Core of Task Sequencing
Identifying Task Relationships
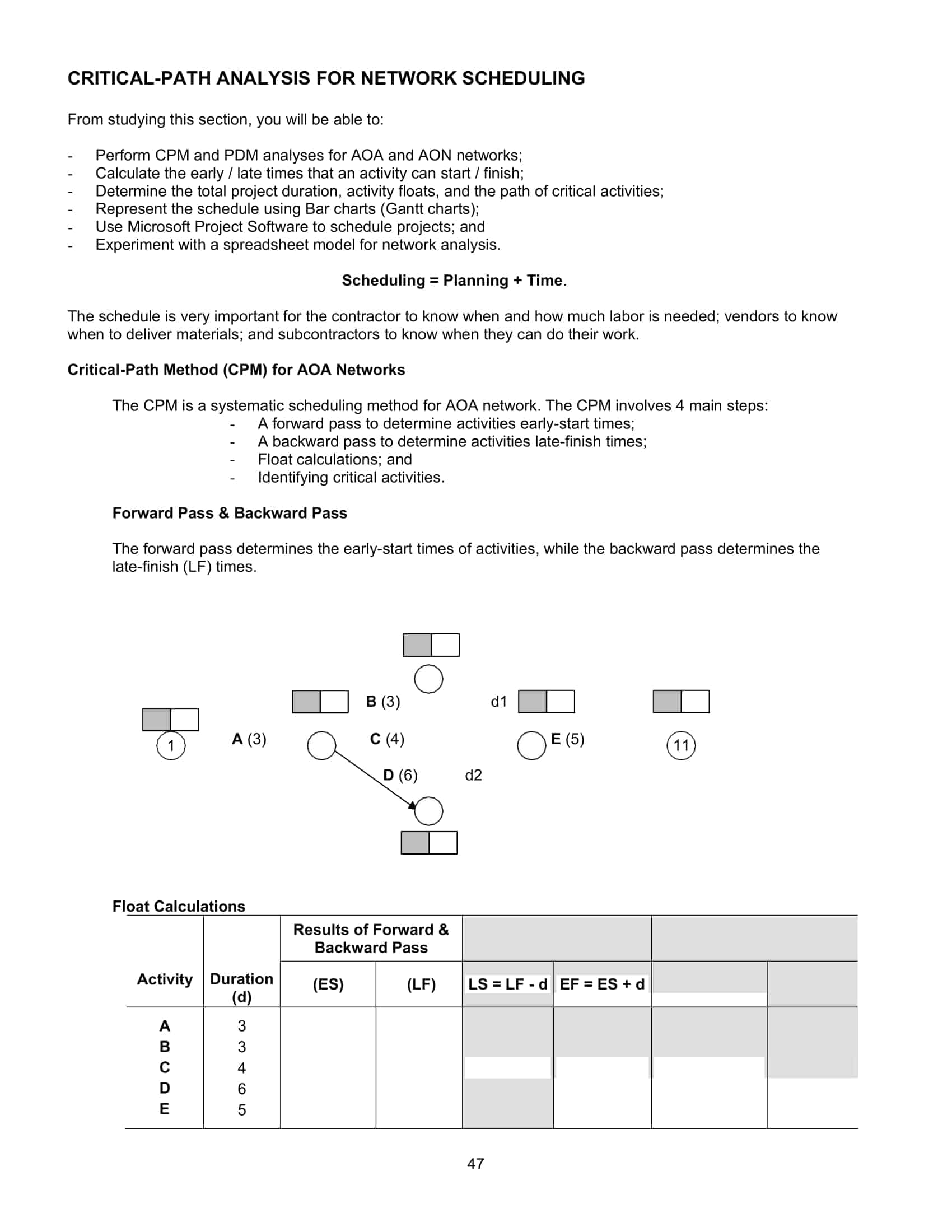
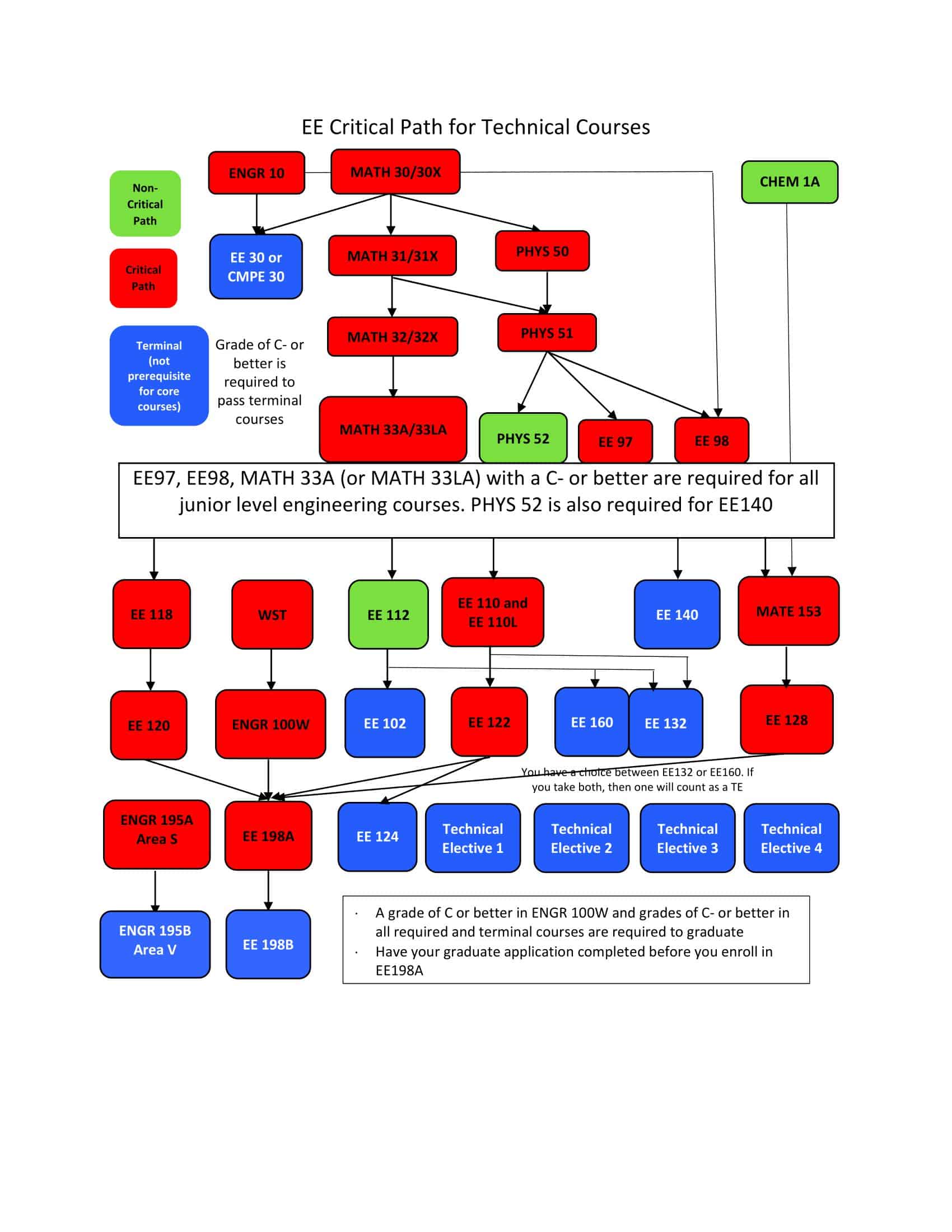
The Dependencies section illuminates the relationships between tasks, specifying predecessors and successors. This critical analysis allows for the determination of task sequencing, which is essential for understanding the project’s critical path—the longest sequence of dependent tasks that dictates the project’s duration.
The Role of Dependencies in Project Management
Recognizing these dependencies is vital for prioritizing tasks, especially those on the critical path. Concentrating on these tasks ensures the project remains on schedule, highlighting the importance of this section in the overall project management process.
Duration: Estimating Task Timelines
Estimation of Task Durations
The Duration section specifies the estimated time required for each task, a crucial factor in resource allocation and scheduling. Understanding the duration of tasks enables project managers to efficiently plan and deploy resources, ensuring tasks are completed within their allocated timeframes.
Managing Time and Resources
A clear grasp of task durations helps in avoiding delays and bottlenecks, enabling a more streamlined project flow. This knowledge is indispensable for effective time and resource management within the project.
The Symphony of a Comprehensive Critical Path Template
A comprehensive critical path template orchestrates project management like a finely tuned symphony, with each component—Task List, Dependencies, and Duration—playing a critical role in the project’s success. Utilizing such a template empowers project teams to navigate project complexities with confidence and precision. Remember, a robust critical path template is key to unfolding your project seamlessly.
FAQs
How do you write a critical path?
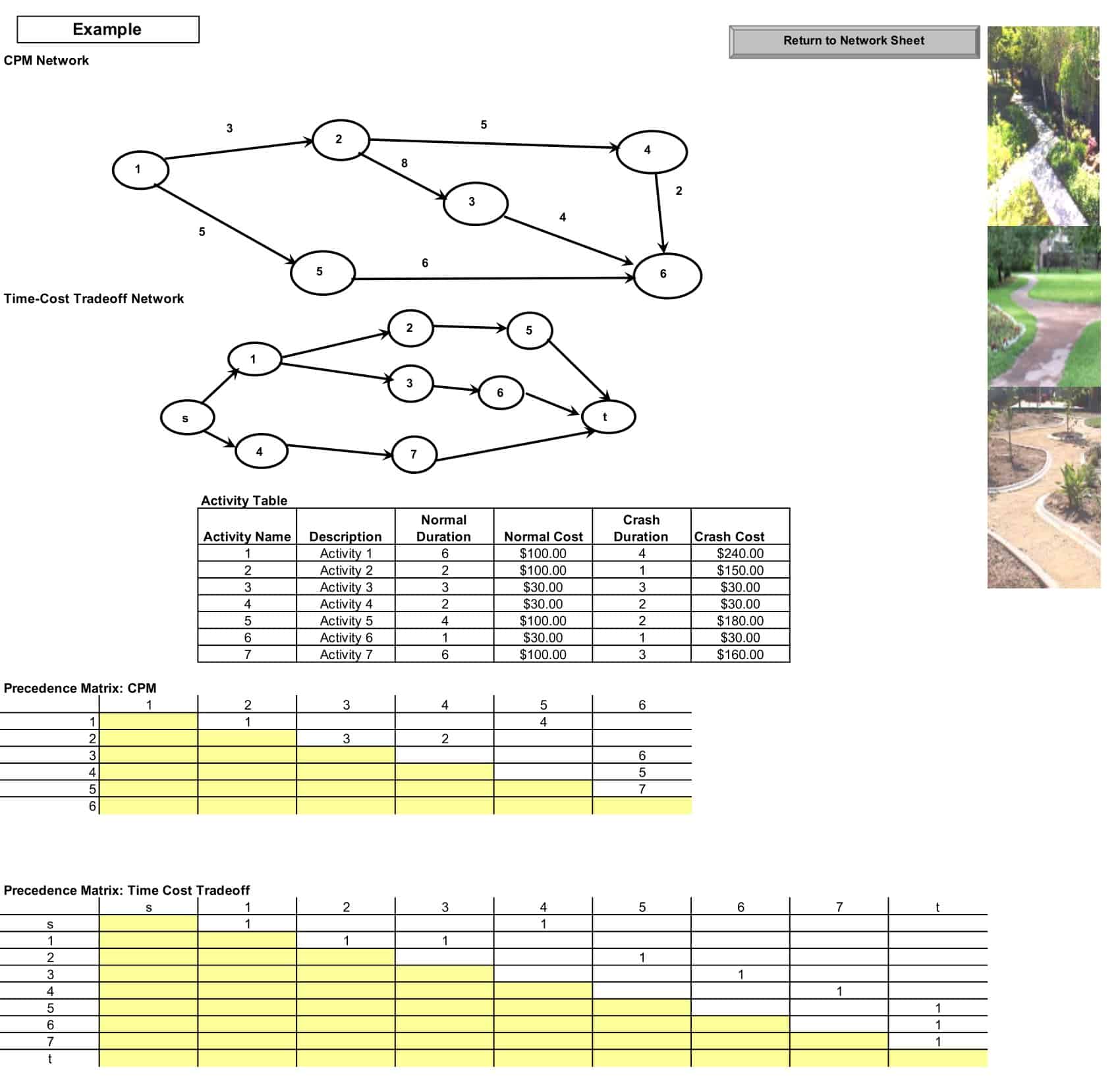
To write a critical path, list all activities in a project. Determine dependencies and the sequence of tasks. Calculate each task’s duration. Identify the longest path of dependent activities that directly impacts the project finish date. Highlight this as the critical path.
Does Excel have a critical path template?
Yes, Excel has downloadable critical path analysis templates. They include pre-formatted columns to enter tasks, durations, dependencies, and will auto-calculate the critical path.
What is the critical path format?
The critical path format displays project tasks in a table with columns for activity name, dependencies, duration estimate, early/late start and finish dates. The critical path is shown in bold or highlighted.
What is the difference between a Gantt chart and critical path?
A Gantt chart maps out task timelines visually while the critical path analysis identifies the specific chain of tasks driving the end date. Both require task sequencing but the critical path highlights dependencies.

































![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 2 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 3 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
