Cost-benefit analysis might be the most important financial technique for businesses to follow. Cash flow analysis is also very important for a business. It can help to decide if you should go on with a project or not. The primary aim of this article is to talk about the cost-benefit analysis in detail.
Table of Contents
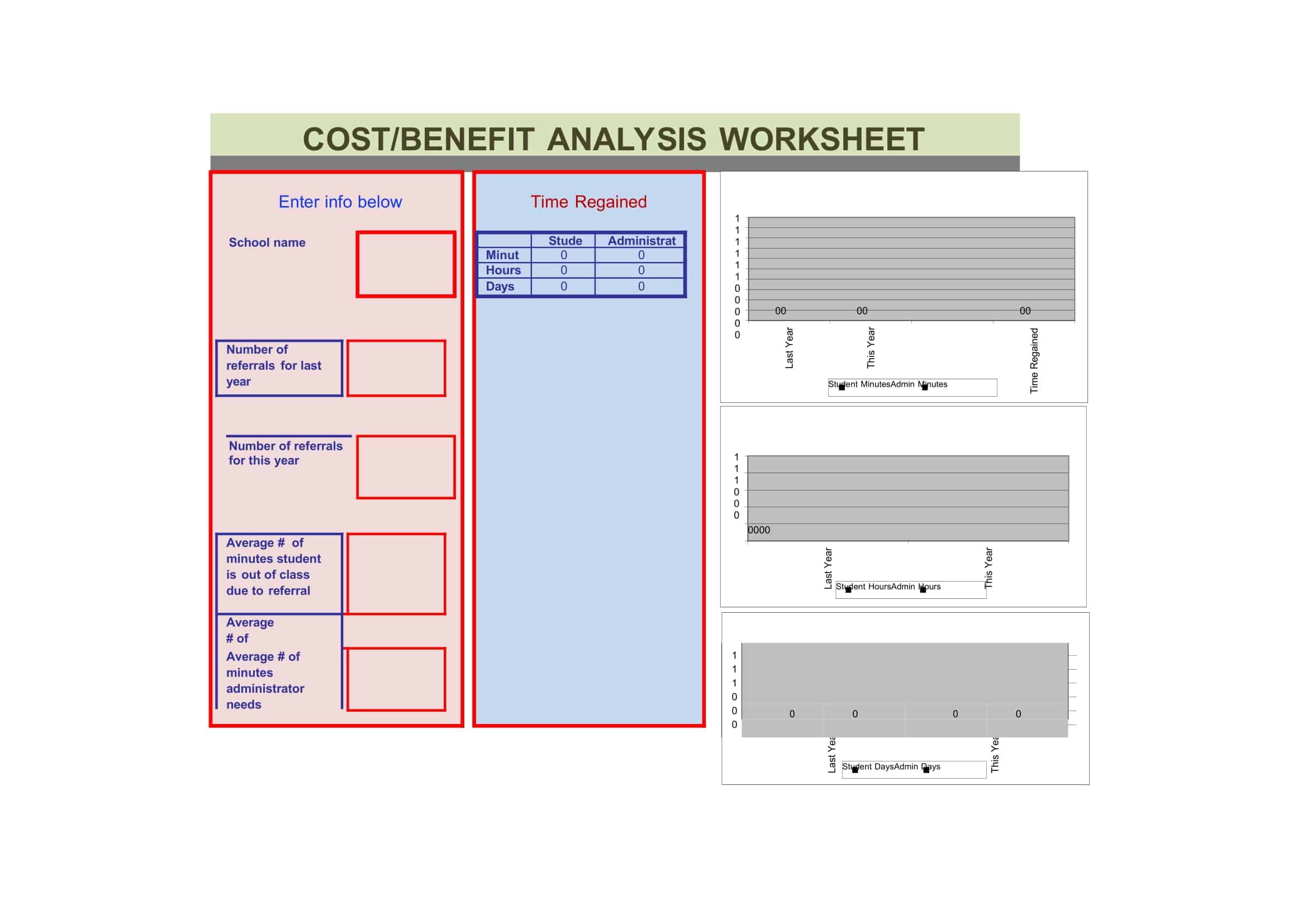
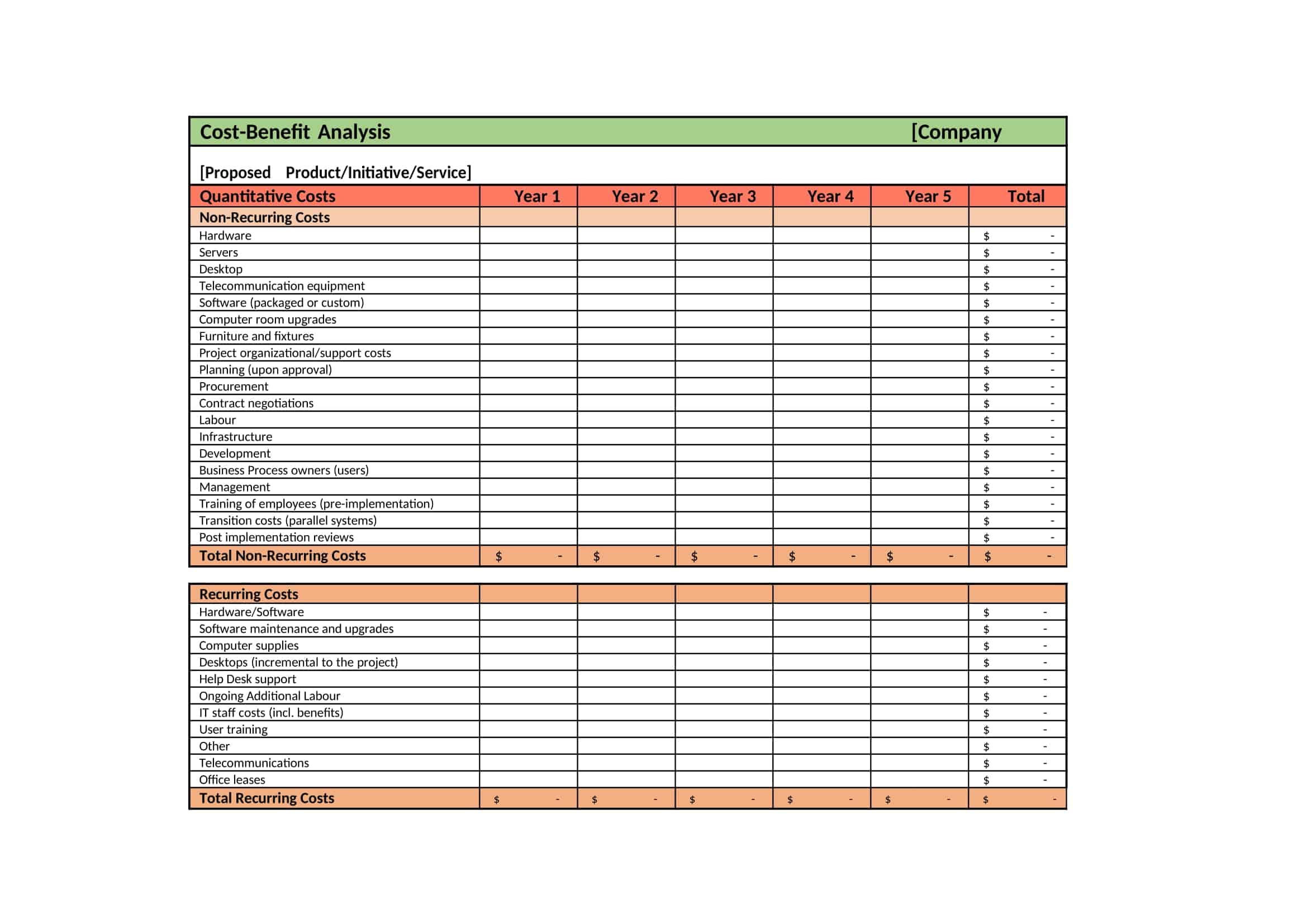
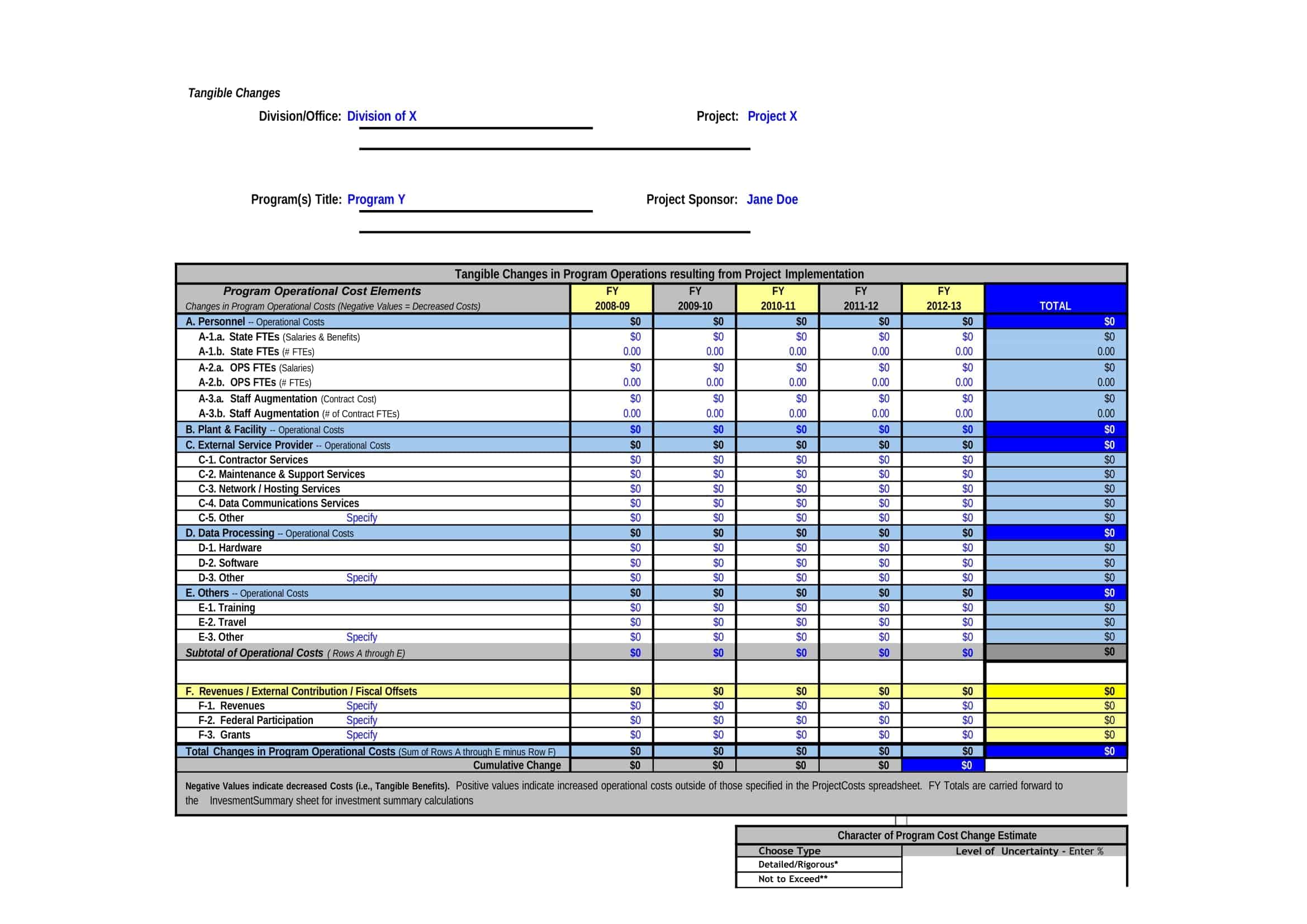
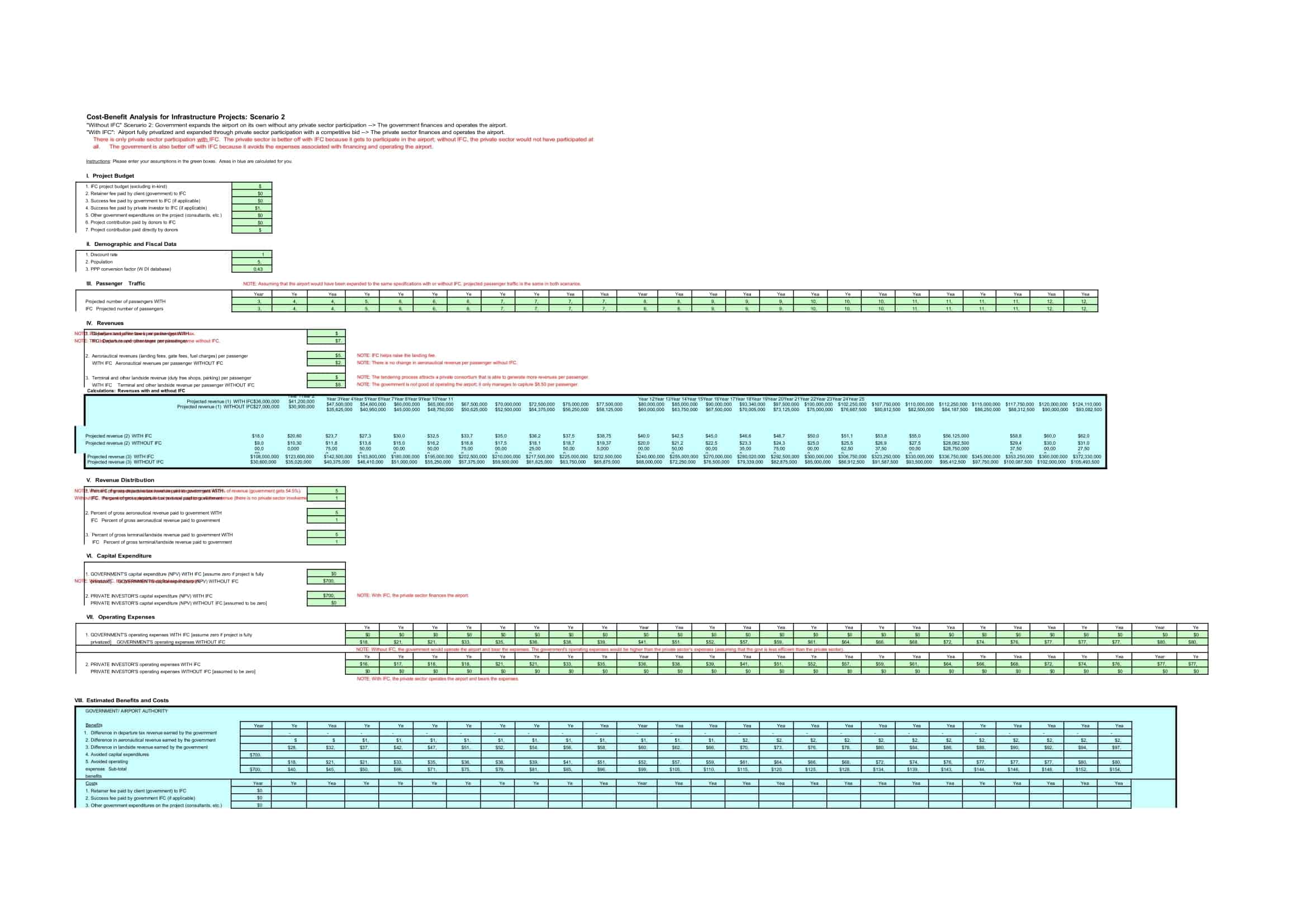
Cost-Benefit Analysis Templates
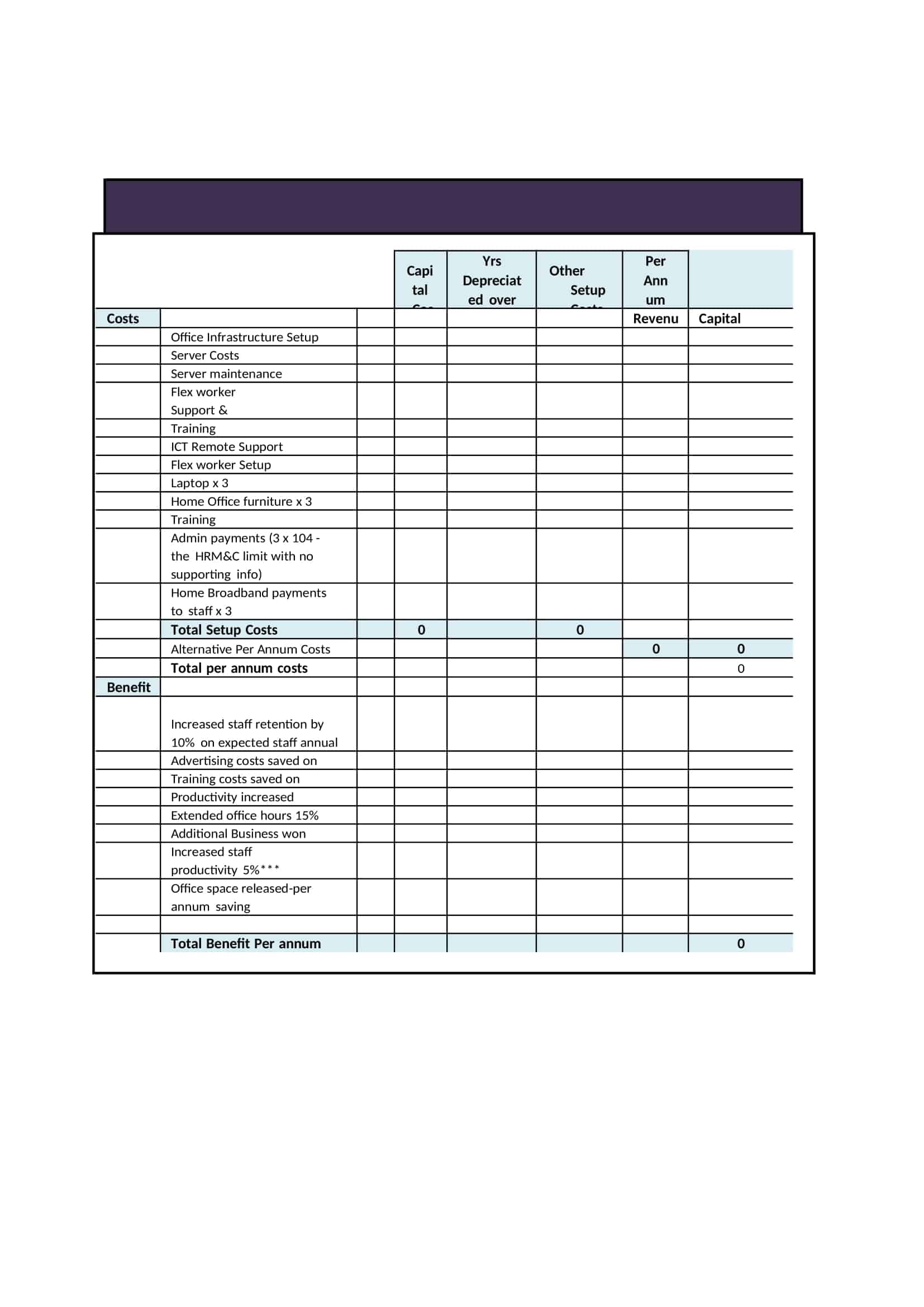
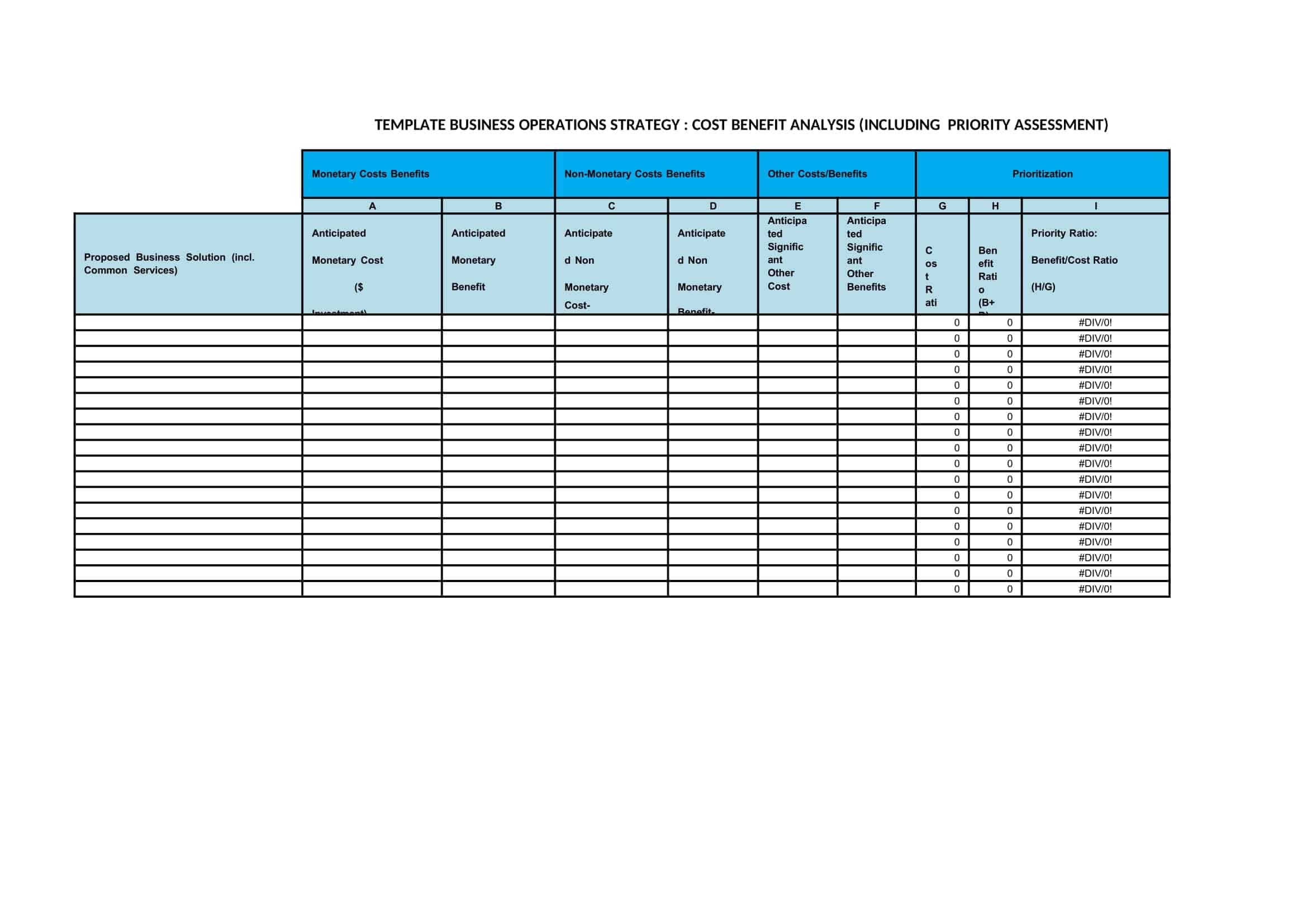
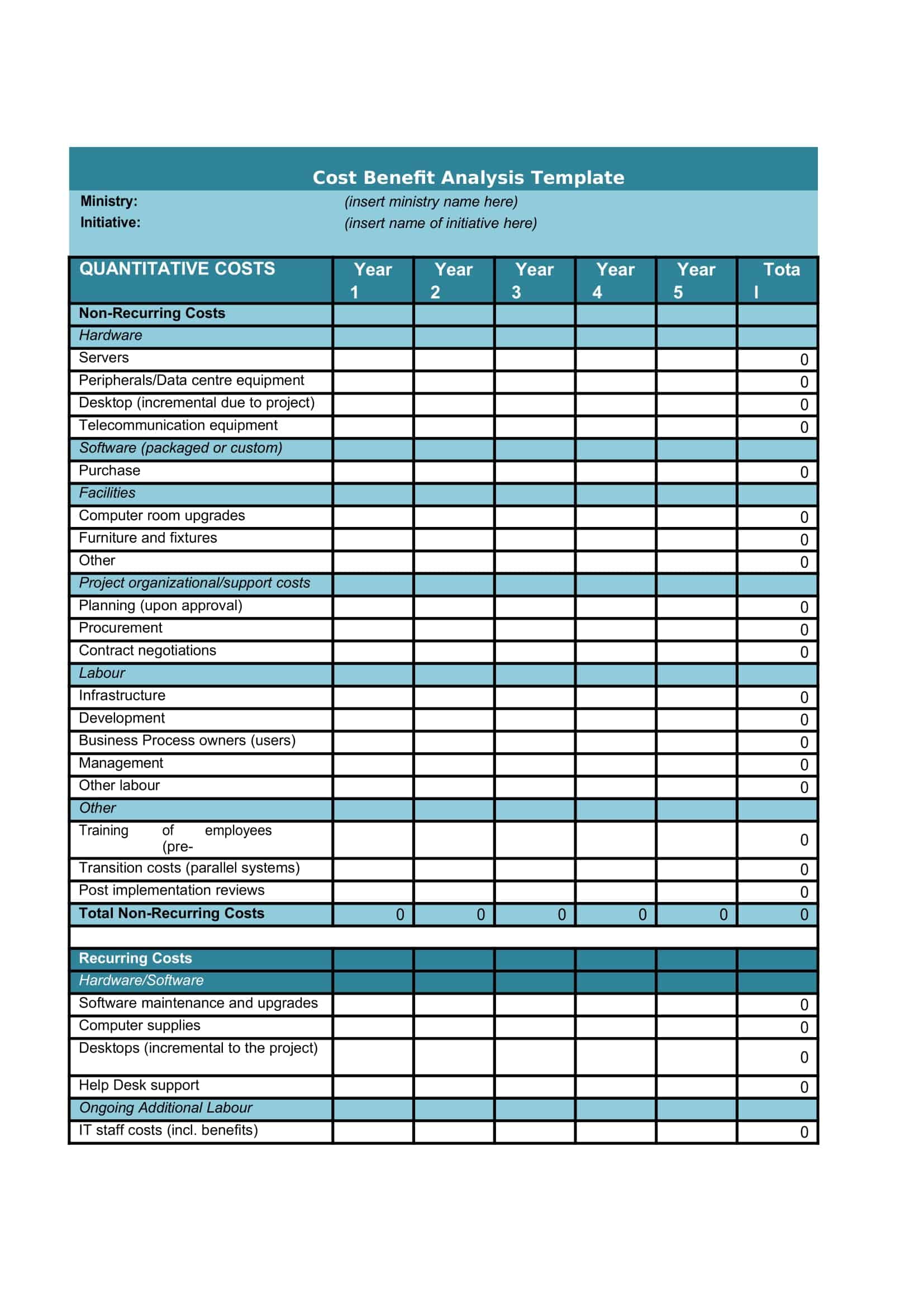
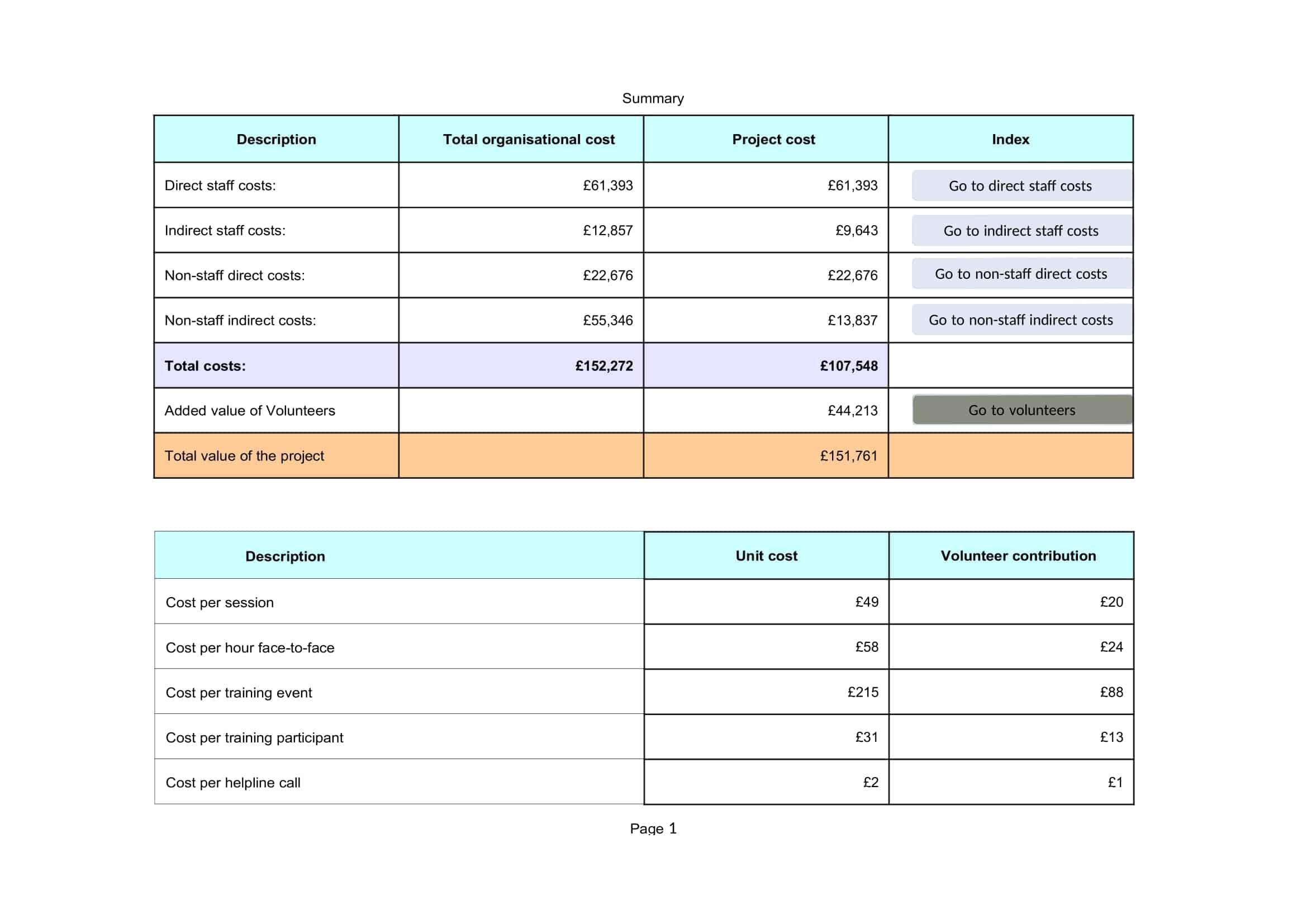
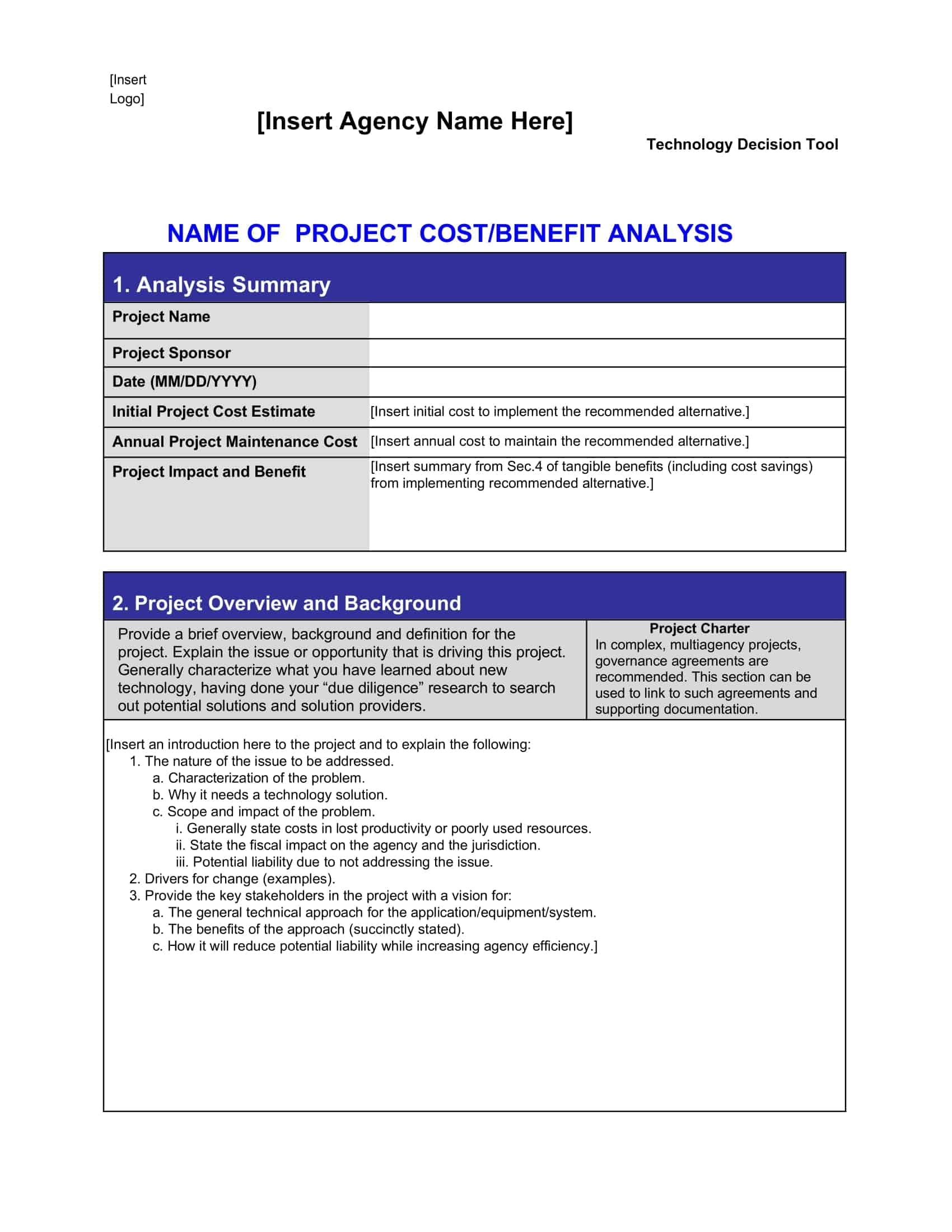
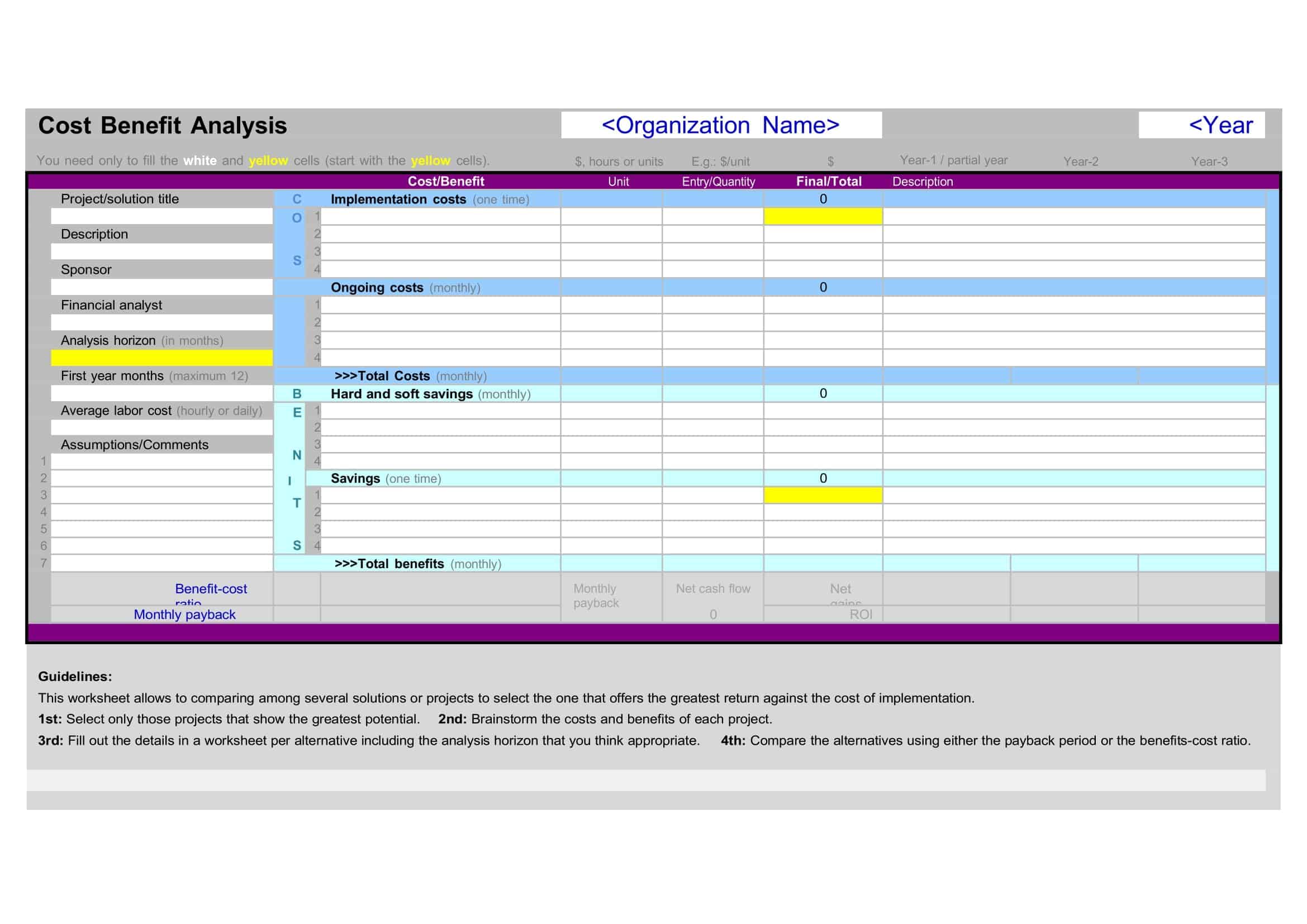
Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) templates are pre-designed documents that provide a structured format for conducting a systematic evaluation of the costs and benefits associated with a project, decision, or investment. These templates offer a convenient and organized way to perform a comprehensive analysis, helping individuals and organizations make informed decisions based on a thorough assessment of the potential costs and benefits.
Cost Benefit Analysis templates typically include sections and fields for capturing relevant information such as project description, cost estimation, benefit identification, monetary valuation, discount rate, and calculation formulas. They provide a framework for listing and quantifying both the financial and non-financial costs and benefits associated with the project or decision.
Using a Cost Benefit Analysis template helps individuals and organizations streamline the process of conducting an analysis by providing a standardized format and guiding the collection and organization of data. The template simplifies the calculation and comparison of costs and benefits, allowing for a more efficient and accurate assessment.
What is Cost-Benefit Analysis?

Benefit-cost analysis is basically an analysis that shows the sum of benefits such as financial gain to be obtained against the costs of a project/product/service to be made by businesses. The technique is often used when trying to decide on investment action. When calculating the activity of the investment, the intangible benefits and the opportunity cost are usually included in the calculations.
Although cost-benefit analysis is used for short-term decisions, it also guides long-term decisions.
Cost-benefit analysis provides the financial projection of a potential project and considers non-financial issues such as indirect benefits or costs such as customer satisfaction and even employee motivation. However, opportunity cost arises when deciding between various options and plays a large role in the analysis.
For example, companies or financial analysts often factor many factors into the calculation when establishing potential benefits and costs, such as labor costs, social benefits, and other uncertain future factors. Cost-benefit analysis is also very similar to the net present value, which investors often use.
The major steps in a cost-benefit analysis
Weigh Future Values Today
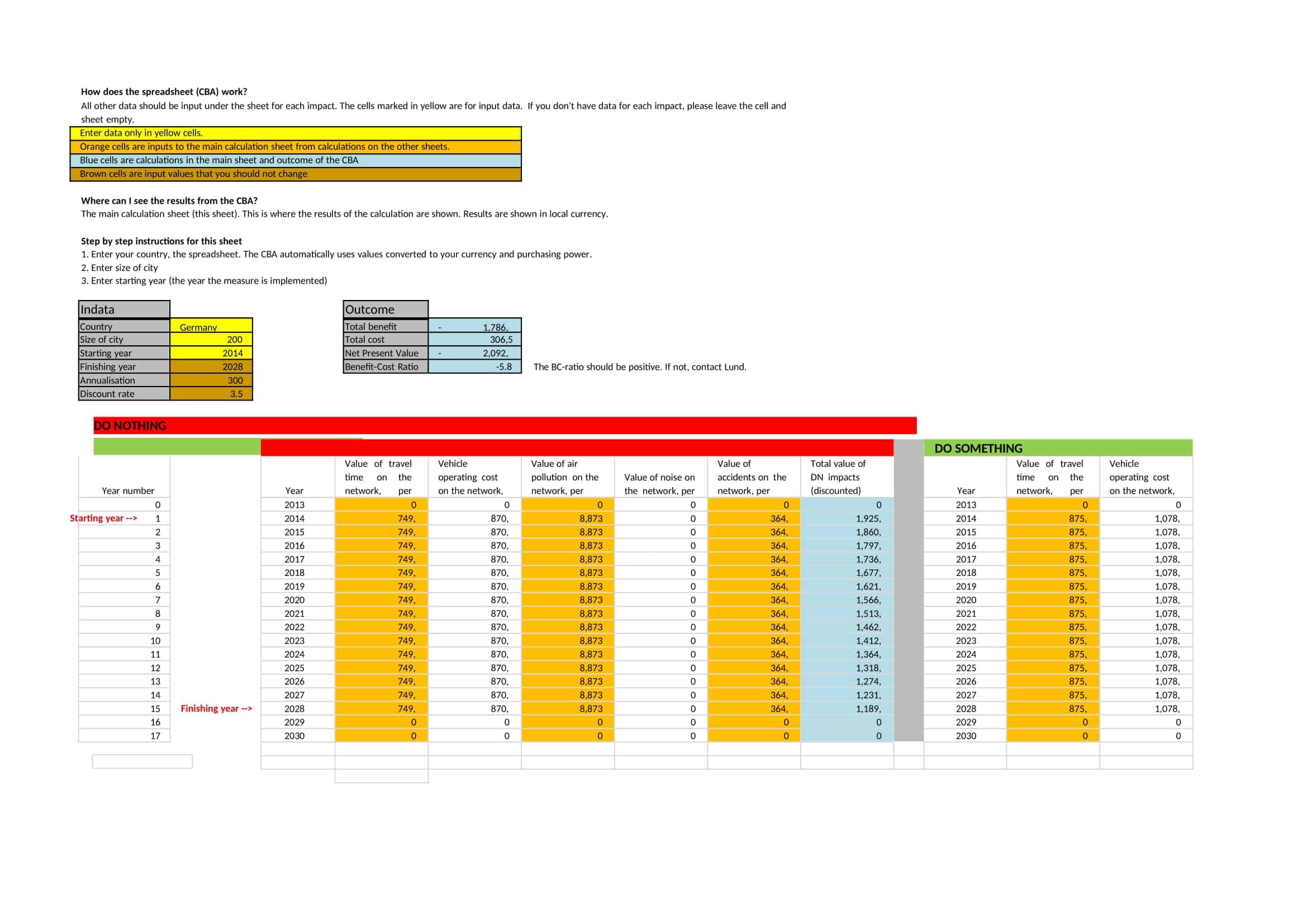
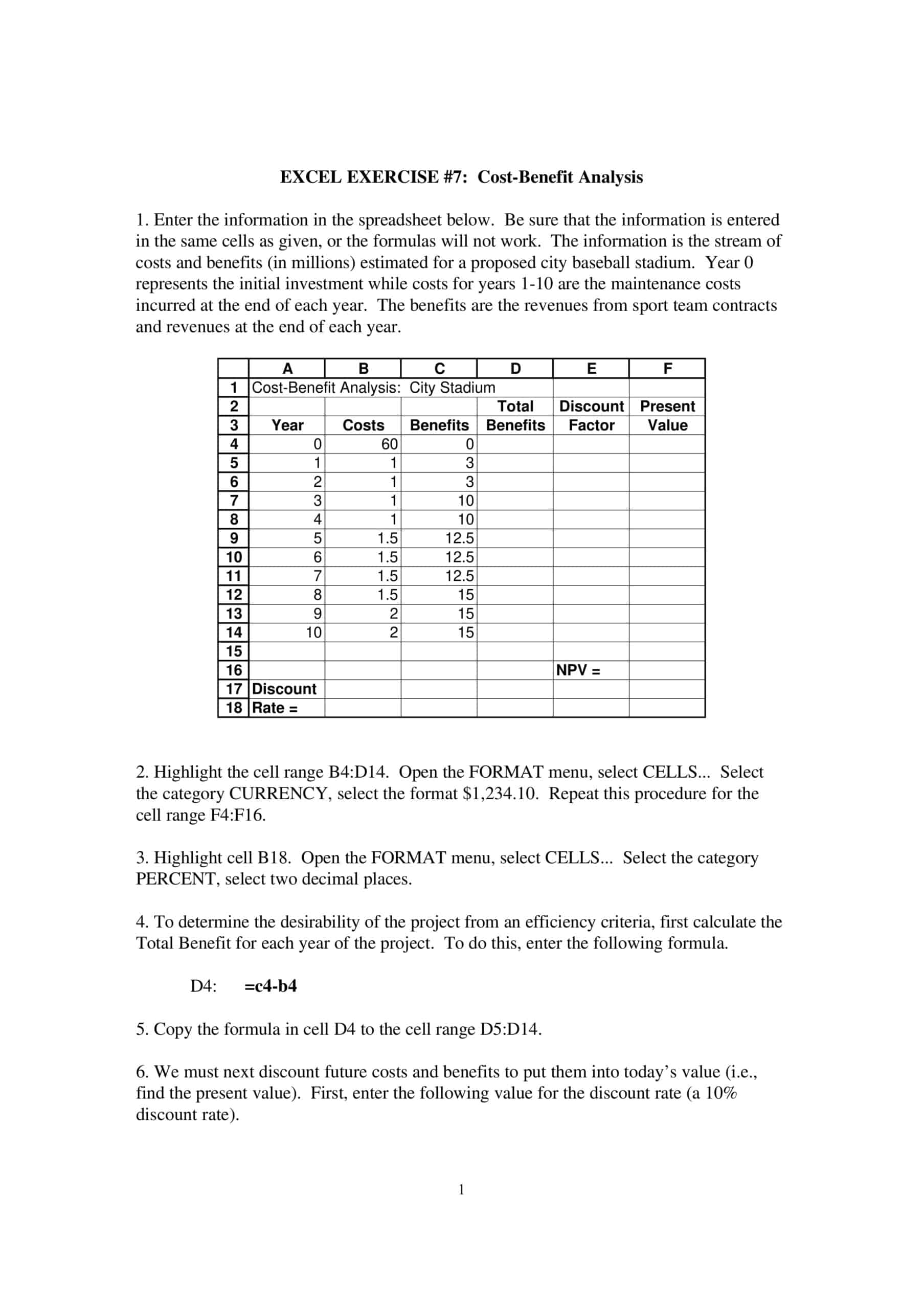
When performing a cost-benefit analysis, it is necessary to evaluate the total future benefits and total costs of a project at its present value. Because cost-benefit analyzes are usually done with a long-term perspective, we consider the net present value of the numbers we analyze when performing cost-benefit analysis because the value of money often changes due to inflation and other factors.
As the name suggests, Net present value is a method used to determine the benefits of investing. Calculates the future benefits or costs of the project in terms of their present value. If the net present value is positive, the action or decision to be taken will usually be a good investment. On the other hand, if it is negative, the opposite is true.
Dollar Value in a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is a process that helps evaluate the cost of a project or activity against its benefits. Cost-benefit analysis is a real-life example of how to determine if something will result in a net gain or loss. Imagine standing in front of two closed doors, one with a $50 bill behind it and the other with a $10 bill behind it. You have to open one door, but you have no idea which one holds the money behind it. The obvious question naturally arises: Why should you bother opening the door with just $10? The answer lies in a cost-benefit analysis.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is a useful tool for evaluating a new project. Using cost-benefit analysis for the feasibility of potential projects helps us see the project’s effects. It is a useful tool for taking action on urgent or medium-sized decisions.
However, there are some disadvantages of cost-benefit analysis in certain situations. When making larger decisions with longer timeframes, sometimes other factors that may not be important in the short term but may affect the long term, such as inflation, interest rates, and other longer-term factors, are not considered. For these calculations, net present value or internal rate of return is generally the better method.
In addition, a cost-benefit analysis evaluates the projects to be decided from a purely numerical perspective. Therefore, it does not consider unseen events or conditions that may affect projects.
How to Make Cost-Benefit Analysis?
The implementation of cost-benefit analysis is quite simple. It helps in decision-making when considering a new investment or strategy process.
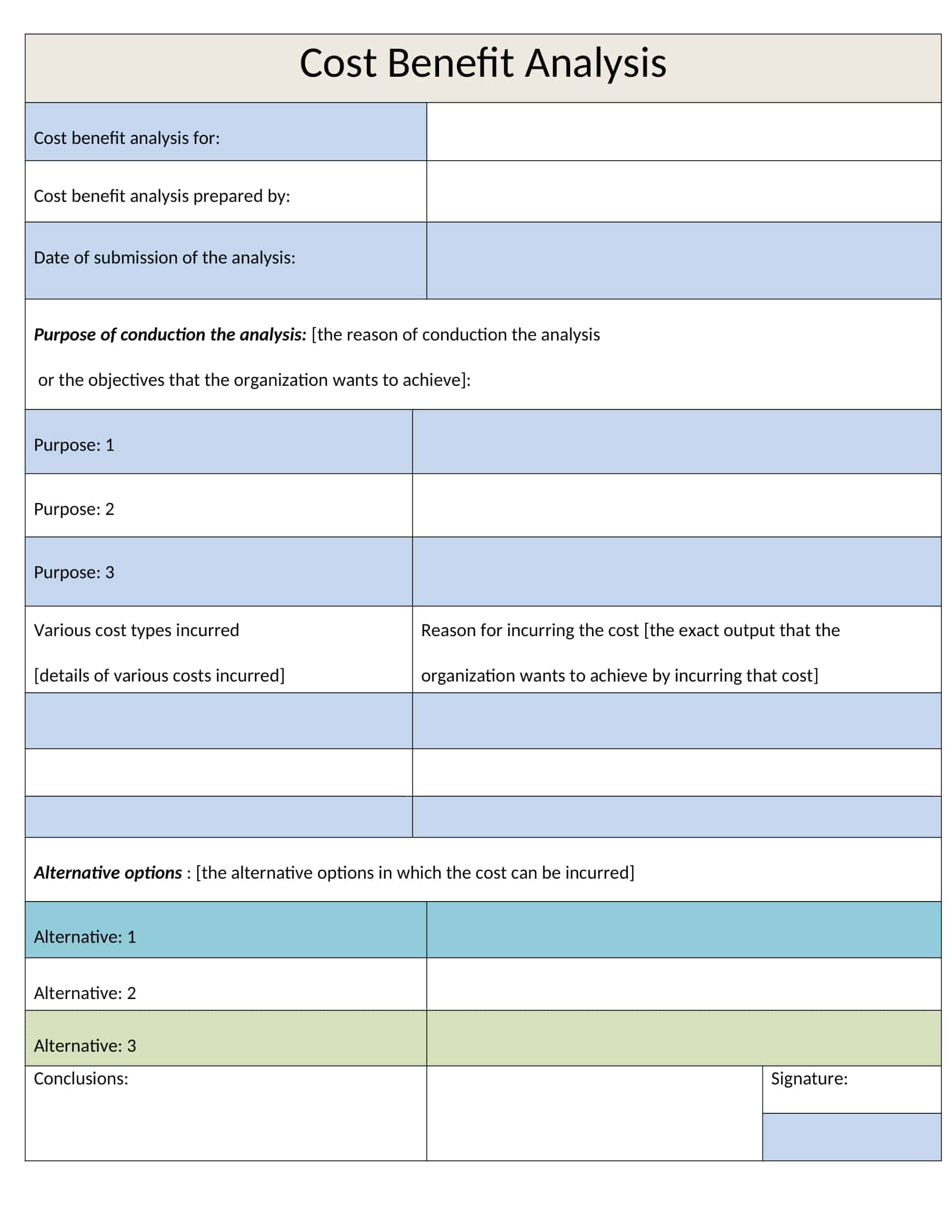
Step 1: Creating a Benefit and Cost List
When performing a cost-benefit analysis, the first thing to do is to create a comprehensive list of all the costs and benefits associated with the potential investment decision.
We need to consider the obvious costs (such as the cost of installing or purchasing new software) and the intangible opportunity cost of choosing other software or the cost of hiring an employee instead of the software.
We must also consider all possible benefits of the investment decision. For example, how much can this project contribute to revenues? What other benefits can there be if the investment is made? For example, will the new software create new business opportunities or streamline existing business and increase productivity? Therefore, we must make sure that you consider the obvious financial benefits and the intangible benefits.
Step 2: Giving Costs and Benefits Monetary Value
After creating a comprehensive list of costs and benefits for analysis, you can assign monetary values to each cost or benefit.
The values are obvious for some of the benefits or costs in the list. For example, costs such as the cost of purchasing software or the cost of installation can be obtained as a result of the bid. However, it is necessary to consider intangible direct or indirect costs or benefits when determining monetary values. For example, installing new software can result in systems inactivity for several hours, so this downtime or reduced productivity can result in a loss of money for the company.
When we determine the monetary values for each cost or benefit, we complete the necessary pieces of the equation.
Step 3: Build and Compare the Equation
Take the sum of the benefits (the sum of all monetary values allocated to the project’s benefits) and the sum of the costs (the sum of all the monetary values of the project’s costs) and apply them to the benefit/cost equation.
Remember, the equation must be numerical. If the numerical benefits (the sum of the financial values for the project’s benefits) outweigh the costs, it is worthwhile to decide on the project. Otherwise, companies should re-examine the potential project and make adjustments accordingly.
This equation can also be used for multiple different options or projects, and it helps to put options side by side and make comparisons.
FAQs
How do you write a cost-benefit analysis?
Identify all costs associated with the potential action or investment. Quantify the benefits and positive impacts. Compare costs and benefits numerically and in qualitative terms. Determine if benefits outweigh costs and by how much. Recommend go/no go.
Does Excel have a cost-benefit analysis template?
Yes, Excel has pre-made cost-benefit analysis template files with columns formatted to enter costs and benefits. Formulas calculate net present value, return on investment, payback period, and cost/benefit ratio.
What is the cost-benefit analysis in Excel?
In Excel, list costs in one column and benefits in another. Add formulas to sum totals. Make a recommendation based on comparing the two amounts and calculating metrics like ROI and NPV using Excel functions. Make a graph. Add conditional formatting.
What are the 5 steps of cost-benefit analysis?
The 5 key steps are:
- List costs
- List benefits
- Assign quantitative values
- Compare costs and benefits
- Interpret results and make recommendation






















![%100 Free Hoodie Templates [Printable] +PDF 1 Hoodie Template](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Hoodie-Template-1-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Gap Analysis Templates [PDF, Excel, Word] Healthcare 2 Gap Analysis](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Gap-Analysis-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Food Diary Templates [Word, Excel, PDF] 3 Food Diary](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-150x150.jpg 150w, https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Food-Diary-1-1200x1200.jpg 1200w)
