A Business Requirements Document (BRD) is a crucial tool for capturing and defining the needs of an organization. It serves as a blueprint that outlines the goals, objectives, and expectations for a project, product, or service. A well-written BRD provides clear and comprehensive information about the project’s stakeholders, scope, constraints, and expected outcomes.
This document acts as a reference point for project teams, stakeholders, and decision-makers throughout the project’s lifecycle. By creating a comprehensive BRD, organizations can ensure that the project is aligned with their goals, reduces misunderstandings, and enhances the chances of success.
Table of Contents
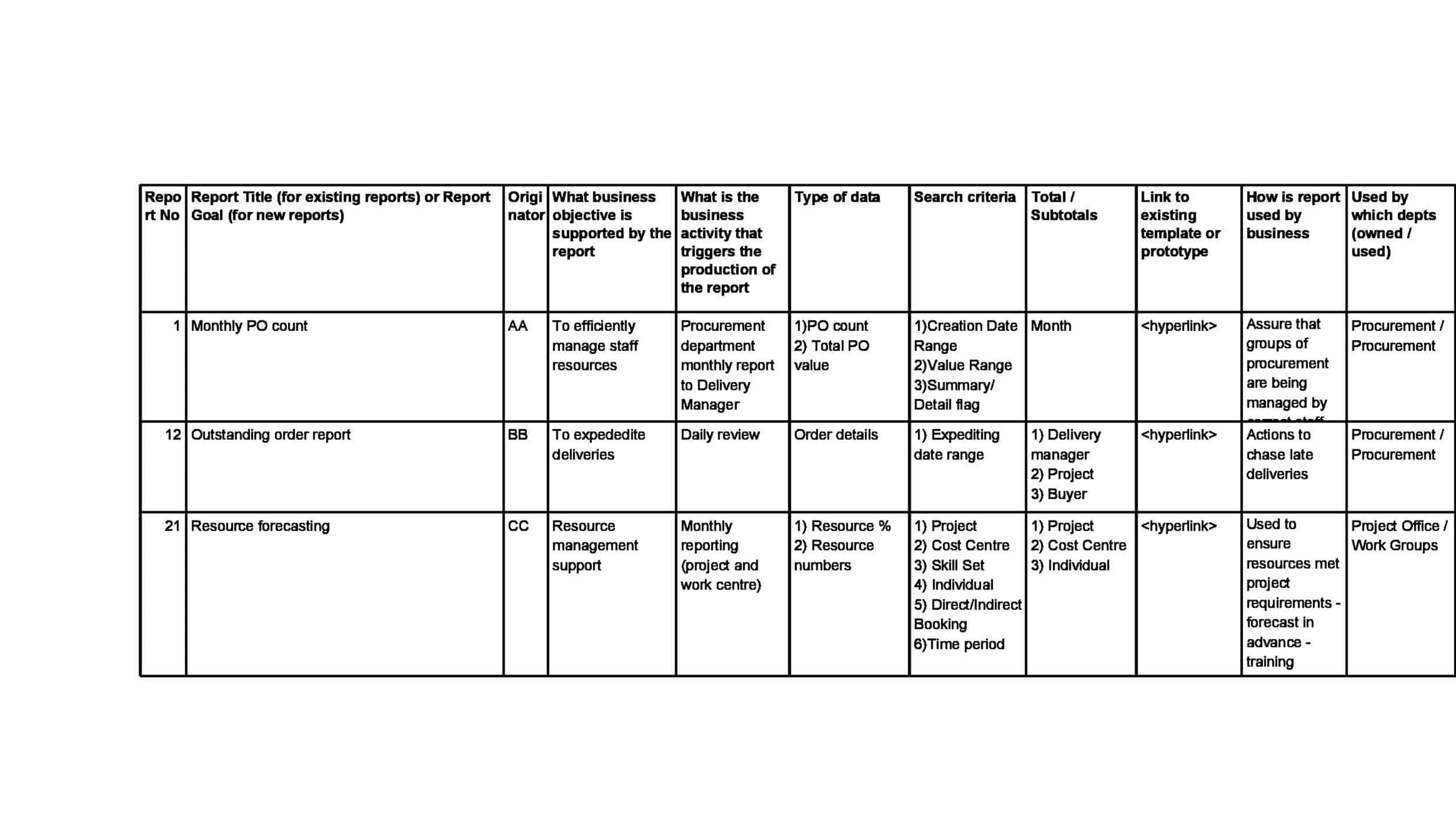
Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates
Business Requirements Document (BRD) Templates are pre-designed formats used by organizations to document and communicate the requirements for a specific business project, initiative, or system development. These templates provide a structured framework for capturing and documenting the business needs, goals, functionalities, and constraints associated with a project or system. Business Requirements Document Templates ensure consistency, clarity, and a shared understanding among stakeholders, enabling effective planning, development, and implementation of business solutions.
Business Requirements Document Templates provide a structured and comprehensive approach to capturing, documenting, and communicating the business requirements of a project or initiative. By using these templates, organizations can ensure consistency, clarity, and a shared understanding among stakeholders, promoting effective planning, development, and implementation of business solutions.
Business Requirements Document Templates serve as valuable tools in project management, system development, and business analysis, facilitating successful project delivery, stakeholder alignment, and the realization of business objectives.
Benefits of documenting business requirements

Documenting business requirements has several benefits, some of which include:
Improved Communication: A clear and concise BRD helps to ensure that everyone involved in the project has a common understanding of the goals, objectives, and expectations.
Better Planning: A well-documented BRD acts as a roadmap for the project, helping teams to identify the steps needed to achieve the desired outcomes.
Enhanced Decision Making: A BRD provides the information needed to make informed decisions about the project, such as resource allocation and budgeting.
Reduced Risks: A BRD helps to identify and mitigate potential risks, reducing the chances of project failure.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: By documenting the requirements of the end-users or customers, a BRD helps to ensure that the final product meets their needs and expectations.
Increased Efficiency: A BRD provides a clear and organized framework for the project, reducing the chances of misunderstandings and rework, and improving overall efficiency.
Better Tracking and Monitoring: A BRD acts as a reference point for project teams, helping to track progress and monitor changes.
Overall, documenting business requirements is an important step in ensuring the success of a project and can lead to improved outcomes, enhanced collaboration, and greater customer satisfaction.
What should a business requirements document include?
A Business Requirements Document (BRD) should include the following key elements:
Executive Summary: A brief overview of the project, including the goals, objectives, and expected outcomes.
Business Context: Information about the organization and its stakeholders, including their goals and objectives.
Scope: A clear definition of the project’s boundaries, including what is included and excluded.
Stakeholder Requirements: A list of the requirements of all stakeholders, including end-users, customers, and business owners.
Functional Requirements: A detailed description of the functional requirements, including the specific capabilities and features that the project must deliver.
Non-Functional Requirements: A description of the project’s performance, security, and other non-functional requirements.
Constraints: A list of any constraints that may impact the project, such as time, budget, and resource limitations.
Assumptions: A list of assumptions made during the requirements gathering process, including any dependencies or risks that may impact the project.
Acceptance Criteria: A description of the criteria that will be used to determine if the project has been successfully completed.
Appendices: Any additional information that supports the BRD, such as diagrams, wireframes, or data models.
A well-documented BRD should provide clear and comprehensive information about the project, including the goals, objectives, and expectations of all stakeholders. By including all of the key elements outlined above, organizations can ensure that their BRD is comprehensive, well-organized, and effective in guiding the project to success.
The Relevance of a BRD Template
A BRD template is a pre-formatted document that provides a structure and framework for documenting business requirements. The relevance of a BRD template lies in several key areas:
Consistency: A BRD template helps to ensure that all BRDs are consistent in terms of format, content, and style. This makes it easier for stakeholders to understand and review the document.
Efficient Documentation: A BRD template provides a structure for documenting requirements, reducing the time and effort needed to create a comprehensive BRD.
Improved Organization: A BRD template provides a clear and organized framework for documenting requirements, making it easier to locate and reference information.
Standardization: A BRD template helps to standardize the process of documenting requirements, reducing the chances of misunderstandings and improving the chances of project success.
Ease of Use: A BRD template makes it easier for stakeholders who are unfamiliar with the process of documenting requirements to get started, reducing the learning curve and improving efficiency.
Overall, a BRD template is an important tool for documenting business requirements. By providing a structured and standardized format, a BRD template can improve the efficiency, consistency, and organization of the requirements documentation process.
The Objectives of a BRD Template
The main objectives of a BRD template are as follows:
To provide a standard format for documenting business requirements: A BRD template defines the structure and format for documenting requirements, ensuring that all BRDs are consistent and well-organized.
To streamline the documentation process: A BRD template reduces the time and effort required to create a comprehensive BRD, making it easier and more efficient to document requirements.
To improve the clarity and accuracy of requirements: A BRD template provides a structured framework for documenting requirements, helping to ensure that all requirements are clear, concise, and complete.
To enhance communication and collaboration: A BRD template facilitates communication between project stakeholders, ensuring that everyone has a common understanding of the goals and objectives of the project.
To support decision making: A BRD template provides the information needed to make informed decisions about the project, including the requirements of stakeholders, the constraints and assumptions, and the acceptance criteria.
To facilitate change management: A BRD template provides a reference point for tracking changes and updating requirements as the project progresses.
To support continuous improvement: A BRD template can be used as a basis for evaluating the success of the project, identifying areas for improvement, and refining the requirements documentation process.
Overall, the objectives of a BRD template are to provide a standardized, efficient, and effective means of documenting business requirements, facilitating communication and collaboration, and supporting the successful completion of the project.
How to Write a Business Requirement Document
Writing a Business Requirements Document (BRD) is an important step in the software development process, as it provides a clear and comprehensive understanding of the requirements and expectations of the project stakeholders. This guide provides a step-by-step process for writing a BRD, including the key elements that should be included and tips for ensuring the success of the project.
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Scope of the BRD
Start by defining the purpose and scope of the BRD. This includes a clear definition of the goals and objectives of the project, and an understanding of the stakeholders and their expectations.
Step 2: Identify the Project Stakeholders
Identify all the stakeholders involved in the project, including customers, end-users, project team members, and management. This will help you understand their requirements and expectations, and ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Step 3: Gather Requirements
Conduct research and gather requirements from all stakeholders. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, focus groups, or reviewing existing documentation.
Step 4: Organize Requirements into Categories
Organize the requirements into categories, such as functional requirements, performance requirements, and constraints. This will help to ensure that all requirements are addressed and that the BRD is well-organized.
Step 5: Define Acceptance Criteria
Define the acceptance criteria for each requirement. This includes defining how the requirement will be tested and verified, and the criteria that must be met for the requirement to be considered complete.
Step 6: Create a Requirements Traceability Matrix
Create a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) that maps the requirements to the project deliverables. This will help to ensure that all requirements are tracked and met, and that the project stays on track.
Step 7: Write the BRD
Write the BRD, using the information gathered in the previous steps. The BRD should include an executive summary, a description of the project and its goals, a list of requirements organized by category, acceptance criteria for each requirement, and a RTM.
Step 8: Review and Approve the BRD
Review the BRD with all stakeholders, including project team members, customers, and end-users. Obtain approval from all stakeholders and make any necessary revisions.
Step 9: Implement the BRD
Once the BRD is approved, implement it by using it as a roadmap for the project. Use the BRD as a reference throughout the project, updating it as necessary to reflect changes in requirements or project direction.
Tips for Writing a Successful BRD
Keep it Simple: The BRD should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoid using technical jargon, and ensure that all stakeholders can understand the requirements and expectations.
Focus on the User: The BRD should focus on the needs and expectations of the end-user, ensuring that the final product meets their needs.
Be Specific: Be specific about the requirements and acceptance criteria, avoiding vague or ambiguous statements.
Use a Template: Use a BRD template as a starting point, and customize it to meet the specific needs of the project.
Collaborate with Stakeholders: Collaborate with all stakeholders, including project team members, customers, and end-users, to ensure that the BRD accurately reflects their requirements and expectations.
Be Agile: Be prepared to make changes to the BRD as the project progresses, and embrace an Agile approach to requirements documentation if appropriate.
FAQs
Who should be involved in the creation of a BRD?
All stakeholders involved in the software development project should be involved in the creation of a BRD, including customers, end-users, project team members, and management.
How often should a BRD be updated?
A BRD should be updated as necessary throughout the software development project, to reflect changes in requirements or project direction.
What is a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)?
A Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a tool that maps the requirements to the project deliverables, helping to ensure that all requirements are tracked and met.
How can I ensure that the BRD is well-received by all stakeholders?
To ensure that the BRD is well-received by all stakeholders, it is important to involve them in the creation process, be clear and specific about the requirements and acceptance criteria, and use a BRD template as a starting point.
What is the difference between a BRD and a functional requirements document (FRD)?
A BRD provides a high-level overview of the business requirements and expectations for a software development project, while a functional requirements document (FRD) provides a more detailed description of the functional requirements. The BRD serves as the starting point for the FRD, and provides the context for the more detailed requirements outlined in the FRD.
What is the role of the BRD in the software development process?
The BRD plays a crucial role in the software development process by providing a clear and comprehensive description of the business requirements and expectations for the project. This helps to ensure that the project is aligned with the needs of the stakeholders and that the final product meets their expectations.
What is the importance of clear and specific requirements in a BRD?
Clear and specific requirements in a BRD are important because they provide a foundation for the development of the software, and help to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal. By outlining the requirements and acceptance criteria in detail, the BRD provides a clear understanding of what the final product should look like and how it should behave.
How can a BRD help to reduce the risk of project failure?
A well-defined BRD can help to reduce the risk of project failure by providing a clear understanding of the requirements and expectations of the project stakeholders. This helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal, and that the final product meets the needs of the end-users. By outlining the requirements and acceptance criteria in detail, the BRD provides a roadmap for the development process, reducing the risk of misunderstandings or misinterpretations.
Can a BRD be used for other types of projects besides software development?
While BRDs are commonly used in software development projects, they can be used for other types of projects as well. BRDs can be used in any project where clear and specific requirements are important, such as construction projects, product development projects, and marketing campaigns.
What is the difference between a BRD and a project charter?
A BRD provides a detailed description of the business requirements and expectations for a software development project, while a project charter provides a high-level overview of the project goals and objectives, project stakeholders, and project scope. The BRD serves as a more detailed follow-up to the project charter, and provides the context for the project deliverables and acceptance criteria.









































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
