Home inspections play a crucial role in the buying and selling of a house. With the growing importance placed on property maintenance, many homebuyers are conducting various types of inspections to ensure they make informed decisions.
From newly built homes to older properties, the inspection process helps both buyers and sellers avoid potential costly repairs and ensures the property is in good condition. Making regular checks like this can ultimately save thousands of dollars.
Table of Contents
What Is a Home Inspection ?

Home inspection is the process of evaluating a property’s condition, typically before a sale, to determine if there are any significant issues or defects. This includes a visual examination of the home’s structure, systems, and components, such as the roof, foundation, plumbing, electrical, heating, and cooling systems. The goal of a home inspection is to identify any potential problems or safety hazards, so that the buyer or seller can make informed decisions about the property and negotiate repairs or price adjustments accordingly.
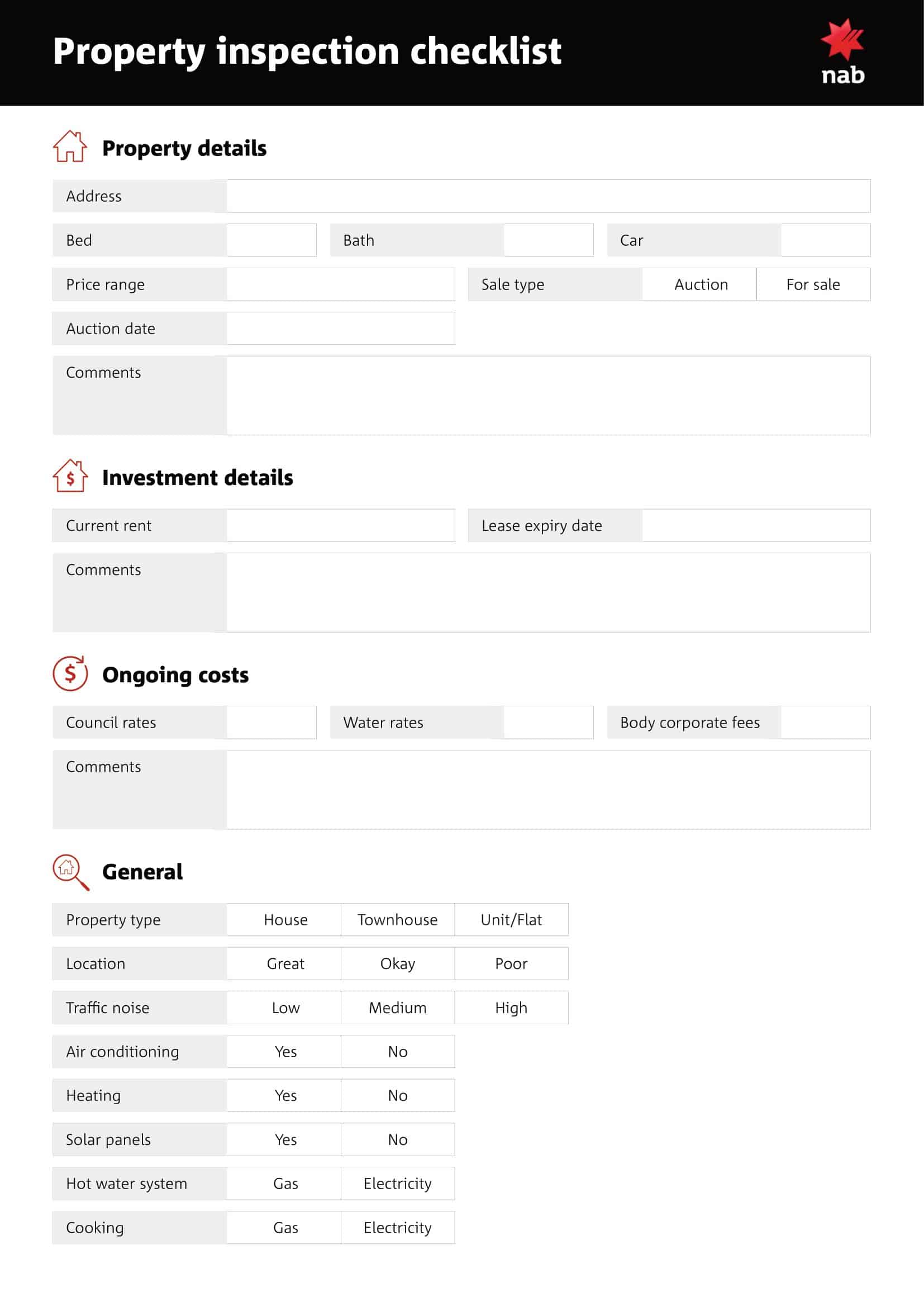
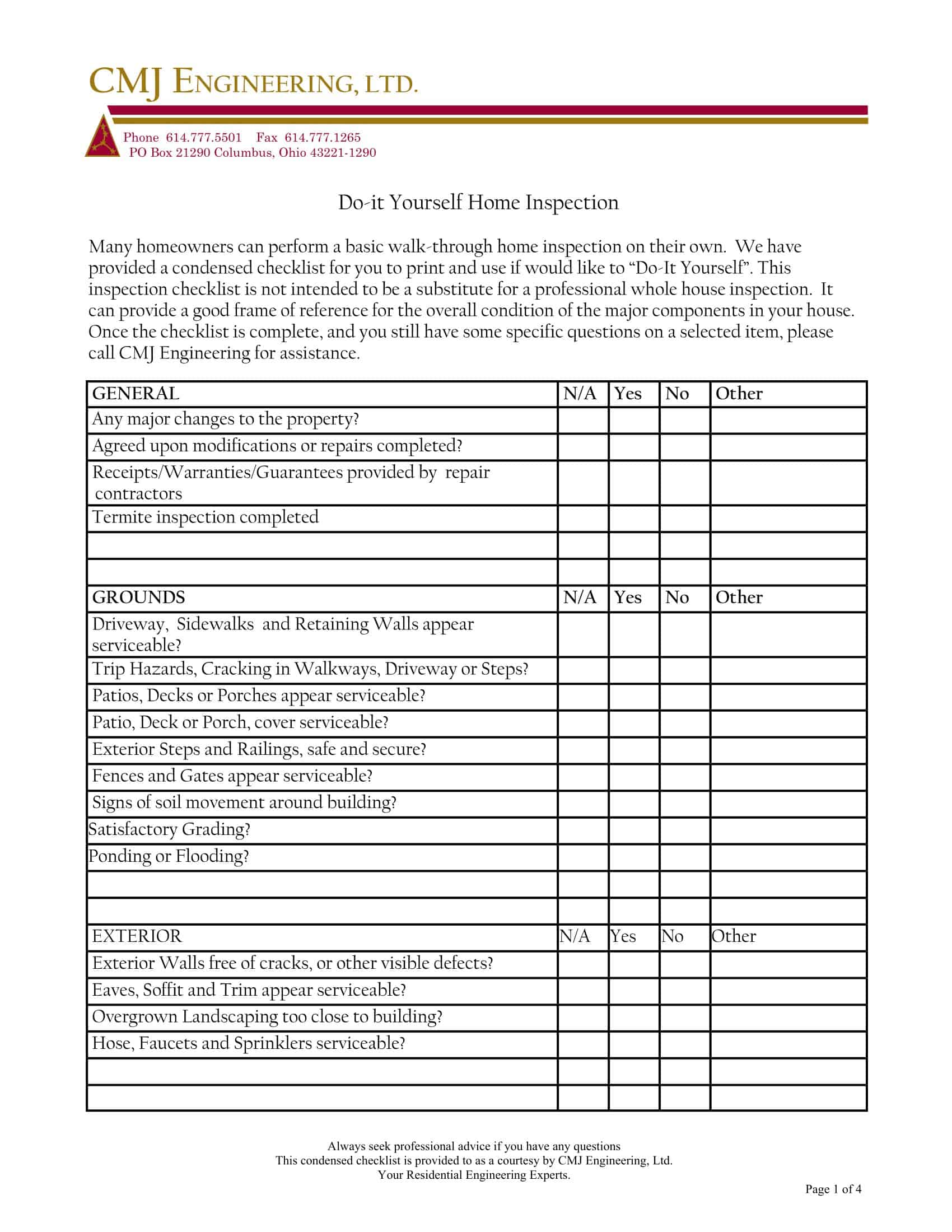
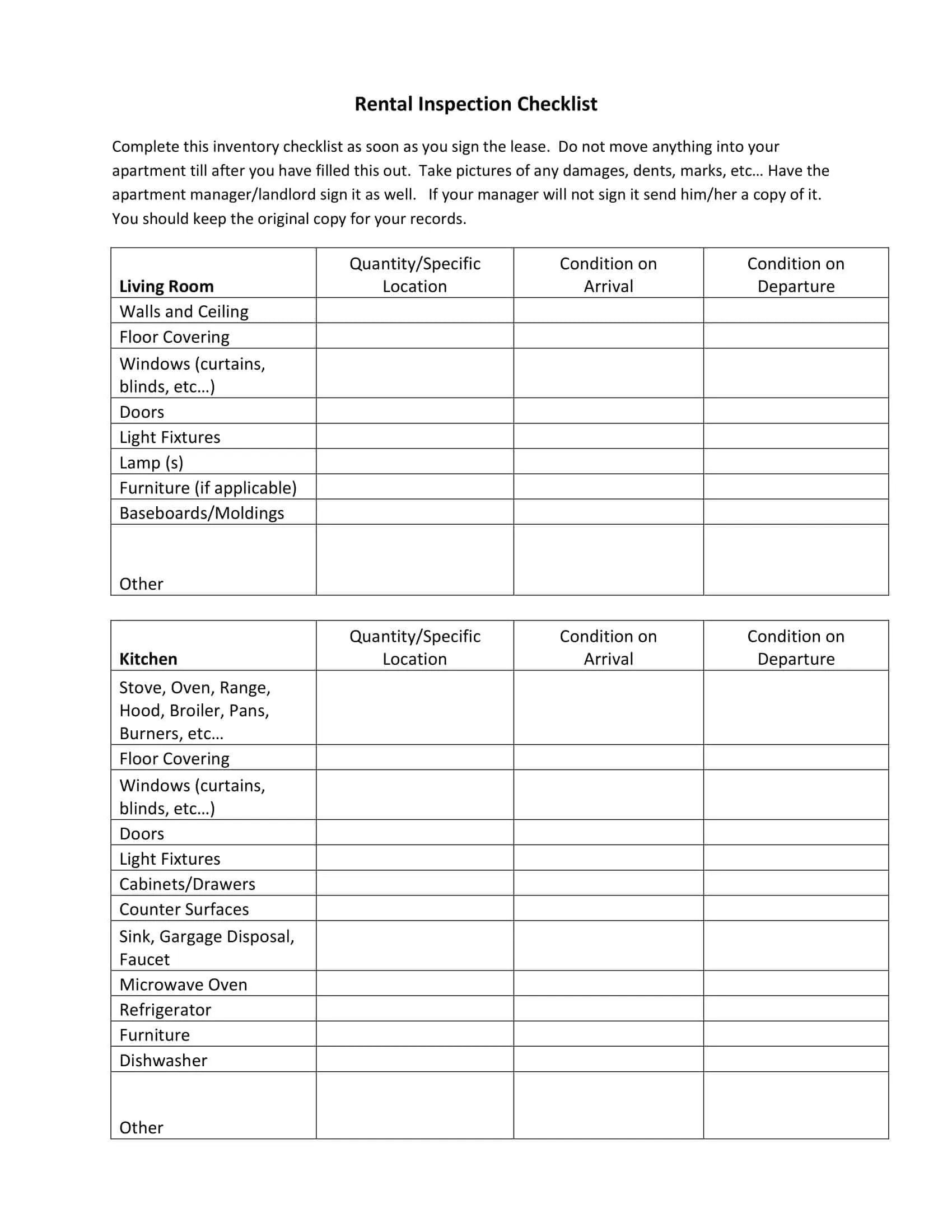
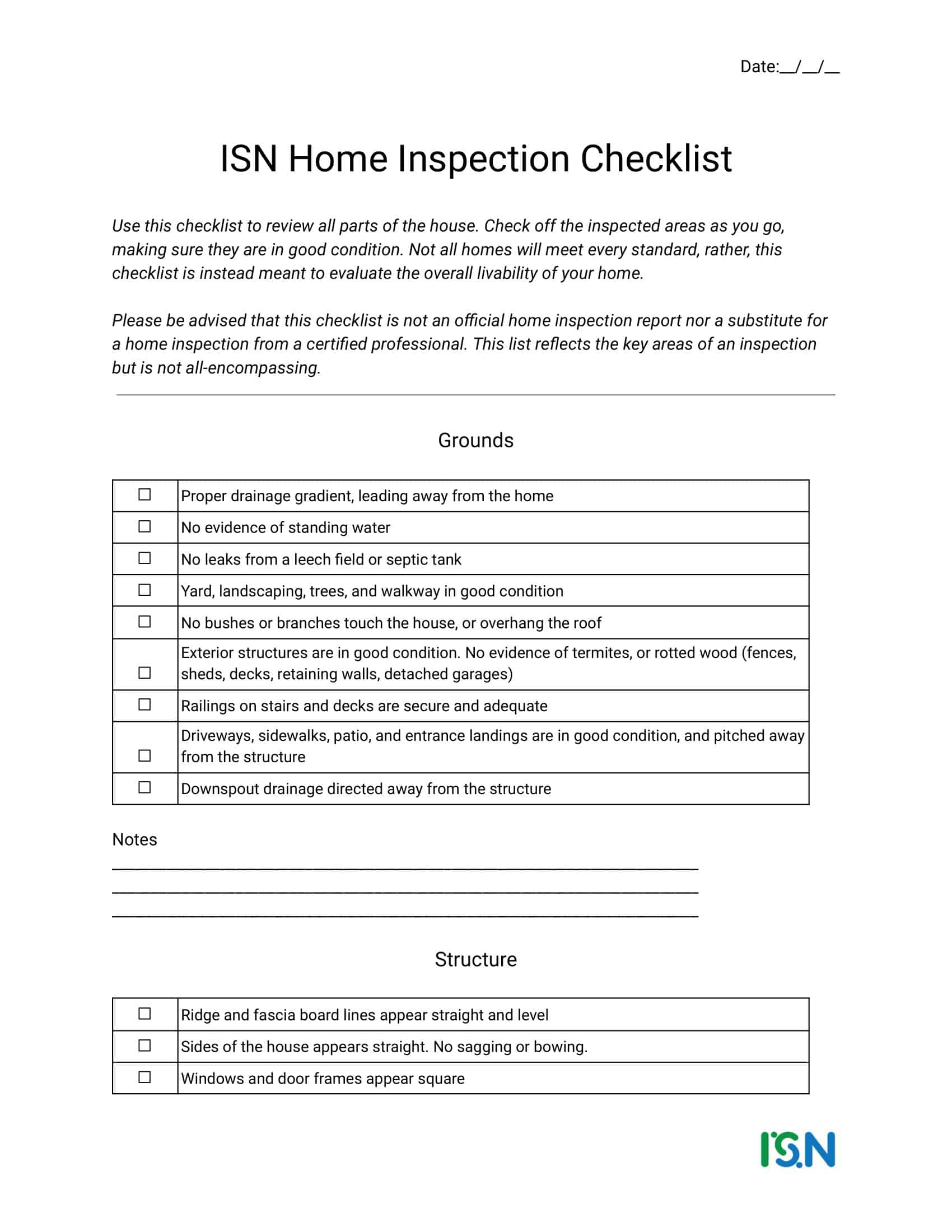
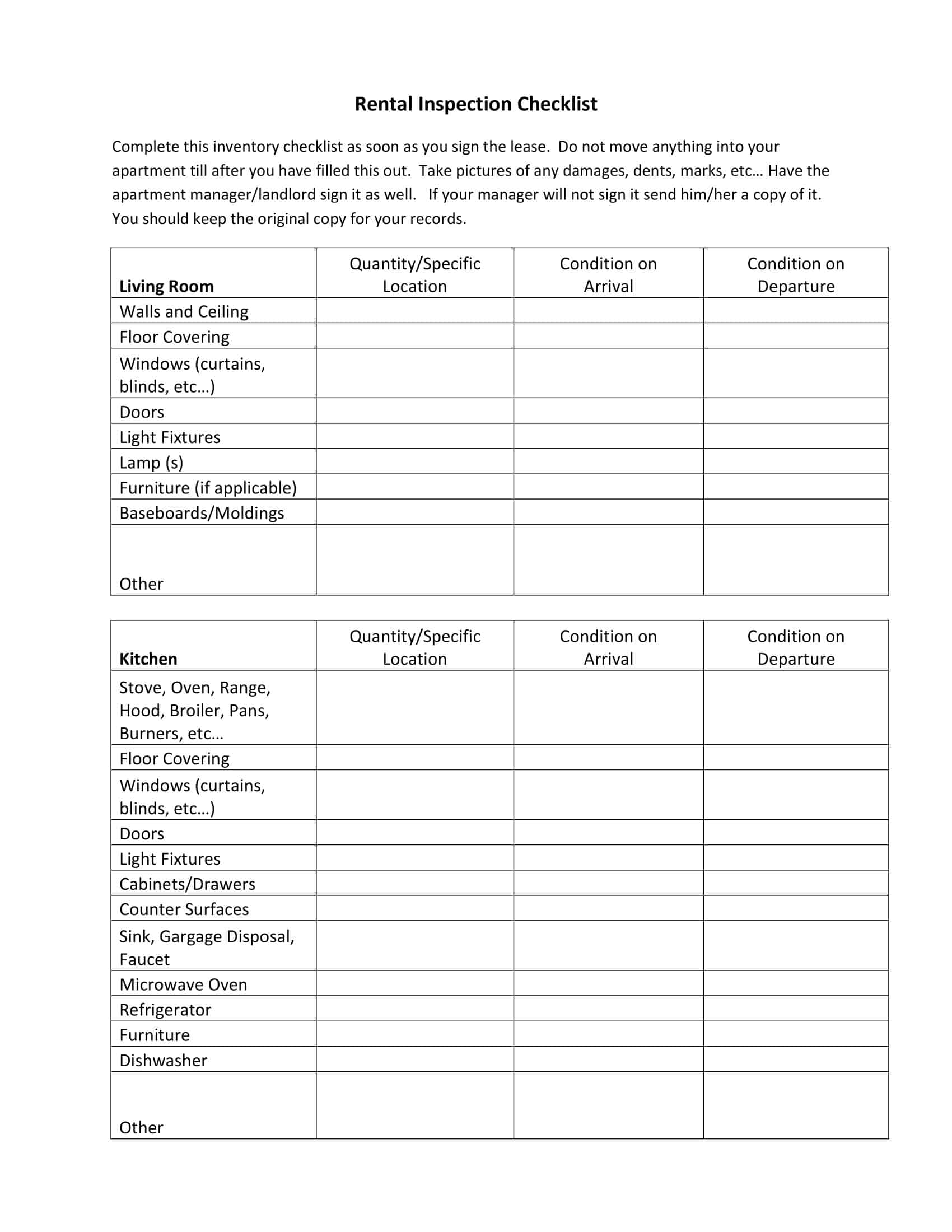
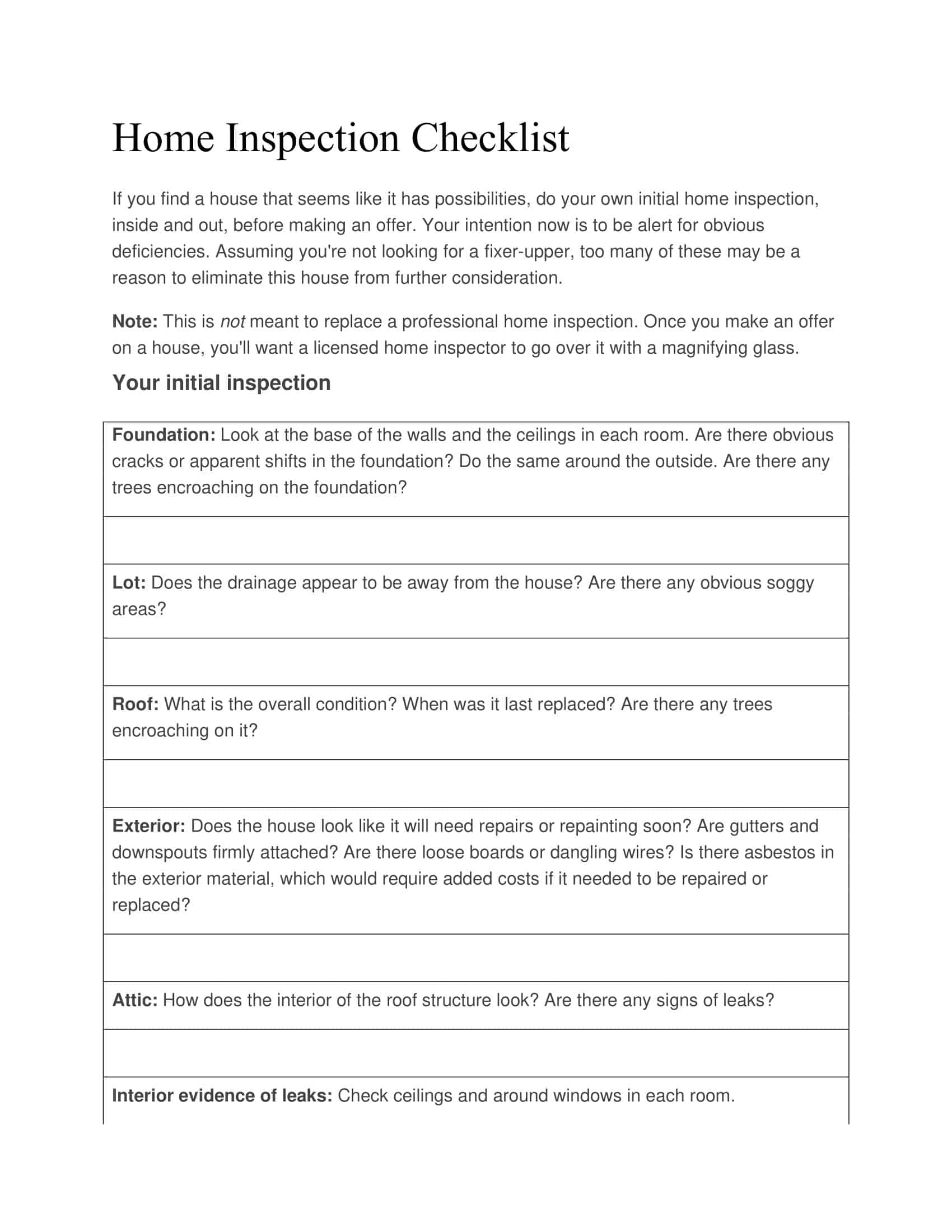
Home Inspection Checklist Templates
Home Inspection Checklist Templates are essential tools used to assess the condition of residential properties during the inspection process. These templates provide a comprehensive and systematic approach to evaluating various aspects of a home, ensuring that no important areas are overlooked. Home Inspection Checklist Templates assist home inspectors, homeowners, or potential buyers in conducting thorough inspections, identifying potential issues or hazards, and making informed decisions regarding the property’s condition.
Home Inspection Checklist Templates serve as a comprehensive guide for conducting systematic and thorough inspections of residential properties. By utilizing these templates, home inspectors, homeowners, or potential buyers can assess the condition of a home, identify any potential issues, and make informed decisions regarding repairs, negotiations, or future maintenance. Home inspections are crucial for ensuring the safety, functionality, and value of a property, and Home Inspection Checklist Templates provide a standardized and organized approach to this process.
Why You Need a Home Inspection?
There are several reasons why a home inspection is important:
To identify potential issues: A home inspector will thoroughly examine the property and identify any major issues or defects that may impact the value, safety, or habitability of the home.
To make informed decisions: A home inspection can help you make an informed decision about whether to move forward with the purchase or sale of a property.
To negotiate repairs: If the inspection reveals any significant issues, you can use that information to negotiate repairs or price adjustments with the other party.
To avoid unexpected costs: An inspection can help you avoid costly surprises down the road, by giving you an accurate understanding of the condition of the property.
To ensure safety: A home inspection can help you identify any potential safety hazards, such as electrical problems or gas leaks, which can be addressed before they become major issues.
To meet legal requirements: In some cases, a home inspection may be required by law, or by the terms of a mortgage loan, before you can close on a property.
To understand the condition of major systems: A home inspection will evaluate the condition of the home’s major systems, such as the roof, plumbing, and electrical, helping you understand what you can expect in terms of maintenance and repairs.
To prioritize future upgrades: A home inspector can also provide you with recommendations for upgrades or improvements, allowing you to prioritize future investments based on your specific needs and budget.
To increase home value: By having a thorough understanding of the condition of your property, you can make improvements that will increase its value, making it more attractive to potential buyers in the future.
To gain peace of mind: Perhaps most importantly, a home inspection gives you peace of mind, by providing a clear understanding of the condition of the property and helping you avoid potential pitfalls and unexpected costs.
Common Types of Home Inspection
There are several common types of home inspections, including:
General Home Inspection: A comprehensive evaluation of the property’s structure, systems, and components to identify any significant issues or defects.
Structural Inspection: A focused inspection of the property’s foundation, roof, walls, and other structural elements to determine their stability and condition.
Electrical Inspection: An inspection of the property’s electrical system, including wiring, panels, and outlets, to ensure they are safe and functioning properly.
Plumbing Inspection: An evaluation of the property’s plumbing system, including pipes, fixtures, and water heater, to identify any leaks, clogs, or other issues.
HVAC Inspection: An examination of the property’s heating and cooling systems, including the furnace, air conditioning, and ventilation systems, to determine their efficiency and condition.
Pest Inspection: A specialized inspection to identify the presence of termites, carpenter ants, or other pests that could damage the property.
Roof Inspection: A focused inspection of the property’s roofing system, including the shingles, flashing, and gutters, to determine their condition and expected lifespan.
Environmental Inspection: An evaluation of the property’s exposure to environmental hazards, such as radon, mold, or asbestos.
Energy Efficiency Inspection: A specialized inspection to evaluate the property’s energy efficiency and identify areas where improvements could be made to reduce energy costs.
Pool and Spa Inspection: An inspection of the property’s swimming pool or spa, to determine its condition, safety features, and efficiency.
Things on the Home Inspection Checklist
A typical home inspection checklist will cover several key areas and items, including:
Exterior: Inspection of the property’s siding, windows, doors, porches, decks, and sidewalks to determine their condition and functionality.
Roof: Examination of the roofing system, including the shingles, flashing, gutters, and downspouts, to identify any leaks, damage, or needed repairs.
Attic: Inspection of the attic space to evaluate insulation, ventilation, and any evidence of leaks or moisture.
Plumbing: Evaluation of the plumbing system, including pipes, fixtures, water heater, and sump pump, to identify any leaks, clogs, or other issues.
Electrical: Examination of the electrical system, including wiring, panels, outlets, and light fixtures, to ensure they are safe and functioning properly.
HVAC: Inspection of the heating and cooling systems, including the furnace, air conditioning, and ventilation systems, to determine their efficiency and condition.
Interior: Inspection of the interior of the property, including walls, floors, ceilings, and doors, to identify any cracks, damage, or needed repairs.
Kitchen: Examination of the kitchen appliances, cabinets, and countertops to determine their condition and functionality.
Bathrooms: Inspection of the bathroom fixtures, tiles, and ventilation to identify any leaks, clogs, or other issues.
Fireplaces: Inspection of fireplaces, chimneys, and flues to determine their condition and safety.
Basement/Crawl Space: Evaluation of the basement or crawl space to identify any evidence of moisture, mold, or other issues.
Grounds: Inspection of the property’s lawn, trees, and landscaping to determine their condition and any potential issues.
The exact items included on a home inspection checklist can vary depending on the inspector and the type of inspection being performed. The goal of the inspection is to provide a thorough evaluation of the property’s condition and identify any significant issues or defects that need to be addressed.
Not Covered in a Home Inspection
A home inspection is designed to provide a thorough evaluation of a property’s condition, but it is not a guarantee of the property’s condition or future performance. There are certain items that are typically not covered during a home inspection, including:
Cosmetic defects: Minor cosmetic issues such as paint cracks, scuffs, or small holes in walls are generally not considered significant issues and are not covered during a home inspection.
Code compliance: The inspector is not responsible for determining if the property meets all local building codes or safety regulations.
Future conditions: The inspector is not able to predict future conditions, such as the lifespan of appliances, the likelihood of future repairs, or the performance of the property over time.
Hidden areas: Areas that are not easily accessible, such as crawl spaces or concealed pipes, may not be fully inspected.
Structures not attached to the main building: Detached structures, such as garages, sheds, or pool houses, are typically not included in a home inspection.
Systems not turned on: Systems that are not functioning at the time of the inspection, such as air conditioning or heating units, may not be fully evaluated.
How much does a home inspection cost?
The cost of a home inspection can vary depending on several factors, including the size of the property, location, and the type of inspection being performed. On average, a home inspection in the United States can cost between $300 and $600. Some inspectors may charge an additional fee for services such as radon testing or termite inspections.
It’s important to keep in mind that a home inspection is a valuable investment that can potentially save you thousands of dollars in the long run by identifying any significant issues with the property before you complete the purchase. It’s a good idea to compare quotes from multiple inspectors and choose one that is reputable and experienced. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to attend the inspection in person to ask questions and learn more about the property’s condition.
Who pays for a home inspection?
In most real estate transactions, the buyer is responsible for paying for the home inspection. However, this is typically a negotiated item between the buyer and the seller, and the responsibility for paying for the inspection can vary depending on the agreement between the parties.
In some cases, the seller may agree to pay for the inspection as a condition of the sale. Alternatively, the buyer and seller may split the cost of the inspection. This is often done to encourage the buyer to purchase the property or to show the seller’s willingness to be transparent about the property’s condition.
It’s important to discuss the responsibility for paying for the home inspection with your real estate agent or attorney, and to have the terms of the agreement clearly spelled out in the purchase contract. In any case, the goal is to ensure that the inspection is performed by a qualified professional and that the results of the inspection are used to make an informed decision about the purchase of the property.
How long does a home inspection take?
The length of a home inspection can vary depending on the size of the property and the extent of the inspection being performed. On average, a home inspection for a typical single-family home can take anywhere from two to four hours.
For larger properties, such as multi-unit buildings or commercial properties, an inspection can take longer. In some cases, an inspection for a larger property can take as long as a full day.
It’s a good idea to attend the home inspection in person to ask questions and learn more about the property’s condition. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to allow ample time for the inspection and to avoid scheduling other activities immediately after the inspection, in case the inspection takes longer than expected.
FAQs
What should you do if the home inspection reveals issues with the property?
If the home inspection reveals issues with the property, the buyer and the seller may need to renegotiate the terms of the sale. The buyer may request that the seller make repairs to the property or offer a credit to cover the cost of the repairs. If the parties cannot reach an agreement, the buyer may choose to walk away from the sale.
Can a home inspection help you save money?
Yes, a home inspection can help you save money. By identifying any significant issues with the property before the purchase is completed, the buyer can negotiate with the seller to address the issues or to receive a credit to cover the cost of repairs. Additionally, a home inspection can potentially save the buyer from paying for repairs that may have been overlooked if the inspection had not been conducted.
What happens if the home inspector misses something during the inspection?
While home inspectors are trained professionals and do their best to thoroughly inspect a property, they are not perfect and may miss something during the inspection. If the inspector misses something, they may be liable for the cost of repairing the issue if they had a professional liability insurance. It’s important to always get a warranty or insurance coverage with your home inspector to protect your interests.
Can a home inspection be performed on a new construction home?
Yes, a home inspection can be performed on a new construction home. While new construction homes are often assumed to be free of defects, an inspection can help identify any issues that may have gone unnoticed during the construction process.
Is a home inspection required by law?
No, a home inspection is not required by law. However, many home buyers choose to have a home inspection as a way to ensure that they are making a well-informed decision about the condition of the property.
What happens if the home inspection is not satisfactory?
If the home inspection is not satisfactory, the buyer and the seller may need to renegotiate the terms of the sale. The buyer may request that the seller make repairs to the property or offer a credit to cover the cost of the repairs. If the parties cannot reach an agreement, the buyer may choose to walk away from the sale.
Can a home inspector test for radon?
Yes, a home inspector can test for radon. Radon is a naturally occurring gas that can be harmful to human health. If the home inspector detects high levels of radon, they may recommend further testing or that the issue be addressed by a radon mitigation specialist.




















































![Free Printable Roommate Agreement Templates [Word, PDF] 1 Roommate Agreement](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Roommate-Agreement-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Credit Card Authorization Form Templates [PDF, Word, Excel] 2 Credit Card Authorization Form](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Credit-Card-Authorization-Form-150x150.jpg)
![Free Printable Stock Ledger Templates [Excel,PDF, Word] 3 Stock Ledger](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Stock-Ledger-150x150.jpg)
